Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
20~88~9
-- 1 --
568~5/000.533
Xmida20Ie~
The present invention relates to novel heterocyclic
imidazoles, processes for their preparation and
pharmaceutical compositions containing them.
We have found that certain new heterocyclic imidazoles
possess interesting and valuable pharmacological
activities making them particularly suitable for the
treatment of hypertension and cardiac insufficiency and
also for treating ischaemic peripheral circulatory
disorders, myocardial ischaemia (angina), for the
prevention of the progression of cardiac insufficiency
after myocardial in~arct and for treating diabetic
nephropathy, glaucoma, gastrointestinal diseases and
bladder ~diseases.
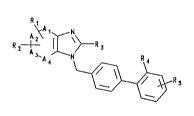
Thus, according to one aspect the present invention
provides,compounds of formula I
~=~ ~ s
(wherein
one or two of A1, A2~ A3 and A4 represent a nitrogen atom
and the remaining two or three of A1, A2, A3 and A4 each
represent a methine group;
R1 represents a fluorine, chlorine or bromine atom, a
hydroxy, alkyl or alkoxy group,
~ : :, ,: -: ,
. .
~ ,
,
: :
:
20~8~09
-- 2
an amino group optionally mono- or disubstituted, or an
N-acylamino group optionally monosubstituted, at the
nitrogen atom by a C16-alkyl, phenyl, C57-cycloalkyl,
phenyl(C13-alkyl)or (C57-cycloalkyl)C13-alkyl group,
which substituents may be identical or different and
which acyl group is a C17-alkanoyl group optionally
substituted in the 3-, 4-, 5-, 6- or 7-position by a
halogen atom or a hydroxy group, a (C13-alkoxy)carbonyl
group, a C16-alkylsulphonyl group, a benzoyl,
benzenesulphonyl, phenyl(C13-alkanesulphonyl),
naphthalenesulphonyl, 2-carboxy-cyclohexylcarbonyl, 2-
. aminocarbonyl-cyclohexylcarbonyl, (C57-cycloalkyl)-
carbonyl, phenyl(C14-alkanoyl) or (C57-cycloalkyl)-
C14-alkanoyl group, in which the above-mentioned phenyl
nuclei are optionally mono- or disubstituted by a
fluorine, chlorine or bromine atom or by a methyl or
methoxy group which substituents may be identical or
different,
~,
a C35-alkylsultam group, a pyrrolidino, piperidino or
hexamethyleneimino group optionally substituted by a
C13-alkyl or hydroxycarbonyl(C13-alkyl)group, a
pyrrolidinone, piperidinone or hexamethyleneiminone
group, an optionally totally or partially hydrogenated
phthalimido or 2-oxo-isoindolin-l-yl group
or a group of formula
~'
R6 / R7
- N - CO - N
\ R
. [in which R6, R7 and R8, which may be identical or
different, represent hydrogen atoms, C18-alkyl groups,
Cs7-cycloalkyl, phenyl, tC57-cycloalkyl)C13-alkyl or
phenyl(C13-alkyl) groups, and
'''~
~. : ' . ' :
, .
. ,
: ~ ~
0~8~0~
-- 3
RA may also represent a 2-chloro-ethyl, 2-bromo-ethyl, 3-
chloro-propyl or 3-bromo-propyl group, and where R6 and
R7 together represent an ethylene or propylene group, R~
may also represent a di(C13-al:kyl)aminocarbonyl group,
or
R6 and R7 together represent an ethylene or propylene
group
and in which the phenyl nucleus of the above-mentioned
phenyl and phenyl(Cl3-alkyl) groups may in each case be
mono- or disubstituted by hydroxy or C13-alkoxy groups
which substituents may be identical or dif~erent~, and
R1 may also represent a hydrogen atom, except where Rz
represents a hydrogen atom, R3 represents an n-butyl
group, R4 represents a carboxy group and Rs represents a
hydroyen atom, and
(i) one of the groups A1, A2, A3 and A4 represents a
nitrogen atom and the remaining groups A1, A2, A3
or A4 each represent methine groups, or
(ii) A2 and A4 or A1 and A3 each represent a nitrogen
atom and the remaining groups A1 and A3 or A2 and A4
each represent a methine group, or
(iii) A4 represents a nitrogen atom and A3 represents a
methine group substituted by a hydroxy or methoxy
: group and the remaining groups A1 and A2 each
represent a methine group, or
: (iv) A4 represents a nitrogen atom, A1 represents a
methine group sub~tituted by a methyl group and
the remaining groups A2 and A3 each represent a
methine group;
,
`,
, '
`
' ~' `
` 2048809
R2 represents a hydrogen atom or a C13-alkyl group;
R3 represents a C16-alkyl group;
R4 represents a carboxy, cyano, lH-tetrazolyl or 1-
triphenylmethyl-tetrazolyl group or a (C14-alkoxy)-
carbonyl group; and
R5 represents a hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine or bromine
atom);
and isomers and salts, particularly the 1-, 3-isomer
mixtures, tautomers, enantiomers and addition salts
thereof, and more particularly for pharmaceutical use
the physiologically acceptable addition salts thereof
with organic or inorganic acids or bases.
Examples of heteroaromatic groups covered by the
definition of the groups A1, A2, A3 and A4 hereinbefore
include pyrido, pyrimido, pyrazino or pyridazino groups.
The following are examples of the definitions of the
groups R1, R2, R3, R4 and Rs as mentioned hereinbefore:
R1 may represent a hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine or
bromine atom, a methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl,
hydroxy, methoxy, ethoxy, n-propoxy, isopropoxy,
formylamino, acetylamino, propionylamino, n-
butanoylamino, isobutanoylamino, n-pentanoylamino, 2-
methyl-n-butanoylamino, 3-methyl-n-butanoylamino, n-
hexanoylamino, n-heptanoylamino, cyclopentylcarbonyl-
amino, cyclohexylcarbonylamino, cycloheptylcarbonyl-
amino, cyclopentylmethylcarbonylamino, cyclohexylmethyl-
carbonylamino, cycloheptylmethylcarbonylamino, (2-
cyclopentylethyl)-carbonylamino, (2-cyclohexylethyl)-
carbonylamino, ~2-cycloheptylethyl)-carbonylamino,
benzoylamino, phenylacetylamino, 2-phenylpropionylamino,
~' ' ' ~ '
4~09
- 5 -
naphthyl (1)-carbonylamino, naphthyl-(2)-carbonylamino,
methoxycarbonylamino, ethoxycarbonylamino, n-
propoxycarbonylamino, methane~;ulphonylamino, ethane-
sulphonylamino, n-propanesulphonylamino, isopropane-
sulphonylamino, n-butanesulphonylamino, n-pentane-
sulphonylamino, n-hexanesulphonylamino, benzene-
sulphonylamino, 2-methylbenzenesulphonylamino, 4-
methylbenzenesulphonylamino, 2-methoxybenzenesulphonyl-
amino, ~-methoxybenzenesulphonylamino, 2-fluorobenzene-
sulphonylamino, 4-fl~orobenzenesulphonylamino, 2-
chlorobenzenesulphonylamino, 4-chlorobenzenesulphonyl-
amino, 2-bromobenzenesulphonylamino, 4-bromobenzene-
sulphonylamino, 2,4-dimethoxybenzenesulphonylamino,
benzylsulphonylamino, naphthalene-(1)-sulphonylamino,
naphthalene-(2)-sulphonylamino, propanesultam-(l)-yl, n-
butanesultam-(l)-yl, n-pentanesultam~ yl, amino,
methylamino, ethylamino, n-propylamino, isopropylamino,
n-butylamino, isobutylamino, n-pentylamino, n-
hexylamino, dimethylamino, diethylamino, di-n-
propylamino, methyl-ethylamino, methyl-isopropylamino,
methyl-n-butylamino, ethyl-n-propylamino, methyl-n-
pentylamino, ethyl-n-hexylamino, cyclopentylamino,
cyclohexylamino, cycloheptylamino, cyclopentylmethyl-
amino, cyclohexylmethylamino, cycloheptylmethylamino,
(2-cyclopentylethyl)-amino, (2-cyclohexylethyl)-amino,
(2-cycloheptylethyl)-amino, (3-cyclopentylpropyl)-amino,
~3-cyclohexylpropyl)-amino, (3-cycloheptylpropyl)-amino,
benzylamino, Z-phenylethylamino, 3-phenylpropylamino,
phenylamino, dicyclohexylamino, dicyclohexylmethylamino,
dibenzylamino, N-methyl-cyclopropylamino, N-methyl-
cyclopentylamino, N-ethyl-cyclohexylamino, N-(n-propyl)
cycloheptylamino, N-methyl-cyclopentylmethylamino, N-
ethyl-cyclohexylmethylamino, N-(n-propyl)-cycloheptyl-
methylamino, N-methyl-(2-cyclopentylethyl)-amino, N-
ethyl-(2-cyclohe~ylethyl~-amino, N-(n-propyl)-(2-
cycloheptylethyl)-amino, N-methyl-(3-cyclopentylpropyl)-
amino, N-ethyl-(3-cyclohexylpropyl~-amino, N-methyl-
,
.
.: '
'
:-- 2~48~09
- 6 -
benzylamino, N-ethyl-benzylamino, N-isopropyl-
benæylamino, N-methyl-(2-phenylethyl)-amino, N-methyl-
phenylamino, N-(n-propyl)-phenylamino, N-acetyl-
methylamino, N-acetyl-ethylamino, N-acetyl-
isopropylamino, N-acetyl-n-butylamino, N-acetyl-n-
hexylamino, N-propionyl-methylamino, N-propionyl-
ethylamino, N-propionyl-n-buty:lamino, N-n-butanoyl-
methylamino, N-n-butanoyl-ethy:Lamino, N-n-butanoyl-n-
pentylamino, N-isobutanoyl-methylamino, N-isobutanoyl-
ethylamino, N-isobutanoyl-isopropylamino, N-isobutanoyl-
n-butylamino, N-isobutanoyl-n-pentylamino, N-n-
pentanoyl methylamino, N-n-pentanoyl-ethylamino, N-n-
pentanoyl-isopropylamino, N-n-pentanoyl-n-pentylamino,
N-n-hexanoyl-methylamino, N-n-hexanoyl-ethylamino, N-n-
hexanoyl-isopropylamino, N-n-hexanoyl-n-pentylamino, N-
cyclopentylcarbonyl-methylamino, N-cyclohexylcarbonyl-
methylamino, N-cyclohexylcarbonyl-ethylamino, N-
cycloheptylcarbonyl-methylamino, N-cyclopentylmethyl-
carbonyl-methylamino, N-cyclohexylmethylcarbonyl-
methylamino, N-cycloheptylmethylcarbonyl-methylamino, N-
(2-cyclopentylethylcarbonyl)-methylamino, N-(2-
cyclohexylethylcarbonyl)-methylamino, N-(2-cycloheptyl-
ethylcarbonyl)-methylamino, N-henzoyl-methylamino, ~-
benzoyl-ethylamino, N-benzoyl-isopropylamino, N-benzoyl-
n-butylamino, N-benzoyl-n-pentylamino, N-benzoyl-n-
hexylamino, N phenylacetyl-methylamino, N-naphthyl~
carbonyl-methylamino, N-naphthyl-(2)-carbonyl-
methylamino, ~-methoxycarbonyl-methylamino, N-
methoxycarbonyl-ethylamino, N-methoxycarbonyl-n-
butylamino, N-methoxycarbonyl-isobutylamino, N-
ethoxycarbonyl-methylamino, N-ethoxycarbonyl-ethylamino,
N-ethoxycarbonyl-isopropylamino, N-ethoxycarbonyl-n-
butylamino, N-n-propoxycarbonyl-methylamino, N-
methanesulphonyl-methylamino, N-ethanesulphonyl-
isopropylamino, N-(n-propanesulphonyl)-methylamino,
isopropanesulphonylmethylamino, N-(n-butanesulphonyl)-
methylamino, N~(n-pentanesulphonyl)-methylamino, N-(n-
' ~' ~ ' .
.
, ~ ' , ' , , .
, .
` 2~8809
~ 7 --
hexanesulphonyl)-methylamino,
benzenesulphonylmethylamino, N-(2-
methylbenzenesulphonyl)-methylamino, N-(4-
methylbenzenesulphonyl)-methylamino, N-(2-methoxy-
benzenesulphonyl)-methylamino, N-(4-methoxybenzene-
sulphonyl)-methylamino, N-(2-f'Luorobenzenesulphonyl)-
methylamino, N-(4-fluorobenzenesulphonyl)-methylamino,
N-(2-chlorobenzenesulphonyl)-methylamino, N-(4-
chlorobenzene-sulphonyl)-methylamino, N-(2-
bromoben~enesulphonyl)-methylamino, N-(4-
bromobenzenesulphonyl)-methylamino, N (2,4-
dimethoxybenzenesulphonyl)-methylamino, N-benzyl-
sulphonyl-methylamino, N-(naphthalene-(1)-sulphonyl)-
methylamino, N-(naphthalene-(2)-sulphonyl)-methylamino,
N-benzoyl-cyclopentylamino, N-benzoyl-cyclohexylamino,
N-benzoyl-cycloheptylamino, N-phenylacetyl-cyclopentyl-
amino, N-phenylacetyl-cyclohexylamino, N-phenylacetyl-
cycloheptylamino, N-benzoyl-cyclopentylmethylamino, N-
benzoyl-cyclohexylmethylamino, N-benzoyl-cycloheptyl-
methylamino, N-phenylacetyl-cyclopentylmethylamino, N-
phenylacetyl-cyclohexylmethylamino, N-phenylacetyl-
cycloheptylmethylamino, N-(3-phenylpropionyl)-
methylamino, N-(3-phenylpropionyl)-ethylamino, N-(3-
phenylpropionyl)-isopropylamino, N (3-phenylpropionyl)-
isobutylamino, N-benzoyl-(2-cyclopentylethyl)-amino, N-
benzoyl-(2-cyclohexylethyl)-amino, N-benzoyl-(2-
cycloheptylethyl)-amino, N-phenylacetyl (2-
cyclopentylethyl)-amino, N-phenylacetyl-(2-cyclohexyl-
ethyl)-amino, N-phenylacekyl-(2-cycloheptylethyl)-amino,
N-benzoyl-(3-cyclopentylpropyl)-amino~ N-benzoyl-(3-
cyclohexylpropyl)-amino, N-benzoyl-(3-cycloheptyl-
propyl)-amino, N-phenylacetyl-(3-cyclopentylpropyl)-
amino, N-phenylacetyl (3-cyclohexylpropyl)-amino, N-
phenylacetyl-[3-cycloheptylpropyl)-amino, N-acetyl-
cyclopentylamino, N-acetyl-cyclohexylamino, N-acetyl-
cycloheptylamino, N-acetyl-cyclopentylmethylamino, N-
acetyl-cyclohexylmethylamino, N-acetyl-cycloheptyl
methylamino, N-acetyl-(2-cyclopentylethyl)-amino, N-
,
.
.:
,
.
