Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
X~
,~
The present invention relates to a new video recorder,
camera or camcorder mounting and tracking system for
automatically tracking, monitoring and recording moving subjects.
The term camcorder will be understood to refer to an integrated
video camera and recorder apparatus. The invention effectively
provides a "robotic" accessory for camcorders which permits the
video recorder or camera to follow or track a moving subject
carrying an appropriate transmitter transmitting the tracking
:. .
signals. -
The present invention is intended primarily as an accessory
assembly for video recorder cameras or camcorders to provide
automatic tracking and recording assemblies for recreational use,
security systems, institutional uses, and military, commercial
and industrial applications. For example the invention may ~ -
advantageously be employed to direct a camera in hazardous
environmental locations.
The invention is particularly suitable for use with video
cameras and camcorders although those skilled in the art will
recognize that the invention may also be used with a conventional
movie picture camera. It will also be understood by those
skilled in the art that there may be some situations where even
still cameras may desirably be used with this apparatus. It will
also be understood that the invention has application to other -
apparatus other than cameras which may desirably be caused to
align a structure with a moving object. For example, a telescope -
could be mounted to track a moving transmitter.
The prior art includes an article entitled "A Television
System With Automatic Target Tracking Capability by Mark G.
Lowenstein, appearing in the December 1967 issue, volume 76, page
30 1189 of the Journal of the Society of Motion Picture and -
Television Engineers. United States Patents which describe
apparatus which is generally relevant include 3,988,S34;
i 4,121,246; 4,438,848; 4,513,317 and 4,515,455. That article
describes an automatic television camera tracking system that -
~U~ '12
tracks a moving target. The apparatus is capable of tracking an .
object that positively or negatively contrasts with the ~ .
background of the objec-t and does not use a discree-t transmitter
as does the present invention. The apparatus is not particularly ~ ~:
5 suited for the markets for which the present apparatus is .:`
intended in that it is more expensi.ve and complicated to build .
and maintain than the present invention. In addition, that .~. .
apparatus is much more vulnerable to losing the object being . : :.
tracked such as when the background of the object becomes similar . .
10 to the object. ;
It is an object of the invention to provide an apparatus . -~
which will positively track an object carrying a transmitter in :.
accordance with the invention. .~;... :
It is another object of the invention to provide apparatus ;- -.
1.~ which will be easy to use.
It is yet another object of the invention to provide
apparatus which smoothly accelerates and decelera-tes when : .;:
following an object so that, in the case of a camera high quality
pictur~s are produced. Still another object of the invention is ~ ~ ;
to provide apparatus that has a relatively simple construction
and thus may be inexpensively constructed and maintained. ..
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
It has now been found that these and other objects of the
invention may be attained in an apparatus for mounting and
25 positioning an associated device which includes a transmitter for :
producing a first control signal, a mounting platform, and a .;.:
first control apparatus disposed on the platform. The mounting
platform includes a first plurality of sensors disposed ~:
substantially in a first plane at angularly spaced intervals : ~;
about a first axis, each of the first plurality of sensors being
constructed to receive the first control signal radiated by the .
transmitter. The apparatus also includes means for ..
discriminating which of the first plurality of sensors is ..
receiving the first control signal from the transmitter, a
servomechanism is disposed intermediate the platform and the
associated device, and means are provided for controlling the
servomechanism to produce alignment: of the associated device
which produces a second signal based on the location of one or
more of the sensors receiving the signal at any instant.
In one form of the invention the sensors in the first
plurality of sensors are disposed :in an array in which an equal
number of sensors are disposed on each side of a first median
plane extending through the first axis. The apparatus may
include means to make the second control signal vary as a
function of the angular displacement of the transmitter from the
median plane. The angular displacement of the transmitter from
the median plane is a function of the location of which the
plurality of sensors receive the first control signal. The first
plane may be generally vertical.
