Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
- l - 2019082
S P E C I F I C A T I O N
Ti tl e of the I nver-ti on
r1ethod of Forming Space Section
D~void of Coupling Elements in
Continuous Slide Fastener Chain
R~ck~ro~ln-l of the Invention
1. Field of the Invention
This invention relates to an improved method of forming space
sections devoid of coupling elements disposed, with a predetermined
10 distance, in a slide fastener chain which is composed of a pair of
continuous rows of interengaged coupling elements.
2. Prior Art
There have been proposed a variety of methods of forming space
sections devoid of coupling elements automatically and continuously,
5 which is disposed, with a predetermined distance, in a slide fastener
chain composed of a pair of continuous rows of interengaged coupling
elements. Since fastener tapes are made of fabric piece, they are
locally elongated or shrunk. Accordingly, in these conventional
methods, cumulative errors in element pitch are produced and the
20 slide fastener chain cannot always be brought to stop at a desired
position for forming the space section precisely. If the slide fastener
chain with the space section were processed under such element
condition, the result would be that terminal coupling elements at
- 2 - 2019~82
either or both ends of the space section and either or both of the
coupling elements adJacent to such terminal coupling elements are
cut only partly away. In Fig. 18, an element B, which is adjacent to
the terminal element of the space section A and whieh is ~ut only
5 partly away, is shown. Due to such faulty elements, high quality
products can not be obtained. In order to prevent such elements from
being produced, methods are disclosed in USP No. 4,428, 264 and
Japanese Patent Publication No. 63-44363.
In the specification of the present invention, a proceeding side as
1 0 viewed from the feed direction of a sl ide fastener chain w i l l be
expressed as a downstream side. Then, a following side will be
expressed as an upstream side.
In the apparatus related to USP No. 4,428, 264, due to an indexing
means disposed at only upstream side of a punch blade, the upstream
15 side terminal elements of a portion to be a space section of a
continuous slide fastener chain can be brought to stop at a desired
position. Then, the slide fastener chain is cut by the punch blade after
being stretched. However, as described before, a fastener tape is
local]y elongated or shrunk. Then, the downstream side terminal
20 elements of the portion can not be brought to stop at another desired
portion. Accordingly, the space section cannot always be formed at a
desired position. On the other hand, a pair of relief portions are
formed at opposite ends of the punch blade so as to protect the
coupling elements disposed adJacent to the terminal coupling
25 elements lying at opposite ends of the space section, from being cut
by the punch blade. However, since the relief portions are not always
placed precisely for the rows of the coupling elements to be
- 20190~2
protected, it is feared that the upper surface of these coupling
elements are damaged by the punch blade.
In the apparatus related to Japanese patent publication No. 6~-
44363, due to two indexing means, the portion of a continuous slide
5 fastener chain to be a space section can be placed below a mechanism
for removing the raws of fastener elements from the fastener chain.
The two indexing means are disposed at the upstream side and the
downstream side of the mechanism respectively and operated
simultaneously. However, as described before, a fastener tape is
10 locally elongated or shrunk, thus, there is a possibility of changing of
a length of the portion. In this case, one of the two indexing means
acts on desired elements precisely while another indexing means can
not act on other desired elements precisely. Therefore, it is feared
that a faulty element as described before is produced in this
1 5 apparatus also.
Sllmm~ry of the In~fention
An obJect of the present invention is to provide a method by
which, even if a fastener tape is locally elongated or shrunk, a space
20 section devoid of coupling elements can be formed in a continuous
slide fastener chain accurately and surely without forming a faulty
element at the opposite ad~acent sides of the space section.
According to the present invention, a method of forming
repeatedly one by one space sections devoid of coupling elements in a
25 continuous slide fastener chain having a pair of rows of interengaged
- 4- 20190
coupling elements is provided. This method of forming one space
section in a one-cycle comprises the following steps.
A portion to be the space section in the slide fastener chain is
transported below an element-removing apparatus and the
transportation of the slide fastener chain is stopped.
