Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2062711
TITLE OF THE INVENTION
INK-JET PRINT HEAD USING ELECTROMAGNETIC PUMPING METHOD
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
This invention relates to a print head of ink-jet printer
of drop-on-demand type, and more particularly to an ink-jet print
head for ejecting ink by an electromagnetic force responding to
an externally applied voltage.
TECHNICAL BACRGROUND OF THE INVENTION
In general, ink-jet recording technique is the method of
reproducing certain visible pattern on recording media such as
paper by a group of electronically controlled ink drops. In the
ink-jet recording, ink drops from the nozzle (orifice) adhere to
the printing media which faces the ink-nozzle, thereby resulting
in visible pattern.
2062711
Although there are more than twenty ink-jet printing
methods, most of the ink-jet printers can be categorized into
either one of:
(1) Drop-on-Demand type (DOD) or
(2) Continuous Ink-jet type,
wherein among several different DOD-type ink-jet printing
methods, most popular types of this category may be:
(A) Thermal Ink-jet or Bubble-jet or
(B) Piezo-electric element type.
The heart of the thermal ink-jet (or bubble-jet) (A) is
resistive heating element placed inside an ink-chamber. One face
of the ink-chamber has a hole connected to an orifice which is
a tiny hole through which ink drop is ejected toward the
recording media. Enormous heat generated instantaneously from
the heating element due to current flow through the heating
element evaporates ink and the pressure from the ink vapor
accelerates the ink inside the ink-chamber toward the orifice to
form a high speed ink drop when it escapes from the orifice.
Ink-jet head of this type has complicated shape and has problem
in reproducing continuous tone since the size of the ink-drop is
hard to control.
- $nk-jet head of type (B) has piezo-electric crystal which
vibrates in accordance with the voltage signal applied across the
- 2 -
206271~
crystal. The vibrating energy is transferred to the motion energy
of the ink-drop to form ink-drops. The drawback of this type is
that the rate of ink-drop formation is low (2-3 KHz) causing low
printing speed.
Continuous steam of ink drop is formed in the type (2) by
using ink pump and vibrating nozzle. The flight path of the ink
drop is modified when it passes through a deflecting electrode
following charging electrode. The rate of the ink-drop formation
is high (lOOKHz or above) and it enables the reproduction of
continuous tone. However, since the system is complicated, the
system tends to be large and high in price. And, in addition,
maintaining the stream of ink-drop steadily still remains as a
problem.
~UIIIIaRY OF THE INVENTION
lS An object of this invention is to provide an electromagnetic
pumping ink-jet print head capable of effective continuous tonal
gradation of print image in response to an input print signal.
The other object of this invention is to provide an ink-jet
print head with simpler structure for ejecting the ink by means
of an electromagnetic pumping method.
According to the present invention, an ink jet print head
of drop-on-demand type for ejecting a conductive ink by
electromagnetic pumping is provided with a magnetic field
- 3 -
2062~11
generating means for generating a uniform magnetic field from afirst space to a second space, and a pumping tube member
comprising a plurality of pumping tubes having isolated first and
second electrodes formed separately in a center of an insulation
S panel at regular intervals, being installed in a magnetic field,
wherein the conductive ink is ejected from the pumping tube by
applying a voltage to the first and second electrode.
BRIEF DE8CRIPTION OF THE DRAWING8
A more complete appreciation of the invention, and many of
the attendant advantages thereof, will be readily enjoyed as the
same becomes better understood by reference to the following
detailed description when considered in conjunction with the
accompanying drawings in which like members indicate the same or
similar components, wherein:
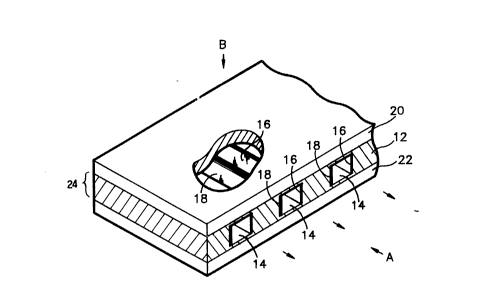
Fig.l is an exploded view of an electromagnetic pumping ink-jet
print head of this invention;
Figs.2A and 2B is a front and plan view of the print head as
shown in Fig.1;
Figs.3A and 3B is a detailed and enlarged view of essential part
of the exploded view as shown in Fig.1;
Fig.4 is a front view of an electromagnetic pumping tube; and
Figs.5A and 5B are a graph of variation of tone responding to a
time and applied voltage.
