Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
20~2~7~
..
~OECI~ST Ai~TIl5~aGE5ELL5C~AFT ElOI~ 91/F 350 Dr.Fl/bw
De~scription
Pyridine~2,4- and - 2,5-dicar~oxalD.ideE~ asld their der~va
tive~, proc~s ~or their praparation, and their use
5 Compound~ whiah irlhibit thz enzyme~ prolin~ hydroxyla~e
and lysine hydroxylAE~e c~3.u~e~ a highly ~el~ctive inhibi-
tion o~ coll~gen bio~ynt}~esi~3 by a~fecting th~ collagen-
specific hydroxylation reactione. During these reaation~,
protein-bound proliE~e or ly~ine i~ hydroxylat0d by the
10 enzymes proline hydroxyla~e ar~d lysine hydroxyla~e, re~-
pectively. If thi~ r~action is pr~vented by inhibitors,
the result i~ a non-funetio~al, subhydr~xylated collag~n
molecule, of which o;lly a 3m21ll ~mount ~an be released
:~ rc:m the c:ellS~ into the e~tracelluar space~ Moreover, ~he
15 subhydroxylatl3d collagen c:almot be i~oorporated ~nto the
collagen matrix and i~ ~ubject to ~ery rapid proteolytic
degradation. A~ a ~:orlsequ~nce o~ the~e efiects, the total
amount of extrac~llulaxly depo~ited collagen decrea~es .
It is known th~t illhibition oiE proline hydroxylass by
known inhibitors, sus:h a~ dipyridyl, re~ult~ in an
inhihitioh of the Clq bio~ynthe~i~ of ~a~rophage~
~W. Muller et al., FEB~ Lett. 90 (19783, 218; Immun-
biology 155 (1978), 47~. ~he cla~ical pathway o~ c~mpl~-
ment activa~ion i~ there~ore not available. Proline
hydroxyla~e inhibitor~ therefore al~o act a~ in~uno-
depressants, for sxample in Lmmune complex di~order~.
It i8 knowm that the e~zyme proline hydroxyla~e i~
inhibited e~fectively by pyridine-2,4- and -2,5-di-
carboxylic aoid ~. Majamaa et al., ~ur. J. ~iochem. 138
~1984) 239-245). When these compound~ are ueed in aell
cultures, however, they only act aq inhibitor~ when
present in very high con~entration~ (Tschank, G. et al.,
~iochem J. 238 (1987) 625-633).
2 ~ 7 ~
-- 2
~ .
D~-A 3~432,0g4 described pyridine-2,4- ~nd ~2,5-di-
carboxylic ~cid die~ter~ h~vin~ lWB carbon ~tom~ in the
~st~r alkyl ~oiety a8 pharmaceutic~l~ for ~nhibiting
proline hydroxylas~ and ly~ine hydroxyla~e~
5 however, the ~hortcomi~g o $he~e low~r~al~ lated
di~sters i~ that they are too rapildly cle~ved in the
organism to giv~ th~ a~id~, and that they do ~ot reach
the site o~ action in the cel~ in suffici3ntly high
concentration~, which ~ak~s th~m le~ ~ultable for
possihle admini~trat~on ~ pharma~eutical~
DE-A-3,703,959, D~-A-3,703,962 a~d D~-A-3,703,963 pro~ide
the general description of mix~d e~ter/~mide~, higher
alkylated die~ter~ and diamide~ of pyridine-2,4- a~d
-2,5-dicarboxylic acid which are ef~icien~ inhibitor~ of
aollagen bio~ynthesi~ ~n the animal ~odel.
For example, DE-A 3,703,959 de~cribes, inter alia, ths
~: synthe~is of N,N'-bis~2-methoxyethyl)pyridine-2,4-di-
oarboxylic diamide and ~ bi~3-i~opropoxypropyl)-
pyridine 2,4-dicarboxylio diamide.
. .
