Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2 ~ 3 ~
WH-8362-91 - 1 -
TITLE: DEVICE FOR CONVEYING AND ALIGNING PAPER
SHEETS AT A FEED TABLE OF A PRINTING
MACHINE COMPRISI~G A SINGLE-SHEET FEEDER
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to a device for conveying and
aligning paper sheets at the feed table of a printing
machine comprising a single-sheet feeder, an aligning
section, and conveying means rotating on shafts and
conveying the sheets across saicl aligning section to the
following feed rollers for feeding the sheets to a gripper
bar provided in the impression cylinder.
The invention also relates to a device for
conveying and aligning paper sheets at the feed table of a
printing machine comprising a single-sheet feeder, an
aligning section and a rotating conveyor roller for
conveying sheets, an aligning means being provided in said
aligning section and being mounted above the feed table so
as to be adjustable in its lateral position.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The DE-OS 20 58 606 discloses such a device which
is a complicated and awkward system of various successive
and partly overlapping conveying and aligning means. First
of all, the aligning section is provided with rotating
conveyor tapes for conveying the paper sheets. Between
said tapes suckers which, via racks, are alternately moved
forward and backward for conveying and pre-aligning the
sheet are provided in a first area of said aligning
section. In a second area of said aligning section
rotating front lays at which the sheet is aligned with its
leading edge are secured on chains and located parallel to
the rotating conveyor tapes. Moreover, awkwardly operating
lateral aligning means performing the final lateral
alignment are located in said second aligning area. Driven
brushes disposed above the feed table convey the sheet
obliquely forward towards the lateral aligning limitations
~ ~3
WH-8362-91 - 2 -
which consist of the -tape surfaces of further rotating
tapes which are driven and laterally tilted. As a whole,
such a device is extremely complicated and awkward with
respect to its setup and its drive control unit. Said
device comprises a plurality of interlocking conveying
and/or aligning means (i.e. suckers, conveyor tapes, front
lays, brushes, lateral alignlng limitations, all running in
a different manner) which have to be driven separately in
accordance with the machine cycle. In order to perform
format adjustments further complicated measures have to be
taken. The guide means for the sucker mo-tion, the brushes
and the rotating lateral aligning limitations must be
laterally displaceable, some of the front lays must be
designed so as to be able to swing away due to the little
space available, and the conveyor tapes must differ in
length. The drive means for the sucker motion, the
brushes, the rotating lateral aligning limitations must be
adapted to the adjustability. Consequently, satisfactory
format adjustments require enormous construction work and
are very time-consuming for the machine operator, not
taking into account the fact that such a device is not
designed for the use of different sheet sizes. Even when
the sheets are transported by the feed rollers which are
arranged downstream of the aligning section, the end
portion of the sheet is still subjected to the force and
the transport effects of the conveyor tapes acting upward
from below, of the brushes acting downward from above, of
the brushes acting outward from inside, of the rotating
lateral aligning limitations acting inward from outside,
and in combination, all acting forward from behind. In
order to enable the feed rollers to grip a sheet, even
given the smallest format size possible with this
construction, these conveying means are, of course,
accumulated close to the feed rollers. However, this means
that longer sheets are subjected with their end portions to
these additional force and transport effects for a
relatively long period of time after having been taken over
2 ~ 3 ~
WH-8362-91 - 3 -
by the feed rollers at their leading sheet edges. The
sheets may be damaged or misaligned. As a result thereof,
such a device does not ensure a reliable and exact
transport and alignment after having changed the sheet
size.
Furthermore, it is often necessary, in practice, to
print paper sheets on both sides without specific
perfecting machines being available in the print shops for
this purpose. In such cases, the pressman turns by 180
the sheet pile containing sheets which have already been
printed on one side thereof and feeds said sheets a second
time to the feeder of the printing machine. However, in
order to apply the second print precisely in-register, it
is advantageous to align each sheet at -the same edge which
was used aligning said sheet for the first print.
SUMMARY OF THE INVFNTION
It is possible with the present invention to design
a device according to the generic part of the main claim so
as to optimize an exact and reliable transport and
alignment of the sheet.
According to the invention, this object is achieved
as described by the features of the characterizing part of
the main claim.
