Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
~ 2017983
_
BACKGROUND OF INVENTION
Field of the Invention
The present invention relates to a metal pole
structure which is comprised of a plurality of inter-
connected elongated hollow pole sections which define a
longitudinal space therein with a plurality of braces
connected across the space all along the pole with the
space providing an access to effect interconnections
between the pole sections and the braces.
Description of Prior Art
Various metal pole structures are known to
provide various functions. The present metal pole
structure was conceived particularly, but not exclu-
sively, to replace wooden poles which are usually treated
with a preservative in a bottom section thereof and
embedded in the ground. A problem of these well known
wooden poles is that the-y deteriorate over time as rot
will set into the embedded portion of the pole. Also,
the embedded portion contaminates the soil surrounding
the pole due to the fact that these pole sections are
treated with a preservative. Because of the preser-
vative, there is also an environmental-hazard when these
poles are disposed of either by being burned or buried in
the soil. Wooden poles also have limited applications
and in certain geographical areas, it is not possible to
utilize these poles because the ground may be too soft
and swampy or the ground may be infested with termites
which would destroy the poles. A still further
disadvantage of these poles is that when utilizing them
in a cable support application, it is necessary to have
poles which are excessively long and heavy and this makes
2017983
it difficult to transport the poles to the site and
also to erect the poles. Such work is expensive,
labor-intensive, and time-consuming. Still further,
these poles are made by cutting large trees which
results in a depletion of our forests.
SUMMARY OF INVENTION
It is a feature of the present invention to
provide a novel metal pole structure which is intended
to replace the well known wooden pole structures and
which substantially overcomes all of the above-
mentioned disadvantages of wooden poles.
Another feature of the present invention is to
provide a novel metal pole structure which is
competitive with known wooden poles.
Another feature of the present invention is to
provide a metal pole structure which is comprised of a
plurality of pole sections which are easy to transport
and which may be assembled on site.
Another feature of the present invention is to
provide a novel metal pole structure which can be
embedded into the ground or in concrete, or secured to
a base structure and which may be used for multiple
applications.
According to the above features, from a broad
aspect, the present invention provides a metal pole
structure which comprises a plurality of separate,
elongated hollow pole sections having longitudinally
interconnected end portions. Each section is formed
with at least two elongated angled wall sections and a
longitudinal space is provided between longitudinally
extending edge portions thereof. An upper pole section
of the pole sections has an upper tapered connecting
portion and a larger lower tapered connecting portion
so that an outer surface of a top portion of a lower
pole section of the pole sections is received within
and engages an inner surface of the lower connecting
,~
- 2017983
portion of the upper pole section. Removable fastening
means is provided for interconnecting the top portion
of the lower pole section with the lower connecting
portion of the upper pole section. A plurality of
braces are provided which interconnect the edge
portions and bridge the space to provide a bracing
structure that undergoes compression and tension
alternatively when the pole is subjected to a bending
moment. The space defines access openings along the
pole sections to permit access to the interior of the
hollow pole to effect interconnection of the pole
sections and the braces.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF DRAWINGS
A preferred embodiment of the present invention
will now be described with reference to the example
thereof as illustrated in the accompanying drawings in
which:
FIG. 1 is a side view illustrating a metal pole
structure constructed in accordance with the present
invention;
FIG. 2 is a view similar to Fig. 1 but
illustrating the longitudinal space provided along the
pole and the braces which are interconnected about the
space and providing access to the interior of the pole;
FIG. 3A is a cross-section of a pole section;
FIG. 3B is a further cross-section showing the
manner in which the pole sections are connected end-to-
end;
FIG. 4 is a side section view showing the bottom
portion of the structural pole as secured in a concrete
footing;
FIG. 5A is a cross-section of a pole section
showing a variation thereof;
FIG. 5B is a cross-section of a pole section
showing a further variation thereof;
2017983
FIG. 5C is a cross-section of a pole section
showing a still further variation thereof;
FIG. 6 is a side view of a top portion of the
metal pole structure showing accessories connected
thereto; and
FIG. 7 is a view similar to Fig. 6 but showing
an electrical line cross-arm assembly secured to the
top end of the metal pole structure.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
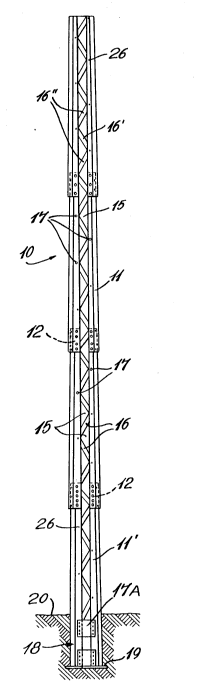
Referring now to Figs. 1 to 3, there is shown
generally at 10, a metal pole structure constructed in
accordance with the present invention and comprised of
a plurality of elongated hollow pole sections 11 having
outer surfaces thereof interconnected end-to-end. Each
section 11 is provided with interconnecting means at
the ends thereof to form the end interconnections 12
which are secured together by a plurality of fasteners
13, herein bolt fasteners.
As can be seen from Figs. 3A and 3B, each
section 11 is a hollow pole section and defines at
least two or more elongated angled wall sections 14
disposed at an angle to one another to provide
structural rigidity. A space 15 is defined in a
portion of the peripheral wall of each pole section and
extends longitudinally thereof, herein entirely across
the pole sections, from end to end.