2~!8~09
acetyl-(2-cyclohexylethyl) amino, N-acetyl-(2-
cycloheptylethyl)-amino, N-acetyl-(3-cyclopentylpropyl)
amino, N-acetyl-(3-cyclohexylpropyl)-amino, N-acetyl-(3-
cycloheptylpropyl)-amino, N-acetyl-benzylamino, N-
acetyl-(2-phenylethyl)-amino, N-acetyl-(3~phenylpropyl)-
amino, N-benzoyl-benzylamino, N-benzoyl-(2-phenylethyl)-
amino, N-benzoyl-(3-phenylpropyl)-amino, 2-carboxy-
cyclohexylcarbonylamino, 2-ami.nocarbonyl-cyclohexyl-
carbonylamino, phthalimido, tetrahydrophthalimido,
hexahydrophthalimido, cis-hexahydrophthalimido, ~rans-
hexahydrophthalimido, pyrroliclino, methylpyrrolidino,
ethyl-pyrrolidino, isopropylpyrrolidino, piperidino,
methylpiperidino, ethylpiperidino, isopropylpiperidino,
hexamethyleneimino, methylhexamethyleneimino, ethyl
hexamethyleneimino, isopropylhexamethyleneimino, 2-
carboxymethyl-pyrrolidino, 2-oxo-pyrrolidino, 2-oxo-
piperidino, 2-oxo-hexamethyleneimino, aminocarbonyl-
amino, methylaminocarbonylamino, dimethylaminocarbonyl-
amino, N-methylaminocarbonyl-methylamino, N-(dimethyl-
aminocarbonyl~-methylamino, N-dimethylaminocarbonyl-
ethylamino, N~dimethylaminocarbonyl-isopropylamino, N-
(dimethylaminocarbonyl)-n-pentylamino, N-methylamino-
carbonyl-ethylamino, N-methylaminocarbonyl-n-
pentylamino, N-methylaminocarbonyl-n-hexylamino, N-
methylaminocarbonyl-n-octylamino, N-methylamino~-
carbonyl-cyclohexylamino, ethylaminocarbonylamino, N-
ethylaminocarbonyl-methylamino, N-ethylaminocarbonyl-
ethylamino, N-ethylaminocarbonyl-n-hexylamino, N-
ethylaminocarbonyl-n-heptylamino, N-ethylaminocarbonyl-
cyclohexylamino, diethylaminocarbonylamino, N-
(diethylaminocarbonyl)-methylamino, N-(diethylamino-
carbonyl)~ethylamino, N-(diethylaminocarbonyl)-n-
butylamino, N-(diethylaminocarbonyl)-n-hexylamino, N-
(diethylaminocarbonyl)-n-octylamino, isopropylamino-
carbonylamino, N-isopropylaminocarbonyl-methylamino, n-
butylaminocarbonylamino, N-(n-butylamino~arbonyl)-
methylamino, N-(n-butylaminocarbonyl)-ethylamino, N-(n-
,
:: ~
, :1
,
, ~
- , '
20~8~09
g
butylaminocarbonyl)-i~opropylamino, N-(n-bu~ylamino-
carbonyl)-n-butylamino, N-(n-butylaminocarbonyl)-n-
hexylamino, N-(n-butylaminocarbonyl)-cyclohexylamino, N-
(di-(n-butyl)-aminocarbonyl)-amino, N-(di-(n-butyl)-
aminocarbonyl)-methylamino, N-di-(n-butyl)-
aminocarbonyl)-ethylamino, N-(di-(n-butyl)
aminocarbonyl)-n-butylamino, N-(di-(n-butyl)-
aminocarbonyl)-n-hexylamino, N (n-pentylaminocarbonyl)-
ethylamino, N-(n-hexylaminocarbonyl)-ethylamino, n-
hexylaminocarbonylamino, n heptylaminocarbonylamino, n-
octylaminocarbonylamino, N-(n-hexylaminocarbonyl)-n-
butylamino, N-(n hexylaminocarbonyl)-n-pentylamino, N-
(n-hexylaminocarbonyl)-n-hexylamino, N-(n-hexylamino-
carbonyl)-cyclohexylamino, di-(n~hexyl)-aminocarbonyl-
amino, N-(di-(n-hexyl)-aminocarbonyl)-methylamino, N-
((n-hexyl)-methylaminocarbonyl)-amino, cyclohexylamino-
carbonylamino, N-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl-methylamino, N-
cyclohexylaminocarbonyl-ethylamino, N-cyclohexylamino-
carbonyl-n-butylamino, N-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl-
isobutylamino, N-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl-n-pentylamino,
N-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl-n-hexylamino, N-
cyclohexylaminocarbonyl-cyclohexylamino, N-(ethyl-
cyclohexylaminocarbonyl) methylamino, N-(propyl-cyclo-
hexylaminocarbonyl)-methylamino, N-(n-butyl-cyclohexyl-
aminocarbonyl)-methylamino, N-benzylaminocarbonyl-
isobutylamino, 2(1H)-imidazolidinon-1-yl, 3-methyl-
2(lH)-imidazolidinon-l-yl, 3-ethyl-2(lH)-imidazolidinon-
l-yl, 3-n-propyl-2(1~)-imidazolidinon-1-yl, 3-isopropyl-
2(lH)-imidazolidinon-1-yl, 3-n-bu~yl-2(lH)-
imidazolidinon-1-yl, 3-isobutyl-2(lH)-imidazolidinon-1-
yl, 3-n-pentyl-2(1H)-imidazolidinon-l-ylr 3-n-hexyl-
2(lH)-imidazolidinon-l-yl, 3-cyclopentyl-2(lH)-
imidazolidinon-1-yl, 3-cyclohexyl-2(lH)-imidazolidinon-
1-yl, 3-cycloheptyl-2(lH)-imidazolidinon-1-yl, 3-benzyl-
2~lH)-imidazolidinon-l-yl, 3-(3-hydroxybenzyl)-2(lH)-
imidazolidinon-l-yl, 3-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-2(lH)-
imidazolidinon-l-yl, 3-(3-methoxybenzyl)-2(lH)-
~`' '~ ~ ' ' ' ,`
,
~"
20~8809
-- 10 --
imidazolidinon l-yl, 3-(4-methoxybenzyl)-2(1H)-
imidazolidinon-l-yl, 3-(3,4-dihydroxybenzyl)-2(1H)-
imidazolidinon-1-yl, 3-(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)-2(lH)-
imidazolidonon-l-yl, 3-cyclopentylmethyl-2(lH)-
imidazolidinon-1-yl, 3-cyclohexylmethyl-2(1~)-
imidazolidinon-1-yl, 3-cycloheptylmethyl-2(lH)-
imidazolidinon-l-yl, 3-(2-phellylethyl)-2(lH)-
imidazolidinon-l-yl, 3-(2-cyclop~ntylethyl)-2(lH)-
.~ imidazolidinon-l-yl, 3-(2-cyclohexylethyl)-2(lH)-
imidazolidinon-l-yl, 3-(2-cycloheptylethyl)-2(lH)-
imidazolidinon-l-yl, 3-(3-phenylpropyl)-2(lH)-
imidazolidinon-~.-yl, 3-(3-cyclopentylpropyl)-2(1H)-
imidazolidinon-1-yl, 3-(3-cyclohexylpropyl)-2(lH)-
imidazolidinon-l-yl, 3-(3-cycloheptylpropyl)-2(lH)-
imidazolidinon-l-yl, 3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(1H)-pyrimidon-
l-yl, 3-methyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-pyrimidon-l-yl,
3-ethyl 3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-pyrimidon-1-yl, 3-n-
propyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-pyrimidon-l-yl, 3-
isopropyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(1H)-pyrimidon-1-yl, 3-n-
butyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-pyrimidon-1-yl, 3-
isobutyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-pyrimidon-l-yl, 3-n
pentyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-pyrimidon-l-yl, 3-n-
hexyl-3,4,5,6~tetrahydro-2(lH)-pyrimidon-l-yl, 3-
cyclopentyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-pyrimidon-l-yl, 3-
cyclohexyl-3,4/~,6-tetrahydro-2( lH) -pyrimidon-l-yl, 3-
cycloheptyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-pyrimidon-1-yl, 3-
benzyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-pyrimidon-1-yl, 3-(3-
hydroxybenzyl)-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH~-pyrimidon-1-yl,
3-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(1H)-pyrimidon-
1-yl, 3-(3-methoxybenzyl)-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(1H)-
pyrimidon-1-yl, 3-(4-methoxybenzyl)-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-
2(1H)-pyrimidon-l-yl, 3-(3,4-dihydroxybenzyl)-3,4,5,6-
tetrahydro-2(lH)-pyrimidon-1-yl, 3-(3,4-dimethoxy-
benzyl)-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(1~)-pyrimidon-1-yl, 3-
cyclohexylmethyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-pyrimidon-1-
yl, 3-cycloheptylmethyl 3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-
pyrimidon-l-yl, 3-(2-phenylethyl)-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro
, . . .
~0488~9
~ 1.1. --
2(1H)-pyrimidon-1-yl, 3-(~-cyclopentylethyl)-3,4,5,6-
tetrahydro-2(lH)-pyrimidon-l-yl, 3-(2-cyclohexylethyl)-
3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-pyrimidon-l-yl, 3-(2-
cycloheptylethyl)-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-pyrimidon-1-
yl, 3-(3-phenylpropyl)-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-
pyrimidon-l-yl, 3-(3-cyclopentylpropyl)-3,4,5,6-
tetrahydro-2(1H)-pyrimidon-l-yl, 3-(3-cyclohexylpropyl)-
3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-pyrimidon-1-yl, 3-(3-
cycloheptylpropyl)-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(1~)-pyrimidon-1-
yl, 2-chloroethylaminocarbonylamino, 3-chloropropyl-
aminocarbonylamino, 2-bromoethylaminocarbonylamino, 3- -
bromopropylaminocarbonylamino, (N-2-chloroethyl-
methylaminocarbonyl)-amino, (N-2-bromoethyl-methylamino-
carbonyl)-amino, (N-2-chloropropylmethylaminocarbonyl)-
amino, tert.butylcarbonylamino, (N-2-bromopropyl-
methylaminocarbonyl)-amino, 2-oxo-isoindolin-1-yl, 3-
dimethylaminocarbonyl-2(1H)-imidazolidinon-l-yl, 3-
diethylaminocarbonyl-2(lH)-imidazolidinon-l-yl, 3-di-n-
propylaminocarbonyl-2(lH)-imidazolidinon-l-yl, 3-
dimethylaminocarbonyl-3,4,5,6-tatrahydro-2(lH)-
pyrimidon-l-yl, 3-diethylaminocarbonyl-3,4,5,6-
tetrahydro-2(lH)-pyrimidon-l-yl, 3-diisopropylamino-
carbonyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-pyrimidon-l-yl, 3-
chloro-propionylamino, ~-chloro-butanoylamino, 5-
chloropentanoylamino, 6-chloro-hexanoylamino, 7-chloro-
heptanoylamino, 3-hydroxy-propionylamino, 4-hydroxy-
butanoylamino, 5-hydroxy-pentanoylamino, 6-hydroxy-
hexanoylamino, 7-hydroxy-heptanoylamino, 2,2-dimethyl-
propionylamino or tert.-butylamino group;
R2 may represent a hydrogen atom, a methyl, ethyl, n-
propyl or isopropyl group;
R3 may represent a methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-
butyl, isobut:yl, tert.-butyl, n-pentyl, n-hexyl, 1-
methylpropyl, 1-methylbutyl, 2-methylbutyl, 3-
methylbutyl, 1-methylpentyl, 2-methylpentyl, 3-
. ,
: .
- 20~8~09
- 12 -
methylpentyl, 4-methylpentyl, 1-ethylpropyl or 1,1-
diethylethyl group;
R4 may represent a carboxy, cyano, lH-tetrazolyl, 1-
triphenylmethyl-tetrazolyl, methoxycarbonyl,
ethoxycarbonyl, n-propoxycarbonyl, isopropoxycarbonyl,
n butoxycarbonyl, isobutoxycarbonyl or tert.-
butoxycarbonyl group; and
~, may represent a hydrogen, fluorine, chlorlne or
bromine atom.
Preferred compounds according to the invention include
those of formula I wherein
one or two o~ A1, A2, A3 and A4 represent a nitrogen atom
and the remaining two or three of A1, A2, A3 and A4 each
represent a methine group;
R1 represents a fluorine atom,
an amino or C16-alkylamino group substituted at the
nitrogen atom hy a phenyl, C57-cycloalkyl, phenyl(C13-
alkyl) or (C57-cycloalkyl)C13-alkyl yroup, an amino group
disubstituted by a phenyl, Cs7-cycloalkyl, phenyl(C13-
alkyl) or (C57 cycloalkyl)C13-alkyl group which
substituents may be identical or dif~erent, or an
acylamino group optionally substituted at the nitrogen
atom by a C16 alkyl group or by a phenyl, Cs7-cycloalkyl,
phenyl(C13-alkyl) or (Cs7-cycloalkyl)C13-alkyl group,
wher~in the acyl group is a C~7-alkanoyl group
substituted in the terminal position by a chlorine atom
or by a hydroxy group, a (C13-alkoxy)carbonyl group, a
C16-alkylsulphonyl group, a formyl, benzoyl,
benzenesulphonyl, phenyl(C13-alkanesulphonyl),
naphthalenesulphonyl, 2-carboxy-cyclohexylcarbonyl, 2
aminocarbonyl-cyclohexylcarbonyl, ~C57 cycloalkyl)-
:
20~8~09
- 13 -
carbonyl, phenylalkanoyl or (C57-cycloalkyl)C14-alkanoyl
group, in which the above-mentioned phenyl nuclei is
optionally mono- or disubstituted by a fluorine,
chlorine or bromine atom or by a methyl or methoxy yroup
which substituents may be identical or different,
a C35-alkylsultam group, a pyrrolidino, piperidino or
hexamethyleneimino group optionally substituted by a
Cl3-alkyl or hydroxycarbonyl(Cl3-alkyl)group, a
pyrrolidinone, piperidinone or hexamethyleneiminone
group, an optionally wholly or partially hydrogenated
phthalimido group
or a group of formula
l6 / R7
- N - CO - N
R8
~in which R6, R7 and R8, which may be identical or
different, represent hydrogen atoms, C18-alkyl groups,
C~7-cycloalkyl, phenyl, (C57-cycloalkyl)C13-alkyl or
phenyl(C13-alkyl) groups, and
R8 may also represent a 2-chloro-ethyl, 2-bromo-ethyl, 3-
chloro-propyl or 3-bromo-propyl group, and where R6 and
R7 together represent an ethylene or propylene group, R8
may also represent a di(C13-alkyl)aminocarbonyl group,
or
R6 and R7 together represent an ethylene or propylene
group,
and in which the phenyl nucleus of the above-mentioned
phenyl and phenyl(C13-alkyl) groups may be mono- or
disubstitutecl by hydroxy or C13-alkoxy groups which
substituents may be identical or different];
,
. ,
~ : .: ,,
.
:. . . . i ~ ~ . .:
-` 2~809
R2 represents a hydrogen atom or a C13-alkyl group;
R3 represents a C16-alkyl group;
R4 represents a carboxy, cyano, lH-tetra~olyl, l-
triphenylmethyl-tetrazolyl group or a (C14-alkoxy)-
carbonyl group; and
R5 represents a hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine or bromine
atom;
and the isomers and salts thereof especially the l-, 3-
isomer mixtures, tautomers, enantiomers and addition
salts thereof with organic or inorganic aaids or bases.
Particularly preferred compounds according to the
invention include those of formula I wherein
one or two of A1, A2, A3 and A4 represent a nitrogen atom
and the remaining two or three of A1, A2, A3 and A4 each
represent a methine group;
R1 represents an amino, methylamino or ethylamino group
substituted by a cyclohexyl, cyclohexylmethyl, benzyl or
: dimethoxybenzyl group, an amino, cyclohexylamino,
cyclohexylmethyl or C14alkylamino group substituted by a
C26-alkanoyl group, by a C14-alkanesulphonyl group, by a
C24-alkoxycarbonyl group or by a cyclohexylcarbonyl,
benzylcarbonyl, 2-aminocarbonyl-cyclohexylcarbonyl,
benzenesulphonyl or chlorobenzenesulphonyl group, a C34-
alkylsultam group, a pyrrolidino or piperidino group
optionally substituted by a methyl or
hydroxycarbonylmethyl group, a pyrrolidin-2-on-l-yl or
piperidin-2-on-l-yl group, an optionally wholly
hydrogenated phthalimido or 2-oxo-isoindolin-l-yl group
or a group of formula
R16 / R7
- N - C0 - N
\R8
. .
.
- .
. ~
2~8809
~in which R6, R7 and R~, which may be identical or
difEerent, represent hydrogen atoms, C14-alkyl groups,
cyclohexyl, phenyl, cyclohexylmethyl, benzyl,
methoxybenzyl or hydroxybenzyl groups, and
R8 may also represent a 2 chloro-ethyl, 2-bromo-ethyl, 3-
chloro-propyl or 3-bromo-propyl group, and where R6 and
R7 together represent an ekhylene or propylene group, R8
may also represent a dimethylaminocarbonyl group, or
R6 and R7 together represent an ethylene or propylene
group];
R2 represents a hydrogen atom or a methyl or athyl group;
R3 represents a C15-alkyl group;
R4 represents a carboxy or lH-tetrazolyl group; and
Rs represents a hydrogen atom;
and the isomers and salts thereof, especially the l-, 3-
isomer mixtures, tautomers, enantiomers and addition
salts thereof with organic or inorganic acids or bases.
More particularly preferred compounds according to the
invention include those of formula I wherein
one or two of A1, A2, A3 and A4 represent a nitrogen atom
and the remaining two or three of A1, A2, A3 and A4 each
represent a methine group;
R1 represents an amino, methylamino or ethylamino group
substituted by a cyclohexyl or cyclohexylmethyl group, a
cyclohexylamino or cyclohexylmethylamino group
substituted by a C26-alkanoyl group, by a C14-
alkanesulphor1yl group, by a C24-alkoxycarbonyl group, by
; ~ :
2048~0g
- 16 -
a benzylcarbonyl, 2-aminocarbonylcyclohexylcarbonyl,
benzenesulphonyl or chlorobenzenesulphonyl group, a
cyclohexylcarbonylamino group, a cyclohexylamino,
cyclohexylmethylamino or C14alkylamino group substituted
by a Cl4-alkanesulphonyl, cycl.ohexylcarbonyl, 2-
aminocarbonyl-cyclohexyl-carbonyl, benzenesulphonyl or
chlorobenzenesulphonyl group, a C34-alkylsultam group, a
pyrrolidino or piperidino group substituted by a methyl
or hydroxycarbonylmethyl group, a pyrrolidin-2-on-1-yl
or piperidin-2-on-1-yl group, an optionally ~ully
hydrogenated phthalimido or 2-oxo-isoindolin-l-yl group
or a group of formula
l6 / R7
- N - CO - N R8
[in which one of the groups R6, R7 or R8 represents a
cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl or cyclohexylmethyl group, and
the remaining groups R6, R7 or R8, which may be identical
or different, represent hydrogen atoms, C14-alkyl
groups, cyclohexyl, phenyl, cyclohexylmethyl, benzyl,
methoxybenzyl or hydroxybenzyl groups, or
R7 represents a 2 chloro-ethyl, 2-bromo-ethyl, 3-chloro-
propyl or 3-bromo-propyl group, and
R6 and R8, which may be ~identical or different, represent
hydrogen atoms, C14-alkyl groups, cyclohexyl, phenyl,
cyclohexylmethyl, benzyl, methoxybenzyl or hydroxybenzyl
groups, or
R6 and R7 together represent an ethylene or propylene
group, and
R8 represents a hydrogen atom, a C14-alkyl group, a
cyclohexyl, phenyl, cyclohexylmethyl, benzyl,
: - :
:
'
2~8~9
- 17 -
methoxybenzyl, hydroxybenzyl, 2-ahloro-ethyl, 2-bromo-
ethyl, 3-chloro-propyl, 3-bromo-propyl or dimethylamino-
carbonyl group];
R2 represents a hydrogen atom or a methyl or ethyl group;
R3 represents a C15-alkyl group;
R4 represents a carboxy or lH-tetrazolyl group; and
R5 represents a hydrogen atom;
and the isomers and salts thereof, especially the 1-, 3-
isomer mixtures, tautomers, enantiomers and addikion
salts thereof with organic or inorganic acids or basss.
Although the present invention relates to new compounds
of formula I, the corresponding cyano, alkoxycarbonyl
and triphenylmethyl compounds, in particular, are
valuable intermediates which can readily be converted to
one of the pharmacologically active compounds and thus
form further aspects of the present invention.
According to a still further aspect, the invention also
provides a process for the preparation of compounds of
the invention, said process comprising at least one of
the following steps:
a) cyclising a compound of formula II
A 2~ ~1/
R 2~ ~ ( I I )
3`AI Yl
.
(wherein
.
. - . ~.
, , .
., .
8 ~ ~
R1, R2, A1, A2l A3 and A" are as hereinbefore defined;
one of the groups X1 or Yl represents a group of formula
R5
Rg
and the other group X1 or Y1 represents a group of
formula
Z1~ /Z2
- NH - C - R3
R3 and Rs are as hereinbefore de.fined;
R~ represents a hydrogen atom or an R3CO group; and R3 is
as hereinbefore defined;
Z1 and Z2~ which ~ay be identical or different, represent
optionally substituted amino g:roups or hydroxy or
mercapto groups optionally substituted by lower
(eg. C16)alkyl groups, or
Z1 and Z2 together represent an oxygen or sulphur atom,
an imino group optionally substituted by a C13-alkyl
group, or a C23-alkylenedioxy or C23-alkylenedithio
group, with the proviso that one o~ the groups X1 or Y
must represent a group of formula
R5 or
\
C o R 3
- ~ ~ . f .,
20~o~
-- lg --
NH - C - R~ ) or an N-oxide thereof
and if necessary subsequently reducing the cyclized N-
oxide;
b) reactiny a compound o~ formula III
R2_ ~ ~ ~ R3 (lll)
(wherein
R1, R2, R3, A1, A2, A3 and A4 are as hereinbefore defined)
with a biphenyl compound of formula IV
R5
(wherein
R4 and R5 are as hereinbefore defined; and
Z3 represents a nucleophilic leaving group such as a
halogen atom, e~g. a chlorine, bromine or iodine atom,
or a substituted sulphonyloxy group, e.g. a
methanesulphonyloxy, phenylsulphonyloxy or p-
toluenesulphonyloxy group);
c) (to prepare a compound of formula I wherein R4
represents a carboxy group) convarting a compound of
.. : ,
. ~ . .
