Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
1337110
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
1. Field of the Invention:
The present invention relates generally to the
manufacture of cross-laminated non-woven fabrics, and more
particularly to a method and apparatus for heat setting a
cross-laminated non-woven fabric composed of warp and weft
webs as they are bonded on and around a hot cylinder.
Throughout the specification and claims, the term
"warp web" is used to refer to a web formed of fibers
arranged to extend substantially in the lengthwise direction
of the web and hence having a larger strength in the
lengthwise direction than in the transverse direction
thereof, the term "weft web" is used to refer to a web
formed of fibers arranged to extend substantially in the
transverse direction of the web and hence having a larger
strength in the transverse direction than in the lengthwise
direction, and the term "cross-laminated non-woven fabric"
is used to refer to a non-woven fabric composed of the warp
and weft webs laminated together, with the fibers in the
warp web extending crosswise the fibers in the weft web.
2. Description of the Prior Art:
Cross-laminated non-woven fabrics, cross-laminated
films or the like cross-laminated sheet materials have
recently been developed and placed on the market. In the
manufacture of such cross-laminated sheet materials, warp
and weft webs are bonded together into layers. In this
instance, it is necessary to heat-set the warp and weft webs
_- 133711~
as they are bonded together. To meet this requirement, a
hot cylinder is utilized in general. The hot cylinder has
the advantage of its small installation space and high heat
efficiency. The hot cylinder has a drawback however that
the warp and weft webs while being heat-set on the hot
cylinder are caused to shrink widthwise. This widthwise
shrinkage lowers the productivity of the cross-laminated
sheet material and also adversely affects the strength,
Young's modulus and other physical properties of the
cross-laminated sheet material.
The foregoing widthwise shrinkage of the webs while
being heat-set can be prevented by using a conventional
tentering process in which the webs are held firmly at the
opposite sides or selvages by pins or clips. The tentering
process, however, requires an expensive apparatus which is
large in size and hence occupies a large space for
instaIlation thereof. Another problem is that a hot air
heating system employed in the tenter frame is low in
thermal efficiency. Furthermore, the tentering process is
totally unsatisfactory when used in the manufacture of a
cross-laminated sheet material in which bonding of warp and
weft webs is major requirement.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
With the foregoing difficulties in view, it is
accordingly an object of the present invention to provide a
method of making a cross-laminated sheet material composed
of warp and weft webs bonded together into layers and heat
1337110
set on a hot cylinder without causing widthwise shrinkage
which would otherwise lower the productivity and physical
properties of the cross-laminated sheet material.
Another object of the present invention is to provide
an apparatus for reducing the foregoing method into
practice, which apparatus is simple in construction and can
be manufactured less costly, and is small in size and
occupies only a small space for installation thereof.
According to a first aspect of the present invention,
there is provided a method of making a cross-laminated
non-woven fabric of the type in which a warp web having a
larger strength in the lengthwise direction than in the
transverse direction and a weft web having a larger strength
in the transverse direction than in the lengthwise direction
are bonded together and heat-set while they are continuously
fed around a rotating hot cylinder, wherein the improvement
comprises: holding the warp and weft webs in superposed
relation to one another by gripping at least their opposite
selvages by and between an outer peripheral surface of the
rotating hot cylinder and a pair of parallel spaced endless
belts held under tension against the outer peripheral
surface of the rotating hot cylinder, thereby preventing the
superposed warp and weft webs from shrinking widthwise as
they are heat-set on the hot cylinder.
According to a second aspect of the present invention,
there is provided an apparatus for making a cross-laminated
non-woven fabric of the type having a rotating hot cylinder
1337110
for bonding and heat-setting a warp web having a larger
strength in the lengthwise direction than in the transverse
direction and a weft web having a larger strength in the
transverse direction than in the lengthwise direction as
they are continuously fed around the rotating hot cylinder
in a superposed relation to one another, wherein the
improvement comprises: an endless belt held under tension
against an outer peripheral surface of the rotating hot
cylinder for gripping at least opposite selvages of the warp
and weft webs therebetween as the warp and weft webs are fed
around the hot cylinder, thereby preventing the warp and
weft webs from shrinking widthwise as they are heat-set on
the hot cylinder.