A downstream locating means, as viewed from the feed direction
of the slide fastener chain, is engaged to a fastener element of a
normal portion not to be the space section adjacent to the
downstream side end of the portion to be the space section. In this
case, a small tension is given to the slide fastener chain so that the
pair of rows of the interengaged coupling elements at the downstream
side of the portion are located below a cutting means of the element-
removing apparatus. Accordingly, if the length of the portion to be the
space section is changed due to being elongated or shrunk of the
fastener tape, the pair of rows of the elements at the downstream
side of the portion are brought to stop precisely for being removed in
a next step.
The pair of rows of the interengaged coupling elements at the
downstream side of the portion are removed.
The downstream locating means and the cutting means are
returned to positions at which the both means are not operated
respectively.
An upstream locating means is engaged to a fastener element of a
normal portion not to be the space section adjacent to the upstream
side end of the portion to be the space section. In this case, a small
tension is given to the slide fastener chain so that the unremoved rest
of the pair of rows of the interengaged coupling elements at the
2019~82
upstream side of the portion is located below the cutting means of the
element-removing apparatus. Accordingly, if the length of the portion
to be the space section is changed due to being elongated or shrunk of
the fastener tape, the unremoved rest of the pair of rows of the
5 elements at the upstream side of the portion is brought to stop
precisely for being removed in a next step.
The unremoved rest of the pair of rows of the interengaged
coupling elements at the upstream side of the portion is removed.
The upstream locating means and the cutting means are returned
10 to positions at which the both means are not operated respectively.
Then, after the one-cycle of the above mentioned steps is
finished, a next one-cycle can be started by transporting the slide
fastener chain again as a first step of the next one-cycie. As a
result, the space sections are formed repeatedly one by one in the
l S slide fastener chain, with the predetermined distance, accurately and
surely without forming a faulty element at the opposite adjacent
sides of the space section.
Further ob~ects and advantages of the present invention will be
apparent from the following description, reference being had to the
20 accompanying drawing wherein preferred embodiments of the present
invention are clearly shown.
P~rief ~escri~ltion of the Dr~win~s
Fig. 1 is a schematic elevational view, partly broken away, of an
apparatus as an example related to the present invention;
201~082
Figs. 2 and 3 are enlarged schematic vertical longitudinal
sectional views showing a step for cutting and removing coupling
heads of fastener elements by a punch;
Figs. 4, 5, 6 and 7 are schematic elevational views, partly broken
5 away, showing operation in an important part of the apparatus in Fig.
1 according to the order of operation;
Figs. 8 and 9 are enlarged schematic elevational views showing
operation of a downstream locating pin according to the order of
operation;
Figs 10, 1 1, 12 and 1~ are enlarged schematic plan views showing
operation of a portion to be a space section, downstream and upstream
locating pins and a punch according to the order of operation,
Fig. 14 is an enlarged schematic elevational view of a punch in
another embodiment;
Fig. 15 is an enlarged schematic elevational view of a punch in
still another embodiment;
Fig. 16 is an enlarged schematic plan view of a part of a slide
fastener chain before a space section is formed;
Fig. 17 is an enlarged schematic plan view of a part of a slide
20 fastener chain after a space section is formed;
Fig. 18 is an enlarged schematic elevational view of one end of a
space section which is formed by a conventional method and which has
a faulty element.
7 201~0B2
Description of the Preferred Fmboniment
The method of the present invention is embodied with an
apparatus such as shown in ~igs. 1, 2, and 3. As shown in Figs. 16 and
17, the rows 34 of coupling elements of a portion 8 are removed from
5 a continuous slide fastener chain 2 to be a space section 7 which has
a predetermined length L.
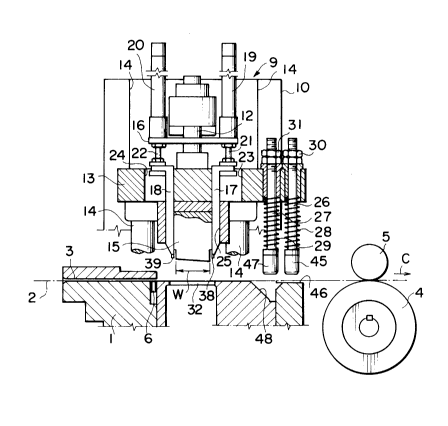
A base 1 has in its top surface a longitudinal guide path 3 along
which the slide fastener chain 2 is transported intermittently in a
direction indicated by an arrow C by operation of a drive roller 4 and a
1 0 pinch rol ler 5.
