Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
WO 91/171~1 PCr/C~B91/00636
-1~ 2~3a~
ISOQUINOLINE AMIDES AND ESTERS AS 5-HT3
RECEPTOR ANTAGONISTS.
This invention rela~es to novel com~ounds having useful
pharmacological proper~ies, to pharmac~uti.cal compositions
5 containing them, tO a process an~ intermediates for their
preparation, and to the'r use as .~narmaceu~lcals.
GB 2145416A (Sandoz Ltd) describes a group of naphthylene, --
chromene and quinolin~ de-i~a~ e-^ with satura.ed
o azabicyclic side chains, and hav_z.g ~-HT3 receptor
antagonis 2ctivi'y.
A c72ss of ~truct-ra''~ ~ sl ?.C_ -^m?O'~ S ~a',~' ~q a.
isoquinoline moie~, ..as now Dee-. aisi-overe~. Thes~
5 compounds have 5-HT3 receptor an~agonist actiYvrity.
Accordingly, the present invention provides a compound of
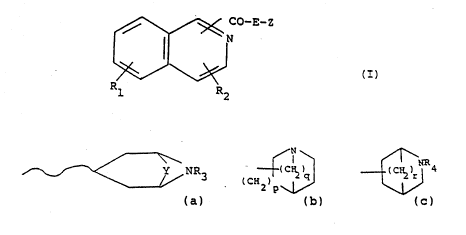
formula (I), or a pharmaceutically accep~able salt thereof:
CO-E-Z
~ (I)
Rl R2
~ wherein
i-s NH or O,
R1 is hydrogen, halogen, C1_4 al'~:yl, C1_4 alkoxy, hydroxy or
nltro;
Z is an;azacycli.c or azabicyclic side chain, such as a group
of formula (a), (b) or (c):
WO 91/1716] PCr/GB91/006~6
3'~
1`1
~ N ~
(CH ) q I
2 p~/ ~b)
.'" .
~:~
~ ~NR~
. ( C )
: whe re in
p is 1 or 2; q is 1 to 3; r is 1 to 3;
30 R3:: or R4 is hydrogen or C1_4 ~lkyl, and Y is a group
CH2-X~-CH2- wherein X is -CH2-, c:~y erl, sulphur or X is a
ond; and: ~
~: ~
:
: .
WO ~1/17161 13 ~- ~3 PCr/C~91/00636
-3-
i) the group CO-E-Z ls in the 1-posltion and either R2 is
in the 3-position and is hydrogen, C1_6 alkyl Dr C1_6
alkoxy, or R2 ls in the 4-position and is hydrogen,
halogen, CF3, C1_6 alkyl, C1_7 acyl, C1_7 acylamino,
phenyl optionally substituted by one or two C1_6
alkyl, C1_6 alkoxy or halogen grou~s, o- amino,
aminocarbonyl or aminosulphonyl, optionally
substituted by one or two C~-6 alkyl or C3_8
cycloalkyl groups or by C~_~ polyme~hylene or by
phenyl, C1_6 alkylsulphony', C'_~ alkvlsulphinyl, C1_~ :
alkoxy, C1_6 alkylthio, hyG~oxy c- nit-o; or
ii) the group CO-E-Z is in the 3 posi~on and either R2 is
1~ in the 1-position and is hydrogen, C1_6 alkyl or C1_6
alkoxy, or R2 is in ~he 4-posi~ion and is hydrogen or
Cl_6 alkoxy;
: having 5 HT3 receptor antagonist activity.
~20
Suitable examples of the group R1 include hydrogen, bromo,
chloro, methyl, ethyl, n- and iso-propyl, n-, lso_, sec- and
tert-butyl, methoxy, ethoxy, n- and iso-propoxy, and n-,
lso , sec- and tert-butoxy.
: 25
Suitab:le examples of Z are descri~ed in the art relating to
5-:HT3 receptor antagonists, ie. as follows:
i) GB 2125398A (Sandoz Limited)
30 li) GB 2152049A (Sandoz Limlted)
P-A-2~15545 (Beecham Grcup ~. .c.)
iv?: EP-A-214772 (Beecham Group ?.1.c.)
v):~ ~ EP-A-377967 (Eieecham Group p.l.c.)
Vl j~ ~ EP-A-3~58903 (Dianippon Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.)
3 5 : : ~
Particular side chains or intereC~ are depicted thus:
~ ,
~,VO 91~ ~ 7161 PCr/GB91/00636
~rop,an~
~ MR
Granatane
/ MR
~ .
15 O.~:a/thia- ranatane
NR
0
Qulnuc idine
. ' ' .