Many other advantages and features of the present
invention will become manifest to those versed in the art
upon making reference to the detailed description and the
accompanying sheets of drawings in which preferred
structural embodiments incorporating the principles of the
present invention are shown by way of example.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
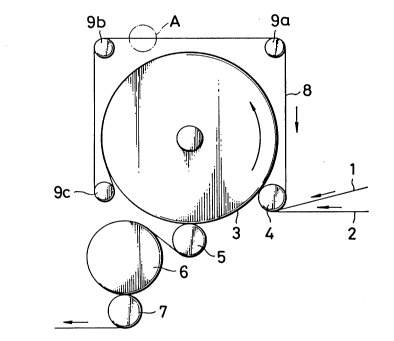
FIG. 1 is a diagrammatical view showing the general
construction of an apparatus according to the present
invention;
FIG. 2 is a schematic plan view of a rotating hot
cylinder and associated endless belts of the apparatus shown
in FIG. l;
FIG. 3 is an enlarged side view of a portion of the
1337110
endless belt which is indicated by a circle A in FIG. l;
FIG. 4 iS a view similar to FIG. 2, but showing
another embodiment of the present invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
FIG. 1 diagrammatically shows the general construction
of an apparatus for making a cross-laminated non-woven
fabric or the like sheet material by bonding and
heat-setting a warp web 1 and a weft web 2 as they are
continuously fed on and along an outer peripheral surface of
a hot cylinder 3 rotatably driven by a motor (not shown).
At least one of the warp and weft webs 1, 2 has a certain
degree adhesiveness or is treated with an adhesive. The
apparatus further includes first and second pinch or nip
rolls 4, 5 held in contact with the hot cylinder 3 and
having their central axes spaced from one another at an
angle of about 60 degrees relative to the central axis of
the hot cylinder 3 so as to guide the warp and weft webs
2 along about five-sixths of the full circumference of the
hot cylinder 3. Disposed downstream of the second nip roll
5 is a cooling cylinder 6 for cooling a cross-laminated
sheet material composed of the warp and weft webs 1, 2 which
have been bonded together and heat-set on the hot cylinder
3. The cooling cylinder 6 is provided with a third pinch or
nip roll 7 for holding the cross-laminated sheet material in
intimate contact with the cooling cylinder 6 as the
cross-laminated sheet material is withdrawn from the cooling
cylinder 6.
1337110
According to an important feature of the present
invention, the warp and weft webs 1, 2 are gripped at least
at opposite sides or selvages while they are fed around the
hot cylinder 3 in superposed relation, so that the warp and
weft webs 1, 2 are prevented from shrinking widthwise. To
this end, the apparatus includes a pair of parallel spaced
endless belts 8, 8 guided around the first nip roll 4 and
first, second and third guide rolls 9a, 9b, 9c so as to be
held under tension against the outer peripheral surface of
the hot cylinder 3. In the illustrated embodiment, the
third guide roll 9c is disposed upstream of the second nip
roll 5 and circumferentially spaced at an angle of about 60
degrees from the second nip roll S so that the endless belts
8 travel about four-fifths of a longitudinal portion of the
superposed warp and weft webs 1, 2 which is retained on the
hot cylinder 3. The endless belts 8 may be arranged to
further extend around the second nip roll 5 in which
instance the endless belts 8 coextend with the respective
selvages of the warp and weft webs 1, 2 retained on the hot
cylinder 3.
The endless belts 8 are made of a heat-resistant
material so as to withstand a temperature of the hot
cylinder 3. As shown in FIG. 3, each of the endless belts 8
has a release coating layer 8a on one surface thereof which
is engageable with the outermost web 1. The release coating
layer 8a preferably comprises a fluorine plastic film or a
silicone plastic film.