,~ , ' , ' ; '~ :
.. ~ .
20~8809
- 20 -
formula V
(wherein
R1, R2, R3~ Rs~ A1, A2, A3 and A4 are as hereinbePore
de~ined; and
R4' represents a group which may be converted into a
carboxy group by hydrolysis, thermolysis or
hydrogenolysis) into a corresponding carboxy compound;
d) (to prepare a compound of formula I wherein R4
represents a lH-tetrazolyl group) cleaving a protecting
group from a compound of formula VI
R
~ ~3
:
(wherein
R1, R2, R3~ R5~ A1, A2, A3 and A4 are as hereinbefore
defined; and
R4" represents a lH-tetrazolyl group protected in the l-
; ~ position by a protecting group);
:::
~, ~...... . . . . . .
- ;, . . . .
~, . ... , ~ .
~, . : ,
2 ~
- 2.1 -
e) (to prepare a compouncl o~ ~ormula I whereln R4
represents a lll-tetrazolyl group) reacting a compound of
formula VII
R ,+ 3~ ~ ~, ( V I I
(wherein
R1, R2, R3~ R5~ A1, A2~ A3 and A4 are as hereinbefore
de~ined) with hydrazoic acid or a salt thereof;
f) (to prepare compounds of formula I wherein R1
represents an amino group optionally substituted by a
(C16-alkyl) group or by a phenyl, C57-cycloalkyl, phenyl
(C13-alkyl) or (Cs7-cycloalkyl)C13-alkyl group)
converting a compound of formula VIII
CN ( V I I I )
~`A
(wherein
R2, R3, R4~ R5~ A1, A2, A3 and A4 are as hereinbefor~
defined; and
R10 represents a group which can be converted by
hydrolysis, hydrogenolysis or transamidation into an
amino group optionally substituted by a Cl6-alkyl group
or by a phenyl, Cs7~cycloalkyl, phenyl(C13-alkyl~ or
:
.
20~88~9
-- 22 --
(C5 7-cyClOal~yl) C13-alkyl group);
g) (to prepare compounds of formula I wherein R
represents a group of formula
R6 / R7
- N - cO - N
reacting a compound of formula IX
R s
(wherein
R2, R3~ R4~ R5, A1, A2, A3 and A4 are as hereinbefore
defined; and
~: R11 represents an R6NH group, wherein R6 i5 as
hereinbefore defined) with a compound of formula X
R7
\ N - CO - Z4 (X)
R8
(wherein
R7 and R8 are as hereinbefore defined;
Z4 represents a nucleophilic leaving group such as a
: chlorine or bromine atom, or
~ Z4 together with R7 represents a nitrogen-carbon bond);
:
h) (to prepare compounds of formula I wherein R
:
::
.
:. , :
2~8~09
- 23 -
repre~ents an N-acylamino group optionally substituted
at the nitroyen atom by a C16-alkyl, phenyl, cycloalkyl,
phenylalXyl or cycloalkylalkyl group~ acylating a
compound of formula XI
(wherein
R2~ R3~ R4~ Rs~ A1~ A2~ A3 and A4 are as hereinbefore
defined; and
R12 represents an amino group optionally substituted by a
C16-alkyl, phenyl, Cs7-cycloalkyl, phenyl(C13-alkyl) or
(C57-cycloalkyl)C13-alkyl group) with a compound of
formula XII
: R13 ~ W - OH (XII)
(wherein
W represents a carbonyl or sulphonyl group; and
R13 represents a C16-alkyl group, a C13-alkoxy group, a
phenyl(C13-alkyl), C5 7-cycloalkyl or (Cs 7-cycloalkyl)C1 3-
alkyl group, a phenyl, naphthyl, 2-carboxy-cycloh~xyl or
2-aminocarbonyl-cyclohexyl group, in which the above-
mentioned phenyl nuclei may be mono- or disubstitutPd by
a fluorine, chlorine or bromine atom or by a methyl or
methoxy group which substituents may be identical or
different, o:r, if W represents a carbonyl group, R13 may
also represent a hydrogen atom) or with a reactive
derivative thereof, such as an acid halide, acid ester
or acid anhydride;
... . .. .
- .
.
. : - . ~ .: . :
. .
, -. . , .
, . . . ~ :
20~L8~09
- 2~ -
i) (to prepare a compou~d of formula I wherein ~6 and R7
together represent an ethylene or n-propylene group)
cyclising a compound of formu:La XIII
, R~Z
H N~ ~R J ( X I I I )
H ~ I I C ~ 2 ) ~ \ ~ R 5
twherein
2~ 3, R4, R5, R8, A1, A2, A3 and A4 are as hereinbefore
defined;
Hal represents a chlorine, bromine or iodine atom; and
n represents the number 2 or 3) and if necessary
subsequently reacting with a compound of formula XIV
R8 ~ Hal (~IV)
(wherein
R8 is as hereinbefore defined, with the exception of the
hydrogen atom; and
~al represents a chlorine, bromine or iodine atom);
j) resolving a 1-, 3- isomer mixture of a compound of
formula I by isomer separation into the 1- and 3-
isomers thereof;
k) converting a compound of formula I into an addition
salt thereof, more particularly, for pharmaceutical use
into a physiologically acceptable salt thereof with an
organic or inorqanic acid or base, or converting a salt
of a compound of formula I into the free compound; and
1) performing a process as defined in any one of steps
(a) to (k) above on a corresponding protected compound
- , .
. . ~
20~8809
- 25
and subsequently removing the pro-tecting group used.
The cyclisation of step (a) may conveniently be carried
out in a solvent or mixture of solvents such as ethanol,
isopropanol, glacial acetic acid, benzene,
chlorobenzene, toluene, xylene, glycol,
glycolmonomethylether, diethyleneglycol-dimethylether,
sulpholane, dimethylformamide, tetraline or in an excess
of the acylating agent used to prepare the compound of
formula II, e.g. in the corresponding nitrile,
anhydride, acid halide, ester or amide. 1'he reaction is
conveniently effected at temperatures between 0 and
250C, preferably at the boiling temperature of the
reaction mixture, optionally in the presence o~ a
condensing agent such as phosphorusoxychloride,
thionylchloride, sulphurylchloride, sulphuric acid, p-
toluenesulphonic acid, methanesulphonic acid,
hydrochloric acid/ phosphoric acid, polyphosphoric acid
or acetic anhydride, or optionally in the presence of a
base such as potassium ethoxide or potassium tert.-
butoxide. However, cyclisation may also be carried out
without a solvent and/or condensing agent.
It is particularly advantageous to carry out the
reaction of step ~a) by preparing a compound of formula
II in the reaction mixture by reducing a corresponding
o-nitro-amino compoundt optionally in the presence of a
carboxylic acid of general formula R3COOH, or by
acyIating a corresponding o-diamino compound. When the
reduction of the nitro group is broken off at the
hydroxylamine stage, the N-oxide of a compound of
formula I is obtained in the subsequent cyclisation.
The resulting N-oxide is then converted by reduction
into a corresponding compound of formula I~ The
subsequent reduction of the N oxide of formula I
obtained is preferably carried out in a solvent such as
water, water/ethanol, methanol, glacial acetic acid,
,,
. ~. , ~
- . .
. . . .
8 ~ 9
- 26 -
ethyl acetate or dimethylformamlde, with hydroyen in the
presence of a hydrogenation catalyst such as Raney
nickel, platinum or palladium/charcoal, with metals such
as iron, tin or zinc in the presence of an acid such as
acetic, hydrochloric or sulphuric acid, with salts such
as iron(II)sulphate, tin(II)chloride or sodium
dithionite, or with hydrazine in the presence of Raney
nickel at temperatures between 0 and 50C, preferably at
ambient temperature.
The reaction of step (b) may conveniently be carried out
in a solvent or mixture of solvents such as methylene
chloride, diethylether, acetone, tetrahydrofuran,
dioxane, dimethylsulphoxide, or benzene, optionally in
the presence of an acid binding agent such as sodium
carbonate, potassium carbonate, sodium hydroxide,
potassium tert.-butoxide, sodium hydride, triethylamine
or pyridine, whilst the latter two may simultaneously
also be used as solvent, conveniently at temperatures
between 0 and 100C, preferably at temperatures between
ambient temperature and 50C. A mixture of the 1- and
3- isomers is preferably obtained.
In step (c) functional derivatives of the carboxy group
such as the optionally substituted amides, esters,
thiolesters, orthoesters, iminoethers, amidines or
anhydrides or the nitrile group may be converted by
hydrolysis into a carboxy group, esters with tertiary
alcohols, e.g. the tert.butylester, may be converted by
thermolysis into a carboxy group and esters with
aralkanols, e.y. the benzylester, may be converted by
hydrogenolysis into a carboxy group.
The hydrolysis o~ step (cl may conveniently be carried
out either in the presence of an acid such as
hydrochloric, sulphuric, phosphoric, trichloroacetic or
trifluoroacetic acid or in the presence of a base such
.
:: ~
.
.
.
- 27 - 2~8~09
as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide in a suitable
solvent such as water, water/methanol, ethanol,
water/ethanol, water/isopropanol or water/dioxane at
temperatures between -10C and 120C, preferably at
temperatures between ambient temperature and the boiling
temperature of the reaction mixture. When the
hydrolysis is carried out in the presence of an organic
acid such as trichloroacetic or trifluoroacetic acid,
any alcoholic hydroxy groups present may optionally
simultaneously be converted into a corresponding acyloxy
group such as the trifluoroacetoxy group.
If R4' in a compound of formula V represents a cyano or
aminocarbonyl group, these groups may also be converted
into the carboxy group with a nitrite, e.g. sodium
nitrite, in the presence of an acid such as sulphuric
acid, which may simultaneously also be used as solvent,
at temperatures between 0 and 50C.
If R4' in a compound of formula V represents for example
a tert.-butyloxycarbonyl group, the tert.-butyl group
may also be thermally cleaved, optionally in an inert
solvent such as methylene chloride, chloroform, benzene,
toluene, tetrahydrofuran or dioxane and preferably in
the presence of a catalytic amount of an acid such as
trifluoroacetic acid, p-toluenesulphonic acid, sulphuric
acid, phosphoric acid or polyphosphoric acid,
conveniently at temperatures between 40C and 100C,
preferably at the boiling temperature of the solvent
used.
If R4' in a compound of formula V represents for example
a benzyloxycarbonyl group, the benzyl group may al~o be
hydrogenolytically cleaved in the presence of a
hydrogenation catalyst such as palladium/charcoal in a
suitable solvent such as methanol, ethanol,
ethanol/water, glacial acetic acid, ethyl acetate,
. .
:
,
~ ~ :
. ~ . .
~ :. i .
.
20~8809
- 2~ -
dioxane or dimethyltormamide, preferably at temperatures
between 0 and 50C, more preferably at ambient
temperature, under a hydrogen pressure of 1 to 5 bar.
During hydrogenolysis, other group.s may be reduced at
the same time, e.g. a nitro group may be reduced to the
amino group, a benzyloxy group to the hydroxy group, a
vinylidelle group to the corresponding alkylidene group
or a cinnamic acid group to the corresponding phenyl-
propionic acid group, or they may be replaced by
hydrogen atoms, e.g. a halogen may be replaced by a
hydrogen atom.
If R1 in a compound of formula V represents one of the
above mentioned hydrolysable groups, it may be converted
during the reaction into a corresponding amino compound.
Suitable protecting groups for use in step (d) include,
for example, the triphenylmethyl, trimethyl tin,
tributyl tin, triphenyl tin, propionic acid nitrile or
p-nitrobenzyl groups. The cleaving of a protecting
group used is preferably carried out in the presence of
a hydrohalic acid, preferably in the presence of
hydrochloric acid, in the presence of a base such as
sodium hydroxide or alcoholic ammonia in a suitable
solvent such as methylene chloride, methanol,
methanol/ammonia, ethanol or isopropanol, conveniently
at temperatures between 0 and 100C, preferably at
ambient temperature or, if the reaction is carried out
in the presence of alcoholic ammonia, at elevated
temperatures, e.g. at temperatures between 100 and
150C, preferably at temperatures between 120 and 140C.
The reaction o~ step (e) is preferably carried out in a
solvent such as benzene, toluene or dimethylformamide at
temperatures between 80 and 150C, preferably at 125C.
Appropriately, either the hydrazoic acid is liberated
during the reaction from an alkali metal azide, e.g.
sodiu~ azide in the presence of a weak acid such as
ammonium chloride, or the tetrazolide salt obtained in
,
, : :
: .` ~ ~ .
.
'
.
20~809
- 29 ~
the reaction mixture from the reaction with a salt of
hydrazoic acid, preferably with aluminium azide or
tributyl tin azide, which is also preferably produced in
the reaction mixture by reacting aluminium chloride or
tributyl tin chloride with an alkali metal azide such as
sodium azide, is subsequently liberated by acidification
with a dilute acid such as 2N hydrochloric or 2N
sulphuric acid.
In the reagent of formula VIII used in step (f),
acylamino groups, e.g. the val~eroylamino, benzoylamino
or phthalimido group, may be converted by hydrolysis
into an amino group, and imino groups, e.g. the
phthalimino group, may be converted by transamidation
into an amino group.
The hydrolysis of step (f) may conveniently be carried
out either in the presence of an acid such as
hydrochloric, sulphuric, phosphoric, trichloroacetic or
trifluoroacetic acid or in the presence of a base such
as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide in a suitable
solvent such as water, water/methanol, ethanol,
water/ethanol, water/iso-propanol or water/dioxane
conveniently at temperatures of between ~10C and 120C,
preferably at temperatures between ambient temperature
and the boiling temperature of the reaction mixture.
When hydrolysis is carried out in the presence of an
organic acid such as trichloroacetic acid or
trifluoroacetic acid, any alcoholic hydroxy groups
present may simultaneously be converted into a
corresponding acyloxy group such as the trifluoroacetoxy
group. If R1o represents a phthalimido group, this group
may, to particular advantage, be converted into an amino
group in the presence of a primary organic base such as
methylamine, ethylamine or propylamine or with hydrazine
optionally in a suitable solvent such as methanol,
ethanol, isopropanol, dimethyl~ormamide, methanol/di-
' ~ ~ !. ; , , ' ~!
'
- ' , ' :
' ':
.
1, ,
.
~, ,
g o 9
- 30 ~
methyl~ormamide or methanol/water by transamidation at
temperatures between 0 and 50C, pre~erably at ambient
temperature.
The reaction of step (g) is preferably carried out in a
solvent such as tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, ethylene
chloride or benzene, optional]y in the presence of an
acid binding agent such as triethylamine or pyridine,
conveniently at temperatures between 0 and 100C,
preferably at temperatures bet:ween 20 and 80C.
Examples of reactive derivatives of a compound of
formula XII in step (h) include, for example, the esters
thereof such as the methyl, ethyl or benzylesters, the
thioesters such as the methylthio or ethylthioesters,
and the halides such as the acid chloride, the
anhydrides or imidazolides thereof.
The reaction of step (h) may conveniently be carried out
in a solvent or mixture of solvents such as water,
methylene chloride, chloroform, ether, tetrahydrofuran,
dioxane or dimethylformamide with a corresponding
carboxylic acid in the presence of an acid-activating or
dehydrating agent such as thionyl chloride, with the
anhydrides thereof such as acetic acid anhydride, with
the esters thereof such as ethyl acetate, with the
halides thereof such as acetyl chloride or
methanesulphonyl chloride, optionally in the presence of
an inorganic or tertiary organic base such as sodium
hydroxide, potassium carbonate, triethylamine or
pyridine, whilst the latter two may simultaneously serve
as solvent, conveniently at temperatures between -~5 and
100C, prefexably at temperatures between 10 and 80C.
The cyclisation of step (i) and, if necessary, the
subsequent alkylation are expediently carried out in a
solvent such as methanol, ethanol, benzene or
,
.' ' . ~
:
. :
~ ' ,' ' ,
20~809
- 31 -
dimethylsulphoxide, optionally in the presence of a
phase transfer catalyst such as benzyltriethylammonium
bromide in the presence of an acid binding agent such as
sodium hydroxide, sodium mekhoxide, sodium ethoxide,
sodium hydride or potassium tert.-butoxide at
temperatures between 20 and 100, preferably at
temperatures between 30 and 70C.
The isomer separation of step (j) is preferably carried
out by chromatography using a substrate such as silica
gel or aluminium oxide.
The compounds of formula I obtained may, if desired, be
converted into the acid addition salts thereof, more
particularly ~or pharmaceutical use the physiologically
acceptable salts thereof with organic or inorganic
acids. Suitable acids for this purpose include
hydrochloric, hydrobromic, sulphuric, phosphoric,
fumaric, succinic, lactic, citric, tartaric and maleic
acid.
Furthermore, the new compounds of formula I thus
obtained, if they contain a carboxy or tetrazolyl group,
may, if desired, subsequently be converted into the
addition salts thereof with organic or inorganic bases,
more particularly for pharmaceutical use into the
physiologically acceptable addition salts thereof.
Suitable bases for this purpose include sodium
hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, cyclohexylamine,
ethanolamine, diethanolamine and triethanolamine.
Some of the compounds of formulae II to XIV used as
starting materials are known from the literature.
Otherwise these compounds may be obtained by methods
known from the literature.
Thus, for example, a compound of general formula II is
:,
:,, , :
. :- -
.
- :
.
.
-
20~8~
- 32 -
obtained by alkylation of a corresponding o-amino-nitro
compound and subsequent reduction of the nitro group.
Compounds of formulae III, V, VI, VII, VIII, IX, XI or
XIII used as starting materials are obtained by
alkylation of a corresponding o-diamine or a
corresponding o-amino-nitro compound, followed by
reduction of the nitro group and subsequent cyclisation
of an o-diamino compound thus obtained, or by NH-
alkylation vf a corresponding lH-compound, whilst the
isomer mixture thus obtained may subsequently be
resolved by conventional methods, e.g. chromatography.