~; 25: ~ ~
~J
~: N : :
Isoqulnuclidlne
i: ~:..
WG91~1716~ PCT/GB91/nO636
: ~5~ 2 0~ ~ 3 ~ a
so~ranatane
~ .
s V
Oxa/thla-isoqranatane
~/
~,J
S Isotropane
or
wherein
R is hydrogen or methyl; and X is oxvgen or sulphur.
.
; : 25 Side chains Z of particular interest include tropane and
oxasranatane,~where~ R ls methyl.
Ejls preferably NH.
O~When~the group~CO~E-Z is in the l-position sultable examples
of~the group R2 when in t~he 4-positlon, include the
following~groups;:hydrogen, chloro, bromo, methyl, ethyl,
amino, me:thylarnino,~dimet~hylamino, phenyl, Cl_4
~ : j ::alkanoylamino such:as formylamino, ace~ylamino,
:~ : 35~propionylam:ino, n- and~lso-butyrylam no, aminosulphonyl, and
~: ami:no and aminosulphony~l op~ionally substituted by one or
wo gl/17161 ~ 3 PCI/GB')1/()0636
two methyl, ethyi, n- or iso-propyl, n-, seC-, iso or
tert-butyl or phenyl groups; nltro, methoxy, ethoxy, n- and
iso-propoxy, methylthio, ethylthio, n- and iso-propylthio,
hydroxy, methylsulphonyl and ethylsulphonyl or when R2 is in
5 the 3-position suitable e:.amples, include the following
groups, hydrogen, methyl, e~nyl, n- or iso-propyl, methoxy,
and ethoxy.
When the grou~ CO-E-~ is in the 3-position, suitable
o examples o ~he c_ou? ~2 when in the 1-position, include the
groups hyGrogen, methyl, et~y', n- or ~so- ~ropvl, methoxy
and ethoxy, or when ~ ~s in the ~-pos~tion, suitable
examples inc'ude the _ol'o"ing crou?s; ~ydrocen, me~ho~y and
etho~y.
~referred R2 groups, in any of the positions specified
above, include hydrogen, methyl and metho~y. R2 is
prefexably in the 1-position.
20 For the avoidance of doubt, all alkyl and alkyl containing
moie~ies are straight chained or branched. -
Examples of R3/R4 when alkyl are methyl, ethyl, n- and
iso-propyl, n , iso-, sec- and tert-butyl, prefe~ably
25 methyl.
Preferab1y p, q and r are 1 or 2.
The pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the compounds of
30 the formula (I) include acid addition salts wlth
conventional acids such as hydrochlo~lc, hyd~obromic, boric,
phosphoric, sulphuric acids and pha-maceutically acceptable
organic acids such as acetic, tartaric, lactic, maleic,
citric, succinic, ben~oic, ascorbic, methanesulphonic,
35 ~-~eto glutaric, a-glycerophosphoric, and
glucose-1-phosphoric acids.
.:
,::
WO~1/17161 PCr/CB~1/0063
_7_ ~ ~ 8~ 3^~ n
The pharmaceutically accep~able salts of the compounds of
the formula (I) are usually acld addition salts Wlth aclds
such as hydrochloric, hydrobromlc, phosphoric, sulphuric,
citric, tartaric, lactic and acetic acid.
s
Examples of pharmaceutically acce?table salts include
quaternary derivatives of the comDourlds of fo-~ula (I) SUC~I
as the compounds quaternised by compounds Ra-T wherein Ra is
Cl_6 alkyl, phenyl-Cl_6 alkyl or r5_7 cycloal.kyl, and T ~s a
lO radical corresponding to an anio.-, o~ an acid. Suitable
examples of Ra include methyl, e~~yl and r.- and iso-DrCDyi;
and benzyl and phenethyl, prefer_~l,y methyl. Suitable
examples of T include halide su :~. as c!.lorid_, bro~ide anc
iodide.
Examples of pharmaceu~ically accep~able salts of compounds
of formula (I) also include internal salts such as
pharmaceutically acceptable N-oxides.
20 The compounds of the formula (I), their pharmaceutically
acceptable salts, (inclu~ing quaternary derivatives and
N-oxides) may also form pharmaceutically acceptable
solvates, such as hydrates, which are included wherever a
compound of formula (I) or a sal~ thereof is herein referred
25 to.
It will of course be realised that some of the compounds of
the formula (Ij have chiral or prochiral centres and thus
are capable of existing in a number of stereoisomeric forms
30 including enantiomers. The invention extends to each of
these stereoisomeric forms (incl~ding enantiomers), and to
:: :
mixtures thexeof (including racema~es). The different
stereoisomeric forms may be separated one from the other by
the usual methods.
