Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2 ~
The present invention relates generally to
supporting members and more particularly to electric
utilities transmission poles such as telephone poles,
electric power poles, and the like.
The prior art has taught the use of supporting
crossarm members which are made of wood and are fastened
by means of an anchoring system to a supporting pole. The
wooden structure of such crossarms causes them to suffer
the effects of degradation and accordingly they must be
replaced with uneconomic regularity. Furthermore, since
the poles normally have a circular cross section, a
separate fastening means is used to fasten the crossarm to
the pole, and generally ensures an interfitting
relationship between the circular cross section of the pole
and the shape of the crossarm. These attaching and
adapting means are also subject to degradation and quite
frequent replacement. Additionally, transmission
conductors are generally supported on separate insulating
means attached to the crossarms, such as porcelain
insulators and metal pins, further increasing the weight
and cost, and requiring increased labour when the insulator
shatters or requires replacement. In the art attempting
to overcome the corrosion factor by using fibreglass and
associated materials, drawbacks are still encountered since
separate conductor carrying insulators are often still
employed.
United States Patent 2,437,375 (Buxton) discloses
a crossarm composed of plastic impregnated wood veneer
using separate conductor carrying insulators. United
States Patent 3,499,973 (Barnes) shows a triangular
crossarm having an arcuate back and separate conductor
supporting insulators. Canadian Patent 664,189 (Ritchie)
discloses a crossarm composed of dielectric material with
separate conductor support means bonded to the crossarm,
and wherein the crossarm is designed to slide over the top
diameter of a mounting pole.
It is an object of the present invention to
provide a light weight, strong crossarm support, fabricated
of corrosive resistant insulating material, shaped and
structured in relation to the cross section of the
supporting pole, to facilitate snug connection thereto
thereby providing increased stability to the crossarm, thus
seeking to inhibit the need for further stabilizing means.
It is a further object of the present invention to
provide a crossarm support that is economical to install,
and reduces the cost of removing accessory parts when wires
must be moved or otherwise relocated.
It is yet a further object of the present
invention to provide means whereby the use of insulators
for supporting the electrical conductors is no longer
required. The transmission wires are attached to the
crossarm, thus seeking to inhibit the need for separate
carrying means for the conductors.
According to one aspect of the present invention
a transmission electrical insulator crossarm support for
mounting on an utility pole comprise: a crossarm structure,
fabricated substantially of a nonconductive, corrosion
resistant material and having a generally concave mounting
surface which substantially adapts to said utility pole
lateral surface; securing means for fixing said crossarm
structure to said utility pole; and attaching means for
fastening the electrical conductors to said crossarm
structure; wherein said crossarm structure is provided
with supporting grooves, each accommodating an electrical
conductor and wherein said attaching means fix the
electrical conductor into said supporting grooves.
The crossarm structure of the present invention is
made of weather and corrosion resistant, electrically
nonconductive material and is dimensioned as required by
the weight of conductors supported thereon and by the
required insulation parameters (which depend on the
voltage, on the conductors and on crossarm structure
2~
material). A proposed material for the crossarm structure
is fibreglass which has the requîred strength and good
electrically insulating characteristics. Other materials
having the required characteristics may be employed.
In another preferred embodiment, an ultraviolet
inhibitor for protection of the crossarm to ultraviolet sun
radiation may also be used for extending the life of the
structure. Furthermore, the crossarm structure can be
suitably treated with fireproof substances for obtaining a
fire resistant support for electrical wires. By the
addition of these protective coatings to the crossarm,
better insulating properties may be obtained along with an
enhanced resistance to factors as overheat, water or
moisture infiltration, etc.
Preferably, the crossarm structure is produced of
a one piece material and, having a substantially
rectangular cross-section throughout.
The structure may also optionally he manufactured
with curvers moulded on and around each of the supporting
arms or stem, for increasing the lateral surface thereof.
In this way, the distance between the electrical conductors
measured over the arms and stem surface may increase
keeping same dimensions of the arms and stem. The leakage
paths of the surface currents are thus beneficially
increased.
In the case of a three phase current
transportation, the present invention comprises an inverted
T-shape structure having a vertical stem and crossarms
extending in both directions from the bottom of the stem.
On one face of the vertical stem and extending its entire
length, a semi-circular groove shaped and adapted for
connection to the mounting pole is provided. Two or more
bolt openings vertically disposed above each other, pass
from the front of the stem to the curved back, and serve
as a means for attaching the crossarm to the mounting pole.
The crossarm support is fixed in a vertical position with
2 ~
the aid of the semicircular groove and thus minimizes the
possibility of pivoting of the crossarm relative to the
pole, thereby substantially avoiding the need for
additional f ixing means such as the supporting forestays.
When the crossarm support is fastened to the mounting pole,
the top of the stem extends above the top of the pole and
provides means for attaching conductors thereto.
Alternatively, either one or two opposite sides of the
extending stem may be provided with semicircular grooves
for additional conductors.
Conductors may be fastened to the crossarm
structure by means of J-shaped bolts in a manner such that
the long arm of the J bolts passes through the crossarm and
is fastened with washers and securing nuts and the short
arm is received into the crossarm.
For a dead-end three phase connection, the
conductors are fastened to the crossarm structure by use
of ball link eye bolts. The use of porcelain type
insulators is avoided since the arms themselves are made
of nonconductive materials.
