Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
WO 91/1~829 lPCr/Fl~ 00191
7 ~ ~
A method for fixing an electrode arrangement ~o be used in the
cathodic protection of concrete s~ructures and a fix~ng elemel1t
The invention relates to a method for ~ixing an electrode a~rangem nt to be usedin the cathodic protection of concrete structures.
10 Tile invention also relates to a fixing element of an electrode arrangement to be
used in the cathodic protection of concrete structures.
In the protection of steel parts of concrete structures, e.g. concrete reinforce-
ments, the anodes of an electrode arrangement are generally fixed to an existing15 concrete surface, and the anode is covered with shotcrete or with another
corresponding conductive material. However, problerns have been caused by the
poor fixability of the electrode arrangement during the casting. Additional
problems have also been caused by the fact that the anode is during the casting
bent into contact with the steel constructions to be protected.
The above-mentioned situtations have made it considerably more difficult and
slower to carry out the actual concrete casting.
The object of the present invention is to provide such an anode fixing arrange-
2~ rnent and method, which, when used, eliminates the above-mentioned problem
situations.
Another object of the invention is to provide such a fixing arrangement, which
well adapts itself to be used in continuos concreting applications.
For reaching the objects mentloned above and to be presented below, the
inventive method is mainly characterized in that the anode is mounted in a
framework and that the framework with its anodes is mounted on the concrete
w~ 9 P~r~
7 (~ ~
structure at a production plant or in the mo1lnting s~ep before the concreting
step~
The inventive fixing element is mainly charac~erized in that the fix~ng element is
S comprised o~ an anode and a frarnework, which framework is provided with
means for ~ing the element to the concrete structure.
Such an inventive anode element placed in position ~efore the concreting is in
certain cases ~he only techn~cally sensible solution. When, for example, protecting
10 underwater concrete stmctures, a considerable ad~antage is obtained in the
preparation step, when the anode arrangement is of an element-stmctional type.
When using the inventive anode fixing arrangernent, the pressing effect of the
additional mass caused by shotcreting is avoided. Furthermore, the number of
15 the work phases needed decreases, since the anode element is prefabricated, and
only the fixing of the anode element has to be perforrned in connection with
concreting.
The fixing of the inventive element is easy and it saves mounting time, since a
20 separate fixing and insulating work o~ the anode in the mounting step is elirnin-
ated.
The inventive element remains fixed on the concrete structures, whereby no
special precautionaly measures are needed in the concreting step, e.g. it is not25 necessary to use a slower concreting ra.te.
The construction of the anode elernent according to the invention is mechanical-ly rigid such that it cannot come into an electrical contact with the concrete
reinforcements to be protect~d. From the point of view of the operaticn of ~he
30 protection, the avoidance of the electrical contact is one of the ~asic prerequi-
sites. In addi~ion, the inventive anode elemen~ cannot move during the concret-
ing owing to its fixing means.
W~ 9~ FY~
When using the inventive element, the unirltermptibility of a cath(l(lic contact is
also ensured, since the cosmection of all concrete reinforcernent layers to the
cathode circ~lit can be ~uaranteed by means of several fia~in~ points.
5 The anode element according to the invention forms a system of several
elemen~s such that each element can, when so desired, be eontrolled as a sepa-
rate electric circuit. The operation of the anode system is ehereby ensur d.
The invention is next described in more detail with reference to the figures of
10 the accompanying drawing, to which the invention is, however, in no way
narrowly limited.
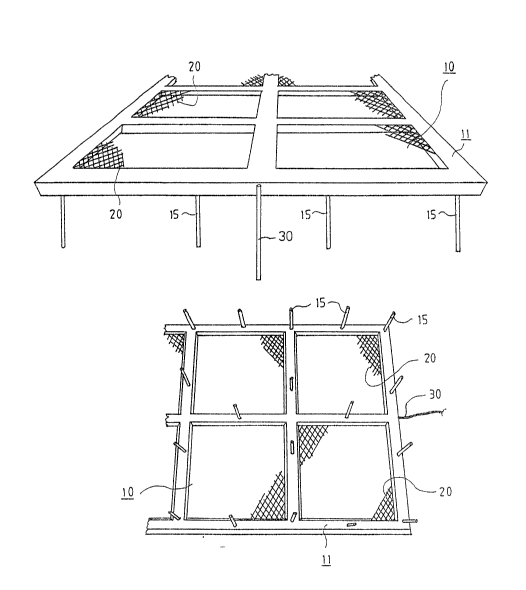
Fig. lA and lB show schematically an inventive anode element.
