Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
~06ll4~
A D13VICE FOR M~NUFACl'URINt3 CONC~ETE BUILDING~ BLOCRS
Backqround of the Invention
The invention relates generally to a device for
manufacturing building blocks made of concrete and, more
particularly, to an improvement in a device of the type
containing at least one insulating insert. The device
consists of a mold, which is open on its bottom side and is
provided on its top side with longitudinally extending
recesses through which concrete material can be introduced. A
web is provided between two side-by-side recesses to cover an
insulating insert situated beneath ito This web protects the
underlying insulating insert from damage when concxete
material is introduced into the mold.
AT Pa~ent 352 602 discloses a device in which the webs
are formed with strips on their bottom side. Pins protrude
from these strips downward, and are utilized to secure the
insulating inserts placed in the mold. Since these strips are
used to strengthen the webs in the reguisite manner, their
thickn~ss is several times that of the thicXness of the webs.
After the concrete material is introduced into the mold
through the recesses situated between the webs, it is
compacted by shalcing and pressing to such an extent that its
top side is situated more or less in the plane of the bottom
side of the strips. Consequently, the top sides of the
.. ~, . : , , .: . .. - . ., . ,. . . ~ :
2~64~14
insulating strips and the end face of the concrete block are
generally coplanar with each other.
If, however, a block-making machine that does not compact
the concrete material that is pouxed into the mold to such an
extent is used, then the top side of the block may become
situated above the bottom side of the reinforcing strips.
This causes unwanted recesses to clevelop above the insulating
inserts after the block is formed. This problem cannot be
solved merely by diminishing the thickness o~ the strips
situated below the webs, since such a strategy could well
reduce strength of the webs to the~ point where they are not
sufficiently strong to satisfy the requirements of the
operation.
There remains a need for a device for manufacturing
building blocks whose webs are reinforced that also provides
that after the concrete material has been poured in and
compacted, the end faces of the insulating inserts are
situated in the end face of the concr~t~ block.
Summary of the Invention
The invention meets this need by forming at least one web
either with a strip that reinforces the web on its top side or
with a strip that provides reinforcement to the web on its
bottom side, and that penetrates into the insulating insert.
The web is preferably formed on the top side of the mold
with a strip that extends over its entire length. This strip
can have a height approximately equal to the width of the web
situated between the recesses, exclusive of the web's lateral
projections. Its thickness can be from one to three times the
thickness of the web. According to another embodiment, this
strip can have a height equal to one to two times the
thickness of the web, and a width equal to the width of the
web, exclusive of the web's lateral projections.
In another embodiment, at least one strip protrudes from
the web downwards; it can likewise extend over the entire
length of the web. It can be designed thereby as a narrow
strip with a rect:angular cross-section, on whose bottom side
pins are configured to secure the insulating insert. However,
it can also widen in cross-section toward the bottom and be
206~
used to secure the insulating inserts in a dovetail like
configuration.
srief Description of the F_qures
Fig. 1 is a vertical sectional view of a device
according the invention taken along the line I-
I of Fig. 2;
Fig. 2 is a top plan view of the device;
Fig. 3 shows a second embodiment of the invention in a
vertical section according to line III-III o~
Fig. 4
Fig. 4 is a top plan view of the second embodiment o~
the device;
~ig. 5 shows a third embodiment of the invention in a
vertical section according to the line V-V of
Fig. 6;
Fig. 6 is a top plan view of the third embodiment of
the device;
Fig. 7 shows a fourth specific embodiment of the
invention in side view; and ,
Fig. 8 is a top plan view of the device according to
the embodiment of Fig. 7.
