Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
20721 ~
1 BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
This invention relates to a video camera
system for automatic photographing such as human body
tracking photograph operation using thermal images.
There is known a remote controllable video
camera which the user can control by use of a motor
while watching the monitor screen.
In the above prior art, however, the user
chiefly controls the camera angle while watching the
monitor screen, and thus it is difficult to make
automatic photographing without the operator by this
video camera.
-
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
It is an object of the invention to provide a
video camera system of a relatively simple constructioncapable of automatic photographing.
According to this invention, there is provided
a video camera system including thermal image detecting
means formed of a group of a plurality of pyroelectric
type thermal detection elements.
In the above video camera system of the
invention, a video camera main body and main body
supporting portion of the video camera system is
connected by lens direction setting means of a one-or
-- 1 --
2~7217~
1 two-axis rotation mechanism, and the thermal image
detecting means is fixed to the main body supporting
portion so as to directly oppose an object being
photographed.
Also, in the invention, a person or persons
are detected by the thermal image detecting means and
human body judging means.
In addition, in the invention, the location of
the detected person or persons is decided by human body
location detecting means, and the lens direction setting
means is operated by picture frame determining means so
that the person or persons are substantially fixed at an
arbitrary position within the picture frame.
Moreover, in the invention, when one of the
persons is specified, the lens direction setting means
and the lens angle-of-view setting means are operated so
that this person can be substantially fixed at an
arbitrary position within the picture frame and to have
an arbitrary size.
Also, in this invention, a plurality of
persons are detected by the human body judging means,
and the zoom mechanism of the camera lens is operated by
the lens direction setting means and the lens angle-of-
view setting means so that all the persons can be caused
25 to enter in the picture frame.
Also, in this invention, zooming up or down is
performed chiefly for the person or persons.
2~72174
1 In addition, in this invention, receiving
means and wireless transmission means are provided, and
photograph scene setting means corresponding to the
above function is provided together with general
operating functions.
Moreover, in this invention, the pyroelectric
type thermal detection element group is made of a
pyroelectric thin film.
Furthermore, in this invention, the
pyroelectric type thermal detection element group is
one-dimensionally arranged in a straight axis and has a
rotation axis which is parallel to the straight axis or
tilted by a constant angle thereto so that the
pyroelectric type thermal detection element group is
rotated around the rotation axis so as to produce a two-
dimensional image.
This invention detects human body or bodies by
use of a thermal image and scans the human body or
bodies, thereby realizing the automatic photographing of
video camera.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Fig. 1 is an external appearance of a video
camera system having thermal image detecting means as
one embodiment of this invention;
Fig. 2 is a block diagram of the construction
of the video camera system of the embodiment of the
invention;
2072174
1 Figs. 3A-3D are diagrams useful for explaining
the function of the embodiment of the invention;
Figs. 4A and 4B are diagrams of examples of
the thermal image detecting means of the embodiment of
the invention; and
Figs. 5A and 5B are diagrams useful for
explaining the way of obtaining the thermal image.
DESCRIPTION OF PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
An embodiment of the invention will be
described with reference to Figs. 1 to 4.
Fig. 1 shows the actual use of the embodiment
of the invention.
Referring to Fig. l, there are shown a video
camera 1, a main body supporting portion 2, thermal
image detecting means 3, lens direction setting means 4
having a two-axis rotating mechanism, and a human body
or persons 5 to be photographed. The lens direction
setting means 4 may have a right, left one-axis rotating
mechanism.
The thermal image detecting means 3 is mounted
on the main body supporting portion 2 so as to rightly
oppose the object to be photographed. This thermal
image detecting means 3 detects the direction, size and
number of the persons 5. The lens direction setting
means 4 controls the video camera 1 to be directed
towards the persons 5.
2072174
1 The thermal image detecting means 3 includes a
group of a plurality of pyroelectric type thermal
detection elements. The non-contact measuring system
includes the quantum type infrared ray sensor, the
infrared CCD and the thermal infrared ray sensor. The
quantum type infrared ray sensor and infrared CCD have a
high sensitivity and high response, but are necessary to
be called (about -100 ~ -200C). Thus, these sensors are
unsuitable for public use. On the other hand, the
thermal type infrared ray sensor have a relatively low
sensitivity and slow response, but are not necessary to
be cooled. Thus, the thermal image detecting means 3
employees the pyroelectric effect of the thermal type
infrared ray sensor.