The conveying means frictionally gripping the sheet
from below is laterally displaced towards the lateral
aligning limitation the moment it reaches the leading sheet
edge. In so doing, the sheet is laterally aligned at the
aligning limitations. The momen-t the sheet reaches the
feed rollers, the conveying means is entirely lowered below
the table plate where it is laterally moved back into its
original position. The sheet is now transported by the
feed rollers away from the radius of action of the
conveying means. For conveying the following sheet, said
conveying means is lifted again upwards into its original
position for conveying the following sheet.
2 ~
WH-8362-91 - 4 -
With the device for conveying and aligning sheets,
according to -the invention, it is merely necessary to drive
one single conveying means and to change its position with
respect to the sheet transport across the aligning section
up to the feed rollers and with respect to its lateral
alignment. All driving and displacing means used may
extend from below the feed table up to the conveying means,
which results in a compact construction of the drive
device. Format changes do not require specific adjustments
of the conveying and aligning means; it is merely necessary
to laterally adjust the lateral aligning limitation by
adjusting the feed plate. Since, once the sheet is
transported by the Eeed rollers, the conveying means is
lowered below the table and thus the sheet is only
subjected to the transport effect of the feed rollers and
the sheet slides across the table along the lateral
limitation with its trailing portion pointing towards the
feed rollers, it is also possible to continuously convey
formats which are longer than the machine-related minimum
sheet size and to ensure lateral sheet alignment as well as
a reliable and exact sheet feed, even given a short feed
table.
Freely rotatable balls resting on the rotating
conveying means during the sheet conveying and lateral
aligning by the rotating conveying means reinforces the
frictional contact between sheet and rotating conveying
means, which guarantees an exact and reliable transport and
lateral alignment of the sheets, above all in view of
greater conveying speeds.
If the rotating conveying means consists only of a
driven shaft having conveyor rollers secured coaxially
thereon, this permits a simple and compact construction of
conveying means and feed table, drive and control of the
conveying means, thus ensuring a particularly reliable
transport and alignment, even given especially short feed
tables and paper sheets having varying sheet sizes.
~;,
2~ 3~
WH-8362-91 - 5 -
Furthermore, mounting the shafts in levers which
are provided at the outer sides of the table and vertically
pivoted in accordance with the machine cycle is also
beneficial to a compact setup and an exact and reliable
pivoting upward and downward owing to a simple design of
the bearing.
If, with such a shaft, also drive means as well as
lateral displacement means act on an extension of the shaft
from outside, this means that it is possible to prevent, to
a large extent, the drive means and the displacing means
from acting on the space between the side frames of the
feed table. The drive means and the displacing means may
be neatly provided outside the side frames in a compact
manner without taking up the little space available between
the side frames. Such a neat and compact arrangement
permits a feed table, which is easy to operate, as well as
the use of precisely working drive mechanisms.
The features contained in Claim 6 represent a
preferred and particularly advantageous embodiment of
simple and reliable lateral displacement means which ensure
an extremely simple and reliable alignment.
The features of Claim 7 relate to an embodiment of
a drive for the conveying means, which is particularly
advantageous in view of design and operational reliability,
the lateral displacing drive and the pivoting upward and
downward of the lever. The control of the axial cam disk
and the radial cam disk is concentrated on one driven
control shaft.
Owing to the feature of Claim 8, all control means
may be gathered in a compact manner on one single feed-
table side.
The feature of Claim 11 includes particularly
advantageous, space-saving and easy-to-operate drive means
permitting a particularly reliable drive.
Lateral aligning limitations in form of feed plates
which are laterally adjustable with respect to their
lateral position and which are out-of-contact with the
. .~ .
.
2 ~
WH-8362-91 - 6 -
rotating conveying means permit a particularly simple
format adjustment. Even given a short feed table, the
sheet may be laterally brought, by means of the conveying
means, into abutting relation with the aligning edges
provided in front of and behind said conveying means and be
precisely aligned at the interrupted edges as it were one
long edge. Such an aligning limitation is adjustable with
respect to the entire format range and is restricted
neither by the conveying means wi-th its drive nor by the
drive nor by the control means for la-teral alignment.
A preferred specimen embodiment of the lateral
aligning limitation is described by the feature of Claim 9.
The developmen-t of the feed plate, the extension of which
is used as lay edges, is easy to design, precisely
adjustable, easy to replace, easy to operate and to
maintain, thus also serving the purpose of exact sheet
alignment.
