Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
13~8~8
R~N 4090/19
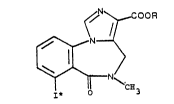
The present invention is concerned with radioiodinated
benzodiazepine derivatives of the formula
~N~OOR
1 o f~ N~
~./
~ ~'C~
I* 3
wherein I~ is a radioactive iodine and R is an alkyl
group with 1-4 C-atoms,
and their use in diagnosing diseases and disordecs of the
brain through their ability to image the brain.
The radioactive iodine is preferably iodine 123. The
alkyl group R is prefeeably methyl, ethyl, isoeropyl,
sec.butyl or tert.butyl, most preferably ethyl.
Thus the most preferred compound according to the instant
invention is ethyl-7- iodo-5,6-dihydro-5-methyl-6-oxo
-4H-imidazo[1,5-a][1,4]benzodiazepine-3-carboxylate.
The compounds of formula I are useful for imaging the
brain. As will therefore be appreciated the compounds of
formula I demonstrate rapid accumulation in the brain
indicative of an ability to penetrate the so-termed
"blood/bcain barrier". The compounds of formula I demonstrate
rapid localization of the radioiodine in the brain following
intravenous administration.
Klt/13.6.89
131~8
-- 2 --
The compounds of formula I can be used to diagnose
diseases or disorders of the brain by imaging changes in the
distribution of the benzodiazepine receptors in the brain. In
this manner the compounds of formula I can be used to
diagnose such brain diseases and disorders as cerebro-
-vascular diseases ~e.g. strokes), neurological diseases
(e.g. epilepsy) and psychotic diseases.
The compounds of formula I can be prepared by methods
recognized in the art. For example a compound of formula I
can be prepared from a cold compound of formula I, i.e. a
compound, wherein I is a stable iodine, by exchange with a
radioactive iodine, preferably iodine 123.
For the exchange radiolabeling process, iodine 123 in a
O.lN sodiumhydroxide solution is utilized. This solution is
heated with a solution of the cold compound of formula I;
i.e. a compound correseonding to formula I but wherein I is
stable iodine and not iodine 123 for from about 1/4 to about
2 hours. The exchange radiolabeling is carried out in the
presence of a solvent such as, for example, glacial acetic
acid.
A further and preferred method for preparing the
compounds of formula I consists in reacting a compound of the
formula
// \_C OO R
\ /1
~ ~
CH3
B~ 0
35 with a radioactive iodine.
Most preferably iodine 123 is used.
~3~8
-- 3
The same reac~ion conditionE; are used as in the case of
the e~change of the non-radioactive iodine by the 123 iodine.
The cold compounds of formula I and the compounds of
formula II are either known from European patent publications
No. 27214 or 59389 or ~.S. Patent No. 4,316,839. These cold
compounds can be prepared according to the methods given in
the above European and US patent publications.
As stated above, the radioiodine containing compounds of
the invention rapidly localize in the brain following
intravenous administration. In most instances, a sufficient
amount of the administered dose will accumulate in the brain
within from about two to ten minutes to permit the taking of
scintiphotos. The comeounds of the invention will show
meaningful presence in the brain for at least 60 minutes so
that significant studies may be carried out.
The radioiodinated compounds of the subject invention may
be administered in an aqueous or aqueous/alcoholic medium.
Such media may also contain conventional pharmaceutical
adjunct materials such as, for example, pharmaceutically
acceptable salts to adjust the osmotic pressure, buffers,
preservatives and the like.
~ preferred vehicle for the parenteral administration of
the compounds of formula I is normal saline which would
contain from about 0.5% by weight to about 2% by weight of a
suitable preservative.
The radioactive benzodiazepine of this invention can be
injected intraveneously into a patient for diagnostic imaging
of the brain. In accordance with this invention, the radio-
active benzodiazepine of formula I is administeced in a
single unit injectable dose. ~ny of the common carriers, such
as sterile saline solution, plasma, etc. can be used for
preparing the injectable solution for use to diagnostically
~, , ..... ~ ~
~3~6~8
image in accordance with this invention. Generally, the unit
dose to be administered contains radioactivity of about 2 mCi
to about 10 mCi, preferably about 4 to 5 mCi. However, any
amount of the compounds which is effective for imaging the
brain can be injected in accordance with this invention. The
solution to be injec~ed is preferably in a unit dosage form
of about from 0.1 milliliters to about 10 milliliters
preferably from about 1 to 5 milliliters and more preferable
4 to 5 milliliters. After intravenous administration, the
radioactive benzodiazepine of formula I will image the organs
ln vivo. Any conventional method of visualizing or imaging
for diagnostic purposes can be utilized in accordance with
this invention. In this respect scintiscanning means can be
used to visualize or image the brain.