Detailed DescriPtion
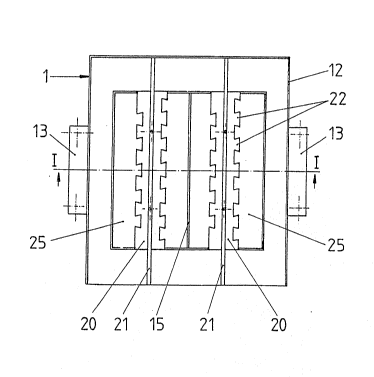
A mold 1 with a prism-shaped housing 11 is depicted in
Fig. 1. It is formed on its top side with a frame 12 that
projects upwardly towards the top. ~n the lower area, flanges
13 protrude ~rom the housing 11. The flanges enable the mold
1 to be gripped, lifted up and lowered> In its middle area,
the mold 1 is subdivided by a partition 15 into two chambers.
Accordingly, with this type of mold 1, two concrete blocks can
be manufactured at the same time.
On its top side, the mold 1 is provided with two webs 20
for covering the insulating inserts 30O These webs 20 extend
from one side of the mold 1 to the other side and are designed
to have lateral projections 22, whereby the formation of the
webs 20 corresponds in each case to the cross-section of two
206~41~
insulating inserts 30 placed in the mold. To secure the
insulating inserts 30, pins 23 protrude downwardly ~rom the
webs 20.
To manufacture a concrete block using mold 1, the mold is
first placed on a level surface. Concrete material is
introduced into the mold through t:he recesses 25 located on
the top side of the mold 1 about t:he webs 20 until the mold is
completely filled. The mold 1 is then simultaneously
subjected to a shaking process and the application of a press,
which plunges from above into the mold 1. The concrete
material is thereby compacted to such an extent that its top
surface lies in the plane of the bottom side of the webs 20,
as indicated in the figure by the broken line 26.
In such a design, however, the thickness of the webs 20
is not suf f icient to guarantee the required mechanical
strength. One must take into consideration that the webs 20
extend over the entire width of the mold 1, and that strong
impacts are exerted on these webs when the concrete material
is introduced into the mold 1, which can cause them to deform.
Accordingly, for the webs 20 to exhibit the required
strength, a strip 21 is provided on their top sides that
extends over the entire width of the mold 1. This strip is
rigidly connected ~e.g., welded) to the webs 20, and these
strips reinforce the webs in the requisite manner. The
thicXness of these strips 21 generally corresponds to the
thickness of the webs 20; their height generally corresponds
to half the width of the webs 20.
The second embodiment depicted in Figs. 3 and 4 differs
from the first embodiment in that the reinforcing strips 21a
which extend over the entire width of the mold 1 for the webs
20 are designed to have a width equal to the width of the webs
20, exclusive of the projections 22, which form a tooth
construction. Also, their thickness is approximately double
the thickness of the webs 20.
The third embodiment depicted in Figs. 5 and 6 differs
from the first embodiment in that the strips 21b which extend
over the length of the webs 20 are provided on the bottom side
,, ; ; , , , ,, , , ,, ~ , . .. . . .: .. , ' ` .! . .~
20~414
of the webs 20 and protrude downwardly therefrom, and bear
pins 23 which protrude downwardly. They are d0signed to be
sufficiently narrow, so that they penetrate, along with the
pins 23, into the insulating inserts 30, in which slits are
molded that correspond to the profile of the strips 21b and
are used to secure the strips within the mold 1. The
thickness of these reinforcing strips 21b thereby approximates
the thickness of the webs 20, and their height is generally
half the width of the webs 20.
The ~ourth embodiment depicted in Figs. 7 and 8 differs
from the third embodiment in that the strips 21c protruding
downwardly from the webs 20 are formed so that they widen in a
wedge shape toward the bottom. This enables them to provide a
secure attachment with respect to the insulating inserts 30
within the mold 1, although they are not formed with pins that r
protrude downward. The average width of these reinforcing
strips 21c is approximately the same as the thickness of the
webs 20, and their height is equal more or less to half the
width of the webs 20. As is apparent from Fig. 8, this mold
is formed with recesses 16 in one of the housing surfaces.
These recesses are provided with guide surfaces 17, through
which means the insulating inserts 30 can be inserted
laterally into the mold 1, in which they are retained by the
strips 21c.