In an especially favourable additional development,
front lays rotating over the region of the rotating
conveying means complete the entire reliable and exact
conveying and aligning process which is effected along the
side edge and additionally at the leading sheet edge, said
front lays having a rear point of reversal in the region of
the feed rollers, seen in conveying direction, and being
driven by a drive shaft in a respective point of reversal,
via a gear train, a drive connection existing between the
printing unit and the drive shaft. The rotating front
lays, the speed of which is somewhat lower than the speed
of the conveyed sheet, favour a continuous and exact
aligning of the sheet at its leading edge, even given great
conveying speeds.
It is also possible wi-th the present invention to
easily convert, in a printing and perfecting machine
comprising double feeding of the sheet pile, the lateral
sheet-aligning means from the one side to the other fxee of
play and with little effort.
3 ~
WH-8362-91 - 7 -
According to the invention, feed plates for
alternately aligning -the fed sheets are provided on both
sides thereof, the sheets to be aligned being moved towards
said feed plates by means of a conveyor roller which is
driven so as to be axially movable by a double control cam
such that the sheets to be aligned are fed by the conveyor
roller so as to abut laterally against one feed plate or
the other. This solution permits the pressman convert the
aligning means provided on the feed table before printing
on the second sheet side so that, even given a sheet pile
which has been turned over, each sheet is aligned at the
same edge in order to achieve an optimum register accuracy,
which is especially advantageous if the paper sheets to be
processed differ somewhat in size.
In an advantageous embodiment of the invention, a
cam roller is assigned to the double control cam; via a
double lever, a first control roller and a grooved disk,
said cam roller transmits the movement of stroke onto a
journal of the conveyor roller; via a connecting rod which
carries a further grooved disk, a compression spring
transmits the spring force onto a control roller which, via
the double lever, presses the cam roller against the one or
the other cam of the double control cam; and, via an
abutment, the direction of force of the compression spring
is reversible with respect to its direction of action.
In a further embodiment, the compression spring is
provided on the connecting rod and is limited on both sides
thereof by means of a respective retaining ring with
respect to its extension; the abutment surrounds said
compression spring in longitudinal direction, and said
abutment is guided in sliding guidances and is axially
displaceable by means of an eccentric pin such that, one
one side, said compression is braced against said abutment
and, on the other side, it is braced against a retaining
ring or vice versa so that the force acts in the one
direction or the other. In this embodiment, the feed
plates provided on both sides of the sheets to be fed may
: :
.
:
2 ~ 3 ~
WH-8362-91 - 8 -
be secured on a common tubular traverse which is mounted on
the connecting rod and is laterally adjustable via a
handwheel having a thread. Owing to this simple solution,
converting the lateral sheet alignment from one side to the
other may be effected free of play and with little
constructional efforts.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
A specimen embodiment of the invention is
schematically illustrated in the drawings, wherein:
Figure 1 is a general side elevational drawing of a
printing machine comprising a device according to the
invention;
Figure 2 is a side elevational view of the device
according to the invention;
Figure 3 is a plan view of the device according to
the invention;
Figure 4 shows, by way of example, a conveying
means having balls resting thereon, according to line 4-4
of Figure 2;
Figure 5 is a cut through device along line 5-5 in
Figure 2 comprising driven return pulleys for the front
lays;
Figure 6 shows a lateral displacing mechanism;
Figure 7 shows, by way of example, a side
elevational view of a control for the feed rollers;
Figure 8 is a fragmentary longitudinal section
through the device;
Figure 9 shows a detail of the control system;
Figure 10 is a fragmentary cross-section through
the device taken along line 3-3 in Figure 9;
Figure 11 is a fragmentary cross-section through
the device taken along line 4-4 in Figure 8;
Figure 12 is a fragmentary longitudinal section
through the converting mechanism;
3 ~
WH-8362-91 - 9 -
Figure 13 is a fragmentary cross-section through
the converting mechanism taken along line 6-6 in Figure 8;
and
Figure 14 is a top view of the converting
mechanism.