The new compounds of general formula I and the
physiologically acceptable addition salts thereof have
valuable pharmacological properties. They are
angiotensin antagonists, in particular, angiotensin-II-
antagonists. Compounds of formula I which are of
particular value are those wherein R4 represents an
alkoxycarbonyl, carboxy or lH-tetrazolyl group.
Thus in a further aspect the present invention provides
a pharmaceutical composition comprising a compound of
formula I or a physiologically acceptable addition salt
thereof together with at least one pharmaceutical
carrier or excipient.
In a still further aspect the present invention provides
the use of a compound of formula I or a physiologically
acceptable salt thereof for the manufacture of a
therapeutic agent for the treatment of hypertension,
cardiac insufficiency, ischaemic peripheral circulatory
disorders, myocardial ischaemia (angina), for the
prevention of cardiac insufficiency progression after
myocardial infarct, or for the treatment of diabetic
nephropathy, glaucoma, gastrointestinal diseases and
bladder diseases.
.
.
. ~ '
2~48~09
- 33 -
In a stil.l yet ~urther aspect the present invention
provides a method of treatment of the human or non-human
animal body to combat hypertension, cardiac
insufficiency, ischaemic peripheral circulatory
disorders, myocardial ischaemi.a (angina), cardiac
insufficiency progression a~ter myocardial infarction,
diabetic nephropathy, glaucoma, gastrointestinal
diseases and bladder diseases, said method comprising
administering to said body a compound of formula I or a
physiologically acceptable addition salt thereof.
By way of example, the following compounds:
A = 4~-[(2~n-butyl-5-methyl-6-phthalimido-3H-im.idazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic
acid;
B = 4'-[(2-n-butyl-5-amino-3H-imidaæo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-
yl)mPthyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid;
C = 4'-[(2-benzylamino-8-n-butyl-9H-purin-9-yl)-methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylia acid;
D = 4'-[[2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-(cis-hexahydrophthal-
imido)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b~pyridin-3-yl]methyl~-
biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid;
E = 4'-[(2-n-butyl-5-cyclohexylamino-3H-imidazo~4,5-b]-
pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid;
F = 4'-[[2-n-butyl-5-~N-cyclohexylcarbonyl-ethylamino)~
3H imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl~methyl]biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid;
G = 4'-[(2-n-butyl-5-methoxy-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-
yl)methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl;
, , .. ~ :
-, :~ :- , .
,
20~09
- 3~ -
H = 4'-[[2-n-butyl-5-(3-benzyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2[1H)-
pyrimidinon l-yl)-3H-imidazoC4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid;
I = 4'-[(2-n-propyl-5-cyclohexylcarbonylamino-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]-2-~lH-tetrazol-5-
y])biphenyl;
J = 4'-[[~-ethyl-5-t2,2-dimethyl-propionylamino)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-
5-yl)biphenyl; and
K = 4'-[[2-n-propyl-5-t2-methyl-propylamino)-3H-imidazo-
[~,5-b]pyridin-3-yl~-methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)-
biphenyl
were tested for their biological effects as follows:
Rats (male, 180-220 g) are anaesthetised with sodium
hexobarbital (150 mg/kg i.p.). After they have become
unconscious, a tracheal cannula is inserted, the animals
are pithed and then immediately artificially respirated
with a ventilator pump. The arterial blood pressure is
recorded by means of a cannula in the carotid artery
using a Bell & ~owell pressure recorder. The substances
are administered in the jugular vein through a cannula.
Test substances are administered in three doses (10, 20
and 30 mg/kg i.Y. ), with one dose of substance being
tested on each animal. Three minutes after the
intravenous administration of the test substance,
angiotensin-II is administered intravenously in
increasing doses and in this way a cumulative dose-
activity relationship is achieved for angiotensin-II in
the presence of the test substances. The increase in
arterial blood pressure is measured.
.
:~ .. . l ~ . . ,
:
~:: . : ' : ! ,
20~8809
- 35 -
These dose activity cuxves are compared with standard
curves for angiotensin-II without the use of any test
substances. Using a computer program, the shifts to
the right in the dose-activity curves for angiotensin-II
as a result of the administrat:ion of the test su~stances
are determined and corresponding pA2-values are
calculated for the test substances.
The PA2 values of the above-mentioned test compounds A to
K are between 5.1 and 7.9.
Moreover, when the above-mentioned compounds were
administered in a dose of 30 mg/kg i.v. no toxic side
effects, e.g. negative inotropic effects or heart rhythm
diosorders, were observed. Accordingly, the compounds
are well tolerated.
The new compounds and their physiologically acceptable
addition salts are suitable for their treatment of
hypertension and cardiac insufficiency and also for
treating ischaemic peripheral circulatory disorders,
myocardial ischaemia (angina), for the prevention of the
progression of cardiac insufficiency after myocardial
infarct and for treating diabetic nephropathy, glaucoma,
gastrointestinal diseases and bladder diseases.
The new compounds and the physiologically acceptable
addition salts thereof are also suitable for treating
pulmonary diseases, e.g. lung oedema and chronic
bronchitis, for preventing arterial re-stenosis after
angioplasty, for preventing thickening of blood vessel
walls after vascular operations, and for preventing
arteriosclerosis and diabetic angiopathy. In view of
the effects of angiotensin on the release of acetyl
choline and dopamine in the brain, the new angiotensin
antagonists are also suitable for alleviating central
nervous system disorders, e.g. depression, Alzheimer's
. : , , , , ~ , ~ , .
.. . .
- .. ~ : , .
. .. . . ' i, , :
';
. .
2~L8809
- 36 -
disease, Parkinson syndrome, bulimia and disorders of
cognitive function.
The dosage required to achieve these effects is
conv~niently, when administered intravenously, 20 to
100 mg, preferably 30 to 70 my, and, when administered
orally, 50 to 200 mg, preferably 75 to 150 mg, 1 to 3
times a day. For this purpose, the compounds of formula
I prepared accordirg to the invention, optionally in
conjunction with other active substances, may be
incorporated together with one or more inert
conventional carriers and/or diluents, for example with
corn starch, lactose, g~ucose, microcrystalline
cellulose, magnesium stearate, polyvinylpyrrolidone,
citric acid, tartaric acid, water, water/ethanol,
water/glycerol, water/sorbitol,
water/polyethyleneglycol, propylene-glycol, cetylstearyl
alcohol, carboxymethylcellulose or fatty substances such
as hard fat or suitable mixtures thereof, in
conventional galenic preparations such as plain or
coated tablets, capsules, powders, suspensions or
suppositories.
The following non-limiting Examples are provided to
illustrate the invention. Unless otherwise specified
all percentages and ratios given are by weight.
,
,
, ,, :
- . .
.: .
~0~809
- 37 --
Example A
2-n-Butyl-7-methyl-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine
.
3.Ç g (29 mMol) of 2,3-diamino-4-methyl-pyridine and
3 ml of valeric acid are refluxed for 2 hours in 30 ml
of phosphorusoxytrichloride. The reaction mixture is
evaporated down in vacuo and the residue is mixed with
100 ml of ice water. By adding 20% sodium hydroxide
solution, the mixture is neutralised and then extracted
twice with 100 ml o~ ethyl acetate. After drying over
magnesium sulphate and evaporation of the solvent, an
oil is obtained.
Yield: 4.8 g (87% of theory),
Rf value: 0.40 tsilica gel, eluant: ethylmethylketone/
xylene - 1:1 by volume)
C11H1sN3 (l89.26)
Calculated: C 69.81 H 7.99 N 22.20
Found: 69.60 7.91 21.96
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
8-n-butyl-2-benzylamino-purine
Oil, ~f value: 0.55 (silica gel; eluant: methylene
chloride/ethanol = 9:1 by volume)
8-n-butyl-2-n-butylamino~purine
Melting point: 111-114C
8-n-butyl-2-cyclohexylamino-purine
Oil, Rf value: 0.60 (silica gel; eluant: methylene
chloride/ethanol = 9:1 by volume)
8-n-butyl-2~ethoxy-purine
Melting point: 181-182C
8-n-butyl-2~methoxy-purine
Melting point: 166C
,
`:
2~48809
- 38 -
8-n-butyl-purine
Melting poi.nt~ 17~ 0C
2-n-butyl-5-bromo-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine
Melting point: 223-225C
Example B
2-n-Butyl-5-va.leroylamino-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine
Prepared from 2,6-bis(n-pentanoylamino)-3-nitro-pyridine
analogously to Example 1.
Yield: 83% o~ theory,
Melting point: 148-150C
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
2-n-butyl-5-dimethylamino-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine
Melking point: 128-129C
2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-amino-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine
Oil, Rf value: 0.23 (silica gel; eluant: ethyl
acetate/ethanol/ammonia = 90:10:1 by
volume)
2-n-butyl-6-amino-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine
Oil, Rf value: 0~15 (silica gel; eluant: ethyl
acetate/ethanol/ammonia = 90lO:1 by
volume)
Example C
2-n-Butyl-5-(cis-hexahydrophthalimido~-imidazor4,5-b]-
pyridine
Prepared by reacting 2-n-butyl-5-amino-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridine with cis-hexahydrophthalic acid anhydride
analogously to ~xample 4.
Yield: 63~ of theory,
Oil, Rf value: 0.50 (silica gel; eluant: methylene
, , j .
. : .
. ` ~ '
. ' , ~' .
. .
2048809
- 39 -
chloride/ ethanol = 9:1 by volume)
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-phthalimido imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine
Oil, Rf value: 0.77 tsilica ge:L; eluant: methylene
chloride/ethano:L = 19:1 by volume)
2-n-butyl-6-phthalimido-imidazot4,5-b]pyridine
Oil, Rf value: 0.68 (silica ge:L; eluant: ethyl
acetate/ethanol/ammonia = 90:10:1 by
volume)
2-n-propyl-5-(2,2-dimethylpropionylamino)-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridine
Oil, Rf value: 0.42 (silica gel; eluant: ethyl
acetate/petroleum ether = 1:1 by volume)
2-n-propyl-5-cyclohexylcarbonylamino-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridine
Oil, Rf value: 0.67 (silica gel; eluant: e~hyl
~cetate/petroleum ether = 1:1 by volume)
- . - .. ..
~ . . . .
..,
:: : ' :' '
- 20~8~09
~ 40 ~
Example 1
Tert.-butyl 4'~[(2-n-butyl-5-methylamino-3H imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methyl]b,iphenyl-2-carboxylate
, . _
1.8 g (3.5 mMol) of 2-[N-~-(2-tert.butoxycarbonyl-
phenyl)benzyl-N-pentanoylamino]-3-nitro-6-methylamino-
pyridine are dissolved in 200 ml of ethanol, mixed with
1.0 g of 10% palladium on activated charcoal and
hydrogenated for 2 hours at ambient temperature under
5 bars of hydrogen pressure. After the uptake of
hydrogen has ended the catalyst is filtered off and the
residue is concentrated by evaporation. The residue is
dissolved in ~0 ml of glacial acetic acid and heated for
30 minutes over a steam bath. Then the reaction mixture
is evaporated down, the residue i5 dissolved in 100 ml
of ethyl acetate and washed with saturated sodium
hydrogen carbonate solution and with saturated sodium
chloride solution. After drying over magnesium
sulphate, evaporation of the solvent and column
chromatography on silica gel ~particle size:
0.06-0.2 mm, eluant: petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 1:1
by volume) a colourless oil is obtained.
Yield: 1.4 g (86~ of th~ory),
Oil, hf value: 0.27 (silica gel; eluant: petroleum
ether/ethyl acetate = l:l by volume)
C29H34N4O2 (470.61)
Calculated: C 74.01 ~ 7.28 N 11.91
Found: 73.86 7.35 12.13
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
tert.butyl 4'-[(2-n-butyl-5-cyclohexylamino-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.45 (silica gel; eluant: petroleum
ether/ethyl acetate = 1:1 by volume)
tert.butyl 4l_~(2-n-butyl-5-n-butylamino-3H-imidazo-
.
, .
:` :
.
,~ .
: i .
,
20~8809
~1 --
[4,5-b]pyridin~3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.43 (silica gel; eluant: petroleum
ether/ethyl acetate = 1:1 by volume)
tert.butyl 4'-~(2-n-b~tyl-5-ethylamino-3H-imidazo-
t4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.3~ (silica gel; eluant: petroleum
ether/ethyl acetate = 1:1 by volume)
tert.butyl 4'-[(2-n-butyl-5-cyclohexylmethylamino-3H~
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3--yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.48 (silica gel; eluant: petroleum
ether/ethyl acetate = 1:1 by volume)
4'-[[2-n-propyl-5-(2-methylpropylamino)-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]-2-(1-triphenylmethyl-
tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl
Melting point: 132-135C
tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-butyl-5~(2,4-dimethoxybenzyl~amino-
3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]biphenyl-2-
carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.40 (si~ica gel; eluant: petroleum
ether/ethyl acetate - 1:1 by volume)
tert.butyl 4'-[(2-n-butyl-5-benzylamino-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b~pyridin-3-yl)~methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.36 (silica gel; eluant: petroleum
ether/ethyl acetate = 1:1 by volume)
tert.butyl 4'-[(2-n-butyl-5-methoxy-lH-imidazo[4,5-b~-
pyridin-l-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf valueo 0.44 (silica gel; eluant: ethylmethyl-
ketone/xylene = 1:2 by volume~
4'-C[2-n-butyl-5-(4-methyl-piperidino)-3H-imidaæo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-ylJmethyl]-2-(1-triphenylmethyl-
",, ~ . .
,
21~8~0g
- 42 -
tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl
Melting point: 147-149C
Example 2
Tert.butyl 4'-[(2-n-butyl-5-vaLeroylamino-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate (I)
and
Tert.butyl ~'-[(2-n-butyl-5-vaLeroylamino-lH-imidazo-
r4 / 5-b]pyridin-1-yl)methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate (II)
8.9 g (10.6 mMol) of 2-n-butyl-5-valeroylamino-3H~
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine are dissolved in 400 ml of
acetone, mixed with 7.3 g (53 mMol) of potassium
carbonate and with 5.5 g (15.9 ~ol) of tert.butyl 4'-
bromomethyl-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and refluxed for 6
hours with stirring. The reaction mixture is filtered
and the filtrate is evaporated to dryness. The residue
is purified over a silica gel column (particle size:
0.063-0.2 mm), using a mixture of petroleum ether and
ethyl acetate in the ratio 3:1 by volume as eluant. The
uniform fractions are evaporated to dryness and
triturated with diethylether. The solids thus
crystallised are washed with ether and dried.
I: Yield: 4.2 g ~73% of theory),
Melting point: 102-104C
C33H39N403 (539.70)
Calculated: C 73.20 H 7.46 N 10.36
Found: 73.18 7.7210.19
II: Yield: 1.1 g (20% of theory),
Melting point: 107-108C
C33H39N403 (539.70)
Calculated: C 73O20 H 7.46 N 10.36
Found: 73.14 7.4410.38
The ~ollowing compounds are obtained analogously:
~ ~ .
. . .
; ~ .
.
~88~9
tart.b~tyl 4'-C(2-n~propyl-5-butanoylamino 3~1-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridirl-3-yl)methyl~biphenyl-2--carboxylate
Melting point: 157-158C
tert.butyl 4'-[(2-n-propyl-5 butanoylamino-lH-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Amorphous, Rf value: 0.38 (silica gel, eluant: ethyl
acetate)
tert.butyl 4'-[(2-n-propyl-5-butanoylamino-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-4-bromo-2-
carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.40 (silica gel; eluant: methylene
chloride/ethanol = ~9:1 by volume)
tert.butyl ~'-[(2-n-butyl-5-dimethylamino-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.37 ~aluminium oxide; eluant: ethyl
acetate/petroleum ether = 1:1 by volume)
tert.butyl 4'-[(2-n-butyl-5-bromo-3H imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.55 (silica gel; eluant: methylethyl-
ketone/xylene = 1:2 by volume)
tert.butyl 4'-[(2-n-butyl-5-bromo-lH-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridin-l-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.20 (silica gel; eluant: methylethyl-
ketone/xylene = 1:2 by volume)
:
tert.butyl 4'-[(2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-phthalimido-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.52 (silica gel; eluant: methylethyl-
ketone/xylene = 1:4 by volume)
tert.butyl ~'-[(2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-phthalimido-lH-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
- - , . .
.
: :
,. ~ ,
20~0g
Oil, Rf value: 0.18 (silica gel; eluant: methylethyl-
ketone/xylene = ~:1 by volume)
tert.butyl ~'-[(2-n-butyl-6-phthalimido-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.62 (silica gel; eluant: methylethyl-
ketone/xylene = 1:1 hy volume)
terk.butyl 4'-[(2-n-butyl-6-phthalimido-lH-imidazo-
t4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl)-methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.43 (silica ge:L; eluant: methyl~thyl-
ketone/xylene = 1:1 by volume)
tert.butyl 4'-~(2-n-buty]-6-hexahydrophthalimido-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b~pyridin-3-yl)-methyl]biphenyl-2
carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.58 (silica gel; eluant: methylethyl-
ketone/xylene = 1:1 by volume)
tert.butyl 4'-[(2-n-butyl-6-hexahydrophthalimido-lH-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl)-methylJbiphenyl-2-
carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.31 (silica gel; eluant: methylethyl-
ketone/xylene = 1:1 by volume)
4'-[[2-n-butyl-5-(cis-hexahydrophthalimido)-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-2-(1-triphenylmethyl-
tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl
Oil, Rf value: 0.45 (silica gel; eluant: ethyl acetate)
tert.butyl ~'-[(2-benzylamino-8-n-butyl-9H-purin-9-yl)-
methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.45 (silica gel; eluant: ethyl acetate)
mathyl 4'-[(2-n-butylamino-8-n-butyl-9H-purin-9-
yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Melting point: 125-126C
~,,
'
....................................... . .
8 ~ 9
- ~5 -
methyl 4'-C(2-cyclohexylamino-8-n-butyl 9H-purin-9-yl)-
methyl]biphenyl~2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.52 (silica gel; eluant: methylene
chloride/ethanol = 95:5 by volume)
methyl 4'-t(2-ethoxy-8 n-butyl-9H-purin-9-yl)methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.55 (silica gel; eluant: methylene
chloride/ethanol - 95:5 by volume)
methyl 4'-[(2-methoxy-8-n-butyl-9H-purin-9-yl)methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylake
Oil, Rf value: 0.50 (silica gel; eluant: methylene
chloride/ethanol = 95:5 by volume)
4'-[[2-n-propyl-5-(2,2-dimethylpropionylamino)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl~-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)-
biphenyl
Melting point: 177-178C
4'-[(2-n-propyl-5-cyclohexylcarbonylamino-3H-imidazo-
~4,5-b~pyridin-3-yl)methyl]-2-tlH-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl
Melting point: 183-184C
Example 3
Tert.butyl 4'-t(2-n-butyl-5-amino-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
3.4 g (6.3 mMol) of ~ert.butyl 4'-[(2-n-butyl-5-
valeroylamino-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylate are dissolved in 75 ml of
ethanol, mixed with 35 ml o~ 2N sodium hydroxide
solution and heated to 80C for 8 hours with stirring.
