Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02024027 2000-OS-29
SEALED LINING TUBE FOR LINING OF PIPELINES OR PASSAGEWAYS
This invention relates to the lining of pipelines or
passageways by a process which has become known as "soft
lining".
A soft lining process involves utilising a flexible tube
which is sized to the diameter and length of the pipeline
or passageway to be lined. The tube is coated or
impregnated with a curable synthetic resin which cures
after the lining tube has been placed in position lining
the surface of the pipeline or passageway in order either
to form an adhesive which anchors the lining tube to the
pipeline or passageway surface or to form in effect a
moulded body defining a rigid pipe which is free standing
inside the pipeline or passageway. The lining tube is
inserted in the pipeline or passageway whilst the resin
is still soft, and is shaped to the passageway surface by
fluid pressure, and whilst it is held in this condition
the resin is cured usually by the application of heat or
more recently by the application of light radiation
supplied for example by ultraviolet lights. In the latter
case, the resin system chosen has to be activatable by
the radiation.
The most widely practised method of soft lining is
disclosed in British Patent No. 1449455 and in such
method the lining tube is everted into the pipeline or
passageway from one end thereof, the lining tube being
provided on its outer side with an impermeable coating or
film, which after eversion becomes the inner surface of
the pipeline providing a smooth flow enhancing surface to
the interior of the re-lined pipeline or passageway.
In accordance with the present invention, there is
provided
~~~~Q~~
a soft lining method wherein a lining tube is
constructed in two sections each at least approximately
equal to the length of the pipeline or passageway to be
lined, the sections being connected end to end, and the
insertion process comprises either pulling in of one of
the sections followed by eversion of the other section
into the first mentioned section, or eversion of one
section which causes pulling in of the other section.
In the preferred arrangement, the lining tube is in fact
made up of three sections each of a length equal to the
length of the section of the pipeline or passageway to
be lined or greater than such length, said three
sections comprising a first section referred to herein
as a preliner tube, a second section being a lining tube
and comprising a tube of a material which is or is
adapted to be impregnated or coated with curable
synthetic resin, and a third section referred to herein
as the inflation tube, the purpose of which is to
inflate the lining tube when it is in position by
eversion of the inflation tube into the lining tube.
the inflation tube may also be of or include a material
which is coated or impregnated with curable synthetic
resin, but as it is everted, it will preferably in such
case have an outer membrane for containing the resin.
For example, the inflation tube may typically be
constructed and impregnated as described in British
Patent No. 1449455.
In the instant invention, the lining method can comprise
only the utilisation of the preliner tube and the lining
tube, the prelining tube typically comprising a strong
fabric coated tube of sufficient tensile strength and
flexibility, which may be everted into the pipeline or
passageway by conventional everting techniques using a
liquid typically water as the eversion medium, as
described in said co~pending
3
application. As the prelining tube is being inserted, the
lining tube which is connected to the tail end of the
prelining tube is pulled into the pipeline or passageway and
it will be buoyantly supported in the everting water as it is
so being pulled in. When in reaches the desired position,
it may be inf lated
by any suitable means, for example by a separate inflation
tube. The lining tube in this embodiment may be sealed at
both ends after being filled with resin to impregnate resin
absorbent layers of the tube, and also after removal of the
air from inside the tube. The removal of air and the sealing
of ends is particularly advantageous insofar as if there are
bubbles of air in the resin, these tend to cause
imperfections in the finished, cured lining which can lead to
Faa.~~eation and mechanical difficulties.
When the lining tube is in position, the trailing end must be
opened to allow insertion of the inflating medium and/or
inflation tube but the ingress of air into the impregnated
lining tube can easily be avoided.
The second inventive aspect comprises the utilisation of the
lining tube to the trailing end of which is ccnrected the
inflation tube. ~rhe leading end of the lining tube and the
trailing end of the inflation tube may be sealed, and where
the two tubes are connected they may also be sealed to each
other to make a continuous tube. This ensures that all air
can be excluded from the inside of the assembly comprising
the two tubes so that resin contained therein will thoroughly
impregnate the absorbent layers of the lining tube and/or of
the inflation tube. The inflation tube and lining tube may be
interconnected by a section referred to as the connection
tube permitting the inflation tube to be everted at the
appropriate stage of the insertion. To this end the
connection tube may be provided with a tuck or fold so that
CA 02024027 2000-OS-29
4
it is folded in upon itself which will facilitate the
operation of the inversion process, as will be explained
in more particular detail with reference to the
embodiment of the invention which is described
hereinafter.
Obviously the best results flow from the combined effects
of the two inventive aspects i.e. when the assembly
comprises first, second and third tubes and the lining
sequence comprises everting the prelining tube into the
pipeline or passageway for the placement of the lining
tube in the pipeline or passageway followed by the
eversion of the inflation tube into the lining tube to
inflate same onto the prelining tube and supported
against the passageway surface and held in such condition
until the resin of the lining tube and/or the inflation
tube is cured.