DETAILED DESCRIPTIQN OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
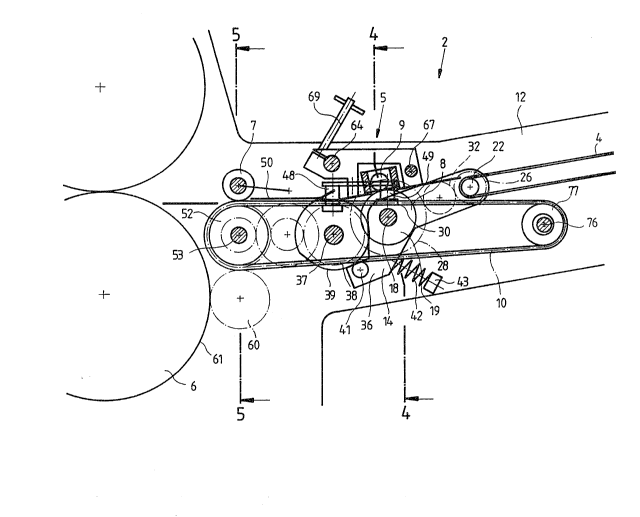
Paper sheets are conveyed from a pile 1 to a
printing unit 3 across a feed table 2 of a sheet-fed offset
printing machine comprising a single-sheet feeder. In the
specimen embodiment, the paper sheets are transported to a
conveying and aligning section 5 by means of conveyor tapes
4. Thereafter, the corresponding feed rollers 7, 52 bring
the paper sheets into an abutting relation with a gripper
bar (not illustrated) provided in the impression cylinder
6. Said impression cylinder 6 is supported in machine side
frames 15, 16; the shafts 17 and 53, respectively, of the
feed rollers 17 and 52, respectively, are supported in the
side frames 11, 12 of the feed table. The rotating
conveying means 8 and the rotating front lays 10 are
located in the conveying and aligning section 5.
The shaft 18 of the rotating conveying means 8 on
which conveyor rollers 19 are secured extends, on both
sides thereof, through openings 20 provided in the side
25 frames 11, 12 of the feed table 2 and is mounted in
bearings 21, outside of the side frames 11, 12, so as to be
rotatable and displaceable. Said bearings 21, in turn, are
secured in through bores provided in the levers 13, 14.
The levers 13, 14 are mounted on a shaft 22 in the
30 bearings 23, 24 provided outside the side frames 11, 12,
said shaft being rotatably supported in the side frames 11,
12 and being followed by the conveyor rollers, seen in
conveying direction. Gearwheels 25, 26 are provided on the
outward extended journals of said shaft 22.
On its journal 27 which extends over the right side
frame 12 and the bearing 21 provided in the lever 14, the
extension of the shaft 18 is provided with a gearwheel 28
'
. .
2 ~ 3 ~
WH-8362-91 - 10 -
and a deep circumferential groove 29 with which the axial
displacement roll 30 is in an operatively sliding contact
relation.
A broad gearwheel 32 meshing with the gearwheels 26
and 28 is rotatably mounted on a bolt 31 provided at the
lever 14.
A control shaft 37 extending - like the shafts 18
and 22 - transversely over the width of the feed table is
provided downstream of the conveyor rollers 19, seen in
conveying direction, and rotatably mounted below the table
plate (which, for the sake of clarity, is not illustrated)
in the side frames 11, 12 carrying the table plate. Said
control shaft 37 extends through and beyond the two side
frames 11, 12 and lies outside the range of action of the
lever 14. A gearwheel 38 is secured on its left extension.
A respective radial cam disk 39 is secured at each of the
two extensions. And an axial cam disk 40 is attached to
the front end of the right extension.
A respective radial sensing roll 41 the
circumferential surface of which is brought into contact
with the corresponding radial cam disk 39 from below is
rotatably mounted on each end 35, 36 of the levers 13, 14,
said lever ends being located opposite the rotatable
bearing of the shaft 22. In order to maintain this
contract relation, a respective spring 42 which is braced
against a support 43 attached to the respective outside of
the side frames 11, 12 engages the underside of the lever
ends 35, 36.
An axial displacement lever 45 having two lever
arms 46 and 47 is pivot-mounted in a mounting support 44
which is secured at the outside of the side frame 12 above
the common tangent planes of the shafts 37 and 18 and
outside the range of action of the lever 14. The ends of
the two lever arms 46 and 47 are provided with bolts 48, 49
pointing downward, an axial sensing roll 50 and the axial
displacement roll 30, respectively, being rotatably mounted
at each lower end of said bolts. Said axial sensing roll
2 ~ 3 ~
WH-8362-91 - 11 -
is in constant contact with the axial cam contour of the
axial cam disk 40. In order to maintain this contact, a
spring 51 is braced, between supporting bearings (not
illustrated), against the axial displacement lever arm 46
and against the side frame 12 of the feed table.
