Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
1
SYNCHRONIZING METHOD IN A MO$ILE RADIO SYSTEM ~%' ~~i ~a ~~''T ~ r~
;", .J r,~ ,.. Vii'
TECHNICAL FIELD
The present invention relates to a synchronizing method in a
mobile radio system which lacks a global time reference, i.e. a
system which lacks a time reference that is common to all mobiles
and base stations in the system. More specifically, although not
exclusively, the present invention relates to a method of synchro-
nizing a random bit flow which is superimposed cryptically on the
normal traffic flow during call transmission or data transmission
between the base stations and the mobiles. The proposed method can
be applied solely to a so-called TDMA-system, i.e. a mobile radio
system in which calls are transferred in frames and time slots by
means of time multiplex.
BACKGROUND ART
It is desirable in mobile radio systems, and in TDMA-systems in
particular, to be able to maintain the security of calls so as to
prevent unauthorized persons from setting-up and making calls
over the network. In order to meet this requirement, it has been
suggested that the calls are ciphered; see for instance
EP-A-273289.
Calls between a base station and a mobile are cipheredby proces-
sing the speech message in a scrambler, which functions to convert
the speech signals into a random sequence an accordance with a
given key. For instance, the speech signals can be superimposed
with a random sequence of bits of relatively long duration
(several minutes). In this case, the cipher key consists in the
knowledge of the total bit pattern of the sequence and also
knowledge of the time at which the sequence was commenced. An
authorized subscriber can plug into a circuit module in the
apparatus which stores this sequence and said starting time-
point, and is thus able to decode incoming calls.
2
r-d ~ e.i ... ~r a)
DISCLOSURE Of THE INVENTION
Some TDMA mobile radio systems lack a global time reference, i.e.
means in the mobile telephone exchange which contains a clack
common to the overall system and operative to produce the same
time reference for all base stations and mobiles in the system.
The purpose of such a common time reference is to enable the
mobiles and the base stations to be synchronized with one another
in certain frames arid time slots when synchronizing from signal-
ling or data/speech signals falls away for some reason or other.
When transferring (hand-off) a call from one radio channel to
another radio channel, synchronization between the mobile and its
base station may be lost, since a brief interruption will occur
during the actual transmission or swithching of the call. If the
call is also ciphered, a further problem can occur as a result of
fall-off of the synchronism of the actual ciphering key concerned,
thereby rendering deciphering impossible.
These problems also occur when setting up ciphered calls, although
said problems are most pronounced during "hand-off'°.
The present invention is based on the time sharing in different
frames of the traffic flow (TDhlA-principle) and also on the access
to a given ciphering sequence of relatively long duration (about
3 minutes) in relation to the time during which coupling or "hand-
off" shall take place. The invention is alsa based on ciphering by
superimposing a bit sequence on the normal traffic flow (data or
speech and signalling). Prior to handing-off a call or during a
given time interval during hand-off where synchronization of the
ciphering sequence has ceased, non-ciphered signalling is effec-
ted and thereafter the traffic flow is ciphered with a periodic
bit sequency whose period is equal to a frame time interval. This
~ enables synchronization data to be transmitted to a mobile from a
base station simultaneously with a ciphered traffic flora and
discloses when normal ciphering shall commence.
CA 02039699 1998-12-16
An object of the present invention is thus to achieve
synchronization of a cryptosequence when setting up or
"handing-off" calls in a mobile telephone system which
lacks a common time reference.
Thus, the present invention provides a method for
reestablishing the ciphering of information in a mobile
radio system which lacks a global time reference, wherein
the data messages and the signalling messages between a
1o first base station and a mobile station are transmitted in
frames having time slots and said messages are ciphered by
combining said messages with a pseudorandom bit stream,
wherein upon handing over the communication of the mobile
from the first base station to a second base station
ciphering is interrupted for a given period of time during
which synchronization of the pseudorandom bit stream with
said messages between the mobile and the first base station
is lost due to the absence of said global time reference
and frame synchronization is established between the mobile
2o and the second base station. The method includes the steps
of generating a first signal which discloses a time point
counted in numbers of frame intervals which shall pass
until said ciphering is recommenced, subsequent to
completing the hand-over of said messages transmitting said
first signal from the second base station to the mobile
station, and recommencing said ciphering upon occurrence of
said time point.
- 3 -
CA 02039699 1998-12-16
By another aspect this invention provides a method for
reestablishing encryption of information in a mobile radio
system having first and second fixed stations and a mobile
station. The method comprises the steps of: encrypting
information exchanged between said first fixed station and
said mobile station using a first encryption code; handing-
off communications with said mobile station from said first
fixed station to said second fixed station, said handing-
off including establishing frame synchronization between
1o said second fixed station and said mobile station;
temporarily ceasing use of said first encryption code for
communications with said mobile station; sending
notification from said second fixed station to said mobile
station informing said mobile station that the use of said
first encryption code is to~be resumed at a time point
after a certain number of frame times have elapsed in
communications between said second fixed station and said
mobile station; and reestablishing encryption upon
occurrence of said time point.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
The invention will now be described in more detail with
reference to the accompanying drawings, in which
Figure 1 is a schematic illustration of two base stations
and a mobile unit;
- 3a -
CA 02039699 1998-12-16
Figure 2 is a time diagram for transmitting and receiving
in accordance with the TDMA-principle;
Figure 3 is a time diagram for ciphering in accordance with
the proposed method; and
Figure 4 illustrates, in more detail, signalling during a
given time interval in accordance with Figure 3.K1
BEST MODE OF CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION
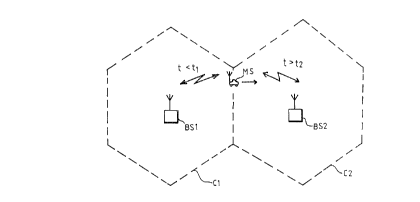
1o Figure 1 illustrates schematically two base stations BS1
and BS2 and a mobile MS which is assumed to move from the
base station BS1 towards the base station BS2. The base
station BS1 serves traffic within the cell C1 and the base
station BS2 serves traffic within the cell C2. The cells
C1 and C2 have a common border G. When the mobile M
approaches the border G, the speech quality for a coupled
call served by the base station BS1 over a given radio
channel K1 will fall-off. Switching of a new radio channel
K2 to MS from BS1 is effected, by measuring the field
2o strength of the radio signal and making calculations in
accordance with known principles. This new channel K2 is
served by BS2. During the actual switching sequence, which
may have a duration of about 100 ms, MS will not receive
and the receiving circuits in MS can loose the synchronism
of the traffic flow, i.e. the time position of frames and
time slots from base station BS1.