:
-- 4 --
2062711
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF PREFERRED EM~ODIMENT8
A pumping tube member incorporating a plurality of pumping
tubes comprising an isolated first and second electrodes into its
body at regular intervals is located in a electromagnetic space
of a given and uniform magnetic field generated from a first
space to a second space.
By applying a positive voltage to the first electrode and
a negative voltage to the second electrode, a given amount of
current flows from the first electrode to the second electrode.
By the current flow between the two electrodes, a conductive ink
in the pumping tube is accelerated and ejected toward an exit
side according to a Fleming's left-hand rule.
For a pumping tube of the pumping tube member, a shape of
quadrangle tube is desirable, and the first and second electrodes
are fitted or coated separately on a right and left inner wall
of the quadrangle tube. The first and second electrodes are of
good conductive metal and positioned to an axial direction.
By placing the pumping tube in an electromagnetic space
where a uniform magnetic field is applied from the first space
to the second space, the conductive ink of the pumping tube is
ejected by applying a drive voltage to the electrodes of the
pumping tubes.
With reference to Fig.l, an electromagnetic pumping ink-jet
- 5 -
2062711
print head comprises a pumping tube member 24 comprising an
insulation panel 12 and a plurality of pumping tubes 14 having
a first and second electrodes 16, 18 installed in the center of
the insulation panel 12 at regular intervals, and a first and
second magnet panel 20, 22 installed on the top and bottom side
of the pumping tube member 24 for applying a uniform magnetic
field to it.
The insulation panel 12 is an insulating material of glass
or silicon wafer, which is treated equivalently. The first and
second electrodes 16, 18 are a positive electrode (+) and a
negative electrode (-) respectively, and are of good conductive
material.
The first and second electrodes 16, 18 are coated on an
inner wall of right and left side of each pumping tube 14 by such
lS a plating method.
With reference to Figs.2A and 2B, a magnetic pole of S, N
of the first and second magnet panel 20, 22 is arrayed from a top
side to a bottom side in order, and each pumping tube 14 has a
given height H and width L3.
With reference to Fig.3A, the insulator 12 of hexahedron
having a given height N, length L and width L2 forms a tube 14
in a direction of length, and the first and second electrode 16,
18 i8 coated on a left and right inner side of the tube 14.
- 6 -
206271~
Fig. 3B is showing a more detailed position of the first and
second electrode 16, 18 in the insulation panel 12. Fig.4 i6 a
front view of the tube 14 as shown in Fig.3A and for describing
a principle of electromagnetic pumping. Fig.5A and 5B is a curve
graph of tone of an electromagnetic pumping ink-jet print head
and shows a correlation of an applied voltage V to the fi-st and
second electrode 16, 18 and a time to be varied. A shape of the
tube is illustrated as a quadrangle for convenience and
simplifying a model in Fig.l to Fig.4.
For describing an operation, it is assumed that a uniform
magnetic field is applied to the pumping tube member 24 by the
first and second magnetic panel 20, 22, and each tube 14 is
filled with an ink of conductive material.
When a given state of voltage V corresponding to a print
signal is applied across the first electrode 16 and second
electrode 18 of the pumping tube 14, current flows from the first
electrode 16 (positive electrode +) to the second electrode
18(negative electrode -).
Assuming that a magnetic field strength of the pumping tube
member 24 is B ( shown as a vector ~), current density per unit
length from the first electrode 16 to the second electrode 18 is
I (shown as a vector I), the conductive material in the pumping
tube 14 experiences a force directed to the direction of axis by
Fleming's left-hand rule. If the force directed to the direction
S of axis is indicated as F (shown as a vector F), F is expressed
- 7 -
2062711
as an equation:
F = L3 ` I x B.. (1)
wherein L3 is an inner width of the pumping tube 14.
Assuming that the applied voltage between the two electrodes
16 and 18 of the pumping tube 14 is V, the current I in the
equation (1) is expressed as:
I = R ~ (2)
wherein R is the resistance.per unit length of a conductive
material filled in the tube 14.
The resistance R of the equation (2) is expressed as:
' R-p L3 ........ (3)
: wherein p is a coefficient of resistance of the conductive
ink~ filled in the pumping tube 14, ~ is its inner width and H is
it8 height.
:~ 15~ ~ Arranging the equation (1),(2),and (3), F can be expressed
~ ~a8 an quation:
,, :
F - ~3IB = L3 x L3 xB
P H
8 -
::
, :
2062~11
. .