,
,:
: ;. :: :
W09~/17~ a- rCI/GI191/0061~1
It will also be realised that the isoquinoline nucleus in
compounds of rormula (I) may adopr an endo or exo
configuration with respect to Z. The endo confi~uration is
preferred.
A group of compo~n~s within formu a (I) is of formula (II): ;
~CO-E ~ N~3
10 ~.
11 ' 1' (r-~
lS
wherein the variables are as def ned in formula (I).
Examples of the variables and preferred variables are as so
described for corresponding variables in relation to formula
20 (I).
A further group of compounds within formula (I) is of , .
formula (III):
.: ,' ' ::. '
2s
~N P~
30 ~ :
2 :.
:
wherein ql is l or 2 and the reTna n:.ng vzriables are as
5 defined in formulae (I) and (II).
: ~ :
:~ :'
WO91/17161 pcT/Gssl/oo636
~ ~ 8 ~
--9-
Examples of the variables and preferred vari.ables are as so
described ~or the corresponding variables ln formula (I).
There is a further group of compounds wlthin formula (T) of
S formula ~IV):
~ j/ CO- E ----~NR4 ;IV)
wherein rl is l or 2 and the remalnlng varlables are as
defined in formulae (I) and (II).
Examples of the variables and preferred variables are so
described as the corresponding variables .in formula (I).
The invention also provides a process for the preparation of
a compound of formula (I) which pxocess comprises reacting a
compound of formula (V):
A ~ :
l 2 ~V)
with a compound Of formula A2-Z' wAerein Z' is Z as defined
: ~ in formula (I) wherein R3 and R4 are replaced by R3' and
,
, .-; `- ~, .' '., ;. . '' . , . , :
W091~l7~ PC~/G~91/00636
-10-
R4', A1 and A2 are moieties which react together to form an
amide or este.r linkage and R3' and R4' are R3 and R4
respectively, as defined in formula (I) or a
hydrogenolysable protectin~ group; and thereaf~er as desired
s or necessary, conve-tina R3', or R~' when other than R3 or
R4 respectively, to R3 and R4 respectlvely, and optionally
forming a pharmaceutically ac^~?table salt of the compound
of formula (I).
o Suitable values of ~1 anà ~ are, for eY.ample, as descrlbed
in the aforemen_ioned pa~ent ~u~lica~io~s. For e.Yam~le, A1
may be an ac~ived ca-~onyI fun ~ on suc:- 2S an acid chloride
or N-hyd-o~.t~succlnm~e es~er a..~ ~, ma~ b~ an a.m,Lno g_~u?,
when E in rorl~ula (I) is `~In .
Intermediates of the formula (V) are generally known or are
prepared by analogous methods to those used for structurally
related known compounds.
20 Intermediates of formula A2-Z' may be prepared from the
corresponding exocyclic keto derivative of the azabicyclic
side chain, prepared by condensation methods, often using a
substituted piperidine, as described in the aforementioned
patent references.
- In a particular aspecl, the invention also provides a
:
process for the preparation of a compound of formula (I), or
- : a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, which process
.
comprises reacting a compound of formula (VI): - .
.
;~ 30 :
: 35 ~ '~;J ~:~
2 (VI)
:
:
WO91~17161 PCT/CB91/00636
2~813a~
with a compound of fo~mula HJ-Z', or when J ls oxygen, an
active derlvatlve thereof, wherein J ls oxygen or NH, Q is a
leaving group; R3~ and R9' respectively is R3 and R4
respectlvely, as deflned, or a hydrogenolysable protectlng
5 group; and the remaining variables are as hereinbefore
defined; and thereafter optionally converting R3' or R~',
when other than R3 or R4, to R3, or R~ respectively, and
optionally forming a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of the
resultant compound of formula (I).
~xamples of leaving groups Q, dis?laceable b~ a nucleop~.~le,
include halogen such as chloro and bromo, C1_4 alko~y, such
as CH30 and C2H~O-, PhO-, or ac~ ~ated hyd-oca~bylox~ uch
as Cl5C6O- or COQ forms a mixed anhydriàe, so .hac Q is
carboxylic acyloxy.
If a group Q is a halide or COQ forms a mixed anhydride,
then the reaction is preferably carried out at non-extreme
temperatures in an inert ncn-hydroxylic solvent, such as
20 benzene, dichloromethane, tolucne, diethyl ether,
tetrahydrofuran (THF) or dimethylformamide (DMF). It is
also preferably carried out in the presence of an acid
acceptor, such as an organic base, in particular a tertiary
amine, such as triethylamine, tximethylamine, pyridine or
25 picoline, some of which can also function as the solvent.