The reaction mixture is concentrated by evaporation,
taken up in ethyl acetate and extracted with water. The
aqueous phase is re~extracted twice with about 100 ml of
ethyl acetate. The organic phases are combined, washed
, . . . ~ . . ~ : ,
.: . .
, ~, , , : : -, : :
.
-', ~ ': ' . ' '' ;. ' '~
%~8~9
- ~6 -
with saturated saline solution and dried over maynesium
sulphate. After evaporation of the solvent the residue
is crystallised by triturating with pet~oleum ether.
Yield: 2.1 g (73% of theory),
Melting point: 112-124C
C2~H32N42 (456.59)
Calculated: C 73. 66 H 7.07 N 12.21
Found: 73.72 7.20 12.12
The following compounds are obtained analoyously:
tert.butyl 4'-[(2-n-propyl-5-amino-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.50 (silica gel; eluant: ethyl acetate)
tert.butyl 4'-[(2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-amino-3H-imidazo-
~4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl~biphenyl-2 carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.56 (silica gel; eluant: ethyl
acetate/ethanol/ammonia = 90:10:1 by
volume)
tert.butyl 4'-[(2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-amino-lH-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.48 (silica gel; eluant: ethyl
acetate/ethanol/ammonia = 90:10:1 by
volume)
Example 4
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-(N-acetyl-cyclohexylamino~-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
. ~
0.3 g (0.62 mMol) of 4'-[~2-n-butyl-5-cyclohexylamino-
3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyxidin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid are dissolved in 3.0 g (38 mMol) of
acetyl chloride and refluxed for 2 hours. The reaction
mixture is evaporated down, the residue is mixed with
water and neutralised with aqueous ammonia solution.
The precipitate formed after acidification with glacial
acetic acid is suction filtered, washed with water and
. . : . . ,
'
.
" ''' . ' = ' ,i . ' . ' . ' . .
, ~ ' ' ~ ',' '
~0~8809
- 47 -
dried.
Yield: 0.22 g (68% of theory),
Melting point: 121-123C
C3zH36N4O3 (524-67)
Calculated: c 73.26 H 6.92 N 10.68
Found: 72.43 6.93 10.96
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
tert. butyl 4'-[(2 n-propyl-5-]benzylcarbonylamino-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.36 (silica gel; eluant: petroleum
ether/ethyl acetate = 1:1 by volume)
tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-butyl-5-(cis-hexahydrophthalimido)-
3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl~methyl]biphenyl-2-
carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.66 (silica gel; eluant: ethyl acetate)
tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-butyl-5-tN-acetyl-n-butylamino)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.21 (silica gel; eluant: petr~leum
ether/ethyl acetate = 1 1 by volume)
tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-butyl-5 tN-ethoxycarbonyl
ethylamino)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.45 (silica gel; eluant: petroleum
ether/ethyl acetate = 1:1 by volume)
tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-butyl-5-~N-cyclohexylcarbonyl-
ethylamino~-3H~imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.34 ~silica gel; eluant: petroleum
ether/ethyl acetate = 1:1 by volume)
tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-butyl-5 N-[(2-methyl-propionyl)-n-
` ~ , : ' ` :
: . , ;. ::
' , .
~0~8~9
- 48 -
butylamino]-3H-imidaæo[4,5-b~pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.48 (silica gel; eluant: petroleum
ether/ethyl acetate = 1:1 by volume)
tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-butyl-5~(N-ethoxycarbonyl-n-
butylamino)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-
biphenyl-2~carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.53 (silica gel; eluant: petroleum
ether/ethyl acetate - 1:1 by volume)
tert.butyl 4'-[(2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-dimethylamino-
carbonylamino-lH-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl)methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Amorphous, Rf value: 0.55 (silica gel; eluant: ethyl
acetate/ethanol/ammonia = 80:20:2
by volume)
tert.butyl 4'-[(2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-
dimethylaminocarbonylamino-3H-imidazot4,5-b]pyridin-3-
yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Amorphous, Rf value: 0.50 (silica gel; eluant: ethyl
acetate/ethanol/ammonia = 90:10:1
by volume)
tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-tN-ethyl-
cyclohexylcarbonylamino)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin 3-
yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, R~ value: 0.46 (silica gel; eluant: methylene
chloride/ethanol = 19:1 by volume)
tert.butyl 4l-[[2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-(5-chloropentanoyl-
amino)-lH-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl]methyl]biphenyl 2-
carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.63 (silica gel; eluant: methylene
chloride/ethanol = 9:1 by volume)
tert.butyl 4'-[~2-n~butyl-5-methyl-6-(N-acetyl-n-
butylamino)-3H-imidazo[4,5~b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-
., , ;
.
.': ; '
,~ , . .
~8~09
- 49 -
biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.48 (silica yel; eluant: methyl
ketone/ethanol = 1:2 by volume)
tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-butyl-5 (4-chlorophenylsulphonyl-
amino)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-
carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.39 (silica gel; eluant: methylene
chloride/ethanol = 9:1 by volume)
Exam~e 5
4'-~[2-n-Butyl-5-(N-acetyl-cyclohexylmethylamino~-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic
acid
.. _ ~ .. . . . . _ .. .
Prepared analogously to Example 4 ~rom 4'-[(2-n-butyl-5-
cyclohexylmethylamino-3~-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)-
methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid and acetylchloride.
Yield: 93% of theory,
Melting point: 180-185C
C33H38N403 (538.20)
Calculated: C 73.58 H 7 .11N 10 . 40
Found: 73.56 7.37 10.46
~ml2~
4'-t(2-n-Butyl-5-propionylamino-3~-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2~carboxylic acid
. .. ..... _ _
Prepared analogously to Example 4 from 4'-[(2-n-butyl-5-
amino-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin 3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and propionic acid anhydride.
Yield: 66% o~ theory,
Melting point: 278-281C
C27H28N4o3 ~456.55)
Calculated:C 71.03H 6.18 N 12.27
Found:70.86 6.23 12.40
, :
.. . , :
.
: ' - ~ ..
20~g809
- 50 -
Example 7
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-(2-mekhylpropionylamino)-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
.
Prepared analogously to Example 4 from 4'-t(2-n-butyl-5-
amino-3H imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid and isobutyric acid chloride.
Yield: 49~ of theory,
Meltiny point: 250C
c28H30Nh3 (~30.58)
Calculated: C 71.47 H 6.43 N 11.91
F'ound: 71.26 6.31 11.66
Example 8
Tert.butyl 4'-[~2-n-butyl-5-(N-(3-chloropropylamino-
carbonyl)-amino)-3H-imidazoC4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylate
1.3 g (2.9 mMol) of tert.butyl 4'-t(2-n-butyl-5-amino-
3H-imidazo~4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-
carboxylate are dissolved in 10 ml of dimethylformamide,
mixed with 1.4 g (12 mMol) of 3-chloropropylisocyanate
and stirred for 40 hours at ambient temperature. After
the addition of 200 ml of ice water the mixture is
extracted twice with 100 ml of ethyl acetate. After
drying over magnesium sulphate the solvent is evaporated
and the residue is triturated with ether. The
precipitate formed is suction filtered and dried.
Yield: 1.5 g (90% of theory),
Melting point: 207-209C
C32H38ClN503 (646-17)
Calculated: C 66.71 H 6.65 N 12.16
Found: 66.71 6.72 12.47
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
.
: ' ` ~'
20~8~9
- 51 -
tert.butyl 4'-[~2-n-propyl-5- (N- ( 3 -chloropropylamino-
carbonyl)-amino) 3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carbo~ylate
Oil, Rf value: 0~20 (silica gel; eluant: ethyl acetate)
tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-butyl-5-(N-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl-
ethylamino)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.30 (silica gel; eluant: ethyl
acetate~petroleum ether = 1:1 by volume)
tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-butyl-5-(N-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl-
n-butylamino)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.55 (silica gel; eluant: ethyl
acetate/petroleum ether = 1:2 by volume)
tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-[N-(3-chloro-
propylaminocarbonyl)amino]-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-
yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.58 (silica gel; eluant: ethyl
acetate/ethanol/ammonia = 90:10:1 by
volume)
4'-[[2-n-propyl-6-(N-benzylaminocarbonyl-isobutylamino)-
3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-2-(l triphenyl-
methyl-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl
Oil, Rf value: 0.67 (silica gel; eluant: methylene
chloride/ethanol = 19:1 by volume)
4'~[[2-n-propyl-5-(N-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl-isobutyl-
amino)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-2-(1-
triphenylmethyl-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl
Oil, Rf value: 0.62 (silica gel; eluant: methylene
chloride/ethanol = 19:1 by volume)
,
.
0 9
- 52 -
Example 9
4'-[(2 n-Butyl-5-cyclohexylaminocarbonylamino-3~-
imidazo[4~5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic
acid
Prepared analogously to Example 8 fr~m 4'-[(2-n-butyl-5-
amino-3H-imida~o[4,5-b]pyridin-3~yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid and cyclohexylisocyanate.
Yield: 46% of theory,
Melting point: 287-291C
C31H3sNsO3 (525.66)
Calculated: C 70.83 H 6.71 N 13.32
Found: 69.01 6.66 13.18
Example 10
Tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-butyl-5-(3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(1H)-
pyrimidinon-1-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin 3-yl]methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylate
. ~
0.26 g (5.3 mMol) of sodium hydride are dissolved in
20 ml of tert.butanol. After 5 minutes at ambient
temperature, 0.58 g (1.0 mMol) of tert.-butyl 4'-[r2-n-
butyl-5-(N-(3-chloropropylaminocarbonyl)-amino)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
are added in batches~ The mixture is stirred for 10
hours at ambient temperature~ By adding 2N hydrochloric
acid the pH is adjusted to 5 and the tert~-butanol is
evaporated off in vacuo. The residue is stirred with
100 ml of ethyl acetate and 100 ml of water, the organic
phase is separated off and the aqueous phase is
extracted twice with 50 ml of ethyl acetate. The
combined organic phases are washed with saturated saline
solution and dried over magnesium sulphate. After
evaporation of the solvent the residue is triturated
with ether, the precipitate formed is suction filtered
and dried.
, ~ ~
: . ~ ' " '
:
:.~
~0488~9
:. - 53 -
Yield: 0.~ g (7~6 of theory),
Rf value: 0.33 (s.ilica gel; eluant: ethyl
acetate/ethanol = 9:1 by volume)
C32H37Ns3 (539-~8)
Calculated: c 71.22 H 6. 91 N 12.98
Found: 70.99 6 . 98 12 . 81
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
tert.butyl ~'-[[2-n-propyl-5-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-
pyrimidinon-l-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Melting point: 175C
;
tert.butyl 4'-~[2-n~butyl-5-methyl 6-(3 t 4 ~ 5, 6-
tetrahydro-2(1H)-pyrimidinon-1-yl)-3H-imidazo[~,5-b]-
pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
~elting point: 200-202C
tert.hutyl 4'-[[2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-(2-oxo-piperidin-1-
yl)-lH-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-
carboxylate
Rf value: 0O49 (silica gel; eluant: methylene chloride/
ethanol = 9:1 by volume)
tert.butyl 4'-~2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-(n-butanesultam-1-
yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-
carboxylate
Rf value: O.S0 (silica gel; eluant: methylene chloride/
ethanol = 19:1 by volume)
tert.butyl 4'-[[2~n-butyl-5-methyl-6 (2-oxo-piperidin-1-
yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl3biphenyl-2-
carboxylate
Rf value: 0.60 (silica gel; eluant: methylene chloride/
ethanol = 19:1 by volume)
' ~
~ , , ,
.
'
20~8809
- 54 -
Example 11
Tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-butyl-5~(3-benzyl-3,4,5,6-
tetrahydro-2(1H)-pyrimidin~n-1-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
0.4 g (0.74 mMol) of tert.butyl 4'-[r2-n-butyl-5-(N-(3-
chloropropylaminocarbonyl)-amino)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate are suspended
in 20 ml of dimethylformamide and mixed with 0.04 g
(0.85 mMol) of sodium hydride. The mixture is stirred
for 10 minutes at 60C, 0.5 ml (4.25 mMol) o~
benzylbromide are added and the resulting mixture is
stirred for 3 hours at ambient temperature. The
reaction mixture i~ poured onto ice and extracted twice
with 100 ml of ethyl acetate. The combined organic
phases are washed with saturated saline solution and
~ried over magnesium sulphate. A~ter the solvent has
been evaporated, a colourless oil is obtained.
Yield: 0.35 g (75% of theory),
Rf value: 0.41 (silica gel; eluant: methylene
chloride/ethyl acetate = 1:1 by volume)
Mass ispectrum: M~ = 629
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
tert.butyl ~'-[[2-n-butyl-5-(3-methyl-3,4,5,6-
tetrahydro-2(1H)-pyrimidinon-1-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.41 (silica gel; eluant: ethyl
acetate/ethanol = 9:1 by volume)
tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-(3-benzyl-3,4,5,6-
tetrahydro-2(1H)-pyrimidinon-1-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Oil, Rf value: 0.44 (silica gel; eluanto methylene
chloride/ethanol = 19:1 by volume)
. :: .
~;
': ~ ' ' :
.
2~488(19
- 55 -
Example 12
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-(3-benzyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-
pyrimidinon-l-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-
oiphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
0.35 g (0.55 mMol) of tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-butyl-5-~3-
benzyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2~lH)-pyrimidinon-l-yl)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl~methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylate are dissolved in 10 ml of methylene chloride
and mixed with 5 ml of trifluoroacetic acid. The
mixture is stirred for 65 hours at ambient temperature.
The solvent is evaporated off, the residue is taken up
in ice water and acidified with ylacial acetic acid.
The precipitate thus formed is filtered off, washed with
water and dried at 60C.
Yield: 0.26 g (82% of theory),
Melting point: 168-170C
C35H3sNsO3 (573-70)
Calculated: C 73.28 H 6.15 N 12.21
Found: 73.37 6.51 12.12
Example 13
4'-[[2-n-Butyl 5-(3-methyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-
pyrimidinon-1-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
. _ . _
Prepared analogously tn Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
E ~ 2-n-butyl-5-(3-methyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-
pyrimidinon-l-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b~pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 64% of theory,
Melting point: 249-252C
Cz9H31NsO3 (497.60)
Calculated: C 70.00 H 6.28 N 14.00
Found: 69.85 6.40 13.89
.
':
20~8809
- 56 -
Example 14
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-(3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-pyrimidinon-
l-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Exampl~e 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-butyl-5-(3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-pyrimidinon-1-
yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 80% of theory,
Melting point: 300-302C
C28H29NsO3 (483.58)
Calculated: C 68.27 H 6.14 N 14.22
Found: 68.47 6.11 14.28
,Example 15
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-5-(3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(1H)-pyrimidinon-
1-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b~pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biph~nyl-2-
carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-5-(3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-pyrimidinon-l-
yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 92% of theory,
Melting point: 265-268~C
C27H27N503 (46g.55~
Calculated: C 69.07 H 5.80 N 14092
Found: 68.87 5.78 15.00
Example 16
4'-[(2-n-Butyl-5-cyclohexylmethylamino-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl~2-carboxylic acid
.
Prepared analogously to Example 12 ~rom tert.butyl 4'-
.. . . . . . ..
. ~ : . ~ . ...
. ;~
. ~ .
... .
:: , ' :
.~ .
,
20~809
- 57 -
t(2-n-butyl-5-cyclohexylmethylamino-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]
pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and
trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 23.6~ of theory,
Melting point: 202-205c
C31H36N4O2 (496.66)
Calculated: C 74.97 H 7.31N 11.2
Found: 74.~2 7.~ 10.98
Example 17
4'-[(2-n-Butyl-5-ethylamino-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-
yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
.... _ . . _
Prepared analogously ko Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[(2-n-butyl~5-ethylamino-3H-imidazot4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)-
methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 76% of theory,
Melting point: 245-247C
C26H2~N4O2 (428.54)
Calculated: C 72.87 H 6.59N 13.09
Found: 72.72 6.65 12.84
Example 18
4'-[(2-n-Butyl-5-n-butylamino-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-
3-yl)~methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
. . _ .
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[(2-n-butyl-S-n-butylamino-3H-imidazot4,5-b]pyridin-3-
yl)-methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic
acid.
Yield: 67% of theory,
Melting point: 217-219C
C2~H32N4O2 (456.59)
Calculated:C 73.66H 7.06 N 12.27
Found:73.46 7.03 12.17
- `
`" '; ;
: '
204880~
- 58 -
_ample 19
4'~~(2-n-Butyl-5-cyclohexylamino-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl 2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Examp:le 12 from tertubutyl 4'-
; t(2-n-butyl-5-cyclohexylamino--3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-
3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic
acid.
Yield: 67% of theory,
Melting point: 221-224C
C30H34N402 (482.63)
Calculated: C 73.29 H 7.18 N 11.40
Found: 73.51 6.95 11.25
Example 20
~'-[(2~n-Butyl-5-methylamino-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-
yl)-methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[(2-n-butyl-5-methylamino 3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-
yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic
acid.
Yield: 61% of theory,
Melting point: 274-277C
C2sH26N402 (414.51)
Calculated: C 72.44 H 6.32 N 13.52
Found: 72.26 ~.26 13.30
Example 21
4'-[(2-n-Butyl-5-amino-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)-
methyl]biphenyl-~-carboxylic acid
...... _
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[(2-n-butyl-5-amino~3H-imidazo[4,5-b3pyridin-3-
yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic
. . ..
: . , . ~ , ,
.. ..
.
~: . ,
, . , ~ . ~ ;
'
20~809
59 -
acid.
Yield: 35% of theory,
Melting point: 238-240C
C24H24N4Oz (400.48)
Calculated: C 71.98 H 6.04 N 13.99
Found: 71.90 5.96 13.86
Example 22
4'-t(2-n-Butyl-5-dimethylamino-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-
3-yl) methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[(2-n-butyl~5-dimethylamino-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-
yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and tri~luoroacetic
acid.