German Patent ~pplication~ DE-A-3,825,471 and
D~-A-3,828~140 propo~e an impxoved proce~ ~or the
i prepara~ion of ~ bis(2-methoxyethyl)pyridine-2,4-di-
~arboxylic diamide. German Patent ~pplioation
DE~A-3,924,093 propose~ novel ~W'-bi6(alkoxyal~yl~-
pyridine-2,4-dicarbo$ylic diamides.
There wa~ ~ need to ~earch for other oompound~ having an
~mproved pharm~cological activity with regard to the
inhibition o~ lysine hydroxyla8e and proline hydroxyla~e.
Surpri~ingly, it ha8 n~w been found that thi~ object ia
achieved by the following pyridine-2,4- and -2,5-di-
carboxylic diamides.
_ 3 _ 2 ~8~7 ~
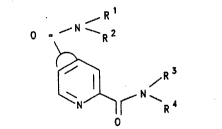
The invention therefore relat~s to ~:cDIipou~d~ of the
~ormula I
R1
O ~--N--R2
R'~ (I)
N ~ ~ ~ ~4
o
in which
S Rl, R2, R3 and R4 are identical or differ~nt and are
A a bran~hed or unbr~n~h~d, aliphatic or ~yclo-
aliphatic (C1-Cl2~-alkyl r~di~al, gCl-C~2~-alke~yl radi~al
or a (C1-Cl2)-alkynyl radieal, ea~h o~ which is mono~ub-
~tituted or poly~ub~tituted, prefer~bly mono~ub~ti.tuted
or di~ubstituted,
by ~ ~ Cl-C9 ) -alkoxycarbonyloxy, (C1-Ca)-alkXY~( Cl~Ca )
alkoxycarbonyloxy, (C6--Cl2)-aryloxy~arbonyloxyt (C7-C
aralkyloxy~arbonyloxy, (C~-C~ aralkylcarbonyloxy,
,:cinn~moyl, ~innamoyloxy, ~C6-Cl2)-~rylc~rbonyloxy, ~C8-C8~-
alkenylcarbonylo~y, ~C3-C~)-al~ynylcarbo~yloxy, (C3oC8)-
cycloalkylcarbonyloxy, (C1-C~-alkoxy-(C~-Cl2)-alkoxy,
::~Cl C~)-alkoxy-amino,(C1-C~)-alkoxy-N (C1-C~-alkyl~mino,
12) -alkoxy-~,N (~l-C5)-dialkylamî~o, aarbamoyloxy,
N-~C1-C~)-alkylcarb~moyloxy, ~,N-di-(Cl-C8~ yl~arba~oyl,
~:20 N-(C3-C~)-cy~lo lkylcarbamoyl, ~-(C~-Cl2)-ar~lamino,
N-(C7 C~ arAlk~lam~no, N-alkyl-aralkylami~o, ~-alkyl-
arylamino, (C3-C8 )-cycloalkanoylamino, ~C1 C~)-alkanoyl-
~mino, (C6-cl2)-aroylamino~ (C~-C~ aralkanoylsmino,
(C~-C8);alkanoyl-(Cl-Ca)-alkylamino,( C3 ~Ca)-cyclo~lkanoyl-
(C1-C8)-alkylamino, (C8-Cl2)-aroyl-lCl-C~)-alkyl d no,
(C7-C~ aralkanoyl-(Cl-Ca)-alkylamino, (cl-c8)~a
mercapto, (C1-CB)-alkyl~ulflnyl, (C1-Ca)-alkylsulfonyl,
(C1-C8)-alkylcarbonyl, (C3-C8)-cycloalkylcarbonyl, nitro,
_ 4 _ 2082~7~
trifluoromethyl~ phenylm~rcapto, phenylsulfonyl~ ph~nyl-
sulfinyl, ~ul~amoyl, X3-(Cl-C~-a~ ul~amoyl, ~ di-
