Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
' r 2~ol55~909~79
PATENT APPLICATION
TITLE: A FABRIC FOR SUPPORTING A WEB
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION:
FIELD OF THE INVENTION:
The present invention relates to a fabric, a process
for making such fabric, and an apparatus incorporating such
fabric, the fabric supporting a web in a papermaking
machine.
INFORMATION DISCLOSURE STATEMENT:
In the papermaking art, a formed web is guided through
a press section for removing as much water as possible from
the formed web before guiding the pressed web into a drying
section.
In view of the high thermal input requirements of a
typical drying section, it is essential to remove as much
water as possible from the web during passage through the
press section.
A long-standing problem has been experienced in
transferring a pressed web from a press section to a dryer
section. Ideally, a press felt for supporting the web
during passage through a pressing nip of the press section
would thereafter convey the web.towards and around at least
an initial portion of the dryer section.
'~ ~ 2~
However, the aforementioned ideal arrangement has not
proved practical because the press felt normally absorbs a
large quantity of water from the web during passage of the
web and press felt through the press nip, and unless the web
and press felt are caused to diverge relative to each other
immediately downstream relative to the press nip, the web
becomes rewetted by the water laden press felt.
Accordingly, in the prior art, typically the press felt
is guided around at least one guide roll such that the press
felt diverges relative to the web immediately downstream
relative to the press nip. Subsequently, a press-to-dryer
transfer felt is led into guiding relationship with the web
downstream relative to the press nip for guiding and
supporting the web into and around the dryer section.
Alternatively, in many press-to-dryer transfer
arrangements, a dryer felt will be extended into proximity
with the press section such that the web is supported by the
dryer felt and conveyed thereby to the dryer section.
In the aforementioned press-to-dryer transfer
arrangements, the web, at some point between the press nip
and the dryer section, is unsupported by either the press
felt, a press-to-dryer transfer felt, or a dryer felt.
Accordingly, such "open draw" of the web has necessitated
relatively complex threading techniques in order to thread a
tail of the web from the press section into a downstream
dryer section.
_ OB153996579
~' ' 205~q~8
The aforementioned "open draw" also involves handling
the web when the web is relatively fragile and subject to
web breakage.
U.S. Patent No. 4,483,745 to L. Wicks et al teaches a
"no draw" press-to-dryer transfer utilizing a non-porous
blanket which extends from an extended nip press arrangement
to a downstream dryer section such that the web is conveyed
by the non-porous blanket from the extended nip to the
subsequent dryer section.
However, the aforementioned non-porous blanket, which
supports the web, necessitates one-sided removal of the
water pressed from the web during passage through the
extended nip. Although in certain applications such
one-sidedness of the resultant web is acceptable, if
"two-sidedness" or uniformity in surface characteristics of
the resul.ant web is req~ired, the web must in some way be
reversed in order tO achieve the desired two-sidedn_ss of
the web.
The present invention provides a fabric for supporting
a web through a press section to a dryer section, the fabric
having a relatively low permeability permitting water to be
absorbed thereby but inhibiting rewetting of the supported
web.
r OB153996579
20~3088
Although the need for the aforementioned fabric has
long been recognized in the art, the manufacture of such
fabric has eluded the efforts of press and dryer felt
manufacturers.
The present invention was made and the unexpected
results were obtained therefrom by passing a particular
sample elt patch through a heated extended nip press of the
type described in U.S. Patent No. 4,738,752. The resultant
fabric had a caliper in the range of 1/15 thousandth of an
inch and displayed a relatively smooth web supporting
surface. When the fabric continued to support the web
downstream relative to the heated extended nip, the
unexpected discovery was made that water had been absorbed
by the fabric, but the web had not been appreciably rewetted
by the fabric during passage of the fabric supported web
downstream relative to the press nip.
Consequently, the implications of such non-rewe~ting
fabric became immediately apparent. One application of such
fabric would be as a press felt extending directly from a
press nip to and around at least an initial portion of a
dryer section. Such press-to-dryer transfer arrangement
would permit complete support of the web without "open draw"
from the press nip to the dryer section without the
aforementioned problems of rewetting.