At the end of the feed table, seen in conveying
direction, the feed rollers 52 and 7 are secured on the
shafts 53 and S4 extending transversely to the conveying
direction and over the width of the feed table 2. The
shaft 53 of the feed rollers 52 is rotatably mounted in the
side frame 11 below the table plate. The gearwheels 55,
56, 57 are secured on its extension projecting outward
through the left side frame. In a known manner, the
gearwheel 55 is drivingly connected with the impression
cylinder 6, e.g. via a gearwheel 40 and the gear rim 61.
Via intermediate gearwheels 58a and 58b, which are mounted
on a bearing bolt rotatably supported at the left side
frame 11, the gearwheel 56 meshes with the gearwheel 38.
The gearwheel 57 i3 drivingly connected with the gearwheel
25 of the shaft 22 via a toothed tape 59.
As shown in Figures 2 and 4, a traverse 61 is
secured between the side frames 11, 12 over the width of
the feed table 2, said traverse having guide bushes 60
which are aligned perpendicularly to the shaft 18 of the
conveyor rollers 19 and to the conveying plane. Below the
traverse 61 there is secured a retaining metal sheet 62.
Below the round guide bushes 60 the retaining metal sheet
is provided with circular through openings 63 the diameter
of which is smaller than the diameter of the balls 9
loosely inserted in the guide bushes 60 such that the
respective ball segments or cups of the balls 9 project
downward through the retaining metal sheet. With the
conveyor rollers 19 being pivotted upwards, the balls rest
freely on the conveyor rollers or on a sheet of paper, if
there is a sheet of paper on said conveyor rollers 19. The
moment the conveyor rollers 19 are moved downward, the
balls 9 are also lowered until they rest on the rims of the
'
. : .
WH-8362-91 - 12 -
openings 63 provided in the retaining metal sheet 62. The
conveyor rollers are lowered below this receiving position.
Depending on the quality of the paper, the format or other
individual requirements the balls may be exchanged from
above with respect to their number or their quality. The
balls 9 may be axially positioned such that they are
axially loca-ted above a conveyor roller during the entire
lateral displacement. Moreover, it is also conceivable to
use other kn~wn ball-res-ting devices, e.g. laterally
adjustable guide bushes.
Above, in front of and behind the guide rollers 19,
the guiding rods 64, 67 extending transversely over the
width of the feed table are fastened to the side frames 11,
12. A mounting support 65 having a metal sheet 68 attached
to the side facing the side frame 11 is mounted on the
guiding rods 64, 67 so as to be axially displaceable, said
mounting support 65 and said metal sheet 68 bridging the
ball-resting traverse 61. In front of and behind the
conveyor rollers 19, the metal sheet 68 is provided with
extensions 66 extending downward below the conveying plane.
These extensions 66 do not contact the conveyor rollers 19
and serve as lateral lay edges. For laterally adjusting
the position of the lay edges, the mounting support 65 may
be laterally fastened by means of a fixing means 69 with
respect to the guiding rod 64.
The device operates as described hereinafter: The
shaft 53 is driven, via the gearwheel 55, synchronously and
in accordance with the machine cycle, a drive connecting
extending from the impression cylinder 6 to said shaft.
The conveyor rollers 19 are driven synchronously via the
drive connections 57, 59, 25, 22, 26, 32, 28 and via the
gear train 56, 58a, 58b, 38 of the control shaft 37, said
control shaft 37 being driven synchronously and in
accordance with the machine cycle. In their upper
position, the conveyor rollers 19 take over, with the aid
of the resting balls 9, the transport of the sheet supplied
from the feed pile 1 by the conveyor tapes 4. By pivoting
2 ~ 3 ~
WH - 8362 - 91 - 13 -
the axial displacement lever 45, the shaft 18, together
with the conveyor rollers 19, is laterally displaced
towards the lay edges 66; this pivoting motion is achieved
by the spring 51 which ensures that the roll 50 runs on the
5 axial cam disk 40. With the aid of the resting balls 9,
the sheets are frictionally moved laterally to the edges 66
by means of the conveyor rollers 19 and aligned along their
side edges. During the lateral displacement, the gearwheel
28 continues to mesh with the gearwheel 32 due to the
broadened design of said gearwheel 32. The moment the
leading sheet edge reaches the synchronously driven feed
rollers 52 which are responsible for its further transport,
the conveyor rollers 19 are lowered with the aid of the
levers 13 and 14. The lowering is controlled by the radia].
15 sensing roll 41 which, by means of the spring 42, runs on
the respective contour of the radial cam disk 39, 75.