In accordance with this invention, the compound of
formula I and particularly ethyl-7- iodo-5,6-dihydro-S-
-methyl-6-oxo-4H-imidazo~1,5-a][1,4]benzodiazepine-3--carboxy-
late is administered to humans intraveneously in a normal
saline solution containing 5% glucose. The dose injected into
humans contained 4 to 5 mCi of this radioactive compound.
Within 40-60 minutes after injection, scintiphotos were made
during Z5 minutes with a Gamma Spect. camera. In accordance
with a preferred enbodiment this compound is injected at a
dose of 0.0543 mCi per kg.
The compound of formula I can be administered as a free
base or as a pharmaceutically acceptable acid addition salt.
The following examples further illustrate the invention.
Unless otherwise noted, all temperatures are in degrees
centigrade.
Example 1
The labelling procedure for halogen exchange
(bromide-iodide) was performed in a conical reaction vial
13~ 8~
tightly closed by a teflon laminated silicon septum. I-123
activity (up to 300 mCi) in O.ln Na~H was evaporated to
dryness by means of a gentle stream of nitrogen at soo. Then
1 mg of ethyl-7-bromo-5,6-dihydro-5-methyl-6-oxo-4H-imidazo
[1,5-a][1,4]benzodiazepino-3-carboxylate dissolved in
200 ~1 glacial acetic acid was added and the r~action
mixture heated for 1 h at 150~ ~fter cooling this mixture
was dissolved in 5 ml water and eufified by HPLC. The HPLC
conditions were as follows: RP-18 column (8 x 250) Knauer
Lichrosorb 10 ~m, MeOH/H20 45/55, 2 ml/min, iodide:
k'=0.0, bromo-derivate: k'=2.75, iodo-derivate: k'=4.00. The
purification was performed on a device consisting of a valco
6-port valve with 20 ml loop, a Waters 510 pump, a Kontron
740 LC detector and a NaI scintillation detector. Labelling
and ~urification was done in a lead box which was equipped
for remote control handling. The labelling was virtually
quantitative.
Example 2
During the HPLC-separation the product peak was collected
and afterwards evaporated to dryness with a Rota-Vapor. The
residue was dissolved in a solution containing 5% glucose and
passed through a silver powder column to adsorb iodine
liberated during the Rota-Vapoc*treatment. ~fter sterile
filtration and adjustment of the activity concentration to
1 mCi/ml the ethyl-7-123iodo-5,6-dihydro-5~-methyl-6-oxo-
-4H-imidazo[1,5-a]tl,4]benzodiazepino-3-carboxylate was ready
for use.
The product quality was monitored with thin layer
chromatography on silica gel, developed with ethylacetate/
NH40H 200/1.
*Trade mark
A
-` 13i8668
-- 6 ---
Example 3
The starting material used in Example 1 was prepared as
follow~:
To a mixture of 167.95 g (624 mmol) of 6-bromo-3,4-
-dihydro-4-methyl-2H-l,~-benzodiazepine -2,5~1H)-dione,
600 ml of N,N-dimethyl-p-toluidine and 800 ml of chloroform
are added dropwise at the boiling temperature of the mixture
160.8 g (1,05 mol) phosphorus oxychloride whereupon the
reaction mixture is boiled under reflux for 4 hours. The
resulting solution is poured on a cold mixture of 500 g
sodium bicarbonate and 2 1 of water and stirred during 40
minutes. The anorganic phase is separated and extracted three
times with chloroform. The combined organic layers are dried
over magnesium sulfate and the chloroform is removed under
reduced pressure.
In the meantime a solution of 76 g (677 mmol) potassium-
-t-butylate in 200 ml of dimethylformamide is cooled to -45,
whereupon first 71 g (625 mmol) isocyanoacetic acid
ethylester are added and then at -50 to -20 the above
mentioned solution of the iminechloride is added dropwise.
~fter removing of the cooling means the reaction mixture is
stirred during 1.5 hours, whereupon 13 ml acetic acid are
added and then the reaction mixture is poured on to 1800 ml
of water and extracted five times with each 500 ml methylene
chloride. The combined organic extracts are washed three
times with water, dried over magnesium sulfate and
evaporated. The raw product is recrystalized from methylene
chloride and ethyl acetate and yields 156.80 g of ethyl
7-bromo-5,6-dihydro-5~methyl-6-oxo -4H-imidazo[1,5-a][1,4]-
benzodiazepine-3-carboxylate of melting point Z14-215.
~3~86~8
-- 7 --
Example 4
Iodide-iodide exchange labelling was performed exactly as
described for bromide-iodide exchange, but ethyl-7-iodo-5,6-
-dihydro-5-methyl-6-oxo -4H-imidazo[1,5-a]rl,4]benzodia-
zepine-3-carboxylate was used as precursor. This labelling
was performed to assure the identity of the labelled product
in HPLC and thin layer chromatography.