Furthermore, in view of the relatively smooth surface
of the fabric, in the case of double felted pressing, it was
- ~ OB153996579
- 20530~8
evident that the web would consistently follow the smooth
surface of the fabric rather than the comparatively rough
surface of the felt on the other side of the web.
Therefore, the web could be automatically guided from the
press nip to and through the dryer section in a double
felted press configuration without the need of suction or
transfer blow boxes and the like.
Therefore, it is a primary object of the present
invention to provide a fabric, a method of making such
fabric, and an apparatus utilizing such fabric that makes a
considerable contribution to the papermaking art.
Another object of the present invention is the
provision of a fabric having a relatively low permeability
which permits water to be absorbed thereby while inhibiting
rewetting of the web.
Another c,bject of the present invention is the
provision of a fabric having a relatively smooth surface
towards the web such that the web predictably follows the
fabric when a felt and the fabric diverge relative to each
other downstream of a double felted press arrangement.
Other objects and advantages of the present invention
will be evident to those skilled in the art by a
consideration of the detailed description contained
hereinafter taken in conjunction with the annexed drawings.
. CA 020~3088 1997-10-07
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION:
The present invention relates to a fabric, a method of
making such fabric, and an apparatus for using such fabric
for supporting a web in a papermaking machine.
The fabric includes a base which defines a first and a
second side. The base comprises a plurality of hydrophobic
filaments. A first layer of fibers is disposed
contiguously relative to the first side with the first
layer of fibers being applied onto the first side of the
base. A second layer of fibers is disposed contiguously
relative to the second side of the base with the second
layer of fibers being applied onto the second side of the
base. At least one of the layers of the fibers includes a
mixture of hydrophobic and hydrophilic fibers. The layers
and the base are combined such that the fabric has a low
permeability which permits water to be absorbed thereby
while inhibiting rewetting of the web.
In a more particular embodiment of the present
invention, the base includes a first plurality of the
filaments which are disposed in a machine direction and a
second plurality of the filaments disposed in a cross-
machine direction with the machine and cross-machine
directional filaments being woven together.
In one embodiment of the present invention, the
hydrophobic filaments are of TEFLON , and the layers are
* Trade Mark
CA 020~3088 1997-10-07
needled into the first and the second sides respectively of
the base. Furthermore, the mixture is of TEFLON and
fiberglass fibers with the first and second layers of
fibers having a denier which is less than the denier of the
filaments.
In another embodiment of the present invention, both
layers of fibers include a mixture of TEFLON and fiberglass
fibers.
In a preferred embodiment of the present invention,
the mixture of TEFLON and fiberglass fibers is in a ratio
within the range 9:1 to 2:1.
In one embodiment of the present invention, the layers
and the base are at least partially fused together by the
application of pressure and heat. The fabric has an
application particularly as a press fabric or as a press-
to-dryer transfer fabric.
The present invention also includes a process for
making a fabric for supporting a web in a papermaking
machine. The process includes the steps of weaving a base
from a first plurality of machine directional TEFLON
filaments and a second plurality of cross-machine
directional TEFLON filaments such that the woven base
defines a first and a second side.
A first layer of fibers is needled into the first side
-- 7
CA 020~3088 1997-10-07
of the base and a second layer of fibers is needled into
the second side of the base. The first and the second
layers of fibers are a mixture of TEFLON and fiberglass
fibers such that the base and the layers of fibers form an
uncompressed mat.
The mat is then pressed at an elevated temperature
such that the layers and the base are at least partially
fused together so that the resultant fabric attains a
relatively smooth surface while retaining water-absorbing
capabilities and inhibiting rewetting of the web.
In a preferred process for making the aforementioned
fabric, the uncompressed mat is passed through a heated nip
of a press such that the layers and the base at least
partially fuse together so that the resultant felt includes
at least one relatively smooth surface while maintaining
water-absorbing capabilities and inhibiting release of
water to the web supported thereon.
The present invention includes a papermaking apparatus
for pressing and drying a web. The apparatus includes a
press and a drying section disposed downstream relative to
the press.
