Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02068521 1998-02-11
- 1 -
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a flat (planar)
antenna of the dipole type which is arranged to be supplied
with an electrical signal, and/or to produce an electrical
signal at one end.
An antenna of the type to which the present
invention relates may be contained in a transponder of a
"passive interrogator label system".
A "passive interrogator label system", so-called, is
a radar system utilizing transponders which are capable of
receiving an interrogating first signal, processing this
signal and transmitting a second signal in reply that is
derived from the first signal and contains encoded
information. Because the encoded information normally
includes an identification code that is unique to each
transponder, and because the transponders of such a system are
relatively light weight and small and may be easily attached
to other objects to be identified, these transponders are
sometimes referred to as "labels". Furthermore, the
transponders, which may be implemented by SAW devices, carry
no self-contained power source, such as a battery, that must
be periodically replaced. Consequently, these transponders
are denominated as being "passive"; hence the name "passive
interrogator label system".
Passive interrogator label systems of the type to
which the present invention relates are disclosed, for
example, in the following U.S. patents:
72003-13
CA 02068521 1998-02-11
- 2 -
U.S. Patent No. 4,737,789 of Paul A. Nysen for
"Inductive Antenna Coupling for a Surface Acoustic Wave
Transponder";
U.S. Patent No. 4,703,327 of Anthony J, Rossetti and
Paul A. Nysen for "Interrogator/Receiver System for Use with a
Remote Transponder"; and
U.S. Patent No. 4,737,790 of Halvor Skeie and Donald
Armstrong for "Passive Interrogator Label System with a
Surface Acoustic Wave Transponder Operating at its Third
Harmonic and Having Increased Bandwidth".
In general, a passive interrogator label system
includes an "interrogator" for transmitting a first radio
frequency signal; at least one passive transponder which
receives this first signal, processes it, and sends back a
second radio frequency signal containing encoded information;
and a receiver, normally located next to the interrogator, for
receiving the second signal and decoding the transponder
encoded information.
The passive transponder, as disclosed in these
patents, comprises a SAW device and a dipole antenna, which is
either electrically or inductively coupled to the SAW
transducers on the SAW device. The dipole antenna may be
formed either by printing conductive ink (e.g. silver ink) on
a substrate in the prescribed antenna pattern, or by stamping
a metal foil into the size and shape of the antenna pattern,
and bonding this foil by heat and pressure to the substrate
(e. g. a polyethylene coated Mylar sheet). The antenna with
its substrate is therefore relatively flat and thin and,
72003-13
CA 02068521 1998-02-11
- 3 -
depending upon the radio frequency of operation, is relatively
modest in its lateral dimensions.
For example, the antenna characteristics required
for this application, operating at a frequency of
approximately 915 MHz., determine that the antenna be
physically approximately one inch wide and three inches long.
The SAW device, to which the antenna is coupled, is also
placed on the substrate to form the complete assembly or
"label".
Whereas the dipole antenna, with the SAW device
mounted between the dipoles, is satisfactory for most ID tag
applications, it would be advantageous, in some applications,
to locate the SAW device at one end of the antenna. Such
arrangement would simplify packaging the SAW device-antenna
combination (label) and would reduce the effect on the label
of an adjacent physical body.
SUI~iARY OF' THE INVENTION
It is an object of the present invention, therefore,
to provide a planar antenna of the dipole type which receives
an electrical signal from, and feeds an electrical signal to,
electrical terminals at one end of the antenna.
It is a further object of the present invention to
provide a planar, end fed antenna which may be inductively
coupled to a SAW device or other signal processing element.
These objects, as well as other objects which will
become apparent from the discussion that follows, are achieved
in accordance with the present invention, by providing (1) a
first quarter wavelength element having a first end and an
72003-13
CA 02068521 1998-02-11
- 4 -
opposite second end; and (2) a second quarter wavelength
element having a third end and an opposite fourth end. The
first end, second end, third end and fourth end, respectively,
of the first and second elements are arranged on a common,
substantially straight line with the second and third ends
adjacent to each other. In addition, a quarter wavelength
third element is positioned adjacent to the first element.
The third element has a fifth end and an opposite sixth end;
the fifth end is arranged adjacent to the first end of the
first element and the sixth end is arranged adjacent to, and
is physically connected with the third end of the second
element.
With this antenna, a SAW device, or other signal
source or sink may be electrically coupled between the first
end of the first element and the fifth end of the third
element to provide an electrical signal to and/or receive an
electrical signal from the antenna.
In a preferred embodiment of the present invention,
this source or sink comprises an inductive loop connected
between the aforementioned first end and the fifth end for
transmitting and/or receiving an inductively coupled
input/output signal to and/or from the antenna.
For a full understanding of the present invention,
reference should now be made to the following detailed
description of the preferred embodiments thereof, taken in
conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
72003-13
CA 02068521 1998-02-11
- 5 -
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
FIG. 1 is a representational diagram of a dipole
antenna.
FIG. 2 is a representational diagram of a dipole
antenna with a quarter wave feedline.