A sensor 6 is equipped at the guide path 3 so as to detect that the
portion 8 is brought to a desired position to form the space section 7
below an element-removing apparatus 9 described hereinafter . In
case that the fastener elements are made of metal, a metal detector
15 is adopted as a sensor 6. The detector detects that the portion 8 is
brought to the desired position below the element-removing apparatus
9 by means of counting the number of the fastener elements which are
fed over the detector. Then, the metal detector sends signals so that
the rotation of the drive roller 4 is stopped. On the other hand, in
20 case that the fastener elements are made of synthetic resin, a photo
electric cell or a roller are adopted respectively as a sensor 6. In case
that the roller is used, it rotates touching the slide fastener chain and
is interconnected to an encorder so that the length of the fed chain is
detected. -
- 8 - 2019~2
In the element-removing apparatus g, a link 12 is interconnected
to a motor (not shown) mounted on a support frame 10 through the
intermediary of an eccentric wheel. Then, a movable block 13 is fixed
to the link 12 so as to move vertically guided by a guide rod.l4
provided at the support frame 10.
A punch lS serves as a cutting member and is connected to the
center of the underside of the movable block 13. The longitudinal
length W of the punch 15, as viewed from the feed direction of the
slide fastener chain 2, is set to be shorter than the longitudinal
length L of the space section 7 and longer than half of the length L.
Air cylinders 19, 20 are mounted on a bracket 16 fixed to the
support frame 10. A downstream locating pin 17 and an upstream
locating pin 18 serve as a downstream locating means and an
upstream locating means respectively. The pins 17, 18 are separately
operated by the cylinders 19, 20 respectively and are connected to
piston rods 21, 22 respectively.
As shown in Fig. 1, the downstream locating pin 17 and the
upstream locating pin 18 are placed to touch the both sides of the
punch 15 respectively over the guide path 3 for the fastener chain 2
so as not to be interfered with each other. Then, they move vertically
through halls 23, 24 and 25 formed in the movable block 13 by means
of the air cylinders 19, 20 respectively. The vertical movement of the
punch 15 does not interfere with the movements of the locating pins
17, 18.
A chain-pressuring rod 26 and a chain-stretching rod 27 are
vertically movably provided at the downstream side end of the
movable block 13 so as to locate over the guide path 3 of the base 1.
9- ~019082
Then, the rods 26, 27 are urged downward by coil springs 28, 29
respectively and their length of the portions which are projected
downward from the movable block 13 can be adJusted by double nuts
30, 31 respectively.
As shown in Figs. 2 and 3, a pair of dies 32, 33 are disposed one
on each side of the guide path 3 of the base 1 so as to support
undersides of legs of the slide fastener chain 2 which are attached to
the fastener tape. Each die 32, 33 has the same longitudinal length
which is corresponding to the longitudinal length W of the punch 15.
Each edge 35, 36 is formed along each fastener tape. Heads 37, 37 of
the both rows 34, 34 of the coupling fastener elements are
interengaged each other. The punch 15 descends to cut and remove a
group of the interengaged heads 37, 37 formed between the edges 35,
36, while the front and back faces of the punch lS having the
longitudinal length W touch the edges 35, 36 respectively.
The legs of the elements of the rows 34, ~4, which are uncut and
are left to be attached to the edges 35, 36 respectively, are removed
by brushing and the like later.
The both locating pins 17, 18 are provided with tip ends 38, 39
respectively. Each tip end 38, 39 is placed so as to be spaced from
each end of the punch 15 with a length.of predetermined élement
pitch. When the fastener elements of the portion are cut and removed,
the chain-pressuring rod 26 and the chain-stretching rod 27 are
operated. In this case, as shown in Figs. 9, 11 and 13, each tip end 38,
39 is set to engage to each leg 43, 44 of each fastener element 41, 42
of one fastener stringer 40 of the slide fastener chain 2. These
fastener elements 41, 42 are adjacent to the downstream side end and
- 1 o - 2 019 ~82
-
the upstream side end of the portion to be the space section
respectively.