L V
3 x B
H
L VH
3 xB
pL3
VH x B ..... - ( 4 )
Consequently the conductive material in the pumping tube 14
is accelerated by a force F calculated by the equation (4) in the
pumping tube member 24 installed between the first and second
magnet panel 20, 22.
Assuming that the density of the conductive material filled
in the tube 14 is "d" and friction and viscosity resistance are
negligible, the acceleration "a" of the conductive material
caused by a force F is expressed as:
a= d~LB = dVLB ,,,,, (5)
Assuming that the conductive material filled in the pumping
tube 14 of the pumping tube member 24 is ink, the ink is ejected
toward the exit of the tube 14 with an acceleration ~ determined
by the equation (5).
Assuming that an initial speed of the ink ejected from the
tube 14 of the pumping tube member 24 is "O"(zero), the amount
of ink Q ejected for a time t at an acceleration determined by
the equation ~5) is expressed as:
2062~
p= lat2= 2Bdt ,,..(6)
Accordingly the conductive ink in the pumping tube 14 of
height "H" and width "L3" is ejected by a force "F" and
acceleration "a" determined in the equation (4) and (5) owing to
a voltage "V" applied between the first and second electrode 16,
18 of the pumping tube 14. So it is proved that the amount of ink
Q ejected with the force F and the acceleration (a) is controlled
by adjusting the applied voltage V or the time t in the equation
(6).
The ink is ejected from the tube and adhere to a printing
paper (not shown in drawings) facing with the pumping tube 14,
and an pictorial image is formed on the paper. The tone of the
pictorial image formed on the paper is varied greatly by the
ejected amount of ink Q.
For simplicity, assuming that the tone is proportional to
the amount of ink, expression of tone of pictorial image is
possible by changing the voltage applied to the first and second
electrode 16, 18 and a time (t) of applied voltage V in the
equation (6).
By applying a voltage V of square wave across the two
electrodes 16, 18 of the pumping tube 14 of the pumping tube
member 24 and changing the time (t), the amount of ink to be
ejected can be controlled, the printed tone having a feature as
shown in Fig.5A.
-- 1 0 --
20`62~
Accordingly the tone of the pictorial image i8 related to
time ~t) as shown in Fig.5A, if an input signal is applied to the
two electrodes 16, 18 of the pumping tube 12 of the pumping tube
member 24 after modulating the input signal by a method of pulse
width modulation.
If the time of applying a voltage to the two electrodes 16,
18 is fixed and the voltage applied to the two electrodes 16, 18
is changed, a more linear feature of tone is obtained as shown
in Fig.5B. For example, a linear feature of tone is produced as
shown in Fig.5B, if a print input signal is applied to the two
electrodes 16, 18 of the pumping tube 14 after modulating the
print input signal by a method of pulse height modulation.
The acceleration a in the equation (5) does not count for
loss factors such as viscosity of the ink filled in the tube 14,
friction force between the ink and the inner wall of the tube 14,
the gravity, an air resistance, etc. under the real situation.
Assuming the loss caused by these factors is f(v), the pumping
acceleration Pa in the equation (5) needs to be modified as the
following equation:
Pa = dH~3 ( v~HB_f (v) ) .. (7)
wherein v represents speed.
The pumping acceleration Pa in fact should be considered in
the relation between the ejected amount of ink Q and the applied
- 11 -
~062711
.
voltage V, or the ejected amount of ink Q and the time of
ejection (t). An expert skilled in the art will be able to decide
the pumping acceleration by experiment. Consequently the ink
filled in the pumping tube 14 is ejected when the signal
responding to a print signal is applied to the pumping tube 14
of the pumping tube member 24.
In this embodiment, a uniform magnetic field is applied to
the pumping tube member by attaching a permanent magnet on the
top and bottom side of the pumping tube member 24. However, the
permanent magnet can be replaced by electromagnet made of such
a coil winding.
In conclusion, the print head ejects conductive ink by the
electromagnetic pumping and can express continuous tone by
regulating an amount of ejected ink by modulating the print
signal in an electromagnetic pumping drop-on-demand ink jet print
head.
While the foregoing provides a full and complete disclosure
of the preferred embodiments of the present invention, various
modifications, alternate constructions and equivalents thereof
may be employed without departing from the true spirit and scope
of the invention. Therefore, the above description and
illustration should not be construed as limiting the saope of the
invention, which is defined by the appended claims.