The press further includes a press member and a
backing roll which cooperates with the press member for
defining therebetween a press nip for pressing the web.
r OB153996579
2 ~ 5 3 ~ 8 ~ - 2053088
A fabric is disposed contiguously relative to the web
and extending through the nip for supporting and guiding the
web through the nip. Furthermore, a felt extends through
the nip, the felt being disposed on the opposite side of the
web relative to the fabric. The fabric defines a relatively
smooth surface towards the web such that when the web exits
the nip and the fabric and felt diverge relative to each
other, the web follows the smooth surface of the fabric
without being rewetted thereby.
The dryer section includes an upstream dryer and a
guide roll which cooperates with the upstream dryer. The
fabric extends from the nip to and around a portion of a
heated outer surface of the upstream dryer, the fabric
thereafter being guided away from the upstream dryer by the
guide roil such that the web is guided without open draw
from the nip to the dryer section without rewetting thereof
by the fabric.
The fabric has a caliper within the range 1/20
thousandth of an inch to 1/10 thousandth of an inch.
In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the
press also includes a backing felt which is disposed
contiguously relative to the fabric for backing the fabric
such that water from the web passes through the fabric into
the backing felt. The fabric also inhibits flow of water
from the backing felt that would otherwise cause rewetting
of the web.
r r ~ ~ ~ 3 ~ % ~ f OB153996579
2053088
Many modifications and variations of the present
invention will be evident to those skilled in the art by a
consideration of the detailed description contained
hereinafter, taken in conjunction with the annexed drawings.
However, such modifications and variations fall within the
spirit and scope of the present invention as defined by the
appended claims.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS:
Figure 1 is a sectional view of ~ fabric according to
the present invention;
Figure 2 is a diagrammatic representation showing the
steps of weaving a base, needling fibers therein, and
pressing the resultant mat according to the present
invention; and
Figure 3 is a side-elevational view of a ~apermaking
apparatus according to the present invention including the
fabric shown in Figure 1.
Similar reference characters refer to similar parts
throughout the various views of the drawings.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS:
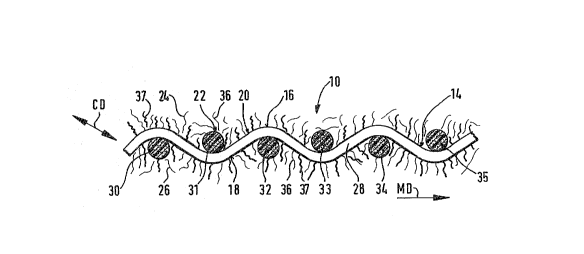
Figure 1 is a sectional view of a fabric generally
designated 10 for supporting a web in a papermaking machine.
The fabric 10 includes a base generally designated 14 which
-- 10 --
(~ ~~ OB153996579
20~3088
defines a first and a second side 16 and 18 respectively.
The base 14 also includes a plurality of hydrophobic
filaments generally designated 20 and 22 respectively. A
first layer of fibers 24 is disposed contiguously relative
to the first side 16 with the first layer 24 of fibers being
applied onto the first side 16 of the base 14.
A second layer of fibers 26 is disposed contiguously
relative to the second side 18 of the base 14. The second
layer of fibers 26 is applied onto the second side 18 of the
base 14. At least one of the layers of fibers 24, 26
includes a mixture of hydrophobic and hydrophilic fibers,
and the layers 24 and 26 and the base 14 are combined such
that the fabric 10 has a low permeability permitting water
to be absorbed thereby while inhibiting rewetting of the
web.
As shown in Fig~lre 1, the base 14 also includes a first
plurality of filaments 28 which are disposed in a machine
direction as indicated by the arrow MD. A second plurality
of the filaments 30,31,32,33,34 and 35 are disposed in a
cross-machine direction as indicated by the arrow CD with
the machine and cross-machine directional filaments 28 and
30-35 being woven together.
The hydrophobic filaments 28 and 30-35 are of TEFLON,
and the layers 24 and 26 are needled into the first and the
second sides 16 and 18 respectively of the base 14. TEFLON
OB153996579
-- 2053088
is a registered trademark of E. I. DuPont De Nemours &
Company.
The second layer of fibers 26 is a mixture of fibers.
The mixture of fibers includes TEFLON and fiberglass fibers,
and the individual fibers of the first and second layers 24
and 26 have a denier which is less than the denier of the
filaments 28 and 30-35.