1337110
Materials eligible for the warp web 1 includes a web
of stretched or oriented tapes arranged in parallel
juxtaposition in the lengthwise direction of the web, a
reticular split fiber web spread widthwise 1.1 - 5.0 times
its original width, and a non-woven fabric formed of fibers
arranged to extend in the lengthwise directions. The weft
web includes a laminated web which is composed of a
continuous warp web of parallel-laid non-woven fabric, and a
succession of discrete weft webs of parallel laid non woven
fabric arrange lengthwise of and bonded with the continuous
warp web, with their adjacent edges slightly overlapping one
another. The laminated web may be made by a cross-
laminating machine such as disclosed in U. S. Patent No.
4,052,243 proposed by the present inventors. In making the
laminated web, a weft web is conveyed laterally over the
warp web in the machine direction and overlaid onto the warp
web in the manner of side by side arrangement without
leaving any gaps between each other, after being cut by the
length corresponding to the width of the warp web. Stated
otherwise, one of two identical continuous warp webs of
parallel laid non-woven fabric is fed transversely over the
other warp web in timed relation to the movement of the
other warp web. The one warp web is severed successively
into individual lengths which are substantially equal to the
width of the other warp webs. The thus severed individual
lengths of warp web are united by bonding to the other warp
web with their adjacent edges slightly overlapping one
1337110
another, as stated above. The weft web may be a continuous
transversely stretched web such as disclosed in U. S. Patnt
No. 4,349,500, or a non-woven fabric formed of fibers
arranged to extend in the widthwise or transverse
directions.
In operation, the warp and weft webs 1, 2 are
longitudinally fed successively around the first nip roll 4,
the hot cylinder 3 and the second nip roll 5. During that
time, the warp and weft webs 1, 2 are firmly gripped at
their opposite selvages by and between the outer peripheral
surface of the hot cylinder 3 and the respective endless
belts 8, 8 with the result the warp and weft webs 1, 2 are
heat-bonded together into a cross-laminated sheet material
and heat-set on the hot cylinder 3 without causing
heat-shrinkage in the widthwise direction. The
cross-laminated sheet material is withdrawn from the hot
cylinder 3 and then fed around the cooling cylinder 6 during
which time the cross-laminated sheet material is cooled to
set. The thus cooled cross-laminated sheet material is
finally withdrown from the apparatus through the third nip
roll 7.
A modified apparatus shown in FIG. 4 is substantially
identical to the apparatus shown in FIGS. 1 and 2 with the
exception that the superposed warp and weft webs 1, 2 are
gripped substantially throughout the width thereof by and
between the outer peripheral surface of the hot cylinder 3
and a single endless belt 10. The endless belt 10 has
- 1337110
substantially the same width as the webs 1, 2 and includes a
multiplicity of small pores or perforations 11 uniformly
distributed over the entire surface thereof. The perforated
endless belt 10 is permeable to vapor and hence allows
smooth vaporization of the moisture content from the webs 1,
2 as the webs 1, 2 are heat-set on the hot cylinder 3.
As described above, at least the selvages of warp and
weft webs are gripped by and between the outer peripheral
surface of a hot cylinder and two endless belts, so that the
warp and weft webs are bonded together into a
cross-laminated sheet material and heat-set without causing
widthwise heat-shrinkage. The thus produced cross-laminated
sheet material is sightly in appearance, is uniform in
structure and posesses improved physical properties such as
tensile strength and Young's modulus. The apparatus of the
present invention which is composed of a hot cylinder and
endless belts is simple in construction and hence can be
manufactured easily at a low cost. Furthermore, the
apparatus is small in size and hence occupies only a small
space for installation thereof.
Obviously, various modifications and variations of the
present invention are possible in the light of the above
teaching. It is therefore to be understood that within the
scope of the appended claims the invention may be practiced
otherwise than as specifically described.