FIGS. 3a, 3b and 3c are diagrams of a dipole antenna
with a quarter wave feedline progressively collapsed toward
one dipole.
FIGS 4-10 are diagrams of antennas in accordance
with various preferred embodiments of the present invention.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED BMHODIMENTS
The preferred embodiments of the present invention
will now be described with reference to FIGS 1-10 of the
drawings. Identical elements represented in these various
figures are designated with the same reference numerals.
FIG. 1 illustrates a typical dipole antenna 10
comprising separate dipole antenna elements 12 and 14. A
signal source or sink 16 is electrically connected to the
inner ends 18 and 20 of the dipole elements 12 and 14,
respectively, for supplying a signal to, or receiving a signal
from the antenna 10.
FIG. 2 shows how the dipole elements may be supplied
via a quarter wave transmission line 22 formed by parallel
conductive bars 24 and 26 spaced apart by a gap width G and
having a length ~,/4, where ~, is the electrical wavelength at
the frequency of operation of the antenna. As is well known,
the significant variables in the design of an RF transmission
72003-13
CA 02068521 1998-02-11
- 6 -
line are the length of the line, the gap width and the
dielectric found in the gap.
FIGS. 3a, 3b and 3c illustrate how the quarter wave-
transmission line may be collapsed into one dipole element so
that the antenna may be electrically connected to a signal
source or sink arranged at one end.
As shown in FIGS. 3a and 3b, the transmission line
may be folded toward one (the lefthand) dipole element; as
shown in FIG. 3c, the feed line and the lefthand dipole
element may be collapsed into a single bar. If the dipole
element is the same length as the transmission line (~,/4, as
indicated above), the apparent signal source or sink is at the
center of the antenna.
The antenna shown in FIG. 3c thus comprises planar,
conductive antenna elements 14 and 24, hereinafter called
"second" and "third" elements, respectively. The third
element has a linear portion 24 extending from one end 30
toward its opposite end. In addition, the antenna includes a
planar, conductive linear coupling element 26, hereinafter
called the "first" element, which extends adjacent to, and in
parallel with, the linear portion 24 of the third element.
The first element has one end 34 arranged adjacent to the end
of the third element and an opposite end 36 located
adjacent to the opposite end 37 of the third element. The
signal source or sink 16 is electrically connected between the
end 30 of the third element and the end 34 of the first
element.
72003-13
CA 02068521 1998-02-11
7 _
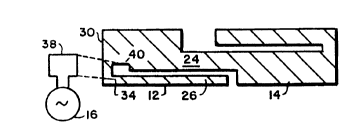
FIG. 4 shows how a signal source or sink may be
inductively coupled to an end fed dipole antenna according to
the present invention. As is there shown, the signal
source/sink 16 is electrically connected to an inductive loop
38 which, in turn, is inductively coupled to a partial loop 40
connected between the ends 30 and 34 of the antenna.
FIG. 5 illustrates an antenna with a meander portion
42 extending from a linear portion 24 of the antenna element.
This meander portion adjusts the resonant length of the
structure.
FIG. 6 shows an antenna which has been enlarged to
its maximum dimensions on a card-like, non-conductive
subst rate 44. The resonant length of the structure is
adjusted by providing a "tail" 46.
FIG. 7 shows an antenna similar to that of FIG. 5
arranged on a non-conductive substrate 44. The antenna is
inductively coupled to a SAW device 47 which is placed
directly over the antenna's inductive loop 40. The SAW device
47 incorporates a complementary inductive loop for coupling a
signal to and from the antenna.
FIG. 8 shows still another antenna configuration,
which is presently the best mode for practicing the invention.
This antenna is similar to that of FIGS. 5 and 7 but includes
an additional planar, conductive, meander element 48, disposed
on the substrate surface, having two ends 50 and 52,
respectively. The end 50 is electrically coupled to the end
of the antenna. This meander element serves to increase
72003-13
CA 02068521 1998-02-11
_ g _
the inductance of the antenna, thereby tuning the antenna to
the inductively coupled source or sink.
FIGS. 9 and 10 show additional antenna structures
according to the present invention which include reflectors 54
and 56, respectively. These reflectors improve the isolation
of the antenna from other reflecting elements in the vicinity.
In summary, the present invention contemplates a
planar (flat) antenna incorporating a transmission line that
permits direct electrical connection (or inductive coupling)
to one end of the antenna. The transmission line is formed of
two legs: a linear portion of one dipole element itself and a
separate, linear coupling element. This transmission line
operates to contain a non-radiating field within the interior
of the antenna (between the two legs) while permitting
radiation to occur on the outside of the antenna. Although
the antenna is driven from one end, the antenna operates as if
the signal source or sink were connected at its center.
There has thus been shown and described a novel
planar antenna which fulfils all the objects and advantages
sought therefor. Many changes, modifications variations and
other uses and applications of the subject invention will,
however, become apparent to those skilled in the art after
considering this specification and the accompanying drawings
which disclose the preferred embodiments thereof. All such
changes, modifications, variations and other uses and
applications which do not depart from the spirit and scope of
the invention are deemed to be covered by the invention which
is limited only by the claims which follow.
72003-13