Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
1333~
11-395 Labelinq Ap~ra~s
Technical Field
The present invention rela~es generally t~ a metho~
and apparatus for labeling products and in particular to
an improved apparatus and method for applying flexible,
tubular labels to product containers such as bottles.
Background Art
Various automated methods and apparatus for
labeling product containers, such as bottles are known.
In particular, U.S. Patent Nos. 4,412,876 and 4,620,888,
both owned by the present assignee, disclose bottle
labeling machines which are capable of automatically
placing tubular labels on product containers such as "2-
liter" soft drinX bottles. In the apparatus describedin the above two identified patents, a grippe~ mechanism
grabs the endmost label of a chain of labels and pulls
it onto a bottle. During the installation procèss, the
endmost label is s~evered from the remainder of the
chain.
With these prior bottle labelers, the final
position o~ the label on the bottle is in large measure
a function o~ its position with respect to the bottle
when it is initially engaged by the gripper mechanism.
In order to consistently and precisely install the
labels onto the bottles, it was found that the initial
position of the label prior to engagement by the label
gripping mechanism, must be precisely controlled.
In U.S. Patent No. 4,565,592, also owned by the
present assignee, an apparatus for monitoring the
position of the "next-to-be-applied" label was
monitored, and adjustments to its initial position were
made prior to engagement by the gripper mechanism. In
particular, the leading edge of the next-to-be-applied
label was ad~usted by a positioning mechanism that
2 133~7~
either raised or lowered a mandrel assembly about which
the label was held in order to adjust the initial
position of the label. As a result the labels would be
substantially at the same position when engaged or
gripped by the label applying mechanism. With the
disclosed apparatus, accurate labeling could be achieved
without disrupting or compromising the speed at which
labels could be applied to the bottles.
Disclosure of the Invention
The present invention provides a new and improved
method and apparatus for precisely locating a "next-to-
be-applied" label prior to engagement with a label
applying mechanism so that even more precise and
accurate positioning can be achieved without substan-
tially increasing the cost of the labeling machine. In
the disclosed embodiment, a monitoring and positioning
mechanism is disclosed which precisely locates the
leading edge of the next-to-be-applied label, while a
label already engaged by the grippers is being in-
stalled. The disclosed monitoring and positioning
apparatus does not substantially effect the speed of the
machine nor its reliability.
The disclosed apparatus can be used with the
labeling machines disclosed in U.S. Patent Nos.
4,412,876 and 4,620,888. In addition, the disclosed
monitoring and positioning apparatus can be used with
the packaging apparatus and method disclosed in co-
pending application Serial No. 621,793, filed September
18, 1989.
According to the preferred embodiment of the
invention, a positioning mechanism controls the final
position of the leading edge of the "next-to-be-applied"
label which forms the lead label in a chain or web of
~, ~
3 1333~76
interconnected sleeve-like labels. In the disclosed
embodiment, the label gripping mechanism engages the
lead label in the chain and pulls it towards a container
located at a label applying position forming part of a
~ labeling station. When the lead label or gripper
mechanism reaches a predetermined position in its
travel, a brake mechanism engages the web upstream of
the lead bag and inhibits further movement. This causes
the lead label to sever itself along a line of weakness
as the gripping mechanism continues its movement.
According to the invention, the brake mechanism is
operated so that the leading edge of the next-to-be-
applied label is at a position that is beyond an ideal
initial position for the leading edge. A drive
mechanism is then activated to reverse feed the web
until the leading edge reaches a desired initial
position. This occurs as the previously severed lead
label is being applied to the container located at the
label applying position of the machine.
According to the invention, the positioning
mechanism comprises a pinch roll assembly which includes
a power driven drive roll and a back-up or nip roll.
The web or chain of labels passes through the pinch roll
assembly. During an initial portion of a label applying
cycle when the label gripping mechanism engages the
leading edge of the lead label, the drive roll and back-
up roll are separated to define a gap in order to allow
the web to freely move through the pinch roll assembly.
After severance of the lead label from the web, the
pinch roll assembly is activated to clamp the web
between the nip and drive roll. The drive roll is
reverse rotated in order to reverse feed the next-to-be-
applied label until its leading edge is retracted to a
predetermined position, preferably sensed by an optical
or similar sensor. When the leading edge reaches the
4 13334~6
desired initial position, the pinch roll assembly is de-
activated in order to disengage the web.
