Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
201~979
This invention relates to improved means for removing
the rubber layer from a laminated conveyor belt and, in
partlcular, employs a heated blade to melt the rubber at its
polnt of attachment to an inner ply of the belt, thereby
enabling the rubber to be readily pulled away.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
An endless conveyor belt ls made by ~olning together the
er-ds of a length of belt materlal. The belt material is
usually made with several plies of material (e.g., a
laminate) and, in general, will have an inner ply made of
cords, usually steel, extending along the length of the belt
in order to prevent excessive stretching of the belt during
use. In general, the conveyor belts to which this invention
applles will have a central layer of steel or other metal
cord covered on each side with an appropriate elastomeric
material.
During use, however, damage frequently occurs to
conveyor belts and lt becomes necessary to make repairs on
the belt. Such repairE require that a layer of the belt
material be removed. One method of removing a layer of belt
material from a conveyor belt is to form a cut in the layer
of materlal across the length of the belt at a predetermined
distance from the end of the belt, and to form one or more
cuts along the length of the belt between the cross cut and
the end of the belt. The strips formed by the cuts in the
layer of belt materlal then can be peeled away from the other
layers of belt material. The peellng away of the Etrip of
2~1~979
material is usually done by hand or by use of a winch and the
strips of material are pulled away while simultAneously
cutting the adhesive or bond between the layers of material
with a knife or other sharp inst.rument. Since t.he layers of
the belt material are us~ally securely bonded together so
that the belt will last a long time when in use, the task of
stripping the outer layers at the ends of a helt is onero-]s
an(~ ti.me corlsllmirlg.
DISCUSSION ~F PRIOR ART
U.S. 3,929,555 discloses a conveyor belt strlpper system
ln which a winch on a portable framework ls used to pull from
the belt strips of material cut by hand.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTIO~
The present lnvention relates to an lmproved method of
stripping a layer of elastomeric material from a laminated
conveyor belt wherein an outer layer of the elastomer is cut
into strips and the strips are pulled away from an adjacent
layer of the belt, the improvement which comprises separating
the elastomeric strip from the adJacent layer with a knife
edge which is heated sufficiently to melt the elastomeric
strip at its point of contact wlth the adJacent layer,
whereby removal of the elastomeric strip is greatly
facilitated.
Another embodiment of the inven~lotl is an a~r~aratus ~sed
in the method of the invention which comprises, in
combination, a knlfe edge adapted to contact the ~uncture of
metal cord and elastomer of a laminated conveyor belt,
201 5q7q
supporting means for the knife edge on a guiding frame and
electrical mean~ to heat the knlfe edge to a temperature
sufficient to melt the elastomeric layer.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Fig. 1 is a perspective view of the apparatus in use.
Fig. 2 is an expanded, detailed view of how the knife
edge is mounted on the apparatus.
Flg. ~ ls a cross-~ectional view showlng the functlon of
the knife edge.
DETAILED OESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The equipment required to carry out the method of the
invention will comprise a power source, an apparatus to hold
and guide the knife edge and means to pull the strips of
elastomer from the conveyor belt, preferably a winch or
similar device which enables a controlled pull of the knife
edge through the rubber at the junction of the layers of the
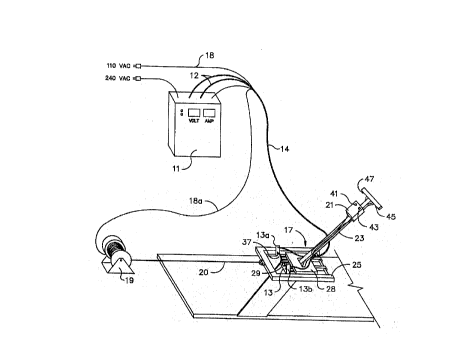
conveyor belt. Referring now to Flg. 1, a power source 11
supplies electrlcal power through two 4/0 weldlng cables 12
and umbilical cord assembly 14 to a knlfe edge 13 through
contact points 13a and 13b. The knlfe edge ls mounted on
a finger assembly 29 (see detail in Fig. 2 and Fig. 3)
which in turn comprise part of a guidlng apparatus shown
generally as 17. A winch 19 is powered by a separate source
of power thro~lgh electric cables 18 and 18a via a power
controller box 21 and serles of on/off switches 41 (toggle)
and A5 (Eprlng off) and a foward/reverse selector swltch 43
mounted on handle 23 of the guldlng frame 17.
