Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2026919
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
1. Field of the Invention
This invention pertains to a velocity change sensor or
accelerometer used in motor vehicles for detecting sudden changes
in velocity and for activating in response a passenger
restraining device such as an air bag. More particularly, this
device employs an element which is biased in a first position by
- a magnet and moves to a second position in response to a sudden
deceleration to establish an electric contact. An element is
provided for shaping and concentrating the magnetic field
generated by the magnet.
~'
2. Background of the Invention
Studies have been made which indicate that injuries in motor
vehicle accidents, especially at high speeds, can be
substantially reduced or eliminated by the use of passenger
restraint systems. These systems include an inflatable balloon
usually termed an air bag which normally is stored away in the
instrument panel or the steering wheel. When the motor vehicle is
subjected to a sudden deceleration, the air bag is inflated and
is deployed automatically in a position which cushions the
passengers, restrains their movement and prevents contact between
them and the automobile interior such as the windshield, the
steering wheel. the instrument panel and so on. Of course, a
crucial element of all such systems is the velocity change sensor
or accelerometer which initiates the inflation and deployment of
'
- 2026~19
- the air bags. The motion of the motor vehicle must be carefully
and precisely monitored so that the air bags can be deployed very
fast, before the passengers suffer any substantial injury. A
velocity change sensor is disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 4,329,549
assigned to the same company as the present invention. This
sensor comprises a tubular housing surrounding a magnetically
permeable metallic shell, a metal ball and a magnet biasing the
ball toward a first end of the shell. At the second end of the
shell there are a pair of electrical contact blades. The sensor
is positioned in the motor vehicle in an orientation such that
when the motor vehicle experiences a deceleration which exceeds a
preset level, the ball moves from the first toward the second
end, making contact with the two blades. Because the blades and
the ball are made of on electrically conducting material, when
the ball contacts the blades, an electrical path is established
between the two blades. This electrical path is used to initiate
the deployment of the air bags. One problem with this type of
device involves the field generated by the magnet. If the sensor
is disposed in a metal enclosure, the sidewalls of the enclosure
usually concentrate and shape the field so that it is bottled in
a region close to the metal sleeve. However if an enclosure
which has no effect on a magnetic field, such as one having a low
magnetic permittivity, such as a non-metallic enclosure, the
field generally diverges away from the housing. Therefore the
intensity of the magnetic field at the sleeve is lower when the
housing the sensor is disposed in a non-metallic enclosure than
in a metallic enclosure. A lower magnetic field degrades the
performance of the sensor. Furthermore, it has been found that
very sensitive and discriminative acceleration sensor systems may
be made by mounting two sensors in a common housing. However, if
2026919
~ these sensors are two close together, the fields from the two
magnets interfere and produce undesirable responses.
OBJECTIVES AND SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION.
In view of the above mentioned disadvantages of the prior
art, it is an objective of the present invention to provide an
accelerometer which performs reliably independently of the type
of housing provided for mounting the sensor or any metal present
in the vicinity of the sensor.
A further objective is to provide a restraint system with a
velocity sensor with several magnetic elements in which
interference between the fields of the elements is eliminated.
Other objectives and advantages of the invention shall become
apparent from the following description. An accelerometer
constructed in accordance with the invention includes a housing
with contact blades and a contacting element which provides an
electric path between the blades when a deceleration above a
threshold level is sensed. Contact between the blades is
established by a contacting member. Normally the contacting
! member is biased toward a first position away from said contact
blades by a magnetic field generated by a magnet disposed outside
the housing. When a deceleration occurs, the contacting element
is urged toward a second position and closes an electrical path
with said contact blades. Thereafter an electric signal is sent
to a control unit which deploys the air bag within the motor
vehicle. A magnetic field keeper element disposed around the
magnet shapes and constrains the field to the vicinity of the
housing, so that the magnetic field biasing the contacting
element is maintained at a constant level independently of the
'enclosure for the housing and concentrates the field to enable
the magnetic field force to return the contacting member to its
,
~ 202~919
first position upon cessation at a deceleration input.