In the preferred and illustrated embodiment, the
drive roll is continuously driven (in the reverse
direction from the normal label feed direction) by an
electric motor and the nip roll is pivotally mounted for
movement towards and away from the drive roll. An
actuator is used to move the nip roll towards and away
from the drive roll. After severance of the lead label
from the web, the actuator is energized to drive the
pinch roll towards the drive roll thereby engaging the
web and causing reverse movement. As soon as the
position sensor senses the leading edge of the next-to-
be-applied label, the nip roll is immediately retracted
to release the web.
With the disclosed construction, extremely precise
positioning of labels onto containers can be achieved.
The disclosed apparatus and method can be added to
existing labeling machines and is extremely cost
effective.
Additional features of the invention will become
apparent and a fuller understanding obtained by reading
the following detailed description made in connection
with the accompanying drawings.
Brief Description of the ~rawinqs
Figure 1 is a perspective view of a bottle labeling
apparatus;
Figure 2 is a plan view of the bottle labeling
apparatus shown in Figure l;
Figure 3 is a fragmentary, side view of the
labeling apparatus with exterior covers omitted to show
interior details;
Figure 4 is a fragmentary, front view of the
labeling apparatus shown in Figure 3;
~ 5 ` 133347~
Figure 5 is a side view of a web positioning
mechanism constructed in accordance with the preferred
embodiment of the invention and forming part of the
labeling apparatus shown in Figure l; and
Figure 6 is a top view of the web positioning
apparatus shown in Figure 5.
Best Mode for Carryin~ Out the Invention
Figure 1 illustrates the external appearance of a
labeling apparatus constructed in accordance with the
preferred embodiment of the invention. The labeling
apparatus includes a sheet metal cabinet formed by a
plurality of removable covers 10, 12, 14, 16. A control
panel 18 contains a plurality of operator controls for
controlling the operation of the apparatus. The
disclosed labeling apparatus is adapted to apply
tubular, flexible labels to containers such as "2-
liter" soft drink bottles 20. It should be ~nderstood
that the present invention is adaptable to a variety of
labeling applications and should not be limited to the
bottle labeling apparatus disclosed herein
Referring also to Figure 2, the bottles 20 are
brought to the machine on a conveyor, indicated
generally by the reference characters 22. The conveyor
does not form part of the present invention and
therefore its details are not shown. The conveyor 22
alone or in cooperation with a bottle advancing
mechanism (not shown) advances a bottle on the conveyor
to a label applying position or labeling station
indicated generally by the reference character 28.
After it is labeled, the bottle is advanced out of the
labeling position by the conveyor or the bottle
advancing mechanism and onto an exit conveyor 26 that
carries the labeled bottles from the exit of the
labeling apparatus.
6 1333~7~
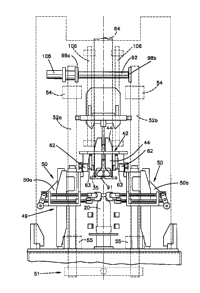
Figures 3 and 4 illustrate in more detail, the
labeling station 28 where a sequence or chain of labels
in the form of a tubular web 32 are applied to in-
dividual containers. Referring in particular to Figure
3, the web 32 (shown in phantom) is unwound from a
supply (not shown) and threaded around a series of
pulleys 36 through a web positioner 38 constructed in
accordance with the preferred embodiment of the
invention, around a guide assembly 40 and over a
mandrel assembly 42. The mandrel 42 expands the labels
prior to separation of an endmost label 32a from the web
32. In addition, the mandrel assembly 42 maintains
tension in the web 32.
The mandrel 42 extends inside the tubular web 32
and the web i8 expanded as it passes over the mandrel.
The mandrel 42 is formed of a tubular sheet metal or
plastic have a frusto-conical section 44 at its upper
end and a generally cylindrical skirt 46 formed at its
lower end. The skirt defines a pair of cut outs 48 on
its lateral sides for enabling a label ~tretched about
the base of the skirt to be gripped and pulled down-
wardly relative to the mandrel by a label applying
assembly 49 including label gripping assemblies 50
(shown in Figure 4).