A fore end pad 45 of the chain-pressuring rod 26 is provided to be
faced to a plane top surface 46 of the base 1. As shown in Figs. 5 and
5 7, when the rod 26 descends, the pad 45 pinches the slide fastener
chain 2 in the guide path 3 with the surface 46 so as to pressure and
clamp the fastener chain 2.
On the other hand, a recess 48 is formed on the top surface of the
base 1 transversely through the guide path 3 below a fore end pad 47
10 of the chain-stretching rod 27. As shown in Figs. 5 and 7, when the
rod 27 descends, the pad 47 pushes the slide fastener chain 2 into the
recess 48 so as to give a small tension to the fastener chain 2. The
both pads 45, 47 are placed so as to be pro~ected downward deeper
than a position of the cutting edge of the punch 15 before cutting and
1 5 removing operati on.
The method of the present invention with this apparatus is
embodied as follows.
As shown in Fig. 1, the continuous slide fastener chain 2 is
transported intermittently along the guide path 3 on the base 1 in the
20 direction indicated by the arrow C by operation of the drive roller 4
and the pinch roller 5. When the portion 8 to be the space section 7 is
brought to below the element-removing apparatus 9, the sensor 6
detects that. Then, corresponding to the signals from the sensor 6,
the rotation of the rollers 4, 5 are stopped. Accordingly, the
25 transportation of the slide fastener chain 2 is stopped.
Next, as shown in Figs. 8 and 10, the air cylinder 19 is operated
to move the downstream locating pin 17 downward to strike against
2019082
the leg of a fastener element, which is adjacent to the fastener
element 41.
As shown in Figs. 11, 12, 16 and 17, this fastener element 41 is
the terminal element of a normal portion 50 not to be the space
5 section 7 and adJacent to the downstream side end 49 of the portion 8
to be the space section 7.
Although- in Figs. 8 and 10, a tip end 38 of the downstream
locating pin 17 strikes against the upper surface of the leg of the
fastener element adjacent to the fastener element 41, the tip end 38
10 might be inserted between the leg 43 of the fastener element 41 and
the leg of the above mentioned fastener element which is adjacent to
the element 41 due to a position at which the slide fastener chain 2 is
- brought to stop.
Then, the motor (not shown) is operated to move the movable
15 block 13 downward through the intermediary of the link 12. As shown
in Fig. 5, the slide fastener chain 2 is pressured and clamped between
the fore end pad 45 of the chain-pressuring rod 26 and the plane top
surface 46 of the base 1, further the chain 2 is pushed slightly into
the recess 48 by means of the fore end pad 47 of the chain-stretching
20 rod 27.
As described before, the tip end 38 of the downstream locating
pin 17 has struck against the upper surface of the leg of the fastener
element adjacent to the fastener element 41 as shown in Figs. 8 and
10 or has been inserted between the leg 4~ of the fastener element 41
25 and the leg of the fastener element adjacent to the element 41,
although this condition is not shown. However, by the above
mentioned operation of the both pads 45, 47, the tip end 38 engages to
- 12 - 20 19 082
the leg 43 of the fastener element 41 as shown in Figs. 9 and 11,
because, the slide fastener chain 2 located below the element-
removing apparatus 9 is stretched slightly toward downstream side.
Accordingly, the downstream side end 49 of the portion 8 to be the
5 space section 7 is located precisely.
The link 12 is operated to move the punch 15 in a way as shown in
Figs. 2, 3, 5 and 11 so that a group of interengaged heads 37 of the
rows 34 of the fastener elements with a length 1I disposed at the
downstream side of the portion 8 is cut by the cutting edge of the
1 0 punch 15 to be removed from the fastener chain 2.
Next, the link 12 and the air cylinder 19 are moved upward and
the punch 15, the downstream locating pin 17, the chain-pressuring
rod 26 and the chain-stretching rod 27 are returned to original
positions at which they can not be operated. By this operation, a
15 forming process for the downstream side part of the space section in
the continuous slide fastener chain is finished.