The utilisation of a prelining tube has the desired
advantage that the prelining tube prevents the ingress of
resin into lateral connections which meet the pipeline or
passageway being lined.
Accordingly, in one aspect, the present invention relates
to a method of lining a pipeline or passageway with a
flexible lining tube assembly comprising: providing a
lining tube assembly constructed in two sections, each
section at least approximate equal to the length of the
pipeline or passageway to be lined, the sections being
connected end to end, and for lining an existing conduit
of a known length with a lining tube section having a
CA 02024027 2000-OS-29
4a
leading end and a trailing end, the tube formed from at
least an impermeable membrane and having a sealed leading
end to prevent ingress of air to the interior thereof;
and an inflation tube section having a leading end and a
trailing end, the inflation tube formed from at least an
impermeable membrane with the leading end sealed to the
trailing end of the lining tube section and the trailing
end of the inflation tube sealed to prevent ingress of
air into the interior thereby forming a continuous air
tight tube; at least one of the lining tube section and
the inflation tube section having a layer of resin
absorbent material with the impermeable membrane bonded
to the resin absorbent layer, the method including the
steps of either pulling in of one of the sections
followed by eversion of the other section into the first
mentioned section, or eversion of one section which
causes pulling in of the other section.
In a further aspect, the present invention provides a
flexible tubular liner assembly having at least one
section of a resin absorbent layer impregnated with a
curable resin for lining an existing conduit of a known
length, comprising: a lining tube section having a
leading end and a trailing end, the tube formed from at
least an impermeable membrane and having a sealed leading
end to prevent ingress of air to the interior thereof; an
inflation tube section having a leading end and a
trailing end, the inflation tube formed from at least an
impermeable membrane with the leading end sealed to the
trailing end of the lining tube section and the trailing
end of the inflation tube sealed to prevent ingress of
air into the interior thereby forming a continuous tube
CA 02024027 2000-OS-29
4b
substantially free of air; at least one of the lining
tube section and the inflation tube section having a
layer of resin absorbent material with the impermeable
membrane bonded to the layer of resin absorbent material;
and each of the lining tube section and the inflation
tube section of a length at least equal to the length of
the conduit to be lined with a curable resin impregnated
into the resin absorbent layer.
In a still further aspect, the present invention provides
a flexible tubular liner assembly having at least one
section including a resin absorbent layer for lining an
existing conduit of a known length, comprising: a lining
tube section having a leading end and a trailing end, the
tube formed from at least an impermeable membrane and
having a sealed leading end to prevent ingress of air to
the interior thereof; an inflation tube section having a
leading end and a trailing end, the inflation tube formed
from at least an impermeable membrane with the leading
end sealed to the trailing end of the lining tube section
and the trailing end of the inflation tube sealed to
prevent ingress of air into the interior thereby forming
a continuous air tight tube; at least one of the lining
tube section and the inflation tube section having a
layer of resin absorbent material with' the impermeable
membrane bonded to the resin absorbent layer, and each of
the lining tube section and the inflation tube section of
a length at least equal to the length of the conduit to
be lined.
In a further aspect, the present invention provides a
flexible tubular liner having at least one section of a
resin absorbent layer for lining an existing conduit of a
CA 02024027 2000-OS-29
4c
known length, comprising: a flexible fluid impermeable
tubular preliner section having a leading end and a
trailing end; a lining tube section having a leading end
and a trailing end, the tube formed from at least an
impermeable membrane and having a sealed leading end to
prevent ingress of air to the interior thereof and
attached to the trailing end of the preliner section; a
flexible tubular connection section comprising a fluid
impermeable membrane secured to the trailing end of the
tubular lining section and sealed to prevent ingress of
air into the interior of the tubular sections; a flexible
inflation tube section having a leading end and a
trailing end, the inflation tube section formed from at
least an impermeable membrane with the leading end sealed
to the trailing end of the connection section to prevent
ingress of air into the tubular sections and the trailing
end of the inflation tube sealed to prevent ingress of
air into the interior thereby forming a continuous air
tight tube; at least one of the lining tube section and
the inflation tube section having a layer of resin
absorbent material with the impermeable membrane bonded
to the., outer surface thin membrane the impermeable layer;
and each of the preliner section, lining tube section and
inflation tube section of at least a length equal to the
length of the conduit to be lined.