The apparatus may include a second control apparatus
disposed on the platform and including a second plurality of
sensors disposed substantially in a second plane at angularly
spaced intervals about a second axis. Each of the second ;
plurality of sensors is constructed to receive the first control
signal radiated by the transmitter and includes means for
discriminating which of the second plurality of sensors is
receiving the first control signal from the transmitter. The
apparatus may further include means for controlling the
25 servomechanism to produce alignment of the associated device ;~
which produces a third control signal based on the location of
one or more o the sensors receiving the signal at any instant.
The sensors in the second plurality of sensors may be disposed in
an array in which an equal number of sensors are disposed on each
side of a second plane extending through the second axis and the
second control signal may vary as a function of the angular
displacement of the transmitter from the second median plane.
The angular displacement of the transmitter from the second ;~
median plane is a function of the location of which of the
4 ' ;~
:: ,
2~
plurality oE sensors receive the third control signal. The
second median plane may be generally horizontal. In many ;-
embodiments the associated device is a video camera. ;
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS .
The invention will be bet-ter understood by reference to the
accompanying drawings in which~
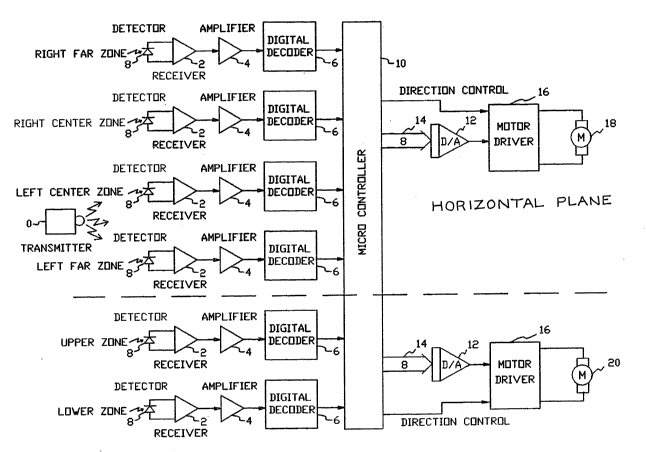
Figure 1 is a diagrammatic block diagram of the system in ;;
accordance with the invention.
Figures 2 and 3 are respectively diagrammatic views of the
manner in which the camera or other device is horizontally or
vertically positioned. -
Figure 4 is a diagrammatic view of the manner in --;
illustrating the construction of the transmitter.
Figures 5 - 8 are collectively a diagrammatic flow chart ~`
illustrating the manner of operation of the software that is used
in the control of the position o the camera or other device. ;
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
Referring now to Figures 1-3 there is shown the apparatus in
accordance with the present invention which includes a video
camera mounting and tracking system comprising a tracking device
60 and a moving transmitter 36. The tracking device 60 comprises ~ ;~
a novel mounting turntable 71 interposed between the conventional
camera or camcoder 62 and a conventional tripod 70. The mounting
.'. '
turntable 71 is an electromechanical tracking device which
permits rotational movement of the turntable 71 about two
perpendicular axes for omnidirectional tracking movement. A ~ -
first reversible motor 18 rotates the turntable 71 in a
horizontal direction around a vertical axis and a second
reversible motor 20 can simultaneously rotate the turntable 71 in ~ -
a vertical direction around a horizontal axis.
The diagrammatically illustrated tracking device 60
comprises mechanical elements including a housing and a gear
train (not shown separately) and electrical elements to be
described in greater detail. The transmitter 36 comprises
essentially only electrical elements. In accordance with the
present invention a moving subject, such as a person or object
"wears": the transmitter 36 and the tracking device 60 tracks the
subject by movement about horizontal and vertical axes, thus
maintaining camera alignment on the subject. The effective
distance between the transmitter 36 and tracking device 60 is 30-
50 feet maximum with the infrared system utilized in the
preferred embodiment. In another form of the invention a hybrid
device is used combining infrared and RF waves for a longer
distance system. The transmitter 36 on the moving subject or
object may, in other forms of the invention, use individually or
simultaneously acoustical or electromagnetic wave energy.