Yield: 81~ of theory,
Melting point: 213-215C
C26H28N4O2 (428-54)
Calculated: C 72.87 H 6.57 N 13.08
Found: 72.~2 6.7312.90
Example 23
4'-[(2-n-Butyl-5-benzylamino-3H-imidazo~4,5-b]pyridin-3-
yl)-methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
.. _ _ . . . . _
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
E ( 2-n-butyl-5-benzylamino-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-
yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic
acid.
Yield: 67% of theory,
Melting point: 224-225C
C31H30N4Oz (490.61)
Calculated: C 75.89 H 6.16 N 11.42
Found: 75.70 6.24 11.37
': ' " , . : : ,
, . .
:
2~8809
-- 60 --
Example 24
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-(2,4-dimethoxybenzylamino)-31~~
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic
acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-butyl-5-(2,4-dimethoxybenzylamino)-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and
trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 73% of theory,
Melting point: 223-226C
C33H34N404 (490.61)
Calculated: C 71.98 H 6.22 N 10.18
Found: 71.70 6.21 10.16
Example 25
4'-~2-n-Butyl-5-(N-isobutyryl-n-butylamino)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl~-methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic
acid
r ~
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-butyl-5-(N-isobutyryl-n-butylamino-3H- midazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl3methyl]biphenyl-2 carboxyIate and
trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 33% of theory;
Melting point- 186-189C
C32H38N4o3 (490-61)
Calculated: C 72.98 EI 7.27 N 10.64
Found: 73.09 7.~5 10.53
. ; ....... .
,
, .
: ~
' .
2~8809
- 61 -
Example 26
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-(N-acetyl-n-butylamino)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic
acid
_ _ _
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-butyl-5-(N-acetyl-n-butylamino)-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and
trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 36% of theory,
Melting point: 173-175~C
C30H34N~,03 (498-63)
Calculated: C 72.26 H 6.87 N 11.24
Found: 72.39 7.00 11.07
Example 27
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-(N-cyclohexylcarbonyl-ethylamino)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic
acid
.
Prepared analogously to Example lZ from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-butyl-5-(N-cyclohexylcarbonyl-ethylamino)-3H-
imidazo-[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 95~ of theory,
Melting point: 203-205C
C33H3aN4O3 (538.70)
Calculated: C 73.58 H 7.11 N 10.40
Found: 73.66 7.19 10.35
Example 28
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-(N-acetyl-ethylamino)-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
. . . _ _ .
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
. ~ :
. .
- : ,, . ~ .
20~8go9
- 62 -
[t2~n--butyl-5-(N-acetyl-ethylamino)~3H-imidazo-
[~,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and
trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 80% of theory,
Melting point: 89-93C
C33H38N4O3 (470.58)
Calculated: C 70.99 H 6.47 N 11.79
Found: ~0.79 6.47 11.52
Example 29
4'-[(2-n-Butyl-5-valeroylamino~3H-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridin-3-yl)-methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
_ _ _ _
Prepared analogously to Example 12 ~rom tert.butyl 4'-
[(2-n-butyl-5-valeroylamino-3H-imidazo-[4,5-b]pyridin-3-
yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic
acid.
Yield: 56% of theory,
Melting point: 240-242C
C33H38N4O3 (484.60)
Calculated: C 71.88 H 6.66 N 11.56
Found: 71.61 6.72 11.47
Example 30
4'-[(2-n-Propyl-5-butanoylamino-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[(2-n-propyl-5-butanoylamino-3H-imidazo-[4,5-b]pyridin-
3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic
acid.
Yield: 68% of theory,
Melting point: 254-255~C
Cz7H2sN43 (456-55)
Calculated: C 71.03 H 6.18 N 12.27
Found: 70.98 6.25 12.36
;, : . . .. ,:
, ~ ~ : ,, . , ; :
- , . .
.
.
2048809
- 63
Example 31
4'-[(2-n-Propyl-5-butanoylamino-3H-imidazo[4,5 b]-
pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-4-bromo-2-carboxylic acid
.... . .
Prepared analogous]y to Exampl,e 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[(2-n-propyl-5-butanoylamino-3H-imidazo-[4,5-b]pyridin-
3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-4-bromo-2-carboxylate and
trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 83% of theory,
Melting point: 244-245C
c27H27N4O3Br (535-54)
Calculated: C 60.56 H 5.08N 10.46 Br 14.92
Found: 60.42 5.07 10.41 14.82
Example 32
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-5-(2-methyl-valeroylamino)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]-pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic
acid
.
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n~propyl-5-(2-methyl-valeroylamino)-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and
trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 97% of theory,
Melting point: 244-245C
Cz9H32N4O3 (484.61~
Cal~ulated: C 71.88 H 6.66 N 11.56
Found: 71.77 6.79 11.51
Example 33
4'~ E ( 2-n-Propyl-5-benzylcarbonylamino-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
~(2-n-propyl-5 benzylcarbonylamino-3H-imidazo-
. .
.
,
20~8~309
- 6~ -
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and
trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 93% of theory,
Meltinq point: 252-254C
C31HzsN403 (504-60)
Calculated: C 73.79 H 5.59 N ll.lo
Found: 73.85 5.78 10.93
Example 34
4'-[(2-n-Propyl-5-butanoylamino-lH-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridin-1-yl)methyl~biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
_ _ .. ..
Prepared analogously to Example 12 ~rom tert.butyl 4'-
~(2-n-propyl-5-butanoylamino-lH-imidazo-[4,5-b]pyridin-
l-yl)methyl~biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic
acid.
Yield: 88% o~ theory,
Melting point: 120C
C27H28N403 (456.55)
Calculated: C 70.34H 6.23 N 12.15
Found: 70.14 6.24 12.34
Example 35
4'-[t2-n-Butyl-5-(N-ethoxycarbonyl-ethylamino)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic
acid
Prepared analogously to ~xample 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-butyl-5-(N-ethoxycarbonyl-ethylamino~-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and
trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 95% of theory,
Melting point: 182-185C
C29H32N404 (500.61)
Calculated: C 69.58 H 6~44 N 11.19
Found: 69.72 6.57 11.13
: .: , :. .
2~88~9
- 65 --
Exa~e 36
4'-[[~-n-Butyl~5-(N-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl-ethylamino)-
3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[(2-n-butyl-5-(N-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl-ethylamino)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 95% of theory,
Melting point: 182-185C
C33H39NsO3 (500~61)
Calculated: C 71.58 H 7.10 N 12.65
Found: 71.77 7.22 12.59
Example 37
4~-[[2-n-Butyl-5-(N-ethoxycarbonyl-n-butylamino)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic
acid
.
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-butyl-5-(N-ethoxycarbonyl-n-butylamino)-3H-
imidazo[4,5~b~pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 37% of theory,
Melting point: 154-156C
C31H36N4O4 (528.66)
Calculated: C 70.43 H 6.86 N 10.60
Found:70.68 7.10 10.50
;:
: . . .
.. ~
2~8~09
- 66 -
Example 3~
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-(N-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl-n-bu-tyl-
amino)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-butyl-5-(N-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl-n-butylamino)-
3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-Z-
carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 89% of theory,
Melting point: 195~198C
C35H43NsO3 (581.47)
Calculated: C 72.26 ~ 7.45 N 12.04
Found: 72.29 7.66 11.81
Example 39
4l-[[2-n-Butyl-5-(n-butylaminocarbonylamino)-lH-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic
acid
_ _
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-butyl--5-(n-butylaminocarbonylamino)-lH--imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and
trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 83% of theory,
Melting point: 290-295C
C2sH33NsO3 (499-62)
Calculated: C 69.72 H 6.66 N 14.02
Found: 69.62 6.76 13.98
.
. ,
-~, . '; , ,
~ . .
~: .
,
2~8809
- 67
Example 40
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-(cis hexahydrophthalimido)-3H-
imidazo[4,5 b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic
acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-butyl-5-(cis-hexahydrophthalimido)-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl~methyl~biphenyl-2-carboxylate and
trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 84~ of theory,
Melting point: 113-115C
C32H32N4o4 (536.6~)
Calculated: C 62.76 H 5.11 N 8.61
Found: 62.79 5.21 8.~8
Example 41
4'~[(2-n-Butyl-5~methoxy-lH-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-
yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid-trifluoroacetate-
hydra~e
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4l_
[r2-n-butyl-5-methoxy-lH-imidazo[4,S-b~pyridin-1-
yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic
acid.
Yield: 80~ of theory,
Melting point: 126-128C
C2sH2sN33 x CF3COOH x H20 (547-54)
Calculated: C 59.23 H 5.15 N 7.68
Found: 59.46 4.99 7.63
Example 42
4'-[(2-n-Butyl-6-bromo-lH-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-
yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
.
Prepared analoyously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[(2-n-butyl-6-bromo~lH-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-
:
20~8~09
~ 68 ~
yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic
acid.
Yield: 79% of theory,
Meltinq point: 239-240C
~24HzzBrN30z (464-36)
Calculated: C 62.08 H 4.77N 9.05Br 17.21
Found: 61.83 4.71 8.92 17.43
Example 43
4'-[(2-n-Butyl-6-bromo-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-
yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
. _ _ . . . .
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[(2-n-butyl-6-bromo-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-
yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic
acid.
Yield: 85% of theory,
Melting point: 221-223C
Cz4HzzBrN30z (464.36)
Calculated: C 62.08 H 4.77N 9.05Br 17.21
Found: 61.95 4.84 8.96 17.38
Example 44
4'-[~2-n-Butyl-5-methyl-6-phthalimido-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
_ _ ... .
Prepared analogously to Example 1? from tert.butyl 4'-
[t2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-phthalimido-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and
trifluoroacetic acid.
Yi~ld: 75% of theory,
Melting point: 336-340C
C33H28N404 (544.62)
Calculated: C 72.78 H 5.18 N 10.29
Found: 72.59 5.1810.26
,.. . .
:" . .,
~ , .. . . ..
,~ . : . . ,
.
.
". ,
~0~8~09
- 69 -
Example_45
4'-[(2-n-Butyl-5-methyl-6-phthalimido-lH-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Exampl,e 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[(2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-phthali~ido-lH-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and
trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 63% of theory,
Melting point: 301-303C
C33H28N404 (544.62)
Calculated: C 72.78 H 5.18 N 10.29
Found: 72.71 5.25 10.18
Example 46
4'-[(8-n-Butyl-2-methoxy-9H-purin-9-yl)-methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
.... . _
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
~(8-n-butyl-2-methoxy-9H-purin-9-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 73% of theory,
Melting point: 146-148~C
C24H24N4o3 (416-48)
Calculated: C 69.21 H 5.81 N 13.45
Found: 68.97 5.84 13.17
Example 47
4'-[(8-n-Butyl-2-methoxy-7H-purin-7-yl)-methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
_ _ _
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
~(8-n~butyl-2-methoxy-7H-purin-7-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 73~ of theory,
"' ~ , . ' ~
.
2048~09
- 70 -
Melting point: 146-1~8C
Cz4H24N403 (416.43)
Calculated: C 69.21 H 5.81 N 13.45
Found: 69.07 5.94 13.27
Example 48
4'-[(2-Benzylamino-8-n-butyl-9H-purin-9-yl)-methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
.... ... _ .
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
r ( 2-benzylamino-8-n-butyl-9H-purin-9-yl)methyl]biphenyl-
2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 13% of theory,
Melting point: 232-234C
C30H29NsO2 (491.60)
Calculated: C 73.20 H 5.95 N 14.25
Found: 73.16 6.05 14.44
Example 49
4'-[(2-n-~utyl-5-methyl-6-(N~acetyl n-butylamino)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methyl3biphenyl-2-carboxylic
acid
_ _
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[(2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-(N-acetyl-n-butylamino)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yi~ld: 56% of theory,
Melting point: 144-146C
C3lH36N403 (512-65)
Calculated, C 72.63 H 7.08 N 10.93
Found:72.39 7.15 ~ 10.79
,
.
. .
20~8809
- 71
Example S0
4'-[(2-n-Butyl-5-methyl 6-amino-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridin-3-yl)-methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 ~rom tert.butyl 4'-
~(2~n-butyl-s-methyl-6-amino-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-
yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic
acid.
Yield: 80% of theory,
Melting point: 168-170C
C26Hz6N402 (414.57)
Calculated: C 72.44 H 6.32 N 13.52
Found: 72.40 6.5013.32
Example 51
4~-[(2-n-Butyl-6-hexahydrophthalimido 3H-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridin-3-yl)-methyl]biphenyl-Z-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[(2-n-butyl-6-hexahydrophthalimido-3H-imidazo-
[4,S-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and
trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 90% of theory,
Melting point: 179-181C
C32H32N4O4 ~536.64)
Calculated: C 71.62 H 6.01 N 10.44
Found: 71.87 6.0010.36
Example 52
4'-[(2-n-Butyl-5-methyl-6-butyrylamino-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl~-methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[(2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-butyrylamino-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b3pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and
., .. ~ , , - . .
, . ~ .~ .
. . . .
,
,.
20~09
72 -
tri~luoroacetic acid.
Example 53
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-methyl-6-(2~oxo piperidin-l-yl)-lH-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic
i acid-trifluoroacetate
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-(2-oxo-piperidin-1-yl)-lH-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 91% of theory,
Melting point: 171-173C
C30H32N403 x CF3COOH t610.65)
Calculated: C 62.94 H 5.45 N 9.18
Found: 62.74 5.49 8.98
.:
Example 54
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-methyl-6-(2-methyl-propionylamino)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic
acid
_
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[~2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-(2-methyl-propionylamino)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl~biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and tri~luoroacetic acid.
Example 55
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-methyl-6-(N-cyclohexylcarbonyl-
ethylamino)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
-
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert~butyl 4'-
E [2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-(N-cyclohexylcarbonyl-
ethylamino)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b~pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]-
:
" . . . . ~ .
"
. :: : :,
,; , . , . , , ,~
: . ; , .
.
20488~9
- 73 -
biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 78% of theory,
Melting point: 164-166C
C34H40N403 (552.72)
Calculated: C 73.88 H 7.29N 10.14
Found: 73.58 7.29 10.04
Example 56
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-methyl-6-(cis-hexahydrophthalimido)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic
acid
. . _ . . .
Prepared analogou~ly to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-(cis-hexahydrophthalimldo)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 81% of theory,
Melting point: 261-263C
C33H34N404 (550.67)
Calculated: C 71.98 H 6.22N 10.18
Found: ~71.78 6.25 9.95
Example 57
4'-~(2-n-Butyl-6-(cis-hexahydrophthalimido)-lH-imidazo-
~4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl~methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid-
dihydrate
Prepared analogously to ~xample 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[(2-n-butyl-6-(cis-hexahydrophthalimido)-lH-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and
trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 70% of theory,
Melting point: 203-205~C
C32H32N404 x 2 H2O (572.68)
Calculated:C 67.11H 6.33 N 9.78
Fou~d:67.25 6.30 9.78
.
, ~ ~
,
:,
. .
,
20~8~09
- 7~ -
Example 58
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-methyl-6-(3-benzyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-
2(1H)~pyrimidinon-1-yl) -3H--imidazo[4,5-b~pyridin-3-yl]-
methyl]biphenyl-2-ciarboxylic acid-tri~luoroacetate
. . ~
Prepared analogously to Examp]e 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-(3-benzyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-
2(lH)-pyrimidinon-1-yl)-3~I-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-
methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 77% of theory,
Melting point: 168-170C
C36H37Ns3 x CF3COOH (701.76)
Calculated: C 65.04 H 5.46 N 9.98
Found: 64.98 5.67 9.91
Exampl,e 59
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-[3-(4-methoxy)benzyl-3,4,5,6-
tetrahydro-2(1H)-pyrimidinon-1-yl]-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxyl;c acid
_ _ .. . . .
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
~[2-n-butyl-5-[3-(4-methoxy)benzyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-
2tl~)-pyrimidinon 1-yl]-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-
yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic
acid.
Example ~0
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-[3-(4-hydroxy)benzyl-3,4,5,6-
tetrahydro-2(1H)-pyrimidinon-l-yl]-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[t2 n-butyl-5-[3-(4 hydroxy)-benzyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-
2(lH)-pyrimidinon-l-yl]-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-
yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and tri~luoroacetic
,
,. .. . .
. . - , . . ~ .
~:
. , .
. .
2048~09
- 75
acid.
Example 61
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-(3-cyclohexylmethyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-
2(lH)-pyrimidinon-l-yl)-3H-imidazo~4,5-b]-pyridin-3-
yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2 n-butyl-5~(3-cyclohexylmethyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-
2(lH)-pyrimidinon-l-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-
yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic
acid.
Example 62
4'-[t2-n-Propyl-$-~(2-carboxymethyl)pyrrolidino]-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic
acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-5-[(2-carboxymethyl)pyrrolidino~-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 37~ of theory,
Melting point: 137-13gC
C2~H30N404 (498-62)
Calculated: C 69.86 H 6.06 N 11.24
Found: 69.59 6.20 11.04
Example 63
4~-[(2-n-Butyl-6-phthalimido lH-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-
yl)-methyl3biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid-trifluoroacetate
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'~
[(2-n-butyl-6-phthalimido-lH-imidazot4,5-b]pyridin-1-
yl)-methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic
,~ . . . . .
: .:
-: :- . , :
. ~
, . . .
~8g~9
acid.
Yield: 74% o~ theory,
Melting point: 168-170C
C32H26N4o4 x CF3COOH (644.61)
Calculated: C 63.35 H 4.22 N 8.96
Found: 63.50 4.53 9.06
Example 64
4'-[t8-n-Butyl-2-(n-butylamino)-9H-purin-9-yl]methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
0.45 g (0.95 mMol) of methyl 4'-[[8-n-butyl-2-(n-
butylamino)-9H-purin-9-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
are dissolved in 20 ml of methanol and 10 ml of water,
mixed with 0.4 g of powdered potassium hydroxide and
re~luxed for 3 hours. The reaction mixture is then
concentrated by evaporation and the residue is dissolved
in 30 ml of water. It is filtered over charcoal and
acidified with glacial acetic acid~ The precipitate
formed is suction filtered, washed with water and dried.
Yield: 0.4 g (92% of theory),
Melting point: 213-~15C
C27H31~52 (457.58)
Calculated: C 70.87 H 6.83 N 15.31
Found: 70.70 6.89 15.19
Example 65
4' C(8-n-Butyl-Z-cyclohexylamino-9H-purin-9-yl)methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 64 from methyl 4'-[(8-n-
butyl-2-cyclohexylamino-9H-purin-9-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and methanolic potassium hydroxide solution.