Alternatively, the acid acceptor can be inorganic, such as
calcium carbonate, sodium carbonate or potassium carbonate.
Temperatures of 0-100C, in par~icular 10~80C are
suitable.
If a group Q is Cl_4 alkoxy, phenoxy or activated
hydrocarbyloxy, or activated es~er, such as N-
hydroxysuccinimide, then the reaction is preferably carried
out in an inert polar solvent, such as toluene or
35 dimethylformamide. It is also p~eferred that the ~roup Q is
Cl3CO- and that the reaction is car-ied out in toluene at
., .
:'
WO91/17161 ~3~ -12- PCT/~91/00636
reflux temperature.
If a group Q is hydro~y, then t~.e reacl on is generally
carried out in an lnert non-hydro~ylic solve~t, such as
s dichloromethane, THF or DM~ o~ti~nally ~n the presence of a
dehydrating agent such as a carbodiimlae, for e.~ample
dicyclohexylcarbodlimide, optlor.ally l~ ~he presence of ~-
hydroxysuccinimiàe. ~he reaction may be car-ied out at any
non-extreme temperature, such as -lO to 100C, for example,
lO 0 to 80C. Generall~r~, higner reaction ,emperatures are
employed with less aC' ive c~m~ounds ~h~reas lower
temperatu~es are emsloye~ wi~h ,'e more ac,ive com~ounds.
If a group Q is caroo.YyIic acyic::y, tnen the reac ion is
preferably carried in substantia`ly the same manner as the
reaction when Ql is halide. Sui,able e.~amples of acyloxy
leaving groups include Cl_4 alkanoyloxy and Cl_4
alkoxycarbonyloxy, in which case the reaction is preferably
carried out in an inert solven~, such as dichloromethane, at
20 a non-ex~reme temperature for example ambient temperatures
in the presence of an acid acceptor, such as triethylamine.
Cl_4 alkoxycarbonyloxy leaving g-oups may be generated ln
situ by treatment or the corresponding compound wherein Q is
hydroxy with a Cl_4 alkyl chloro^ormate.
If a group Q is activated hydrocarbyloxy then the reaction
is preferably carried ou~ in an nert polar solvent, such as
dimethylformamide. It is also p-eferreà that the activated
hydrocarbyloxy group is a pentachlorophenyl ester and that
30 the reaction is carried out at ambien~ temperature.
When J is 0 the compound of formula HJ-Z', may be in the
form of a reactive derivative thereof, which is often a
salt,~ such as the lithium, sodium o- po~asslum salt.
: .
':
W~91/17161 T'~/~B9!/0063~
2~g ~ ~'0
-13-
R3' and Rql when other than R3 and R4 respectlvely, may be a
hydrogenolysable protectlng group which is benzyl optionall~
substituted by one or two groups selected from halo, Cl_~
alkoxy and Cl_4 alkyl. Such benzyl groups may, for example,
5 be removed, by conventional transitlon metal catalysed
hydrogenolysls to give compounds of the formula (VII) or
(VIII) respectlvely:
CO-J ~ ~N-r.
11 T
~ ~
Rl R2
(VII)
~
CO-J ~ (c~)lH
I ~1
2S Rl ~ R2
(VIII)
: wherein the variables are as hereinbefore defined.
30 This invention also pro~ides a further process for the
preparation of a compound of the formula (I) wherein Z is a)
or c) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, which
: compr1ses N-alkylating a compound of formula (VII) or (VIII)
;
.
.... , . . , . , , , .. ,. ~ " ~, , ,. .. , ,, .. . .. .. . ., . . . . ~ .
WO 9]/1'7161 PC~/CB~1/00636
3~
respectively, and optionally forming a pharmaceutically
acceptable salt of the resultln~ compound of the formula
tI).
s In this further process of the ~nvention 'N-alkylation'
comprises the substitutlon of -the N-atom aepicted in forrnula
(VII) or (VIII) respectively, bv a grou? R3 or R4
respectively as hereinbefore der led. Thls mav be achleved
by reaction with a compo~nd ~3Q3 or R9Q^; as .~ecessary
o wherein R3 and R4 are as he-ein'v~-~ore àe__ned ~nd Q3 is a
leavlng group.
Suitable values for Q3 include c-ou~s à~s?~ 2ced b~
nucleophiles such as C', 3r, , _SO2C.ï3 _- Cv~2~6.14pCH3.
Favoured values for Q3 include C:, B- anc I.
The reaction may be carried out under conventional
alkylation conditions, for example in an inert solvent such
20 as dimethylformamide in the presence of an acid acceptor
such as potassi~m carbonate. Generally the reaction is
carried out at non-extreme temperature such as a~ ambient or
slightly above.