In a still further aspect, the present invention provides
a method A method for lining a passageway which comprises
(a) providing an assembly comprising a prelining tube, a
lining tube and an inflation tube, each of said tubes
having leading and trailing ends, the trailing end of the
pre-lining tube being connected to the leading end of the
lining tube and the trailing end of the lining tube being
CA 02024027 2000-OS-29
4d
connected to the leading end of the inflation tube, (b)
everting into the passageway the prelining tube that is
impermeable to fluids so that during the course of
eversion the lining tube is pulled along the length of
the passageway, said lining tube having walls comprising
absorbent material impregnated with a curable synthetic
material and being sealed to such an extent to prevent
contact between the atmosphere and the resin and being in
a collapsed condition, (c) everting said inflation tube
into the interior of said collapsed lining tube after
said lining tube has been positioned in the passageway so
that the lining tube will thereby be progressively
expanded outward toward the interior walls of said
passageway while maintaining said resin sealed from the
atmosphere, and (d) curing said curable synthetic resin.
One embodiment of the invention will now be described, by
way of example, with reference to the accompanying
diagrammatic drawings, wherein -
Fig. 1 is a perspective view of a tubular assembly for
insertion into a pipeline or passageway in accordance
with one embodiment of the present invention;
Figs. lA, 1B and 1C respectively show in enlarged detail
the respective sections of the tube assembly shown in
Fig. 1, and in cross section;
Fig. 2 shows a connecting section of the assembly shown
in Fig. 1;
2~~~~2"~
Figs. 3 - 7 show respective stages in the installation of the
tube assembly of Fig. 1 in an underground sewer;
Fig. 8 shows in enlarged detail a section of the lining tube
when in the sewer and lining same; and
Fig. 9 is a sectional elevation to an enlarged scale
illustrating one side of the installed lining.
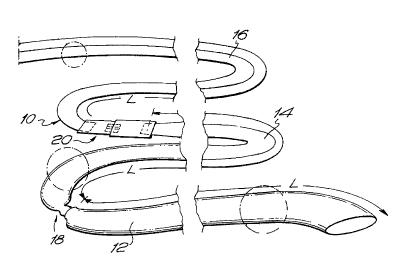
Referring to the drawings, a flexible tubular liner assembly
is illustrated by reference 10 in Fig. 1. The assembly is
shown as being made up of three sections namely a first
section or preliner tube 12, a second section or lining tube
14 and a third section or inflation tube 16, these being
connected end to end for example at joint regions 18 and 20.
Each of the sections 12, 14 and 16 as shown is of a length at
least equal to a length L, which is the length of the
pipeline or passageway to be lined by the assembly.
The joint 18 is formed in that the sealed end of lining tube
14 is tied to the sealed trailing end of preliner tube 12,
but the junction between lining tube 14 and inflation tube 16
indicated by reference 20 is constituted by a connection
section 22 which is referred to herein for convenience as an
inversion tube, whose function will be explained in more
detail hereinafter.
As shown in Fig. lA the prelining tube 12 is a single layer
tube which may be made up of a woven fabric 24 which is
covered with a plastic or rubberised coating so as to give
the tube 12 the required strength. The requirements of the
tube 12 are that it should be of sufficient strength to
perform its function and also should be impexmeable to a
fluid, especially water, which is used to evert this tube 12
into the pipeline or passageway to be lined.
6
The tube 14 on the other hand as shown in Fig. 1B comprises
an outer coating 26 of an impermeable film material such as
polyurethane or a laminated material. The coating 26 is
bonded to a relatively thick felt layer 28, and in order to
form the tubular structure as shown in Fig. 1B, this
material is coiled into tubular form and abutting seam 30 has
stitching 34 bridging same in order to connect the butting
ends. The stitching is covered by a sealing strip 36.
Inside the layer 28 is a further felt layer 36 which is
formed into a tube so that the edges overlap, and through the
overlapped edges there is stitching in order to form the
tubular structure. As many layers 36 as are required may be
embodied in the tube 14. The layers 28 and 36 are of a
material i.e. needled felt which has an excellent resin
absorbency characteristic insofar as it will soak up
synthetic resin introduced into the interior of the tube 14
so that the layers 28 and 36 become impregnated with said
resin.
The inflation tube 16 in the embodiment illustrated is
similar to tube 14 insofar as it is provided with an outer
membrane 40 which is bonded to an inner felt layer 42 and
this material is coiled sewn and sealed in a similar fashion
to material of the tube 14, but there is no additional
thinner layer 36 and the felt layer 42 is thinner than the
layers 28 and 36. The tube 16 furthermore is sized so as to
be smaller than tube 14 because eventually it will fit inside
this tube. The tube 16 can however be of a single layer
material such as tube 12.
The inversion tube 22 as shown in Fig. 2 is simply a length
of tube similar to tube 12 for it may be an extension of tube
16 or tube 14) connecting the ends of the tubes 14 and 16,
but~in addition tube 22 is formed with a central tuck 44 for
~~~~~~~'~
a purpose to be explained. The length of the inversion tube
22 with the tuck 44 is to D for a purpose to be explained in
relation to the installation procedure illustrated with
reference to Figs. 3 - 7.