Furthermore, the keeper eliminates interference between the
magnetic fields of adjacent sensors disposed in a common enclosure.
Accordingly, the invention herein comprises an accelerometer sensor
for sensing velocity changes comprising: a housing; contact means
disposed in said housing; a non-magnetized sensing element movably
disposed in said housing; and biasing means for generating a
biasing force on said sensing element for urging said sensing
element toward a first position, said sensing element being
constructed and arranged to move along said path from said first to
a second position in response to an acceleration greater than said
biasing force for making contact with said biasing means, said
biasing means including a permanent magnet disposed at one end of
said houslng adjacent to said first position and a magnetic field
concentrating means disposed outside said housing and extending
substantially over said permanent magnet and being substantially
coextensive with said path, said magnetic field concentrating means
being arranged and shaped for restricting and concentrating the
magnetic field of said permanent magnet to said path.
The invention also comprises a passenger restraint system for
motor vehicles comprising: an air bag disposed in a motor vehicle;
a control unit for selectively deploying said air bag in said motor
vehicle for protecting a passenger in a crash; and an accelerometer
for sensing a velocity change of said motor vehicle coupled to said
control unit and comprising: a housing disposed in said motor
vehicle, said housing defining a path; contact blades disposed in
said housing; contact closing means arranged in said housing for
making electrical contact with said contact blades when said motor
vehicle decelerates at a level exceeding a threshold level; and
biasing means for biasing said contact closing means away from said
contact blades along said path and including a permanent magnet
coupled to said housing for generating a magnetic field and a
magnetic field concentrating means for concentrating said field to
said path, said magnetic field concentrating means being disposed
outside ~aid hou~ing substantially co-extensively with said path.
f)r 4
~-- 2026919
The invention still further comprises a passenger restraint
system for a motor vehicle comprising: an air bag disposed in a
motor vehicle; a control unit for selectively deploying said air
bag in said motor vehicle for protecting a passenger in a crash;
and an accelerometer for sensing a velocity change of said motor
vehicle coupled to said control unit and comprising: an enclosure
disposed in said motor vehicle; a first sensor disposed in said
enclosure including first contact means, first contact closing
means movable along a first path for selectively closing said first
contact means in response to a change in velocity of said motor
vehicle, a first magnetic generator for generating a first magnetic
field and a first magnetic concentrating member for concentrating
said first magnetic field to said first path, said first magnetic
concentrating member being substantially coextensive with said
first path; and a second sensor disposed in said enclosure
including second contact means, second contact closing means
movable along a second path for selectively closing said second
contact means in response to a change in velocity of said motor
vehicle, a second magnetic generator for generating a second
magnetic field and a second magnetic concentrating member for
concentrating said second magnetic field to said second path, said
second magnetic concentrating member being substantially
coextensive with said second path; said first and second magnetic
concentrating members cooperating to reduce interference between
said first and second magnetic fields by concentrating said
magnetic fields to the corresponding paths.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FIGURES
Figure 1 shows a side elevation view of an accelsrometer with
a single sensor constructed in accordance with the invention
disposed in an enclosure;
Figure 2 shows a side cross-sectional view of the
accelerometer of Figure 1;
Figure 3 shows a cross-sectional view of the accelerometer of
Figure 2 taken along line 3-3;
4a
2026919
Figure 4 shows side view of the accelerometer of Figure 2;
Figure 5 shows a side elevation view of an accelerometer
similar to Figure 1 but having two sensors; and
Figure 6 shows another embodiment of the invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Turning now to the Figures, an accelerometer or velocity
change sensor 10 constructed in accordance with this invention is
usually disposed in a case 12 mounted on the motor vehicle (not
shown). The sensor is connected by a cable 14 with at least two
conductors 16, 18 to a control device for the deployment of the air
bag.