~ ..
25 Alternatively, 'N-alkylation' may be effected under
conventional reductive alkylation condi~ions.
Intercon-verting R3 and R4 respec-ively in the compound of
the formula (VII~, or (VIII) respectively, before coupling
30 with the compound of the formul2 (VI) is also posslble.
Such interconversions are effected conveniently under the
above conditions. It is desirabie ~o pro~ec~ any amine
function with a group readily removable by acidolysis such
as a C2_7 alkanoyl group, before R3 or R~ interconversions.
3s
It is~often convenient in the preparatlon of such a compound
of formula ~VII) or (VIII) to pre~are the corresponding
: '
WO9t/17161 PCT/GBs)1/0~63~
3 :~ ~
compound wherein the methylene group is replaced by -Co-, or
for R3 or R4 is methyl, where the methyl group is replaced
by alkoxycarbonyl. Such compounds may then be reduced using
a strong reductant such as llthium aluminium hydride to the
5 corresponding compound of formula (VII) or (VIII)
respectively.
The compounds of formula (VI) are known or are preparable
analogously to, or routinely from, known isoq~inoline
0 compounds.
It will be realised that in the compounds of _he formula (T)
having a ~ropane, granatane or o~a/thia-grana-ane side
chain, the -COE- linkage has an e~do orien~ation wit;n
lS respect to the rlng of the bicyclic moiety to which it is
attached. A mixture of endo and exo isomers of the compound
of the formula (I) may be syntheslsed non-stereospecifically
and the desired isomer separated conventionally therefrom
e.g. by chromatographyi or alternati~ely the endo isomer may
20 if desired by synthesised from ~he corresponding endo form
of thé compound of the formula (II). Corresponding
- geometric isomeric pairs are possible for the
isoquinuclidine, isogranatane, oxa/thia-isogranatane and
isotropane side chains.
~harmaceutically acceptable salts of the compounds of this
invention may be formed conventionally. The acid addition
salts may be formed for example by reaction of the base
compound of formula (I) with a pharmaceutically acceptable
30 organic or inoryanic acid.
The compounds of the present invention are 5-HT3 recep~or
antagonists and it is thus believed may generally be used in
the treatment or prophylaxis of ~ain, emesis, CNS disorders
3s and gastrointestinaI disorders. ~ain includes migraine,
1uster headache, trigemlnal neuralgia and visceral pain;
:~: ::
~,VO '~1/17161 ", ~ P'CT/GB~1,'00636
~ -16-
emesis, includes in particular that of preventing vomiting
and nausea associated wlth cancer thera?y, and motion
sic~ness. Examples of such cancer the-apy include that
using cytotoxic agents, such as clsplatln, doxorubicln and
5 cyclophosphamide, particularly cisplati.~i and also radlatlon
treatment. CNS disorders include an~ y, psychosis, senlle
dementia and drug dependence. Gastrointestinal disorde~s
include irritable bowel syndrome and àiarrohea.
0 S-HT3 receptor antagonis~s may also be c~ ?o~ential ~s_ in
the treatmen~ of obesity and/or ~--hyt:n~ia.
The invention also provides a pharmaceu ical co~pcsi^_ioo
comprlsing a compound c for~ul~ (~ 2h~_,~ace~
5 acceptable salt thereof, and a pharmaceu~ieally acceptable
carrier.
.
Such compositions are prepared by admixture and are sui~ably
adapted for oral or paren~eral administration, and as such
20 may be in the form of tablets, capsules, oral liquid
preparationS, powders, granules, lo~enges, reconstitutable
powders, injectable and infusable solutions or suspensions
or s~uppositories. Orally administrable compositions are
preferred, since they are more convenient for general use.
TabIets and capsules fo~ oral adminis~.ration are usuall~
presented in a unit dose, and contain conventional
excipients such-as binding agents, fillers, diluents,
: tabletting agents, lubricants, disin~egrants, colourants,
30 flavourings, and wetting agents. The tablets may be coated
according to well known methods ln the art, ror example wi~h
an enteric coating.
.: ~:
: : SultabIe ~illers for use include cellulQse, mannitol,
3s lactose and other similar agen~s. Sui~able disintegrants
:.
.
::
WO 91/171~1 PCT/~ 1/0063f~
2~135~
~17-
include starch, polyvinylpolypyrrolidone and starch
deri~atives such as sodi~m starch glycollate. Sultable
lubricants include, for example, magnesium stearate.