Then, the slide fastener chain 2 is transported again in the
direction indicated by the arrow C. When the rest of the rows 34 of
the fastener elements in the portion 8 to be the space section 7 are
20 brought to below the punch 15, the sensor 6 detects that. Therefore,
corresponding to the signals from the sensor 6, the rotations of the
rollers 4, 5 are stopped. Accordingly, transportation of the slide
fastener chain 2 is stopped.
Next, as shown in Figs. 6 and 12, the air cylinder 20 is operated
25 to move the end tip 39 of the upstream locating pin 18 downward to
strike against the leg of a fastener element which is adJacent to the
fastener element 42 of a normal portion 52 not to be the space
2019082
section 7. As shown in Figs. 12 and 13, this element is adjacent to
the upstream side end 51 of the portion 8 to be the space section 7.
This striking operation of the tip end 39 for the elements is same
as that of the tlp end 38 of the downstream locating pin 17. That is
5 to say, the tip end 39 strikes against the upper surface of the leg of
the fastener element ad~acent to the fastener element 42 as shown in
Fig. 12, or is inserted between the leg of the fastener element 42 and
the leg of the fastener element ad~acent to the element 42.
Then, as shown in Fig. 7, by operation of the link 12, the chain-
10 pressuring rod 26 and the chain-stretching rod 27 act on the slide
fastener chain 2 in the same manner as the above mentioned forming
process for the downstream side part of the space section.
Accordingly, as shown in Fig. 13, the upstream side rest of the portion
8 to be the space section 7 with a length 12 iS located precisely, even
15 if the slide fastener chain 2 is locally elongated or shrunk.
The link 12 is operated to move the punch 15 in a way as shown in
Figs. 7 and 13 so that a group of interengaged heads 37 of the rows 34
of the fastener elements with the length 12 disposed at the upstream
side of the portion 8 are cut by the cutting edge of the punch 15 and
20 removed from the fastener chain 2.
Next, the link 12 and the air cylinder 19 are moved upward and
the punch 15, the upstream locating pin 18, the chain-pressuring rod
26 and the chain-stretching rod 27 are returned to the original
- positions at which they can not be operated. By this operation, a
25 forming process for the upstream side part of the space section in the
continuous slide fastener chain is finished. By the above mentioned
two forming processes for the downstream side part and the upstream
~ ~ 14- 2019082
side part of the space section respectively, the one-cycle for formlng
one space section 7 is finished.
Therefore, the continuous slide fastener chain 2 is transported
again as a first step so that a next one-cycle is started. As a result,
the space sections 7 are formed repeatedly one by one in the slide
fastener chain 2, with a predetermined distance.
In the above mentioned embodiment, the slide fastener chain 2 is
moved within a part of the guide path 3 which has a longitudinal
length corresponding to the length L of the space section 7 and the
1 0 punch 15 is moved on only a vertical line. On the other hand, in
another embodiment shown in fig. 14, during cutting and removing
operation for the rows of fastener elements, a continuous slide
fastener chain 2 is kept at one position. Then, a punch as a cutting
means composes of a downstream punch 53 and an upstream punch 54,
both of which serve as cutting members respectively and both of
which have the same length corresponding to the half of the length L
of a space section. In the forming process for the downstream side
part of the portion, a downstream locating pin 17 as a downstream
locating means and the downstream punch 53 are operated, then in the
forming process for the upstream side part of the portion, an
upstream locating pin 18 as an upstream locating means and the
upstream punch 54 are operated. A chain-pressuring rod and a chain-
stretching rod are operated in the same manner as the above
mentioned embodiment.
In still another embodiment in~Fig. 15, during cutting and
removing operation for the fastener elements, a continuous slide
- fastener chain 2 is kept at one position, while a punch 55 as a cutting
- 15 - 2019Q82
member moves downstream side and upstream side (backward and
forward) within a part which has a length corresponding to the
longitudinal length L of a space section. In this case, the punch 55 has
a longitudinal length being shorter than the longitudinal length L of
5 the space section and longer than the half of it. A downstream
locating pin and an upstream locating pin, both of which serve as
locating means respectively, a chain-pressuring rod and a chain-
stretching rod are operated in the same manner as the above
mentioned embodiment.
While preferred embodiments have been described, it is apparent
that the present invention is not limited to the specific embodiments
thereof .