Yield: 55% of theory,
Melting point: 213-215C
C2sH33Ns2 t483 62)
- ~ ~
.
, .
.-: : . ... . .
.
i~
. .
20~88~9
-- 77 --
Calculated: C 72.02 H 6.88 N 14.48
Found: 71. 84 6 . 98 14 . 62
xample 66
4'-[(8-n-Butyl-2-ethoxy-9H-purin-9-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid
-
Prepared analogously to Exampl!e 64 from methyl 4'-[(8-n-
butyl-2-ethoxy-9H-purin-9-yl)m~ethyl]biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and methanolic potassium hydroxide solution.
Yield: 48~ of theory,
Melting point: 190-192C
C2sH26N4O3 (430.51)
Calculated: C 69.75 H 6.09 N 13.01
Found: 69.75 6.13 12.83
Example 67
4'-[(~-n-Butyl-2-ethoxy-7H-purin-7-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid
. ~
Prepared analogously to Example 64 from methyl 4'-[(8-n-
butyl-2-ethoxy-7H-purin-7-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and methanolic potassium hydroxide solution.
Yield: 10% of theory,
Melting point: 155-158C
C2sH26N4O3 (430.51)
Calculated: C 69.75 H 6.09 N 13.01
Found: 69.95 6.10 :L1.83
Example 68
4l-[[2-n-Propyl-5-(2-methylpropylamino)-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl~-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl
0.32 g (0.42 mMol) of 4'~[~2-n-propyl-5-(2-methylpropyl-
amino)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-2-(1-
.
.
'' ~ ' ;' :
' `
,~
~0~809
~ 7~ -
triphenylmethyl-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl are dissolved in
20 ml of methanolic hydrochloric acid and stirred for 2
hours at ambient temperature. The solvent is
concentrated by evaporation, the residue is triturated
with 20 ml of water, suction filtered and dried. After
column chromatography on silica gel (particle size:
0.06-0.2 mm, eluant: methylene chloride/ethanol 0-10%) a
white solid is obtained.
Yield: 0.1 g (51% of theory),
Melting point: 128-130C
C27H30N~ (466.60)
Calculated: C 69.50 H 6.4~ N 24.02
Found: 69.44 6.73 24.04
Example 69
4'-[[Z-n-Butyl-5-(2-aminocarbonyl-cyclohexylcarbonyl-
amino)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methylJ-2 (lH-
tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl
Prepared analogously to Example 68 from 4'-[[2-n-butyl-
5-(2-aminocarbonyl-cyclohexylcarbonylamino)-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-2-(1-triphenylmethyl-
tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl and methanolic hydrochloric acid.
Yield: 37% of theory,
Melting point: 165-175C
32H35NsOz (577 70)
Calculated: C 66.53 H 6.11 N 2~.82
Found: 65.73 6.13 21.84
Example 70
`:
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-(cis-hexahydrophthalimido)-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)-
biphenyl
. . .
Prepared analogously to Example 68 from 4'-[[2-n-butyl-
5-(cis-hexahydrophthalimido~-3N-imidazo~4,5-b]pyridin-3-
: , ~ ~ , ~ ' ' : '
.
.
. : : ~ '
' ' : :
~OA8~09
- 79 -
yl]methyl]-2-(1-triphenylmethyl-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl
and glacial acetic acid.
Yield: 30~ of theory,
Melting point: 127C
C32H32N8O2 (560.66)
Mass spectrum: M~ - 560
Example 71
4'-t[2-n-Butyl-5-t4 methyl-piperidino)-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)-
biphenyl
. . _ . . . _ . . . _
Pre~ared analogously to Example 68 ~rom 4'-[[2-n-butyl-
5-t4-methyl-piperidino)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-
yl]methyl]-2-(1-triphenylmethyl-tetrazol-5-yl~biphenyl
and methanolic hydrochloric acid.
Yield: 39% o~ theory,
Melting point: 187-189C
C30H34N8 (506-70)
Mass spectrum: M~ = 506
Example 72
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-5-[N-(3-phenylpropionyl)isobutylamino]-
3H-imidazo~4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-2~(lH-tetrazol-5-
; yl)-biphenyl
Prepared analogously to Example 68 from 4'-[t2-n-propyl-
5-[N-(3-phenylpropionyl)-isobutylamino]-3~-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin~3-yl]methyl]-2-(1-triphenylmethyl-
tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl and methanolic hydrochloric
acid.
~,,: . ,,
. , , , ~ ..... .
. . .: :
:
2~88~9
- 80 -
Example 73
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-5-(N-benzylaminocarbonyl-iscbutylamino)
3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-~-(lH-tetrazol-5-
yl)-biphenyl
_ _
Prepared analogously to Example 68 from 4'-[[2-n-propyl-
5-(N-benzylaminocarbonyl-isobu-tylamino)-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-2-(1-triphenylmethyl-
tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl and methanolic hydrochloric
acid.
Yield: 37% of theory,
Melting point: 195-196~C
C3sH37N9O (599~75)
Calculated: C 70.09 H 6.22 N 21.02
Found: 69.95 6.3220.86
Example 7
4~~E[2-n-propyl-5-(N-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl-
isobutylamino)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin 3-yl]methyl]-2-
(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl
Prepared analogously to Example 68 from 4'-[[2-n-propyl-
5-(N-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl-isobutylamino)-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl] 2-(1-triphenylmethyl-
tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl and methanolic hydrochloric
acid.
Yield: 38% of theory,
Melting point: 112-113C
C3~H41N9O (591.77)
Calculated:C 69.01H 6.g8 N 21.30
Found:68.86 6.88 21.18
. .
: ' ' '
` '~ ` .
, `
,
20~18~09
- 81 -
_xample 75
4'~[[2-n-Butyl-5-(3-benzyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-Z(lH)-
pyrimidinon-l-yl)-3~-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-
methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl
Prepared analogously to Example 68 from 4'-[[2-n-butyl-
5-(3-benzyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-pyrimidinon-1-yl)-
3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-2-(1-triphenyl-
methyl-tetrazol-5-yl) biphenyl and methanolic
hydrochloric acid.
Example 76
4'-[(2-n-Butyl-5-methyl-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)-
methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
. _
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[(2-n-butyl-5-methyl-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)-
methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 65% of theory,
Melting point: 233-235C
C2s~2sN3o2 (399.50)
Calculated: C 75.16 H 6.31 N 10.52
Found: 75.06 6.3510.46
Example 77
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-(2-oxo-pyrrolidino~-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl
Prepared analogously to Example 68 from 4'-[ E 2-n-butyl-
5-(2-oxo-pyrrolidino)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-
yl]methyl]-2-(1-triphenyl-methyl-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl
and methanolic hydrochloric acid.
'
~ . . . .
''
,~ :
20418809
- ~2 -
Example 78
4'[[2-n-Propyl-5-(2-oxo-pyrrolidino)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl
_
Prepared analogously to Example 68 from 4'-[[2-n-propyl-
5-(2-oxo-pyrrolidino)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-
methyl]-2-(1-triphenyl-methyl-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl
and methanolic hydrochloric acid.
Example 79
4'[[2-n-Butyl-5-(2-oxo-piperidino)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)-hiphenyl
_ _
Prepared analogously to Example 68 from 4'-[[2-n-butyl-
5-(2-oxo-piperidino)-3H-imidazo[~,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-
methyl]-2-(1-triphenyl-methyl-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl
and methanolic hydrochloric acid.
Example 80
4'[[2-n-Propyl-5-(2-oxo-piperidino)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-2~(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl
Prepared analogously to Example 68 from 4'-[[2-n-propyl-
5-(2-oxo-piperidino)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-
methyl]-2-(l-triphenyl-methyl-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl
and methanolic hydrochloric acid.
Example 81
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-methyl-6 (cis-hexahydrophthalimido)-lH-
imidazo[4,5~b]pyridin-l-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic
acid-trifluoroacetate
.. . . _ . _
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[t2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-(cis-hexahydrophthalimido)-lH-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-l-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate
2~)~880.9
- 83 -
and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 79~ of theory,
Melting point: 188-l90~C
C33H34N~04 x CF3COOH (664.68)
Calculated: C 63.24 H 5.31 N 8.4~
Found: 63.5Z 5.65 8.69
Example 82
4'-[(2-n-Butyl-5-methyl-6-dimethylaminocarbonylamino~
imidaæo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic
acid trifluoroacetate
. . _ _ . _ . _ . . . _
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6 dimethylaminocarbonylamino-lH-
imidazo[4~5-b~pyridin-1-yl]methyl]biphenyl 2-carboxylate
and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 83~ of theory,
Melting point: 147-149C
c28H31N53 x CF3COOH (599.61)
Calculated: C 60.09 H 5.37 N 11.6~
Found: 60.31 5.39 11.51
Example 83
4'-[(2-n-Butyl-5-methyl-lH-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl)-
methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'
E (2-n-butyl-5-methyl-lH-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl)-
methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 77~ of theory,
Melting point: 230-232C
C25H25N302 (399 50)
Calculated:C 75.16 H 6.31 N 10.52
Found:74.86 6.39 10.46
-. : : ~
,
.
,.;.
. ~ .
.
20~8~9
Example 84
4'-[(2-n-~utyl-6-phthalimido-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3~
yl)-methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
. ~ . _ .. ~ . .
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
t(2-n-butyl-6-phthalimido-3H-imidazo[4,5-b~pyridin-3-
yl)-methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylalte and tri~luoroacetic
acid.
Yield: 78% of theory,
Melting point: 271-272C
C32H26N404 (530 59)
Calculated: C 72.44 H 4.94 N 10.56
Found: 72.37 4.99 10.48
Example 85
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-(4-chlorophenyl)sulphonylamino-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic
acid-hydrate
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-butyl-5-(4-chlorophenyl)sulphonylamino-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and
trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 63% of theory,
Melting point: 158-160C
C30~1z7N404ClS X H20 (593
Calculated: C 60.75 H 4.93 N 9.45
Found: 60.62 4.76 9.27
Example 86
4'-[(2-n-Butyl-5-n-butylsulphonylamino-3~-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
... _ . .. . . _
Prepared analogously to Example 4 from 4'-~(2-n-butyl-5-
amino-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl~biphenyl-2-
.: , ' . ~
.
:,
-
:
20~8809
- 85
carboxylic acid and butanesulphonyl chloride in
pyridine.
Yield: 16% of theory,
Melting point: > 250C
C28H3zN404S (520-70)
Calculated: C 65.59 H 6.19 N 10.76
Found: 65.41 6.28 10.58
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
4'-[(2-n-butyl-5-n-propylsulphonylamino-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl 2 carboxylic acid
4'-t(2-n~butyl-5-isopropylsulphonylamino-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3~yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
4'-[[2-n-butyl-5-(3-chloropropylsulphonylamino)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2~carboxylic
acid
[(2-n-butyl-5-n-hexylsulphonylamino-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
4'-[(2-n-butyl-5-benzylsulphonylamino-3H-imidazot4,5-b]-
pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Example 87
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-(n butanesultam-1-yl)-3H-imidazo-
~4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)-
biphenyl
Prepared analogously to Example 68 from 4'-[~2-n-butyl~
5-~n-butanesultam-1-yl)-3H-imidazot4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-
methyl]-2-(1-triphenylmethyl-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl and
methanolic hydrochloric acid.
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
.
- . : . `
:' , .
-
,
.
2~g80~
- ~6 -
4'-[~2~n-propyl-5-(n-butanesultam-1-yl~-3H-ilnidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridi.n 3-yl]-methyl]-2-(~H-tetrazol-5-yl)-
biphenyl
4'-[[2-n-butyl-5-(n-propanesultam-l-yl)-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-
yl)biphenyl
4'-[[2-n-propyl-5-(n-propanesultam-1-yl)-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)-
biphenyl
4'-[[2-n-butyl-5-(n-butanesultam-1-yl)-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
4'-[[2-n-propyl-5-(n-butanesultam-l-yl)-3H-imidazo-
~4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
4'-[[2-n-butyl-5--(n-propanesultam-1-yl)-3H-imidazo-
[~,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
4'-[[2-n-propyl-5-(n-propanesultam-l-yl)-3H-imidazo
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl~biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Example 88
~`
4'-[(2-n-Butyl-5-methoxy-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3~yl)-
: methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl
. . _ . .
Prepared analogously to Example 68 ~rom 4'-[(2-n-butyl-
5-methoxy-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]-2~
triphenylmethyl-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl and methanolic
hydrochloric acid.
Yield: 43% of theory,
Melting point: 206-207C
C25H25N7 (439.52)
Calculated:C 68.32 H 5.73N 22.31
Found: 68.11 5.88 22.19
.. . .
;, ~ ~ , :,
,
: '
.
,:
20~09
- 87
Example 89
~'-t(2-n-Butyl-3E~-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-5-on-3-yl)-
methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl
Prepared analogously to Example 68 from 4'-[(Z-n-butyl-
3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-5-on 3-yl)methyl]-2-(1-
triphenylmethyl-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl and methanolic
hydrochloric acid.
Yield: 18% of theory,
Melting point: amorphous
C24H23N7 (425.50)
Calculated: C 67.7S H 5.45 N 23.04
Found: 67.54 5.42 22.91
Example 90
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-5-(2,2-dimethylpropionylamino)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)~
biphenyl
Prepared analogously to Example 68 from 4'-[[2-n-propyl-
5-(2,2-dimethylpropionylamino) 3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-
3-yl]methyl]-2-~1-triphenylmethyl-tetrazol-S-yl)biphenyl
and methanolic hydrochloric acid.
Yield: 81% of theory,
Melting point: 217-220C
C28H30N80 (49A.60)
Calculated: C 67.99 H 6.11 N 22.66
Found: 67.82 6.22 22.46
Example 91
4'-~(2-n-Propyl-5-cyclohexylcarbonylamino-3H imidazo-
t4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]-2-~lH-tetrazol-5-yl)-
biphenyl
_
Prepared analogously to Example 68 from 4'-[(2-n-propyl-
~ ~ .
. j .
~'' .. ~
,
204880~
88 -
5-cyclohexylcarbonylamino-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-
yl)methyl]-2-(1-triphenylmethyl-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl
and methanolia hydrochloric aaid.
Yield: 89% of theory,
Melting point: 229-231C
C30H32Ns (520.64)
Calculated: C 69.21 H 6.20 N 21.52
Found: 69.14 6.20 21.32
Example 92
4~-[~2-n-sutyl-5-methyl-6-dimethylaminocarbonylamino-3H
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic
acid
. _ . . . . . _ ...
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from ter-t.bu-tyl 4'-
[(2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-dimethylaminocarbonylamino 3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methyl]biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 74% of theory,
Melting point: 220-221C
C28H31N503 (485.58~
Calculated: c 69.26 H 6.44 N 14.42
Found: 69.08 6.47 14.25
Example_93
4'-[(2-n-Butyl-4-chloro-3H-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridin-3-yl)-
methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
. .
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[(2-n-butyl-4-chloro-3H-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridin-3-yl~-
methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 85% of theory,
Melting point: 221-222C
C24H22ClN3o2 (419.92)
Calculated: C 68.65 H 5.28 N 10.00
Found: 68.66 5.15 10.19
:, ~
.
'
- . ~ ~ . . - ;
.
- 20~09
- 89 -
Example 94
4'-[(2-n-Butyl-4-chloro-lH-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridin-1-yl)-
methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[(2-n-butyl-4-chloro-lH-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridin-1-yl)-
methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 85~ o~ theory,
Meltin~ point: 221~222C
C24H22ClN302 (419-92)
Calculated: C 68.65 H 5.28 N 10.00
Found: 68.56 5.18 10.09
_xample 95
4'-[(2-Ethyl-5 propionylamino-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-
3-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2 carboxylic acid
. . . _ . . . _ .
Prepared analogously to Example 12 ~rom tert.butyl 4'-
[(2-ethyl-5-propionylamino-3H-imidazo[4,5-b~pyridin-3-
yl)-methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic
acid.
Yield: 99% of theory,
Melting point: 283-293C
C25H24N403 (428.50)
Calculated: C 70.08 H 5.65 N 13.08
Found: 69.87 5.68 13.05
Example 96
4'-[t2-n-Propyl-5-(5-hydroxy-valeroylamino)-3H-
imidazo[4,5 b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic
acid
. .
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
t[2-n-propyl-5-(5-hydroxy n-valeroylamino~-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methyl]biphenyl-2-
. - -, . :,
.
: : .
~ .
204L8809
-- 90 --
carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yie]d: 80% o~ theory,
Meltlng point: 220C
C28H30N404 (486.60)
Calculated: C 69.12 H 6.22 N 11.52
Found: 68.97 6.~411.39
Exam~le 97
4'-[[2-Ethyl-5-(3-methyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(1H)-
pyrimidinon-l-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid semihydrate
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-ethyl-5-(3-methyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-
pyrimidinon-1-yl)-3~-imidazo~4,5-b~pyridin~3-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 62% of theory,
Melting point: from 250C (decomp.)
C27H2~NsO3 x 1/2 HzO (478.60)
Calculated: C 67.77 H 5.90 N 14.64
Found: 67.98 5.84 14.66
Example 98
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-5-(3-methyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-
pyrimidinon-l-yl)-3H-imidazot4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[~2-n-propyl-5-(3-methyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH~-
pyrimidinon-1-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 74% of theory,
Melting point: 202-205C
Cz8H29NsO3 (483.57)
Calculated: C 69.55 H 6.04 N 14.48
Found: 69.30 5.9814.62
.~~, ... .
" . . .. .
~8809
91
_x mPle 99
4'-[[2~Ethyl-5 (3-benzyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(1H)-
pyrimidinon-1-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-
methyl~-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid-semihydrate
Prepared analogou~ly to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-ethyl-5-(3-benzyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-
pyrimidinon-l-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 66% of theory,
Melting point: 137-138C
C33H31NsO3 x 1/2 H20 (545.70)
Calculated: C 72.64 H 5.73 N 12.84
E'ound- 72~40 5.76 12.~8
Example 100
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-5-(3-benzyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-
pyrimidinon-1-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-5-(3-benzyl-3,4,5,6 tetrahydro-2(lH)-
pyrimidinon-l-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 77% of theory,
Melting point: 149-152C
C34H33N503 (559.67)
Calculated:C 72.97H 5.94 N 12.51
Found:73.11 5.91 12.39
,
~ .