5 Suitable pharmaceutically acceptable wetting agents include
sodium lauryl sulphate. Oral liquid preparations may be in
the form of, ~or example, aqueous or oily suspensions,
solutions, emulsions, syrups, or elixirs, or may be
presented as a dry product for reconstitution with water or
o other suitable vehicle before use. Such liquid preparations
may contain conven~ional additives such as suspending
agents, for example sorbitol, syrup, methyl cellulose,
gelatin, hydroxyethylcellulose, carboxymethylcellulose,
aluminium stearate gel o- hydrogenated edible îa~s,
15 emulsifying agents, for example lecithin, sorbitan
monooleate, or acacia; non-aqueous vehicles (which may
include edible oils), for example, almond oil, fractlonated
coconut oil, oily esters such as esters of glycerine,
propylene glycol, or ethyl alcohol; preservativesl for
20 example methyl or propyl p-hydroxybenzoate or sorbic acid,
and if desired conventional flavouring or colouring agents.
Oral liquid preparations are usually in the form of aqueous
or oily suspensions, solutions, emulsions, syrups, or
2s elixirs or are presented as a dry produc~ for reconstitution
with water or other suitable vehicle before use. Such
liquid preparations may contain conventional addltives such
; as suspending agents, emulsifying agen~s, non-aqueous
vehicles (which may include edible oils), preservatives, and
30 flavouring or colouring agents.
The oral compositions may be prepared by conventlonal
methods of blending, filling or tabletting. Repeated
blending operations may be used to àistribute the actlve
s agent throughout those compositions employing large
WO91/17161 P~T/GBs)1/0~636
" ~
~ 18-
quanti~ es of fillers. Such operatlons are, of course,
conventional in the art.
For parenteral a~ninistratlon, fluid unit dose forms are
5 prepared containing a compound of the present invention and
a sterile vehicle. The compound, depending on the vehicle
and the concentration, can be either susoend~d or dissolved.
Parenteral solutions are normally prepared by dissolving the
compound in a vehicle and filter sterilising before f lling
lO into a suitable vial or ampoule and sealinc.
Advantageously, adjuvants such as â local anaes~het.c,
preservatives and buffering agents are also àissolvec in the
vehicle. To enhance the stabil1 y, the o^mp^s.tion can ~e
frozen after filling in~o the v al ana ~he wa~er removed
15 under vacuum.
~arenteral suspensions are prepared in subs~antially the
same manner excep~ that the compound is suspended in the
vehicle instead of being dissolved and sterilised by
20 exposure of ethylene oxide before suspending in the sterile
vehicle. Advantageously, a surfactant or wetting agent is
included in the composition to facilitate uniform
distribution of the compound of the invention.
25 The invention further provides a method of treatment or
prophylaxis of pain, emesis, CN5 disorders and/or
gastrointestinal disorders in mammals, such as humans, which
- comprises the administration of an effective amount of a
compound of the formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable
30 salt thereof.
~ . , .
:
An amount effective to treat the disorders nereinbefore
described depends on the relative efficacies of the
compounds of the invention, the nature and severity of the
35 disorder being treated and the weignt of the mammal.
Howeverj a unit dose~for a 70kg adult will normally con~ain
'
WO 91/17161 P(~/G E~9 1~006~6
3 ~ ~
0.05 to lOOOmg for example 0.1 to 500mg, of the compound of
the inven~ion. Unlt doses may be administered once or more
than once a day, ~or example, 2, 3 or 4 times a day, more
usually 1 to 3 times a day, that ls in the range of
5 approximately 0.0001 to 50mg/kg/day, more usually 0.0002 to
25 mg/kg/day~
No adverse toxicological effects are indicated at any of ~he
aforeme~tioned dosage ranges.
The inventlon also provides a pharmaceutical composition for
use in the treatment and/or prophyla~ls of pain, emesis, CNS
disorders and/or gastrointestinal disorders whi~h
composition comprises an effect non-toxic amount of â
compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceu~ically acceptable
salt thereof and pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
The invention also provides â compound of formula (I) or a
pharmaceutically acceptable salt thexeof for use as an
20 acti~e therapeutic substance, in particular for use in the
treatment of pain, emesis, CNS disorders and/or
gastrointestinal disorders.
The invention further provides the use of ~ compound of
25 formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof
for the manufacture of a medicament for the treatment and/or
prophylaxis of pain, emesis, CNS disorders and~or
gastrointestinal disorders.
30 The following ~xamples illustrate the preparation of
compounds of ~ormula (I~, the following descriptions
illustrate the preparation of intermedia~es.
.
' ~
WO9l/17161 PCT/GB~ 063O
'~s9
~ 20-
Desc~iption 1
4-Methy,l-l-isoquinoline carbo:~aldeh~d~ ~ ~
s To a solution of 1,4-dimethyl isoc~inoline (C'.465) (- -.