A supporting tongue or mandrel fin 53 below which
the mandrel 42 hangs, extends upwardly from the mandrel
42 and carries rollers 54 which coact with a mandrel
support 56 including rollers 57. The web 32 passes over
the roller 54 and then the mandrel 42.
A web position detector 60 senses indicia on each
successive label 35. When the label 35 is properly
positioned with respect to the mandrel 42, the detector
60 produces a web brake operating signal for activating
a solenoid actuated brake 62. The web position indicia
are accurately located on each label and the detector 60
13~3~7~
and mandrel 42 are positioned so that each indicia is
sensed as it moves over the mandrel 42.
A preferred detector 60 detects visible light
fluorescing from the invisible indicia on each label and
is constructed as disclosed in U.S. Patent, 4,392,056 to
Weyandt entitled "Control Marking Detector" which issued
July 5, 1983. The position of the detector 60 relative
to the mandrel 42 can be adjusted by a support assembly
indicated generally by the reference character 61 and
including a slot 61a and link arm 61b. The adjustment
enables the detector 60 to be moved vertically and side
to side.
Referring also to Figure 4, label gripping
assemblies 50a, 50b positioned on either side of a
center line 64 of the mandrel 42 (and web 32) are
operative to grip a label positioned about the mandrel
42 and pull it downwardly over a container 20 positioned
directly beneath the mandrel 42. The gripper assemblies
50a, 50b release the label when its properly positioned
on the container and then are driven upwardly to grasp
the next label and repeat the labeling cycle. As the
gripper assemblies 50 move an endmost label downwardly
with respect to the mandrel 42, the detector 60 senses
the arrival of the next succeeding label and it
activates the brake 62.
Two brake pads 63 (shown best in Figure 4) are
driven into engagement with the web to pin the web
against the mandrel 42. The force of engagement between
the brake and web prevents the web from moving relative
to the mandrel. As continued movement of the gripper
assemblies 50 move the endmost label away from the
mandrel 42, a line of weakness gives way and the end
most label is severed from the web 32.
The label applying assembly is reciprocally movable
in a vertical plane by a carriage 51 (indicated
133~7~
generally in Figure 4) operatively connected to a drive
system located in the base of the apparatus. The
carriage 51 includes a pair of slide rods 52a, 52b that
are slidably supported by upper and lower slide bearings
54, 55. The left and right hand halves 50a, 50b of the
labeling applying apparatus 49 are adjustably clamped to
the left and right slide rods 52a, 52b, respectively.
The drive system for driving the label applying assembly
is preferably of the type disclosed in U.S. Patent
4,620,888. In summary, the drive system includes a
drive motor which rotates a cam that operates an arm
connected to the carriage 51 such that rotation of the
cam produces vertical, reciprocating motion in the arm
and hence the label applying assembly 49. The drive
system does not form part of the present invention and
will not be discussed further. Reference should be made
to U.S. Patent No. 4,620,888 for additional details.
The description of the labeling apparatus has been
substantially similar to the description in U.S. Patent
Nos. 4,412,876 to Lerner et al. and U.S. Patent No.
4,620,888 to Easter et al. The description regarding
the indicia detector 60 is substantially similar to the
description in U.S. Patent No. 4,565,592 to Wehrmann and
U.S. Patent No. 4,392,056 to Weyandt. Additional
details regarding the construction, arrangement or
operation of the brake 62, gripper assemblies 50,
mandrel 42 and indicia detector 60 can be obtained by
reference to these aforementioned patents.
In U.S. Patent No. 4,565,592 a method and apparatus
for adjusting the position of the mandrel 42 and hence
the label surrounding the mandrel, prior to installa-
133~47~
tion, was disclosed. In U.S. Patent No. ~,565,592, a
detector was used to monitor the position of the label
about to be installed, and in conjunction with a control
system, activated a stepper motor attached to the
mandrel support (i.e. 57) for raising and lowering the
mandrel 42 in order to ensure that the bottom of the
label about to be applied, was at a pre-set distance
above the container. By precisely locating the bottom
of the label, the final installed position of the label
lo on the container was made relatively consistent.
In the present invention a detector 90 which may be
the same type of detector disclosed in U.S. Patent No.