201 5~79
The guiding frame 17 comprises a sled frame assembly 25
made of structural material such as aluminum, a support 27
made of insulating material, such as wood, which supports a
finger assembly made of structural material, such as steel,
shown generally as 29, a knife edge blade 13 mounted on the
finger assembly, which blade is electrically heated, a handle
23 attached to a metal plate 28, preferably aluminum, which
ls fastened to the support 27 and a spring switch 47 (also
known as a trigger switch) to provide on/off control of the
power source 11 via umbilical cord 14 to supply electrlcal
energy to the blade for heating.
In using the unlt, the operator ls requlred to pull
swltches 45 and 47 ln such a way to preheat and malntain heat
to the blade and to pull the sled arrangement 25 toward the
winch. The directlon of the sled arrangement is controlled
by the directional orlentation of the winch llne 20 and the
operator's input via the handle.
The knlfe edge blade used ln the lnventlon must have
certain characterlstlcs to make lt practlcal. The back
section of the blade must be sufflclently strong for mountlng
and have higher electrlcal resistant propertles than the
front sectlon so as to dlrect most of the electrical current
to the front edge whlch is to be heated. The front edge,
however, must have good edge holding abillty and for these
reasons, a blade fabrlcated from two dlsslmllar metals ls
preferred. The preferred blade for use ln the lnventlon has
a back section conslstlng of sprlng steel havlng a Rockwell
20 1 5979
hardness of from about 38 to about 40 and a front edge
sectlon conslstlng of AISI M~2 alloy which has been treated
to achieve a Rockwell C hardness of from about 65 to about
68. Such material is readlly available as lt is used to make
band saw blades and the preferred knlfe edge blade for use ln
the lnventlon is readily made from an appropriate length of
such a band saw blade before it is toothed. It ls deslrable
also to sharpen the front knlfe end sectlon of the blade and
to bend the ends of the blade to provlde contact polnts for
the electrlcal cords to the power source.
Referrlng now to Fig. 2, the mountlng of the knlfe edge
blade 13 on flnger assembly 29 is shown in expanded detail.
The blade 13 is mounted on fingers 15 whlch extend from the
front of the lnsulating support 27. The mountlng may be
accomplished by means of bolts, screws, or other fasteners 31
which attach the rear portion 30 of the blade 13 to the
flngers 15. The ends of the blade 13a and 13b are bent at an
angle from the portion of the blade attached to the fingers
to provide connection points for attaching the electric
cables 12a and 12b to the knlfe edge blade.
To remove a layer of belt material from the conveyor
belt, a cut is made in the upper layer of material across the
length of the belt and, if the belt ls wide enough, one or
more cuts are made along the length of the belt between the
cro~s cut and the end of the belt. The heated knlfe edge
bl~de is then positloned at one edge of the strip to be
removed and as the elaEtomerlc materlal melts, lt iE pulled
B 5
2 ~ 7 9
away by hand or by attachment to a winch as shown in U.S.
3,925,555.
Referring now to Fig. 3, which is a sectional view taken
along line 3-~ of Fig. 2, the conveyor belt is shown as a
three layer laminate; viz., a bottom elastomeric layer 33, a
middle section 35 composed of steel cable and an upper
elastomeric layer 37 which is pulled away as the heated blade
13 meets and melts elastomeric layer 37 at its print of
attachment to the cable layer 35.
As indicated, the movement of the sled 25 is dependent
upon the winch 19 which is readlly controlled by the operator
using the forward/reverse selector switch q3 on control box
21. Similarly, the electrlc power to the blade may be
readily controlled by a rheostat control (not shown) on the
power source 11 and a spring switch ~7 in handle 23 to turn
the pnwer off and on to the blade to maintain it at a desired
constant heat level. The sprlng on/off swltch 47 ls used by
the operator to optimize the heating of the blade during the
stripplng process.
The apparatus and method of the invention greatly
enhances the speed and eaEe of removing an ela~tomerlc layer
from a conveyor belt and as work tlme is reduced, so is the
cost of the operation. As an indication of the lmproved
efflciency that the lnventlon provides, lt has heretofor
required about 20 minutes to remove 10 feet of elastomer from
a conveyor belt, whereas u6ing the method of the lnventlon,
the same length of elastomer can be strlpped from the belt in
201~79
8 mlnutes, thus achle~lng a signlflcarlt reduction of wnrk