Agrawal, P.D. Mooney and A. C. Sar~orelll, v Med. C~e~.,
1976, 19, 970) in 1,4-dioxane (250 ml) was added selenium
dioxide (6.65g) and the mixture heated under _eflux, unaer
an atmosphere of nitrogen, ror 4h. Af~er al_owing rhe
o reaction mixture to cool to room temDerature, the
precipitated selenium was removeà oY~ r ' o~ Q
filtrate concentrated to dryness. Tne res-d~e wa~ pur ~e~ -
hy flash chromatograDhv on sil-c~ ~ s .~ _o'eum
ether (bp 60-80C) ana dle~hyl e~;.er (up 5 ~% V/vj as
5 eluent, to afford the aldehyde (~1) (3.78g) as a ~an solld.
Mp. 61-63.
M.S. M+ 171
n.m.r. (CDC13, 250 MHz~
20 S 2.74 (s, 3H)
7.71-7.87 (m, 2H)
8.05 ~d, lH)
8.63 ~s, lH)
9.38 (d, lH)
10.35 ~s, lH)
DescriD~ion 2
4-Methyl-1-isoquinoline carboxylic acid (D2)
30~ ~
To an aqueous solution of silver o.~ide (prepar5~d by the
addition of silver nitra~e (5g) in water (10 ml) to a
stirred solution of sodium hydroxide (2.40g) in water (lO
ml)) was added, at 0C, 4-methyl-1-~ soquinoline
.
:
. ' ~ ', . '.' ' . ' ' , . - ' . ., ' ' . ' I ~ ' ' ' ' ' . .
YO91.~17161 PCT/~391/5)063~
2~$ ~3~
-21-
carboxaldehyde (D.l) (2.50g), in portions. The reaction
mixture was stir~ed at ambient temperatures overnight. The
silver suspension was removed by filtration and washed with
hot water (3x5 ml). The combined filtrate and washlngs were
5 acidified with conc. HCl and extracted with chloroform (3x50
ml). The organlc phase was dried (MgSO4) and concentrated
ln vacuo to afford the title compound (D2) (980 mg) as a
beige solid mp. 155-57.
10 M.S. MH+ 188
n.m.r. (CDC13, 250 MHz)
2.75 (s, 3H)
7.79-7.92 (m, 2U.)
8.07 (d, lr.)
8.43 (s, lH)
9.67 (d, lH)
10.58 (bs, lH)
ExamPle-l
,.
endo-N- ~9-Methyl-9-azabicYcloL~3.1 ~nonan-3-yl)isoquinolin-
l-carboxamide (E1)
:
I ~ ~-Me
- ~ CO-NH J ~
~ (El)
::
:
: ~ :
.
:
WO ~1/17161 ,~ PCr/GB91/00636
Q ~J
~ -22- -
A solution of ~soquinolin-l-carboxylic acid (2g),
N-hydroxysuccinimide (1.5g) and
1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimicle (2.6g) was
stlrred in dry DMF (SOml) at room temperature for 4 hours.
5 The reaction mixture was cooled at 0C,
endo-N-(9-me~hyl-9-azablcyclo[3.3.1]nonan-3-am1ne (~g) ln
CH2Cl2 (30ml) was added and the mi~ture s~irred at 30m
temperature overnight. The solvent was remo~ed and ~he
residue dissolved in CH2C12, washed with saturated aqueous
o NaHC03 solution, dried and concent~ateà. The residue was
recrystallised from Ethyl acetate and ~etrol (~p~. -ange
60-80C), to glve the title compound (2.4g).
m.p. 155-157C.
:
ExamDles 2 to 6 .
, . . .
The following compounds arP prepared analogously to example
1 or as hereinbefore descri~edO
. :
_ ._ .............. _ . . ._
Example Point of R2l Zl
2s attachment
of CO-NH Zl :.
_ ~ ~ _
E2 1 H N-methyltropane :
~3 H N-methyltropane
1 H quinuclidin-3-yl
: ~ E5 : 1 4-CH3 N-methyltropane
: :
. ~6 : 1 H N-methyloxagranatane
~ ~ , ,' , ':
:
. ,.
, .