In the embodiment described, the leading end of the tube 14
is sealed as is the trailing end of the tube 16, and the
inversion tube 22 forms a seal between the trailing end of
tube 14 and the leading end of tube 16, but prior to sealing
the leading end of tube 14 and the trailing end of tube 16, a
sufficient amount of synthetic resin is introduced into the
tubes 14 and 16 in order to impregnate the felt layers 28, 36
and 42, and also to expel all air from inside the tubes. In
fact therefore these tubes 14 and 16 will be in a flattened
collapsed state, full of resin, but devoid of any air
therein.
If reference is now made to Figs . 3 - ?, an explanation is
given as to how the tube assembly of Fig. 1 is inserted into
an underground sewer in order to create a lining for same.
In Fig. 3, the sewer is indicated by reference 50 and in fact
is a length of sewer extending between two manholes 52 and
54. The sewer length 50 may require restoration or
rehabilitation because of deterioration as a result of usage
and age, which is a common problem with sewers of developed
areas throughout the world.
It is also to be mentioned that in order to effect the lining
operation to be described appropriate equipment must be
provided on site such as pumps, vehicles, scaffolding etc.,
but such equipment has been omitted from the drawings in the
interests of simplicity and also because the equipment for
performing the methods is now well known.
8
Into the manhole 52 is placed an elbow pipe 56 so that the
open lower end of the elbow 58 faces the end of the sewer 50
to be lined. The leading end of the tube 12 is fed into the
pipe 56, and is folded back as shown so as to be connected to
the lower end of the elbow. Filling of the pipe 56 with water
as indicated by arrow 60 in Fig. 4 causes the tube 12 to
avert out of the, end of the pipe 56 and into and along the
sewer length 50 as shown clearly in Fig. 4. As the tube 12
averts so it pulls the next section of the tube assembly
namely the lining tube 14 into and along the sewer length 50
as shown in Fig. 4. Fig. 5 shows the position when the
prelining tube 12 has completed its aversion and the lining
tube 14 is now in the correct position with its respective
ends at the ends of the sewer section 50 to be lined. At this
point the procedure is stopped, and it will be noticed that
the inversion tube 22 is now located so that the leading half
of same is in the pipe 56 and the tuck 44 is adjacent the top
end of the pipe 56.
At this juncture, the end of the prelining pipe 12 adjacent
the manhole 54 is punctured in order to allow release of the
water which was used for the initial inversion step, as
indicated by arrow 62 in Fig. 6, and at the same time the
tuck 44 in the inversion tube is folded over the top edge of
the pipe 56 also as shown in Fig. 6 and is anchored thereto.
The tuck can now be filled with aversion fluid e.g. water as
indicated by arrow 64 in Fig. 6, which causes the second half
of the inversion tube to avert into the first half and down
the pipe 56, at the same time forcing the water from the
puncture 62. To thus fold the tuck over the top of pipe 56 it
may be necessary to remove adhesive strips 66 as shown in
Fig. 2 which are applied across the tuck so that same will be
retained during the initial inversion step and other handling
of the tubular assembly.
9
With the continued supply of water 64 to cause the second
half of the inversion tube to event into the pipe 56, so the
last pipe section 16 is pulled through pipe 56 and events
into the lining tube 14 and inflates same as indicated in
Fig. 7. Therefore, the inner felt face 68 (Fig. 1C) of the
lining tube 16 comes face to face with the inner felt face 70
of the tube 16.
As these felt layers are impregnated with uncured synthetic
resin, so the felt layers of the respective tubes 14 and 16
in effect coalesce into a single integrated resin mass as
shown in Figs. 8 and 9.
The resin subsequently is cured by any suitable means such as
by hot water or by light radiation, ultrasonics or other
means and when the resin cures hard, a rigid pipe lining the
sewer length 50 results.
Instead of using a preliner tube 12, the main tube 14 may be
pulled directly into the passageway, especially when the
passageway is smooth, using for example a xope.
Many advantages flow from the various aspects of the present
invention which not only include the methods referred to
herein, but also include the tubular assembly.
These advantages include that by using a preliner tube and by
pulling the liner tube into the passageway using the preliner
tube and water, the liner tube can be supported by the water
and will slip easily into position. Secondly, as the liner
tube does not require to event during any stage of the
process, heavier liner tubes can be installed and they will
easily pass raund bends and corners.
The utilisation of an inflation tube which is integrally
CA 02024027 2000-OS-29
connected to the lining tube ensures accuracy of
positioning and accuracy of inflation of the lining tube,
and sealing of the ends of the tubes means that all air
can be excluded, which is highly desirable for this
process as the entrapment of air in the felt layers 28,
36 and 42 creates undesirable problems.
Although tubes which are impregnated with uncured
synthetic resin are described, it is to be mentioned that
these tubes could be constructed essentially of pre-preg
materials.