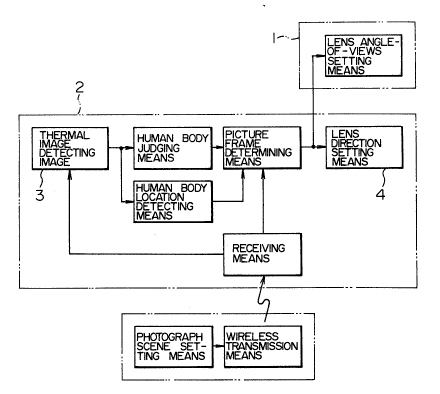
Fig. 2 is a block diagram of the internal
construction of the video camera system of the
invention.
The video camera 1 includes lens angle-of-view
setting means for zoom operation. The main supporting
body 2 includes the thermal image detecting means 3,
human body judging means, human location detecting
means, picture frame determining means, lens direction
setting means and receiving means.
The wireless remote control includes
25 photograph scene setting means and wireless transmission
means.
When a desired function is selected by the
photograph scene setting means, a thermal image
2072174
1 including a person or persons i3 detected by the thermal
image detecting means 3 through the wireless transmis-
sion means and receiving means. In addition, the human
body judging means and the human body location detecting
means decide the number, locations and sizes of persons.
The picture frame determining means determines the angle
and size of the picture frame including the persons at
the center. The lens direction setting means and the
lens-angle-of-view setting means are operated to
determine the direction of the lens of the video camera
and the amount of zoom, and then the video camera starts
to photograph.
Figs. 3A to 3D are diagrams useful for
explaining the functions of the embodiment of the
invention.
As shown in Fig. 3A, the detected person or
persons are fixed at an arbitrary position within the
picture frame by controlling the lens direction. As
shown in Fig. 3B, the detected person or persons are
fixed to be an arbitrary size at the given position
within the picture frame by controlling the lens
direction and the angle of view. As shown in Fig. 3C,
all the detected persons are caused to enter in the
picture frame by controlling the lens direction and the
25 angle of view.
In addition, as shown in Fig. 3D, the detected
person is zoomed up or down at around an arbitrary
207217~
1 location within the picture frame by controlling the
lens direction and the angle of view.
Figs. 4A and 4B show the construction of an
example of the thermal image detecting means 3 of the
invention. 6a to 6e represent pyroelectric type thermal
detection elements (hereinafter, called simply as
elements), 7 the group of the pyroelectric type thermal
detection elements, and 8 the rotation axis. Fig. 4A
shows that the rotation axis 8 is parallel to the
pyroelectric type thermal element group 7, and Fig. 4B
shows that the rotation axis 8 is tilted by a constant
angle ~ to the pyroelectric type thermal element group
7. The angle ~ depends on the setting of the structure
of the main body supporting portion 2 combined with the
video camera and the detection field of angle.
The way to obtain a thermal image by use of
the pyroelectric type thermal detection element group 7
will be described with reference to Figs. 5A and 5B.
Fig. 5A shows the cubic field angle of view of a thermal
image to be detected, and Fig. 5B shows the detected
thermal image. The pyroelectric type thermal detection
element group 7 includes 5 elements each of which takes
charge of 1/5 the angle of view in the vertical
direction.
The pyroelectric type thermal detection
element group 7 is combined with optical lenses. The
horizontal field angle of view is set to be narrow, and
it is moved in the horizontal direction by the rotation
207217~
1 of the rotation axis 8. At each movement of the
horizontal angle of view, the pyroelectric type thermal
detection element group 7 measures temperature to
produce a two-dimentional thermal image as shown in
5 Fig. 5B.
The generally used pyroelectric type infrared
ray sen~or is of the so-called bulk type using a
sintered pyroelectric thick film. However, this bulk
type cannot be formed to have a small thermal time
constant and thus it has a slow response. If the
pyroelectric type thermal detection elements are formed
of a pyroelectric thin film of, for example, PbTiO3, the
response time can be reduced to about 1/10 that of the
bulk type. Use of the elements of this pyroelectric
thin film, since the response time can be reduced, makes
it possible to precisely detect the movement of human
bodies. In addition, use of the pyroelectric thin film
makes it possible to further reduce the size of the
elements.
According to this invention, since a group of
a plurality of pyroelectric type thermal detection
elements is provided on the video camera, automatic
scanning photographing chiefly for human bodies can be
performed by detecting the person or persons. Also,
25 since operatorless photographing is possible, there are
no troublesome operations in photographing and thus the
freedom of photographing increase~. In addition, since
various different functions can be provided on the
8 --
2072174
1 remote control, the camera operation becomes simpler,
and thus any one can easily produce a video drama, news
and so on in which the hero or heroine is oneself.
Moreover, according to this invention, the
thermal image can be detected by a relatively simple
system in which the group of one-dimensionally arranged
pyroelectric type thermal detection elements is rotated.
Furthermore, the response speed of the thermal
image can be increased by the element group of the
pyroelectric thin film, and the system can be small-
sized.
_ g _