Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
- 1 _ 2054859
DOWN CONVERTER FOR SATELLITE COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
The present invention relates to a down converter for use
in satellite communication system, and, more particularly, to
a down converter for microwave digital satellite
communication.
The local signal used for frequency conversion by the
down converter in a microwave digital satellite communication
system requires a high quality in terms of frequency
probability, frequency stability, and phase noise
characteristic.
To enable the prior art to be described with the aid of a
diagram, the figures of the drawings will first be listed.
Fig. 1 is a block diagram of a down converter for use in
a satellite communication system according to an embodiment of
the present invention; and
Fig. 2 is a block diagram of a conventional down
converter for use in a satellite communication system.
The prior art down converter DC' described below with
reference to the Fig. 2 has a microwave signal MS of a
frequency such as 12 GHz input to a microwave low noise
amplifier 5 through a microwave input terminal 1. The
amplifier 5 amplifies the signal MS and produces an amplified
microwave signal MSa that is input to a mixing circuit 6.
Through an input terminal 3, a standard signal SS' having
a frequency in the order of MHz is inputted to a phase locked
oscillator (PLO) 9 which produces a phase synchronized signal
SSs' having a frequency such as 2.15 GHz. The phase
synchronized signal SSs' is input to a frequency multiplier 8
which produces a local signal sse ~ of a microwave band at a
frequency range of ten GHz, by multiplying the signal SSs' by,
e.g. five (2.15 GHz X 5 = 10.75 GHz). The local signal sse
is input to the mixing circuit 6.
In the mixing circuit 6, the frequency difference between
the amplified microwave signal MSa and the local signal sse
is obtained to produce an intermediate frequency signal IF'
2054859
_ - 2
having a frequency range of, for example, 950 MHz. The
intermediate frequency signal IF' is input to an intermediate
frequency amplifier 7 and is thereby amplified to produce an
amplified intermediate frequency signal IFa' at an output
terminal 2. DC power is supplied at a terminal 4 to a power
source circuit 10 for driving the down converter DC'
According to this prior art down converter DC', the
terminals 2, 3 and 4 are provided for connection to a next
stage circuit component, such as a receiver. Thus, if a cable
is used, a 3-line cable is necessary to connect the terminals
2, 3, and 4 to the next stage component.
As a result, this conventional down converter DC'
requires a number of lines in a cable, or a number of separate
cables, for connection to the next stage component, resulting
in difficulties of installation and maintenance, degradation
of reliability, and an increase of cost.
The present invention has been developed with a view to
substantially solving these disadvantages and has for its
essential object to provide an improved down converter for use
in a satellite communication system.
To this end, the invention consists of a down converter
for converting a microwave signal to an intermediate frequency
signal using a standard signal having a frequency range of
several to several tens of MHz, and for applying said
intermediate frequency signal to a next stage component, said
down converter comprising: a mixing means for producing said
intermediate frequency signal indicative of a frequency
difference between said standard signal and said microwave
signal; and a separator means comprising: a first terminal for
receiving said intermediate frequency signal; a second
terminal for producing and supplying said intermediate
frequency signal to said next stage component and for
receiving said stAn~rd signal from said next stage component;
a first filter means for separating said standard signal; and
a third terminal for producing said standard signal to said
mixing means.
205485~
- 3 -
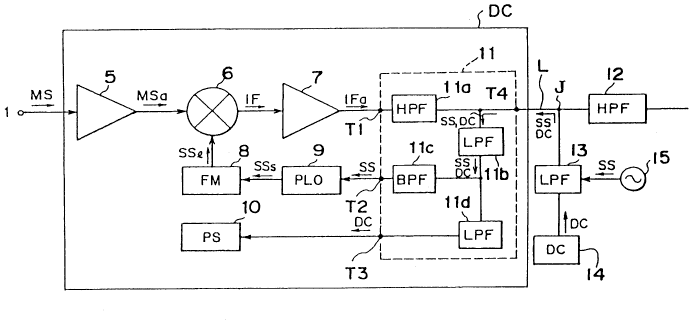
Referring to Fig. 1, the microwave input terminal 1 is
connected to the low noise amplifier 5 which is further
connected to the mixing circuit 6 which is in turn connected
to the intermediate frequency amplifier 7. The intermediate
frequency amplifier 7 is then connected to a signal separator
11 which has four terminals T1, T2, T3 and T4. Terminal T1 is
connected to the intermediate frequency amplifier 7. Terminal
T2 is connected to the phase synchronizing oscillator 9 and in
turn to the frequency multiplier 8, which is further connected
to the mixing circuit 6. Terminal T3 is connected to the
power source circuit 10. Terminal T4 is connected to a
junction J that is connected to a high pass filter 12 and a
low pass filter 13. The low pass filter 13 is further
connected to a DC generator 14 and a standard signal generator
lS which generates a standard signal SS having a frequency of
several to several tens of MHz.
According to the present embodiment, the down converter
DC is defined by circuits 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 and 11. The
circuits 12, 13, 14 and 15 are provided in a next stage
component, such as a receiver. The connection between the
down converter DC and the receiver, i.e., between the terminal
T4 and the junction J is by a single line cable L.
The signal separator 11 includes a high pass filter lla,
a first low pass filter llb, a band pass filter llc, and a
second low pass filter lld.
In operation, a standard signal SS having a frequency of
several to several tens of MHz, for example 10 MHz, is
generated from the generator 15. This standard signal SS and
a DC current from the generator 14 are supplied to the low
pass filter 13. The DC current and the standard signal are
thus transmitted from the junction J to the terminal T4
through the line L. Because of the high pass filter 12, the
standard signal SS and the DC current will not be transmitted
to the next stage circuit connected to high pass filter 12.
In the signal separator 11, the standard signal SS and
the DC current are transmitted through the first low pass
filter llb and are separated by the band pass filter llc and
2054859
- 4 -
the second low pass filter lld. The band pass filter llc thus
produces the standard signal SS of 10 MHz to the oscillator 9
through the terminal T2, and the second low pass filter lld
provides the DC current to the power source circuit 10 through
the terminal T3.
In the oscillator 9, a phase synchronized signal SSs
(2.15 GHz) is produced with reference to the standard signal
SS (10 MHz) and is applied to the frequency multiplier 8. In
the frequency multiplier 8, the phase synchronized signal SSs
is multiplied, e.g., by five, so that a local signal SS~
(10.75 GHz) is applied to the mixing circuit 6.
In the meantime, a microwave signal MS having a high
frequency range, such as in the order of 12 GHz, is input to
the amplifier 5 through the terminal 1 and further applied to
the mixing circuit 6.
In the mixing circuit 6, the frequency difference between
the signal MSa (about 12 GHz) and the signal SS~ (10.75 GHz)
is obtained to produce an intermediate frequency signal IF
having a frequency in the range of 950 to 1450 MHz. This
intermediate frequency signal IF is input to the amplifier 7
and further to the frequency distributor 11 through the
terminal T1.
The amplified intermediate frequency signal IFa passes
through the high pass filter lla, and is further applied
through the line L to the high pass filter 12.
It is noted that the signal IFa will not pass through the
low pass filters llb and 13.
The down converter DC thus requires only one cable line L
for its connection to the next stage component.
Although the present invention has been fully described
in connection with the preferred embodiment thereof with
reference to the accompanying drawings, it is to be noted that
various changes and modifications are apparent to those
skilled in the art. Such changes and modifications are to be
understood as included within the scope of the present
invention as defined by the appended claims unless they depart
therefrom.