Additionally, the present invention may be used in
pairs to support an increased number of conductors.
In the case of a single phase current
transportation, only a vertical stem is mounted on the
pole. A semi-circular mounting groove extends along the
surface facing the pole. The two grooves for supporting
the electrical conductors are formed transversely at the
upper area of the stem and J bolts are used for securing
the conductors.
The invention will be described hereafter with
reference to the accompanying drawings, in which:
Figure 1 shows a perspective view of an embodiment
of the present invention for a three phase current
transportation crossarm support, mounted on a utility pole;
Figure 2 shows a top view of the embodiment of
Figure l;
2 ~
Figure 3 shows a perspective view of another
embodiment of the present invention for a mono-phase
current transportation crossarm support mounted on a
utility pole;
Figure 4 illustrates a front view of an embodiment
for a three phase current transportation crossarm support
provided with curvers; and
Figures 5a-5b show two preferred embodiments of
the curvers, moulded on the crossarm.
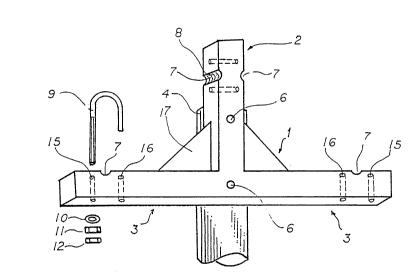
Referring to Figures 1, 2 and 4 of the
accompanying drawings, the T-shaped crossarm support
designated generally as 1 is shown with the top of the stem
2 extending from the top of the mounting pole. The T-
shaped assembly may be of substantially rectangular cross-
section or may be substantially square throughout and may
be composed of fibreglass or similar material.
A semicircular groove 5 extends vertically along
the lateral surface of the stem of the support 1 which will
interface with the utility pole 4 when mounted thereon.
The groove 5 is shaped and dimensioned to conform generally
with the portion of the surface of the pole to be received
by the groove. Passing from the front of the vertical
stem 2 to the semicircular groove 5, are two or more
horizontally disposed bolt passages 6, for fastening the
crossarm assembly to the pole 4. The crossarms 3 are
fabricated as an integral unit of the vertical stem 2.
The upper portion of the stem 2 has conductor
supporting grooves 7. Conductor gripping ridges 8 may be
formed into the conductor supporting grooves 7. The
conductor (not shown) is held in place by means of a J bolt
9. The long arm of the J bolt 9 extends through bolt hole
16 into the body of the stem 2 and the threaded section of
the bolt 9 is fastened by means of washer 10, nut 11 and
locking nut 12. The hole 15 receiving the short stem of
the J bolt 9 may optionally extend through the body of stem
2, but should be of sufficient depth so as to allow the
2 ~
curved portion of the bolt to grip a conductor passing
between it and the conductor supporting grooves 7.
Alternatively, the hole 15 may be used for the long arm of
the J bolt and hole 16 for the short arm. C o n d u c t o r
supporting grooves 7 are also located near the outside ends
of the crossarms 3. These grooves may have gripping ridges
8 to better fix the conductor. On either side of conductor
supporting grooves 7 are provided holes 15, 16 to receive
the J bolts. The conductor is held in place by J bolts in
the same manner as described above. Fibreglass armours are
placed into the supporting grooves in order to improve the
electrical insulation where the J bolt contacts the
conductor. A fibreglass armour includes three quarters of
the lateral surface of the conductor and is formed so as
to be slipped over the conductor and arranged in the
desired place.
Strain support wings 17 may be formed as separate
units and inserted into appropriate receiving grooves (not
shown) or may be formed as an integral part of the crossarm
3 and stem 2. The support wings 17 are triangular and are
sheet like in shape and structure. Alternatively, the
support wings 17 may be of triangular shape and formed of
strips wherein the central portion of each wing has an
opening to reduce wind drag. The crossarm 3 need not have
the strain wings in every operable embodiment, but it is
desirable to include them in the structure when the
conductors are of heavier gauge, or when the next conductor
support means is at an extended distance from the present
one.
Figure 3 shows a perspective view for an
embodiment where a mono-phase current transportation
crossarm support is mounted on a utility pole. The
crossarm structure is made of vertical stem 2 only. The
stem is provided with the semicircular groove 5 (as in the
embodiment of Figures 1 - 3) which will interface with the
utility pole 4 when mounted thereon. The electrical
2~
conductors are supported in grooves 7 and fixed with J
bolts 9 and washer 10, nut 11 and locking nut 12.
In the embodiment of Figures 4 and 5 curvers 18
are moulded into the structure on crossarm 3 and stem 2.
The curvers 18 have a discoidal or saucer-like shape (see
Figures 5a and 5b) and extend peripherally around the arms
and stem. They are formed adjacent the conductor
supporting grooves 7, for increasing the length of the
surface leakage current path.
The curvers also assist in the shedding of water
during rainfall, thereby accelerating the drying of the
crossarm and stem and, in any event, reducing the amount
; of surface water thereon.
In a further embodiment, the conductor supporting
grooves 7 may increase in diameter at their ends so as to
facilitate the passage of conductors in the event the
conductors approach the crossarm 3 or stem 2 at an angle.
It will be readily apparent to those skilled in
the art that modifications and improvements may be made to
the invention without departing from the essential scope
of the invention taught herein.