- 3b -
4
f:~ ';i :~ '' _<;~ ~3
Figure 2 illustrates a transmitting frame and a receiving frame
(RX and TX respectively) for the mobile MS.
It is assumed that prior to "hand-off", the traffic flow is
ciphered with a certain key E2. This key consists of a bit sequence
or a section of a longer, random bit sequence E (e.g. about 3
minutes long), which is superimposed on the traffic flow
through modulo 2-addition bit for bit. As will be understood, the
key E is known to 'the mobile MS when this is authorized to transmit
and receive calls, and the base station BS1 transmit data concer-
ning the starting time point, i.e. the place in the sequence E at
which the bit Flow shall commence, i. e. E2 is known to the mobile
MS. This ciphering technique is known in the art.
Figure 3 is a time diagram which illustrates application of the
method during "hand°off" . It is assumed that the base station BS1
communicates with the mobile MS and that the communication (the
speech) is ciphered by means of a crypto key E2 up to the time
point t1. Hand-off takes place at the time t1.
Upon termination of the °°hand-off" process at time t2, MS
has
synchronized with the new base station BS2. There is namely
transmitted from this base station on a given control channel (SY
in Figure 2) during the time t1-t2 a synchronizing sequence which
denotes the time position of the frames and the allotted time slot
for the continued call communication between BS2 and MS. This is
effected in a known manner by means of a correlation process in MS.
Thus, at the time t=t2, there is frame synchronization for
speech/data transmission between BS2 and MS, but not for the
ciphering. At t=t2, the base station BS2 transmits a non-ciphered
signal which denotes when ciphering in accordance with the key E2
shall recommence, i.e. BS2 announces the time point t3. The
traffic flaw (speech/data) is ciphered in subsequent frames with
a key E1 which consists of a periodic, random bit sequence having
a period equal to the frame interval. This enables the mobile MS
to count the number of frame intervals (announced by the non-
ciphered signal) until ciphering in accordance with the key E2 is
commenced by BS2. Possibly the ciphering key E1 can consist of
5
~ ,.
~~eb . :~N. .~
zeros only, i.e. the traffic flow in subsequent frames is trans-
mitted unciphered (interval t2-t3) . The mobile MS can anyway count
the number of frame intervals in spite of absence of 'the periodic
bit sequence in the key E1, due to the presence of frame synchroni-
zation in the control channel SY from the time point t2.
Figure 4 illustrates the sequence during the time interval t2-t3
more clearly.
According to Figure 3, at time t2 the mobile MS is synchronized to
the new base station BS2 and the normal traffic flow (data,
speech, synchronization) should have commenced if no ciphering has
been employed. Synchronization with respect to the bit flow in the
ciphering key E2 up to the time tl, however, has been lost. The
base station therefore sends to MS a signal S1 which indicates how
many frames shall pass until ciphering according to key E2 is to
be commenced. This frame number is assumed to be 13 in the Figure
4 illustration. This message can be transmitted in a non-ciphered
form on the so-called FACCH (Fast Associated Control Channel)
formed by a reserved time slot within a frame, see Figure 2. This
time slot is thus located in frame R1. During the frames R2, R3,
... R6 following the frame R1, the ciphered call information is
transmitted and ciphered with the key E1. As before mentioned,
this key is a periodic bit sequence whose period equals one frame
interval and which can be superimposed on the call information by
modulo-2 addition. Consequently, the mobile MS is aware of the
time at which counting shall commence and also of the number of
frame intervals to be counted. When this is understood by the
mobile, a confirmation signal A1 is transmitted back to the base
station BS2 and received in frame R6. When the base station BS2
receives this signal, the station will wait for a period of time
which equals the agreed number of frames, i.e. to frame R13 (t=t3)
where ciphering in accordance with the key E2 is commenced.
The base station BS2 thus 'waits a given length of time ( in Figure
4 a time equalling 5 frame intervals) for receipt of the confirma-
tion signal A1. If, for some reason or other, this signal is not
received by the base station BS2 within a given period of time, a
"~a'~'~~~;i~°~
f~vrns.._ ,c
signal S2 is again transmitted in frame R7 and a new confirmation
signal A2 is awaited. The signal A1 can fall away because, e.g.,
of fading or difficult surrounding conditions at precisely the
interval in which the signal A1 is transmitted. Thus, the number
of frames (=R13) from the base station BS2 should be sufficien-
tly large to enable repeated signalling according to the above to
be carried out.
The signal delay between base station and mobile has been assumed
to be about 2-3 frame intervals (~15 ms) in the Figure 4 illustra-
Lion. This delay should also be taken into account. Thus, the
ciphering time point t3 will preferably be chosen so that t2-t3 >
4 times the maximum propagation time. This calculation offers no
difficulties, since the mobile is located on the border between
two cells C1, C2 according to Figure 1, i.e. at a maximum distance
from a base station.