Electromagnetic signals may, for example, be in radio,
microwaves, infrared or visible light frequency ranges. Some
~ .. _............................................................ : ` :
other orms of the invention may also have a remote control
manual override feature.
The transmitter 36, which is worn by the moving subject, is ~ ;~
a digital circuit comprising a square wave clock generator 80 or
¦ oscillator, operating at 35 Khz. This square wave is fed into
20 the digital encoder 82 which modulates the 35 Khz square wave ;
into a pulse train. This digital encoding is necessary for ~ ~
discrimination when multiple apparatus, in accordance with the ;~ -
~ present invention, are used in the same field. The digitally ;~
j encoded signal is fed into the current driver 84 which drives the
infrared emitter 86. The emitter generates the electromagnetic
energy which in the preferred embodiment is pulsed infrared light ~;
necessary to excite one or more detectors 8. ~--
~ In order to track a moving subject emitting appropriate -;~
`~ signals, the mounting turntable 71 is formed with a "face" on one ~
-, 30 side with multiple sensors 46, 48, 50, 52, 72, 74 for receiving ~-
the control signal from the transmitters. Each sensor 46, 48,
50, 52, 72, 74 comprises one of six identical circuits which each
comprise an infrared detector 8, a receiver 2, an amplifier 4 and ~ ~;
a digital decoder 6. This combination of circuits detect, ;
~ 6
, , , : ::, . , .~.~,: .~
ampli~y and process the infrared signals emitted by the
transmitters 36. Four of the identical circuits are used for the
horizontal plane and two are used for the ver-tical plane. The
positions of the detectors form zones in the field of view of the
tracking device.
In the horizontal plane these zones are right Ear zone 38,
right zone 40, left center zone 42 and left far zone 44. In the ;
vertical plane, the zones are upper zone 64 and lower zone 66.
It is the position of the single transmitter 36 in these 6 zones
10 that will determine the direction and rate of rotation about the ;
plane of rotation in the horizontal plane 34 and plane of -
rotation in the vertical plane 76. Clockwise rotation in the
horizontal plane is determined by detector 48 and 46 being
activated by the transmitter 36. No rotational motion will occur
in the horizontal plane when detectors 48 and 50 are activated by
the transmitter 36.
Four rates of rotational velocity (including stopped or zero
... :.....
velocity) in each direction are provided in the horizontal plane.
The four sensors 46, 48, 50, and 52 are coupled through
appropriate logic to a microprocessors 10 to provide four speed
control of the horizontal plane motor 18. The outer sensors 46,
52 in the outer field of view of the face of the turntable 71 ~ -
initiate high speed tracking motion in the horizontal direction
when one of the outer sensors 46, 52 alone in the far zone or
25 left far zone receive tracking signals from the transmitter 36 ;~
on the moving subject. When signals are received by both outer
sensors 46, 52 and an inner sensor 48, 50 on the same side an
intermediate control signal actuates an intermediate speed
response by the horizontal motor 18 in the direction of the
moving subject. If an inner sensor 48, 50 is the only sensor
receiving a signal from the transmitter 36 and thus from either
the left center zone 42 or the right zone 40 receives signals
from the moving subject a slow speed motion by the horizontal
`motor is actuated. Finally when signals are sensed by the inner
sensors 48, 50 in the left center zone 42 and the right center
zone 40 the motor is stationary.
Similarly, the vertical plane clockwise rotation is
determined by the detector 74 being activated by transmi-tters 36
and vertical plane counterclockwise rotation is determined by the
detectors 72 being activated by transmitter 36. Two rates of
rotational velocity (including stopped or zero velocity) are
provided in the vertical plane.
Because the primary motion will be in the horizontal plane,
10 the variable speed motion control by multiple sensors is provided -
only in the horizontal plane. The sensors 72, 74 may be provided
in the vertical plane to control vertical motion about a ~ ~
horizontal axis at a single speed. Thus, the vertical control ~ ```
motor 20 drives the tracking device 60 either up or down at one
rate of movement or is disposed in a stationary position.