15 Fig. 2 shows as a schematic partial view an inventive anode element -fixed to a
concrete structure.
An inventive anode element 10 showrl in Fig. lA and lB comprises a Framework
11, anodes 20 and fixing rneans 15. The framework 11 is made of an electrically
20 insulating material, e.g. of plastics or ceramics or of an electrolytically conductive
material~ e.g. of concrete, plastics or ceramics. When so desired, a steel reinfor-
cement OI` some other reinforcement is used for improving the strength prop-
erties of the framework 11, which is, however, not necessary.
25 In one preferred embodirment of the invention, the framework 11 of the anode
element 10 is made of concrete, since a good adherence to the concreting is ehenobtained. Furthermore, when ehe framework 11 is made of concrete, possible
detrimental heat expansion phenomena are eliminated.
.
30 The ànode elernent 10 is fixed to a concrete surface, to concrete reinforcements
or to other fixed parts of ~he construction or to parts usecl during the moun~ing
with the fixing means 15 of ~he framework 11, e.~. ~vieh plastic hooks, nails,
Wl~ 2~1 ~P~ 313~/q)Ol~l
wires9 screws or the like.
The fixing IlleallS lS shown in Fig. lA and lB are made of concrete reinforce-
ment pins, which are fixed to ~he corlcrete reinforcerllents of the actual concrete
5 rein~orcement structure.
Tbe anode 20 is placed in the concreting of the framework 11, or ~he anode ~0
is mechanically ~ed e.g. with metallic or plastic na.ils, screws, anchors~ lists or
the like to the framework 11.
The anode 20 is located on the opposite side relative to the fixing means 15 of
the ~amework 11.
The anode 20 is a net, wire, strip, rod, plate or the like.
The material used in the anode 20 is a composite material, e.g. an alloy-me~al
coated titan, magnetite, platinated titan or an iron ~xture, e.g. ferrosilicon or
graphite or a noble metal, e.g. platinum or a conductive plastic.
20 ~s described above~ the anode element 10 can either be comprised of the
material of the anode 20 or of the material of the anode 20 and another materialjoined thereto. Several anode elements 10 fonn a system, by means o~ which the
steel parts of the concrete structure can be cathodically protected. Electricity is
supplied to the ;~node element 20 e.g. via a conductor 30. The electricity is
25 supplied separately to each anode elernent 20 via one or more of its points or to
all anode elements 20 of the systern together or by means of some combina~ion
of the two separate a~ove-mentioned systems.
The framework 11 of the anode elemen~ is ananged in a wedge~like form such
30 that the width of the crosspiece of the ~amework ll is on the side of the anode
20 greater than on the side of the fL~ing means 15, whereby the concrete can
during the casting easily flow also inside the frarnework.
~0 gl/~9~9 ~ J~ 3 1
s
In accordance w~th Fig. 2, the anocle elerneIlt 1û is ~ixed to ~he steel parts S0 of
the concrete reinfQrcement structure so that ~he fixing means 15 of the anode
elemerlt 10 are fLxed to the steel parts 50. ~he anode element 10 is fit~ed
between the outermost concrete reinforcement layer and ~he concreting wood
S liIling 6Qs into which the concrete 70 is cast.
As shown in :Fig. 2, the anodes 20 of the anode element 10 are located on the
other side of the framework 11 relative to the steel parts 50, whereby the anode20 cannot come into contact with the steel parts S0.
The invention has above been described only with reference to an example of its
preferred ernbodiment. However, the intention is in no way to lirnit the ir,~ ntion
to this example, but many changes and modi~lcations are possible within the
inventive idea defined in the following patent claims.