In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, as
shown in Figure 1, both layers of fibers 24 and 26 include a
mixture of TEFLON and fiberglass fibers 36 and 37
respectively. The mixture of TEFLON and fiberglass fibers
is in a ratio within the range 9:1 to 2:1.
Figure 2 shows a process for making the aforementioned
fabric 10 and shows the layers 24 and 26 and the base 14 as
being at least partially fused together by the application
of pressure and heac.
According to the present invention, the fabric 10 is a
press fabric which extends through either a conventional
roll couple defining a press nip or a press fabric extending
through an extended nip press defined between an elongate
press member and a cooperating backing roll for defining an
extended nip.
- 12 -
_ f OB153996579
20530~8
The fabric 10 is also a press-to-dryer transfer fabric
for fully supporting the web from a press nip to a
downstream dryer section.
Figure 2 shows a process for making the fabric 10 for
supporting a web 12 in a papermaking machine. The process
comprises the steps of weaving a base 14 from a first
plurality of machine directional TEFLON filaments 28 and a
second plurality of cross-machine directional TEFLON
filaments 30-35 such that the woven base 14 defines a first
and a second side 16 and 18 respectively. A first layer of
fibers 24 is needled by a needling means 25 into the first
side 16 of the base 14, and a second layer of fibers 26 is
needled by a needling means 27 into the second side 18 of
the base 14. The first and the second layers of fibers 24
and 26 respectively are a mixture of TEFLON and fiberglass
fïbers 36 and 37 such that the base 14 and the layers 24 and
26 form an uncompressed mat 38.
The mat 38 is then pressed at an elevated temperature
by a roll press 39 such that the layers 24 and 26 and the
base 14 are at least partially fused together so that the
resultant fabric 10 attains a relatively smooth surface 40
while retaining water-absorbing capabilities and inhibiting
rewetting of the web.
Preferably, the mat 38 is-passed through a nip 42 of
the press 39, which is heated by induction heaters 44, such
f OB153996579
2053088
that the layers 24 and 26 and the base 14 at least partially
fuse together.
Figure 3 is a side-elevational view of a papermaking
apparatus generally designated 46 for pressing and drying a
web W shown by the dashed line. The apparatus 46 includes
an extended nip press generally designated 47 and a drying
section generally designated 48 disposed downstream relative
to the press 47. The press 47 further includes a press
member 50 and a backing roll 52 cooperating with the press
member 50 for defining therebetween a press nip 54 for
pressing the web W.
The fabric 10, as described hereinbefore, is disposed
contiguously relative to the web W and extends through the
nip 54 for supporting and guiding the web W through the nip
54.
A felt 56 extends-through the nip 54 with the felt 56
being disposed on the opposite side 58 of the weh W relative
to the fabric 10.
The fabric 10 defines a relatively smooth surface 40
towards the web W such that when the web W exits the nip 54,
and the fabric 10 and felt 56 diverge relative to each
other, the web W follows the smooth surface 40 of the fabric
10 without being rewetted thereby.
- 14 -
~ OB153996579
~-- 2053088
The drying section 48 includes an upstream dryer 60. A
guide roll 62 cooperates with the upstream dryer 60, and the
fabric 10 extends from the nip 54 to and around a portion 64
of a heated outer surface 66 of the upstream dryer 60. The
fabric 10 thereafter is guided away from the upstream dryer
60 by the guide roll 62 such that the web W is guided
without open draw from the nip 54 to the drying section 48
without rewetting thereof by the fabric 10.
In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the
fabric 10 has a caliper within the range 1/20 thousandth of
an inch to 1/10 thousandth of an inch.
In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, as
shown in Figure 3, the press 47 also includes a backing felt
~8 which is disposed contiguously relative to the fabric 10
for backing the fabric 10 such that water from the web W
passes through the fabric 10 into the backing felt 68. The
fabric 10 inhibits flow of water from the backing felt 68
that would otherwise cause rewetting of the web W.
The present invention provides a unique fabric which
permits absorption thereby of water from a web supported on
the fabric while inhibiting rewetting of the supported web.
Additionally, the present invention enables the fabric of
the present invention to support the web from the press nip
to the dryer without rewetting the web while assuring
predictable transfer of the web to the fabric in the case of
a double felted pressing configuration.