The balls 9 are now carried by the retaining metal
sheet 62. With its trailing edge, the sheet slides over
the guide plates of the feed plate. In cooperation with
20 the spring 51, the axial cam disk 40 now causes the axial
return of the conveyor rollers 19, the radial cam disks 39,
75 and, in cooperation with the spring 42t the lifting of
the levers 13, 14 and the conveyor rollers 19 in time for
conveying the following sheet.
The feed rollers 52 are driven by the gearwheel 55
via the shaft 53. AS illustrated in Figures 5 and 7, the
feed rollers 7 cooperating with the feed rollers 52 in
accordance with the machine cycle may be secured, e.g., on
a shaft 17 extending over the width of the feed table 2 and
30 being supported, on both sides thereof, in a lever 70.
Each of the levers 70 iS rotatably mounted on a
respective bearing bolt 71 provided at the side frames 11,
12. A sensing roll 72 iS rotatably mounted, at least, on
one lever arm of a lever 70. Via a spring 73 acting on the
35 lever 70 and being braced against a mounting support 74
provided at the side frame 11 the sensing roll 72 is in a
friction contact relation with a cam of the radial cam
2 ~
WH-8362-91 - 14 -
disk 75 which, e.g., is also secured on the control shaft
37 (s. Figures 3 and 7). Thus, it is possible to pivot
also the feed rollers 7 up and down in accordance with the
machine cycle as well as the conveyor rollers 19 by means
of one and the same con-trol shaft 37.
In a preferred embodiment of the device for
conveying and aligning, according to the invention,
additional front lays are designed in the form of rotating
front lays 10, as illustrated in the figures. Seen in
conveying direction, a shaft 76 is rotatably mounted
between the side frames 11, 12 and upstream of the conveyor
rollers 19, as shown in Figures 2 and 3. Synchronously
running tapes 79 having leading-edge stops 80, which are
secured thereon and which project upwards through slits
provided in the guide plates 81 of the table plate, run
around the rollers 77 attached on the shaft 76 and around
the rollers 78 secured on the shaft 53 between the feed
rollers, as can be seen in Figure 5.
In the area of the rotating conveyor rollers 19 the
tapes 79 pass between the spaced conveyor rollers 19, as
illustrated in Figures 2 and 3. The distances between the
conveyor rollers 19 with respect to each other are such
that there is still axial play between the tapes during the
lateral displacement of the conveyor rollers 19. The
distance between the upper and the lower strand of the
tapes 79 is selected such that there is radial play with
respect to the strands during the up-and-down-pivoting of
the shaft 18 arranged between both strands (s. Figure 2).
The tapes 79 are also driven by the shaft 53.
In this embodiment the sheets arriving from the
conveyor tapes 4 are simultaneously laid laterally against
the side lay edges 66 and against the leading-edge stops
80.
The table plate between the conveyor rollers 19 and
the feed rollers 52, 7 consists, e.g., of plates (not
illustrated for the sake of clarity) secured between the
side frames ll, 12; however, it may alternately consist of
WH-8362-91 - 15 -
rails located below the tapes 79 of the front lays 10
rotating in accordance with the machine cycle.
The shaft 22 drives the conveyor tapes 4
additionally.
Owing to the conveying plane being bent slightly
upwards between conveyor roller 19 and front lays 10, as
illustrated in Figure 2, the stability of the sheet is
increased during the aligning.
It is also conceivable to provide a respective
axial cam disk having two displacing lever configurations
on each side of the control shaft 37.
In Figure 8 two feed plates 103 for laterally
aligning the sheets on the feed table are provided between
the side frames 101, 102. The feed plates 3 are fastened
to holders 4 which, in turn, are clamped on-to a tubular
traverse 5. Said tubular traverse 5 is mounted on an
axially displaceable connecting rod 6 by means of a bearing
7 and may be laterally adjusted via a handwheel 8 and a
thread 9. The handwheel is braced against a bearing body
10 which is fastened to the side frame 1. The
counterpressure is generated by a compression spring 11
which is provided on the opposite side, said compression
spring being braced against a bearing body 12 which, too,
is fastened to a side frame 2. Thus, it is possible to
precisely adjust the feed plates 3 for the sheets to be
printed via the handwheel 8. The bearing bushings 13, 14
which permit the axial movement of the connecting rod 6 are
provided in the bearing bodies 10, 12.