,, - . ,
.
20~880~
- 92 -
X~,_ 101
4'-[~2-n-Propyl-5-(N-cyclohexy:Laminocarbonyl-
ethylamino)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
.
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-5-(N-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl-ethylamino)-
3H-imidazot4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]--methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 10% of theory,
Melting point: 166-167nC
C34H33Ns3 (S3g-69)
Calculated: C 71.22 H 6.91 N ~2.98
Found: 71.37 6.7012.80
Example 102
4'-[[2-Ethyl-5-(N-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl-ethylamino)-
3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl~-biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-ethyl-5-(N-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl-ethylamino)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 25% of theory,
Melting point: 95-100C (decomp.)
C31H35NsO3 (525.66)
Calculated: C 70.83 H 6.71 N 13.32
Found: 70.69 6.65 13.30
' '
,: '`
~0~8809
- 93 -
Example 103
4'-C[2-n-Propyl-5-(N-cyclohexylcarbonyl-ethylamino)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-5-(N-cyclohexylcarbonyl-ethylamino)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl] biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 83% of theory,
Melting point: 112-115C
C32H36N403 (524.67)
Calculated: C 73.26 H 6.92 N 10.6~
Found: 73.18 7.19 10.67
Exampl_ 104
4'-[[2-Ethyl-5-(N-cyclohexylcarbonyl-ethylamino)-3H-
imida30[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid
. . _ _ . . _
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
t[2-ethyl-5-(N-cyclohexylcarbonyl-ethylamino)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b] pyridin-3-yl ] -methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yieldo 91% of theory,
Melting point: 223-224C
C31H34N403 (510.65)
Calculated: C 72.92 H 6.71 N 10.97
Found: 72.97 6.65 10.93
Example 105
4'-[[2~(N-Isobutyryl-n-butylamino)-8-n-butyl-9H-purin-9-
yl~ methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 4 from 4'-~[2-(n-
.
' ~ : : ' ,,
` 204~809
~- 94 -
butylamino3-8-n-butyl-9H-purin-9-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2
carboxylic acid and isobutyric acid chloride.
Yield: 38% of theory,
Melting point: 80OC
C31H37NsO3 (527.68)
Calculated: C 70.56 H 7.07 N 13.27
Found: 70.45 7.22 13.06
Example 106
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-methyl-6-(2-oxo-piperidin-1-yl)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid
. _ . . _ . . _ . . . _
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-(2-oxo-piperidin-1-yl)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl] biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 77Po of theory,
Melting point: 266-268c
C30l~32N403 (496.62)
Calculated: C 72.56 H 6.50 N 11.23
Found: 72.46 6.73 11.10
Example 107
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-methyl-6-(n-butanesultam-1-yl)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]~methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
~[2-n-butyl-5 methyl-6-(n-butanesultam-1-yl)-3H-
imidazo~4,5-b~pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 78% of theory,
Melting point: 287-288C
C29H32N404S (532-67)
Calculated: C 65.39 H 6.06 N 10.52
;
. ,,
'
.
- 2~8~09
95 -
Found: 65.26 6.25 10.37
Example 108
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-methyl-6-(N-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl-
ethylamino)~lH-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl]-methyl]-
biphenyl-2~carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Exampl,e 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
~[2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-(N-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl-
ethylamino) lH-imidazo[4,5-b]p~yridin-1-yl]-methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 88% of theory,
Melting point: 177-179C
C34H31N503 (567.74)
Calculated: C 71.93 H 7.28 N 12.34
Found: 71.76 7.20 12.13
Example_109
4'-[[2,5-Dimethyl-6-(3-benzyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(1H)-
pyrimidinon-l-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b~pyridin-3-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 ~rom tert.butyl 4'-
[t2,5-dimethyl-6-(3-benzyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(1H)-
pyrimidinon-l-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 74% of theory,
Melting point: 277-280C
C33H~1Ns3 (545.65)
Calculated: C 72.64 H 5.73 N 12.84
Found: 72.87 5.57 12.66
,, . . , -
.
- 20~880~
~ 96 -
E mple 110
4'-~[2,5-Dimethyl-6-(3-benzyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(1H)-
pyrimidinon-1-yl)-lH-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2,5-dimethyl-6 (3-benzyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro 2tlH)-
pyrimidinon-l-yl)-lH-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-y:L]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 77% of theory,
Melting point: 142-144C
C33H31NsO3 (545.65)
Calculated: C 72.64 H 5.73 N 12.84
Found: 72.59 5.51 12.60
Example 111
4'-~[2-Ethyl-5-methyl-6-(3-benzyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-
2(lH)-pyrimidinon-1-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-
methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[~2-ethyl-5-methyl-6-(3-benzyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(lH)-
pyrimidinon-l-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5~b]pyridin-3-yl~-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 73% of theory,
Melting point: 272-274C
C34H33Ns3 (559-68)
Calculated: C 72.97 H 5.94 N 12.51
Found: 72.87 5.97 12.37
. . .
: ' ; -
:''- ' , ' ~
:,
.. . .
20~88~9
- 97 -
Example 112
4'-[(2~n-Butyl-5-ethyl-6-dimethylaminocarbonylamino-3H-
imidazo~4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic
acid-trifluoroacetate
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
Ct2-n-butyl-5-ethyl-6-dimethylaminocarbonylamino-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 72% of theory,
Melting point: 180-182C
C2sH33Ns3 x CF3C00~ (613.65)
Calculated: C 60.67 H 5. 58 N 11.41
Found: 60.81 5.81 11.65
Example 113
4'-[(2-n-Propyl-5-methyl-6-dimethylaminocarbonylamino-
3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid-trifluoroacetate
_ _ . .
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[(2-n-propyl-5-methyl-6-dimethylaminocarbonylamino-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 81% of theory,
Melting point: 243-245C
C27H29N503 x CF3COOH (585.60)
Calculated:C 59.48 H 5.16 N 11.96
Found:59.68 5.26 11.99
.
" : ~ ~
,
. . . .
2~809
_ 9~ _
Exam le 114
4'-[(2-n-Propyl-5~methyl-6-dimethylaminocarbonylamino-
lH-imidazo[4,5-b~pyridin-1 yl)methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid-trifluoroacetate
.
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[(2-n-propyl-S-methyl-6-dimethylaminocarbonylamino-lH-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl)-methyl~-biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 90% of theory,
Melting point: 213-216C
Cz7H2sNsO3 x CF3COOH (585.60)
Calculated: C 59.4~ H 5.16 N 11~96
Found: 59.61 5.13 11.77
Example ~15
4'-[(2-n-Butyl-5-methyl-6-diethylaminocarbonylamino-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]-biphenyl-2 carboxylic
acid-trifluoroacetate
. . _ . _ . . . _ . . _ _
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[(2~n-butyl-5-methyl-6-diethylaminocarbonylamino-3H-
imidazo[4~5-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 90% of theory,
Melting point: 137-140C
C30H35N5O3 x CF3COOH (627.67)
Calculated: C 61.23 H 5.78 N 11.16
Found: 60.975.33 10.9~
,, ~, . .. . ..
:: ,
.'' . ' ' .
:
~ '
~0~8~0~
. 99
Example 116
4'-[t2-n-Butyl-5-ethyl-6-(3-benzyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-
2(lH)-pyrimidinon-l-yl)-3H-imidazot4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-
methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
. . . _ . . _
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-butyl-5-ethyl-6-(3-benzyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-
2(lH)-pyrimidinon-1-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl~-
methyl] biphenyl-2~carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 85% of theory,
Melting point: 173-175C
C37H39NsO3 (601.76)
Calculated: C 73.85 H 6.53 N 11.64
E'ound: 73.63 6.40 11.41
Example 117
4~-[[2-n-Propyl-5-methyl-6-(3-benzyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-
2(lH)-pyrimidinon-1-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-
methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
. . _ . . _ ~
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[~2-n-propyl-5-methyl-6-(3-benzyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-
2(lH)-pyrimidinon-l-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 64% of theory,
Melting point: 199-201C
C35H35NsO3 (573.69)
Cals~ulated: C 73.27 H 6.05 N 12.21
Found: 73.20 6.19 12.08
. . . . .. .
- , . .
., , ~ -
. :. . . : .
.. . . .
.
2~8~V9
-- 100 --
Example 118
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-methyl-6-(3-dimethylaminocarbonyl-
3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(1H)-pyrimidinon-1-yl)-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
. _ _
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[t2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-(3-dimethylaminocarbonyl-3,4,5,6-
tetrahydro-2(1H)-pyrimidinon-l--yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyr.idin-3-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and
trifluoroacetic acid.
_ample 119
4'-[[2-n-Butyl-5-methyl~6~(3-benzyl-3,4,5-trihydro-
2(lH)-imidazolinon-l-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
. . . _ _ , .
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-butyl-5-methyl-6-(3-benzyl-3,4,5-trihydro-2(lH)-
imidazolinon-l-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]-pyridin-3-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield. 92% of theory,
Melting point: 149-151~C
C3sH3sNsO3 (573-70)
Calculated: C 73028 H 6.15 N 12.21
Found: 73.16 5.9812.07
Example 120
4'-[(2-n-Propyl-5-methyl-6-(cis-hexahydrophthalimido)-
3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
~(2-n-propyl-5-methyl-6-(cis-hexahydrophthalimido)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]-pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
.. . . .
.
'; ' ~ ;
2~8809
- 101 -
Yield: 77% of theory,
Melting point: 269~270C
C32H3zN4O4 (536-64)
Calculated: C 71.62 ~ 6.01 N 10.44
Found: 71.48 6.24 10.31
.
Example 121
4'-[(2-n-Propyl-5-methyl-6-(c.is-hexahydrophthalimido)-
lH-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl)methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[(2-n-propyl-5-methyl-6-(cis-hexahydrophthalimido)-lH-
imidazo[4,5-b]-pyridin-1-yl)-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 79% of theory,
Nelting point: 219-221C
C32H32N4O4 (536.64~
Calculated: C 71.62 H 6.01 N 10.44
Found: 71.45 5.86 10.21
Example 122
4'-t[2-n-Butyl-5-(N-phenylsulphonyl-methylamino)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid
. _ _ .. _ ... . . _ ..
Prepared analogously to Example 12 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-butyl-5-(N-phenylsulphonyl-methylamino)-3H-
imidazo[4,5-b]-pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 83% of thaory,
Melting point 226-227C
H30N4O4S (554.60)
Calculated: C 67.14 H 5.45 N 10.10 S 5.79
Found: 67.00 5.51 10.25 5.78
..:, ......
~. , ,' :, ' ~ ~
- ' '' , : ,
,'. ~ ~ , ' ' . : '
-
20~8~09
102 -
Example 123
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-5-(3-benzyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(1l~)-
pyrimidinon-l-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-
methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl
. _ . . _ _ . . _ , . .
Prepared analogously to Example 68 from 4'-[[2-n-propyl-
5-(3-benzyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(1H)-pyrimidinon-1-yl)-
3H-imidazo~4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]-2-(1-triphenyl-
methyl-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl and methanolic
hydrochloric acid.
Yield: 72~ of theory,
Melting point: amorphous
C34H33Ns (583.70)
Calculated: C 69.96 H 5.70 N 21.60
Found: 70.11 5.5721.49
Example 124
4'-~2-n-Propyl-5-(2-oxo-indolin-1-yl)-3H-imidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)-
biphenyl
Prepared analogously to Example 68 from 4'-[[2-n-propyl-
5-(2 oxo-indolin-1-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5 b]pyridin~3-yl]-
methyl]-2-(1-triphenylmethyl-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl and
methanolic hydrochloric acid.
Yield~ of theory,
Melting point- sinters from 190C
C31H26N8 (526.51)
Mass spectrum: (M-~H)+ a 527
' ,, ~,
.
., .
204~8~9
- 103 -
Example 125
4'-[(2-n-Butyl-5-methyl-6-dimethylaminocarbonylamino-3H-
imidazo~4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)-
biphenyl
._ _
Prepared analogously to Example 68 from 4'-[(2-n-butyl-
5-methyl-6-dimethylaminocarbonylamino-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridin-3-yl)-methyl]-2-(1-triphenylmethyl-tetrazol-5-
yl~-biphenyl and methanolic hydrochloric acid.
Example 126
4'-[[2-Ethyl-5-(2,2-dimethyl-propionylamino)-3~-imidazo-
~4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)-
biphenyl-hydrochloride
Prepared analogously to Example 68 from 4'-[[2-ethyl-5-
(2,2-dimethyl-propionylamino)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-
3-yl]-methyl]-2-(1-triphenylmethyl-tetrazol-5-yl)-
biphenyl and methanolic hydrochloric acid.
Yield: 52% of theory,
Melting point: sinters from 188~C
C27H2sNsO x E~Cl (517.04)
Calculated: C 62.95 H 5.65 N 21.90 Cl 6.85
Found: 62.73 5.47 21.75 5067
Example 127
. .
4'-[(2-n-Butyl-5-ethyl-6-phthalimido-lH-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridin-1-yl)-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example l~ from tert.butyl 4'-
[(2-n-butyl-5-ethyl-6-phthalimido-lH-imidazo[4,5-b]-
pyridin-1-yl)-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and
trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 56% o~ theory
Melting point: 277-279C
.. . . . :
-, .. .
: : .
~0~809
- 104 -
C34H30N~04 (558.64)
Calculated: C 73.10 H 5.41 ~7 10.03
Found:72.97 5.52 10.16
Example 128
4'-~(2-n-Butyl-5~methoxy-lH-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl)-
methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl
Prepared analogously to Example 68 from 4'-E(2-n-butyl-
5-methoxy-lH-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl)-methyl]-2-(1-
triphenylmethyl-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl and methanolic
hydrochloxic acid.
Yield: 60% of theory,
Melting point: 170-171C
C2sH2sN70 (439-53)
Calculated:C 68.32H 5.73 N 22.31
Found:68.19 5.53 22.06
....... . . .
. ~. . ; ,
.
, :, ,
20~gO9
105 -
In the Examples of Pharmaceutical Formulations which
follow, any suitable compound o~ formula I, particularly
compounds A to K of the pharmacological test report, may
be used as the active substance:
Exam~le I
Ampoules containing 50 mg of active substance per 5 ml
_ _
Active substance 50 mg
KHzPO4 2 mg
NazHPO4 x 2Hzo 50 mg
NaCl 12 mg
Water for injections ad 5 ml
Preparation:
The buffer substances and isotonic substance are
dissolved in some of the water. The active substance is
added and, once it has completely dissolved, water is
added to make up the required volume.
Example II
Ampoules containing 100 mg of active substance per 5 ml
. ~
Active substance 100 mg
Methyl glucamine 35 mg
Glycofurol 1000 mg
Polyethyleneglycol-polypropylene-
glycol block polymer 250 mg
Water for injections ad 5 ml
Preparation:
Methyl glucamine is dissolved in some of the water and
. , ; . ,
:
: .
'
20~88~
- 106 -
the active substance i8 dissolved with stirring and
heating. After the addition of solvents, water is added
to make up the desired volume.
Example IIl
Tablets containing 50 mg of active substance
.
Active substance 50.0 mg
Calcium phosphate 70.0 mg
Lactose 40.0 mg
Corn starch 35.0 mg
Polyvinylpyrrolidone 3.5 mg
Magnesium stearate __1 5_~
200.0 mg
Preparation:
The active substance, CaHP04, lactose and corn starch are
uniformly moistened with an aqueous PVP solution. The
mass is passed through a 2 m~ screen, dried at 50C in a
circulating air dryer and screened again.
After the lubricant has been added, the granules are
compressed in a tablet making machine.
Example IV
Coated tablets containing 50 mg of active substance
Active substance 50.0 mg
Lysine 25.0 mg
Lactose 60.0 mg
Corn starch 34.0 mg
Gelatin 10.0 mg
Magnesium stearate 1.0 ma
,
. .
i
,.
.; ~ ' ' . ' ' :
. '' ~ ~ ~ . ' ' " .
2~809
- 107 -
180.0 mg
Preparation:
The active substance is mixed with the excipients and
moistened with an aqueous gelatin solution. After
screening and drying, the granules are mixed with
magnesium stearate and compressed to form tablet cores.
The cores thus produced are covered with a coating by
known methods. A colouring may be added to the coatiny
suspension or solution.
Example V
Coated tablets containing lO0 mg of active substance
. . . _ _
Ac-tive substance 100.0 mg
Lysine 50.0 mg
Lactose 86.0 mg
Corn starch 50.0 mg
Polyvinylpyrrolidone2.8 mg
Microcrystalline cellulose 60.0 mg
Magnesium stearate 1.2 mg
350.0 my
Preparation:
The active substance is mixed with the excipients and
moistened with an aqueous PVP solution. The moist mass
is passed through a 1.5 mm screen and dried at 45C.
A~ter drying, it is filtered again and the magnesium
stearate is added. This mixture is then compressed into
cores.
The cores thus produced are covered with a coating by
known methods. Colourings may be added to the coating
"~ ' :, ~ . ` .
`
:
2048~09
- 108 -
suspension or solution.
Example VI
Capsules containing z50 mg of active substance
. _ .
Active substance 250.0 mg
Corn starch 68.5 mg
Magnesium stearate 1.5 mg
320.0 mg
Preparation:
The active substance and corn starch are mixed together
and moistened with water. The moist mass is screened
and dried. The dry granules are screened and mixed with
magnesium stearate. The final mixture is packed into
size l hard gelatin capsules.
Example VII
Oral suspension containing 50 mg of active substance per
5 ml
Active substance 50.0 mg
Hydroxyethylcellulose50.0 mg
Sorbic acid 5.0 mg
70% sorbitol 600.0 mg
Glycerol 200.0 mg
Flavouring 15.0 mg
Water ad 5.0 ml
Preparation:
Distilled water is heated to 70C. Hydroxyethyl-
cellulose is dissolved therein with stirring. By the
,, .
, . ., ~ .
! .
~8~0~
-- 109 --
addition of sorbitol solution and glycerol the mixture
is cooled to ambient temperature. At ambient
temperature, sorbic acid, flavouring and active
substance are added. The suspension is evacuated with
stirring to remove any air. One dose of 50 mg is
contained in 5.0 ml.
Example VIII
Suppositories containing 100 mg of active substance
. .
Active substance 100.0 my
Solid fat 1600.0 mq
1700.0 mg
Pre~aration:
The hard fat is melted. At 40C the ground active
substance is homogeneously dispersed in the melt. It is
cooled to 38C and poured into slightly chilled
suppository moulds.
. . , -
.
-