4,565,592 also monitors the position of the endmost
label 35. However in the present invention, the web
positioner assembly 38 is used to precisely adjust the
position of the endmost label prior to installation.
According to the invention, the machine is ad;usted
such that when severance of the label being applied
occurs, a bottom edge 91 of the next-to-be-applied label
35 is lower than a desired initial ideal position. In
the preferred embodiment, this is achieved by adjusting
the web detector 60 such that the web brakes 62 are
applied to the web 32 after the line of weakness 32a has
moved past an ideal or desired position.
After severance occurs, the web positioner 38 is
activated to reverse feed the web 32 in order to retract
the label until the leading edge 91 of the next-to-be-
applied label is at a desired position. With the
disclosed invention, the rather complex mechanism for
making position adjustments to the mandrel is eliminated
and replaced by a relatively straight forward mechanism
for moving the web in only one direction, i.e. retrac-
tion, without sacrificing reliability or cost.
Referring also to Figures 5 and 6, the construction
of the web positioner 38 is illustrated. In the
- lo 1~33~76
preferred embodiment the web positioner 38 comprises a
pinch roll assembly including a driven roll 92 and a nip
roll 94. Referring also to Figure 3, the web positioner
includes frame structure indicated generally by the
reference character 96 and in particular includes side
plates 98a, 98b. A support plate 100 extends between
the side plates and also mounts a clamping bar arrange-
ment 102. The clamping bar 102 enables the web
positioner to be adjustably clamped to a pair of support
rods 106. This arrangement enables the vertical
position of the web positioner 38 to be easily adjusted.
In the preferred construction, the driven roll 92
is rotatably mounted between the side plates 98a, 98b
and is connected to an electric motor 108. In the
preferred operation, the driven roller is continually
reverse rotated by the motor 108 during machine
operation.
The nip roll 94 is rotatably supported between
bearing members 110 that are attached to a pivot bar
112. The pivot bar is pivotally connected to the side
members 98a, 98b at pivot points 113 so that the nip
roll 94 can be moved towards and away from the driven
roller 92. An actuator 114 which may be pneumatically
operated, is operatively attached to the pivot bar 112
and is used to move the nip roller 94 into frictional
contact with the driven roller 92. In particular, the
actuator 114 includes an actuating rod 116 operatively
connected to a yoke member 118 bolted to a central
portion of the pivot bar 112. When pressurized, the
actuator rod 116 extends to drive the nip roller 94 into
frictional contact with the driven roller 92. As seen
best in ~igure 3, the web 32 passes through a gap G
defined between the driven roller 92 and the nip roller
94 when the actuator 114 is de-energized. The web
passes freely between the rolls during a label applying
1333~7 5
11
cycle. When the label being applied is severed from the
remainder of the web, the sensor 90 is enabled to sense
the position of the leading edge of the next-to-be-
applied label 35. As indicated above, the web brakes
62 and control system are ad~usted so that the leading
edge 91 of the next-to-be-applied label 35 is below the
desired position and as a result, the leading edge of
the web is not detected. The control system associated
with the detector 90 actuates the actuator 114 to cause
the nip roll 94 to frictionally clamp the web between
itself and the driven roller 92. As indicated above,
the driven roller is continuously rotated by the drive
motor 108 in a reverse feed direction. Movement of the
nip roller 94 into frictional contact with the web 32
causes the web to be reverse fed. As soon as the
detector 90 senses the leading edge 91 of the next-to-
be-applied label, the actuator 114 is immediately de-
energized thereby retracting the nip roll 94 and
immediately releasing the web. The next-to-be-applied
label (now the endmost label) is now accurately
positioned and is ready to be applied to the next
container located at the labeling station. With the
disclosed apparatus, very precise positioning of the
lead label 35 in the chain of labels 32 can be achieved.
By precisely locating the lead label, accurate position-
ing of the label on the product container is also
achieved. This is effected with a relatively simple
control mechanism that is highly reliable and is
believed capable of a positioning precision not
achievable with prior mechanisms.
Although the invention has been described with a
certain degree of particularity, it should be understood
that those skilled in the art can make various changes
to it without departing from the spirit or scope of the
invention as herein after claimed.