A double control cam 15 having two radial cam disks
16 is secured on a drive shaft 24 (Figures 8 and 9). In
the specimen embodiment illustrated, a cam roller 17 abuts
one one side thereof against a cam disk 16. The cam roller
17 is fastened to a double lever 18 which is tiltably
mounted in a bearing body 19, said bearing body 19 being
fastened to the side frame 2. At the opposite end of the
double lever 18 there is provided a first control roller 20
engaging in a grooved disk 21. Said grooved disk 21 is
3 ~
WH-8362-91 - 16 -
secured on the journal 22 of a conveyor roller 23 which,
too, is mounted in the side frames l and 2.
Figure 10 shows the double lever 18 having a cam
roller 17 engaging in the control cam 15. Opposite said
cam roller 17 said double lever 18 is provided with a
further control roller 25 engaging in a grooved disk 26
which, in turn, is secured on the connecting rod 6. If the
drive shaft 24 imparts to the control cam 15 a rotary
motion, the cam roller 17 transmits a pendular motion onto
the double lever 18. Due to this pendular motion the
control roller 25 drives the grooved disk 26 and causes the
connecting rod 6 to execute an axial movement of stroke.
Simultaneously, the conveyor roller 23 is axially displaced
in opposite direction, via the first control roller 20, as
indicated by the double arrow in Figure 9.
Figure 11 shows the feed device for single sheets
27 which are moved by the conveyor roller 23, in connection
with a ball 28 resting thereon, in the direction of the
arrow and perpendicularly thereto up to the contact
surfaces 29 of the feed plates 3. For laterally adjusting
the feed plates their holders are clamped onto the tubular
traverse 5 by means of a tommy screw 30 so as to be
detachable. The range of adjustment of the handwheel 8 is
limited by the stop 31. For this purpose the handwheel 8
is provided with a trip dog 32 and the stop 31 is provided
with a further trip dog 33~ said trip dogs colliding with
each other during the ro-tary motion of the handwheel 8,
thus avoiding further rotation. In order to prevent the
holders 4 of the feed plates 3 from being affected due to
the rotary motion, there is provided a guiding rod 34 on
which the holders 4 are supported.
Figures 12 through 14 show the end of the
connecting rod 6 which lies opposite the grooved disk 26;
on said connecting rod there is provided a compression
spring 35 which, on both sides thereof, is limited by means
of disks 36 and retaining rings 37 with respect to its
extension. An abutment 38 surrounds the compression spring
2 ~ 3 ~
WH-8362-91 - 17 -
in longitudinal direction. Said abutment 38 is guided on
two sliding guidances 39 and is axially displaceable by
means of an eccentri.c pin 40 for converting the direction
of the spring force. Said eccentric pin 40 is fastened to
a tommy 41 which is mounted in its bearing 42 provided at
the side frame 1. The abutment 38 has a recess 43 which
extends around the connecting rod and which is dimensioned
such that the disks 36 may come into contact with the
respective side of said abutment. With said abutment 38
being located as shown in Figure 5, the compression spring
35 is in a right position so that, on its left side, it is
braced against the right side of the abutment 38 and abuts
against the left retaining ring via the disk 36. In this
connection, the force of the compression spring 35 present
in the connecting rod 6 is directed to the left (Figure
12). As shown in Figure 14, the eccentric pin 40 may be
moved into a middle position (tommy 41 indicated by a dash-
dot line) in which no spring force acts on the connecting
rod.
Depending on the fact in which direction the force
of the compression spring 35 acts, the connecting rod 6
transmits a spring force onto the double lever 18, via the
grooved disk 26 and the control roller 25, so that the cam
roller 17 located opposite the double lever 18 abuts
against the one cam disk 16 or the other, which makes it
possible to control the axial movement of stroke of the
conveyor roller 23 via the first control roller 20 and the
grooved disk 21 such that the fed sheet abuts against
either the right or the left feed plate 3. If the backside
of a sheet is to be printed on, the pressman has only to
shift the tommy 21 into the other position after having
turned the sheet pile and inserted it in the sheet feeder,
and the same edge of the fed sheet abuts against a feed
plate 3 so that differences in the size of the sheets have
no detrimental effects on the register.
Although various preferred embodiments of the
present invention have been described herein in detail, it
2 ~
WH-8362-91 18 -
will be appreciated by those skilled in the art, that
variations may be made thereto without departing from the
spirit of the invention or the scope of the appended
claims.
': .
',