Example 5
The starting material used in Example 4 was prepared as
follows:
To a mixture of 185.5 g t558.8 mmol) ~f 3,4-dihydro
-5-iodo-4-methyl-2H-1,4-benzodiazepine -2,5(lH)-dione, 70 ml
of N,N-dimethyl-~-toluidine and 800 ml of chloroform are
added dropwise at the boiling temperature of the mixture
91.6 ml (979 mmol) phosphorus oxychloride whereupon the
reaction mixture is boiled under reflux for 2 hours. The
resulting solution is poured on a cold mixture of 490 g
sodium bicarbonate and 2 1 of water and stirred during 40
minutes. The anorganic phase is separated and extracted three
times with chloroform. The combined organic layers are dried
over magnesium sulfate and the chloroform is removed under
reduced pressure.
In the meantime a solution of 75.5 g (626.6 mmol)
potassium-t-butylate in 500 ml of dimethylformamide is cooled
to -50, whereupon first 65.2 ml (585.8 mmol) isocyano acetic
acid ethylester are added and then at -50 to -15 the above
mentioned solution of the iminechloride is added dropwise.
~fter removing of the cooling means the reaction mixture is
stirred during 1 hour, whereupon 120 ml of acetic acid are
added and then the reaction mixture is poured on to 1900 ml
of water and extracted five times with methylene chloride.
The combined organic extracts are washed three times with
13~6~
water, dried over magnesium sulfate and evaporated. The raw
product is chromatographed on silica gel and yields afte{
recrystallization from ethyl acetate 96.02 g of eehyl
5,6-dihydro-7-iodo-5-methyl-6-oxo -4H-imidazo[1,5-a][1,4]-
benzodiazepine-3-carboxylate of melting point 244-246.
Example 6
3 rats (female, Wistar, s~f) are measured at 7 diffeLent
points of time (2',10',20',40',1h, 6h, 15h). The weight of
the animals was between 113-144 g. The feeding was effected
ad libitum. The i.v. injected doses varied between 184 and
355 ~Ci in each 0,2 ml at injection solution.
~ 3 ~
g
Percentage of the injected activity per gram of the
corresponding organ (rat)
2' 10' 20' 40' 60' 6h 15h
blood 0.70 0.87 0.46 0.17 0.11 0.04 0.013
10 brain 2.12 3.22 2.99 2.70 1.80 0 05 0.001
thyorid
gland 0.60 0.54 1.22 0.08 0.06 0.03 0.007
liver 2.38 5.66 2.62 0.58 0.19 0.02 0.016
spleen 0.60 0.53 0.29 0.14 0.07 0.02 0.010
15 kidneys 2.68 7.06 5.26 1.35 0.68 0.03 0.010
stomach 0.19 0.41 0.35 0.27 0.48 0.73 0.080
bowel 0.75 1.10 1.73 2.02 1.97 1.55 0.143
lungs 1.22 0.87 0.44 0.15 0.10 0.03 0.011
heart 0.86 0.66 0.30 0.10 0.06 O.OZ 0.007
20 ovary 0.88 0.73 0.53 0.22 0.16 0.03 0.011
thigh
bone 0.54 0.45 0.24 0.10 0.07 0.02 0.007
bladder 0.59 1.07 0.69 0.24 0.42 0.57 0.023
muscle 0.68 0.4Z 0.20 0.09 0.04 0.01 0.003
~318~68
-- 10 --
Percentage of the injected activity in the
corresponding organs (rat~
2' 10' 20' 40' 60~ 6h 15h
brain3.115.38 4.20 4.02 2.42 0.08 0.0015
thyroid
gland0.180.15 0.18 0.03 0.02 0.008 0.0015
liver16.9034.3717.6]3.90 1.29 0.15 0.107
spleen0.260.210.11 0.06 0.03 0.008 0.0035
kidneys 3.15 7.48 6.25 1.53 0.79 0.04 0.009
15 Stomach 0.81 1.20 1.28 1.37 1.96 1.35 0.346
bowel9.2812.7022.5325.54 28.48 19.50 1.012
lung 1.040~81 0.40 0.15 0.09 0.03 0.0095
heart0.580.37 0.17 0.06 0.03 0.009 0.0035
ovary0.090.06 0.05 0.02 0.02 0.003 0.0008
20 tigh
bone 0.390.25 0.14 0.06 0.04 0.01 0.004
bladder 0.03 0.06 0.03 0.01 0.03 0.09 0.0022
rest
body 63.9429.9225.9211.04 7.98 2.88 1.30
25 total
body 99.7592.9678.8747.8043.1724.16 2.80
faeces
and
urine0.056.1719.39 48.72 51.71 48.81 42.69