:
WO 9 l / l 7 1 6 l ~Cl /Gns 1/00636
~23- 2~
F.xample 2
endo-N-(8-Methvl-8-azabicyclo[3 2.11octan-3-vl~isoqulnolin-
1-carboxamide (E2)
mp 87-88
H-NMR (CDC13)
3.67 (d, lH)
o 8 . 75 (d, lH)
8 . 48 (d, lH)
7 . 9-7.6 (m, 4H)
4.42-4 .28 (m~ lH)
3.25 (brs, 2H)
2.42-1.70 (m, ~IH including 2.35, s, 3H)
~= _~_
20 1soquinolin-3-carboxamide (E3)
mp 133-136
1H-NMR (CDC13)
25 ~ 9.19 (s, lH)
8.85 (brd, lH)
8.60 (s, lH)
8.10-7.95 (m, 2H)
- 7 . 80-7 . 65 (m, 2H)
4.36 (dt, lH)
3.25 (brs, 2H)
2 . 44-1.95 (m, 9H including 2 . 36, s, 3H)
1.85 (brd, 2H)
WO91tl7161 ~ ~ ~ PCr/Cn91/00636
-24-
Example 4
N~ouinuclidin-3-yl)isoquinolin-l-carboxamide(E4)
s mp 115-117
H-NMR (CDCl3)
9.62 (d, lh)
8.51-8.40 (m, 2h)
7 . 9-7. 62 (m, 4h) :
4. 35-4 .15 (m, lh)
3.58-3.41 (m, lh)
3.10-2.82 (m, 4h) . .
:
2. 75 (dd, lh) ~.
2.41-l.S (m, 5h)
_ ~=~_
20 ~ in-l-car}:oxamide (E5L
; .
mp 148 150 ~ .
lH-NMR (CDCl3)
2s ~ 10 . 03 (brd, lH)
9.42 (d, lH)
8.50 (d, lH)
- 7.9-7.62 -(m, 4H)
4 . 88-4 . 72 ~m, lH)
~ 4.10 (d, 2H)
3.68: ~ (d, 2H)
2 . 75 (brs, 2H) .
: 2 . 67-2 .50 (m, SH including 2.60, s, 3H)
1. 60 (d, 2H)
3s ~ ~
.:
~:~ :: ~ .',
~: :
WO91/17161 PCT/GB91/0~63~
2 ~ o 1 3 S 13
-25-
Example 6
endo-N-(8-Methvl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.11octan-3-yl)-4-methyl-
l-isoquinolin-l~carboxamide hydrochloride (~L
A solution of 4-rnethyl-1-isoquinoline carboxyllc acid (500
mg) (D2) and N-hydroxy succinimide (368 mg) in dry DMF (15
ml) was stirred under an atmosphere of nitrogen at amblent
temperatures for 30 min. 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dime~hylamlnopropyl)-
o carbodiimide (768 mg) was added in one portion and stirrlngcontinued for lh. The reaction mix~ure was cooled to 0~C
and a solution of endo-8-met~yi-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-
amine (374 mg) in DMF (5 ml) was added dropwise and stirrina
continued fo- 20h at ambient tempe-atures. The solvent W2S
15 removed in vacuo and the residue partitioned between
chloroform (50 ml) and 10% aq. NaOH (5 ml). The organlc
phase was dried (MgSO4) and evaporated under reduced
pressure. The residue was purified by flash chroma~ography
on silica gel, using chloroform and ethanol (up to 10% v/~)
20 as the eluent to afford an oil~ Treatment with ethanolic
HCl gave the title compound ~200 mg) as a pale yellow solid.
m.p. 140~43.
M.S. M+ 309 (Free base)
25 1E~-NMR (d4-MeOH, 250 MHz)
2.33-2.52 (m, 5H)
2.59-2.65 (m, 2H)
2.84 (s, 3H)
- 2.92 (s, 3H)
30 ~ 3.02 . (d, lH)
: 3.89-4.06 (m, 2H)
4O40-4.53 (m, lH)
8.10 (t, lH)
8.30 (t, lH)
8.44-8.60 (m, 3E~)
WO 91/17161 ,~,3~`J PCrt(;B~ )0636
q,9~
-26-
5-HT3 ~eceptor ~ntaqonlSt Activity
Compounds are evaluated for antagonism of the von
Bezold-Jarisch reflex evoked by 5-HT in ~he anaesthetised
5 rat according to the following method:
Male rats 250-350g, are anaesthetised ~ith urethane
(1.25g/kg intraperitoneally) and blood pressure and heart
rate are recorded as described by Fozard J.R. et al,, J.
lO Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2, 229-245 (1980). A subma~imal dose
of 5-HT (usually 6~cj/kg) is given repea~edlv by the
lntravenous route and changes in heart rate quantified.
Compounds are given intravenously and the concentration
required to reduce the 5-HT-evoked res?onse to 5~% 3- ~:.e
15 control response (ED50) is then determined.
'.
,
, '':
;
,~
` '
::
:
. . :