The micro controller 10 has two primary functions. The are:
1) monitor inputs o digital encoders 6 or all six zones and 2)
provides rotational position and velocity commands to the ; ` `;
horizontal plane motor 18 and the vertical plane motor 20. These
20 motion commands are provided to the motors by 8 digital bits ~;
which are directed via an 8-bit bus 14 to a digital-to-analog ~
converter 12 which converts the digital representation to an ~ `
analog DC voltage level. This analog voltage, proportional to
motor speed, is applied to an 'H' bridge configuration motor
driver circuit 16. The motor driver circuits 16 drive the
horizontal motor 18 and vertical motor 20 bidirectionally which
results in clockwise or counterclockwise rotation o the tracking
device 60 in the horizontal and vertical axes. '~
Two additional features are provided by the micro-controller ;-
~
10. They are: 1) simultaneously positioning of the trackingdevice 60 about horizontal and vertical axes and 2) smooth
ramping or rotational velocity in both horizontal and vertical
axes. A major feature and advantage of this multispeed control
of the universal motion of the mounting table 71 is that it
` ` ` ;-- 2al 0~
provides smooth movements of the recording camera. -
Referring now to Figures 5-8 there is shown a flow chart for
the software used with the microcontroller 10. Pro~ram operation :~
begins by turning on the power switch (not shown) to initiate a
5 power on reset vector in the ~icroprocessor or microcontroller -
10. This executes a series of initialization operations 102 such
as setting up registers, port assignments and the D/A converter
to null value so the motors 18, 20 will not rotate. The program
then enters the main loop where it continuously circulates from
items 104 through 136. The main loop begins by checking the left
center and left far zone sensors 50, 52. If either is active,
i.e. the transmitter infrared energy is falling on the sensor,
the program will continue to 106 or else it will skip to 110.
The chec~ at 106 determines if the right center sensor 40 is
inactive. If so, the horizontal motor 18 will ramp up or
accelerate in the left direction.
The rest oE the chart is much the same as the example
described above, i.e. combinations of active sensors 46, 48, 50,
52, 72, 74 will cause motion of the motors 18, 20. If none of ;
the sensor conditions are met, there is no motion. Each ramping
routine is called from the main loop. The ramp profiles are
determined by incrementing the D/A converter count each time a
ramp routine is called and using a delay value. A given ramp
value is incremented to cause acceleration, decremented to cause
deceleration or not changed to cause constant velocity each time
the main loop is traversed. This scheme allows smooth linear
ramping and simultaneous motor motion in both horizontal and
vertical directions.
~, The apparatus, in accordance with the invention, is fully
30 automatic and is a battery powered microprocessor controlled ~;
i camera accessory. The apparatus will keep a camera 62 in viewing
range within a 30 ft radius. The preferred form of the invention
` is limited to a +/- 20 degree vertical view but will encompass a ;
full 360 degree horizontal view. A 4 hour normal operation
1, ':
2~ 12
without recharging is possible. Continuous operation is possible
with an AC adaptor.
The invention has been described with reference to it
illustrated preferred embodiment. Persons skilled in the art oE
5 camera and mounting ~or cameras may, upon e~posure to the -
teachings herein, conceive other variations. Such variations are
deemed to be encompassed by the disclosure,, the invention being
limited only by the appended claims.
.: : ~ .:
., , . ,~,
': ., ;: :'
.: ~ ~ ::,: ;
"' . ~' . '`'' '
' . ' '' '':~.~ .'
. `. ~ ` ' .:
:. :,.. :: :~
,:.: : .; ~:
'` ,`,.'~ `~: "..'
` ' ~ ', .'''
... ~. ~ .
'~, :,-: '` ' - '
1 0
,.,', ',., .~,. ':,. ~ ,"'
. ~: ,:"
. ~