As can be seen in Fig. 2, when these pole
sections 11 are connected end-to-end, this space 15
extends all along the pole structure and a plurality of
braces 16, here in a zig-zag array of diagonal braces,
are connected across the space 15 all along the pole.
These diagonal braces 16 are formed of angled straight
metal struts interconnected at their opposed ends by
bolt fasteners 17. The space 15 provides access
openings in order to position and secure these bolt
~;~
.~
2017983
fasteners 17 and 13 to interconnect the pole sections
end-to-end and the braces 16 all along the pole.
The braces 16 are, as mentioned hereinabove,
connected diagonally in a zig-zag arrangement wherein
when the pole structure 10 is subjected to a bending
moment by wind or otherwise, one of the struts, for
example strut 16', will be placed in tension while the
adjacent braces 16" will be subjected to compression,
thereby providing a bracing structure across the space
all along the pole. It is pointed out that it is
within the ambit of the present invention to provide
reinforcing braces of different shapes and, for
example, a different type brace 17A is provided at the
bottom connecting portion 18A of the pole. It is also
conceivable that longitudinal space 15 may not extend
from end to end.
As shown in Fig. 1, the bottom connecting
portion 17 may also be provided with a base plate 19
which is also bolted to the bottom end of the lower
pole section 11' to constitute an anchoring means to
stabilize the pole structure when anchored in the
ground 20. The plate 19 could also be bolted to a
support base structure, not shown. Alternatively, as
shown in Fig. 4, the bottom pole section 11' need not
be provided with a base plate if it is set in a
concrete footing, such as shown at 21. When anchoring
the bottom section 18 into the ground, as shown in Fig.
2, the embedded section is usually 10% of the height of
the pole plus 2 feet below the ground surface to
provide excellent pole stability.
As is also shown in Fig. 1, the pole 10 tapers
longitudinally from the bottom section thereof to the
top section. This taper provides for the ends to mate
one into the other to form the interconnection 12
~017983
between the pole sections. As herein shown, each pole
section is provided with an upper tapered connecting
portion 22 and a larger lower tapered connection
portion 23 so that the upper connecting portion 22 of
an adjacent pole section 11 can be received in close
fit in the lower section 23. Each pole section is also
progressively small in cross-section. A plurality of
holes 26, 26 are provided in both sections 22 and 23 at
predetermined locations whereby these holes will align
with one another when the end sections are
telescopically mated and bolt fasteners 13 are inserted
in these holes through the spaces 15 provided in the
slotted wall section of the pole.
After the pole sections 11 are assembled, the
metal struts 16 are then interconnected. Of course,
some of these struts 16 may be connected before the
pole sections 11 are assembled and the struts in the
end interconnection section 12 may be connected after
the sections are assembled.
As can be seen more clearly in Fig. 3, the
struts 16 are preferably disposed inside the hollow
pole sections 11. However, as shown in Fig. 5C, these
struts 16 may also be disposed on the outside of the
pole structure. As shown in Fig. 3A, the edge portions
25 of the pole side walls, on each side of the opening
15, are formed as narrow wall sections and define
connecting flanges on opposed sides of the space and
are disposed in a
- ~ 2017983
common plane. A plurality of holes 26 are disposed at
predetermined locations along these flanges to permit the
interconnection of the struts 16 by the fasteners 17.
The pole sections as illustrated in Figures 3A and 3B are
comprised of six wall sections 14 of equal widths and
this is a preferred cross-section for the assembly of a
pole structure having a length of between 70 to 80 feet.
Referring to Figure 5A, there is shown a pole
structure having a different cross-section configuration
and this is suitable when the pole height is shorter, say
between 50 and 60 feet. As herein shown, the pole
section 11 is comprised of four wall sections, two wall
sections 30 which are disposed parallel to one another,
and two other integrally formed wall sections 31 disposed
on a common side of the parallel wall sections to form a
pole section with a wall section of V-shaped cross-
section.
Figure 5B shows a still further cross-section
wherein the pole sections are rectangular and comprised
of three equal width sections 32 disposed at right angles
to one another.
Figure 5C shows a still further embodiment
wherein the pole section is of V-shaped cross-section and
defined by two wall sections 33 disposed at an angle to
one another and of substantially equal width. These
latter cross-sections are for poles of heights shorter
than 40 feet.
Figures 6 and 7 illustrate the connection of
different accessories, such as a horizontal cross-arm 34
or a top cross-arm assembly 35 or a lamp 36 as connected
at different locations along the pole structure. For
~ 2017983
these specific applications, holes would be provided at
predetermined locations in predetermined pole sections to
permit the interconnection of these accessories. Again,
the interconnection would be made through the space 15
provided all along the pole. Many other accessories may
be connected to the pole, along its length, as is obvious
to a person skilled in the art. It would also be obvious
to a person skilled in the art to provide end inter-
connections 12 which are different from those shown in
the drawings and the pole sections 11 need not be tapered
sections. It can be appreciated that a pole structure as
defined herein provides for a very economical design in
that it utilizes hollow metal sections which- are easily
transportable and easy to assemble. The interconnections
are also made by bolt fasteners eliminating the need to
provide welding, which is also more expensive and
time-consuming. The pole is also easily dismantlable,
easy to transport in a disassembled form, easy to erect,
and has longevity as well as being able to be anchored in
all types of soil surfaces and in areas of varying
climatic conditions. Other various modifications of the
preferred embodiment described herein are intended to be
covered by the present application, provided such
modifications fall within the scope of the appended
claims.