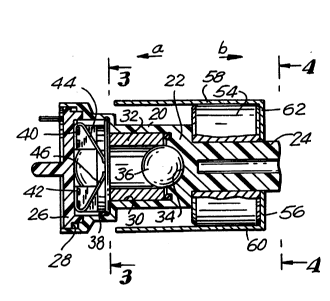
The sensor 10 has a tubular body 20 terminating at one end
with an end wall 22 with an external hollow extension 24. At end
opposite wall 22, the body 20 has an enlarged crown 26 to form a
seat for rubber gasket 28. The body 20 is preferably made of a
plastic material. The body 20 has an inner cylindrical wall 30.
Secured to this wall 30 there is a metallic sleeve 32. End wall 22
is formed with a spherical depression 34 for holding metallic
- ' 4b
; 2~26~19
ball 36. The diameter of ball 36 is slightly smaller than the
diameter of sleeve~32.
Crown 26 holds a plastic cap 38 having two metallic pins 40,
42, each supporting a corresponding contact blade 44, 46
respectively. As shown in Figure 3, contact blades 44 and 46 are
connected serially in an electrical circuit comprising a battery
48, and an actuating mechanism 50. Actuating device 50 controls
and deploys one or more air bags 52.
A toroidal permanent magnet 54 is disposed on extension 24 as
shown. The magnet generates a magnetic field which biases the
ball 36 toward the end wall 22 in the position shown in Figure 2.
The shape of the magnetic field is controlled by a restrainer 56
comprising a U-shaped member made of a magnetic permeable
material. The restrainer 56 includes two generally parallel arms
58, 60 extending from the magnet to a shoulder formed by crown
26. The restrainer also has a base 62 joining the two arms 58,
~60. The restrainer base has a hole 64 for receiving the end of
~extension 24. In this manner the keeper 56 can be positioned
~ adjacent permanent magnet 54 so that it limits its magnetic field
in the axial direction. The two arms 58, 60 limit the magnetic
,field to the vicinity of the housing and increase its strength
within the housing, at sleeve 32. As seen in Figure 4, base 62
is provided with cut-outs 66 which facilitate the installation of
the sensor within enclosure 12.
Housing 12 is oriented within the motor vehicle so that cap
38 is toward the front of the motor vehicle, while end wall 22 is
disposed toward the rear of the vehicle. In Figure 2 the normal
direction of movement of the vehicle is indicated by arrow a.
When the vehicle hits an object it is decelerated in direction b.
If the force of deceleration is larger than the preset biasing
force of the magnet 56 , the ball 36 overcomes the force applied
.,
2~91Y
by the magnet 56, and moves in direction a toward cap 38 until it
hits the contact blades 44,46. The ball then continues its
movement in direction a until it is brought to a halt by the
blades or the cap 38.
s Meanwhile the contact between the ball 36 and blades 44, 46
allows current to flow from battery 48 to actuating device 50
which in response deploys air bag(s) 52. As previously
mentioned, without the restrainer member or keeper 56, the
intensity of the magnetic field generated by permanent magnet 54,
and therefore the reaction time and movement of ball 36, would be
dependent on the enclosure 12. However the restrainer constricts
the field to the housing so that the enclosure 12 becomes
immaterial.
In a further embodiment of the invention, two sensors 108 and
110 having the structure shown in Figures 2-4 are mounted in a
single housing 112 as shown in Figure 5. The two sensors could
have different sizes or different sized magnets to provide
different responses. Alternatively, the sensors could be mounted
in different relative orientations. This arrangement provides a
very sensitive accelerometer which could differentiate between
actual crashes, and apparent changes in velocity produced by road
irregularities such as pot holes. Each of the sensors is
provided with a keeper to limit the magnetic field of the
corresponding magnets and eliminate magnetic interference
therebetween.
Figure 6 shows a different restrainer 156 having an enlarged
- base 162.
Obviously numerous modifications may be made to the invention
without departing from its scope as defined in the appended
claims.