(Cl-C~)-alkylaulfamoyl, ~Cl-CB)-Alkyl~ulfonamido and
~ryl~ulfonamido, where the ~ d ~ralkyl radicals in
S the above ~ubotituents c~n ~l~o h~ve a heteroc:yclic
natu:re and/or, lik~ lkyl, are sub~;titut~d ~ 1, 2, 3, 4
or 5 id~ltic:al or d~ ff~ar~nt ~ubl3tituentl3 ~elected :Erom
the ~eriee c:omprising halogsn, cy~no, tlitro, trifluoro-
methyl, ( Cl~C~ allcyl, hydroxyl, ~ ICl-C,3 ) -hydroxyalkyl,
10 (Cl-C6~-alkoxy, ~Q-tCEI2-~sc~ +, "F" -OCF2Cl, -O-CF2-C~FCl,
trif luorom~thyl ~ Cl-Ca ) -alkylDI2roapto ~ B ) -allcyl-
~ulfinyl, tCl-C630alkylsulfoslyl, (Cl-~6)-alkylcarbcnyl,
( Cl-C6 ) -alkoxya~rbonyl, I:arbamoyl, N- ( C~-C" )
carbamoyl, N,N-di-(Cl-C~)-alkylc:arbamoyl, ~Cl~C~)-alkyl-
carbonyloxy, tC3-C8)-cyaloalkyl, phenyl, b~yl, ph¢noxy,
benzylo~y, NR'-R", phenylmercapto, phenyl~ul:Eonyl,
phenyl~ulfinyl, ~ulfamoyI, N-~Cl-C4)-alkylsul~a~oyl or
~,N-di-~C1-C4)-al~yl~ulf~moyl, in p~r~icular by up to 3 of
the abovementioned identiaal or differeAt ~ub~tituent~r
and a CH2 group of the ~lkyl chai~ i~ optionally replaced~
by 0, S, SO, SOz or ~R'9
or by a substituted (C~-C~)-aryl radical or heteroa~yl
radical havin~ 1, 2, 3, 4 or S identical or different
6ub~tituent~ from the series ~omprising hydroxyl, tri-
fluoromethyl, ~C~oC6)-hydroxyal~yl, -O-[C~2~]3C~2~l8)E~
OCF2Cl, -OCF2 C~FCl, (Cl-C6)-alkylmercapto, ~Cl-C~3-~lkyl-
~ulfinyl, (Cl-C6)- lkyl~ul~onyl, ~C~-C6~alkylcarhonyl,
~Cl-C6)-alkoxycaxbonyl, carbamoyl, N-~Cl~C~ yl-
carbamoyl, ~,N-di-(Cl-C~)-alkylcarbamoyl, (C~-C~)-alkyl-
3Q carbonyloxy, (C3-Ct)-cyclo~lkyl, phenyl, benzyl, ph~noxy,
benzyloxy, NR',R", phenylmercapto, phenylsul~onyl,
phenyl~ulfinyl, sulfamoyl, N-(Cl-C~)-alkyl~ulf~moyl,
N,N-di-~C~-Cs)-alkylsulfamo~l, (Cl-C8)-alkoxycArbonyloxy,
(C1-C8)-alkoxy-(Cl-C~)-alkoxycarbonyloxy, (C6-C~)-aryloxy
carbonyloxy, (C7-C1l)-aralkyloxycarbonyloxy, ~C7-C1l)-
aralkyloarbonyloxy, cinnamoyl, cinna~oyloxy, (C6-C~)-
arylcarbonyloxy, ( C3-C~ ) -alkenylcarbonyloxy, ~C3-C8)~
2~7~
- 5 -
alkynylcarbonyloxy, ~C3-C~ ) -cycloalkylcarbonyloxy,
(C~-C~)-alkoxy-~C~-Cl23-~lkoxy, ~Cl-Cl2) alko~y-aminv,
l~l-Cl2)-~lkoxy-N 5Cl C5)-alkylamino, ~Cl-Cl2~-alkoxy-~l,N
(Cl-C~)-dial~yl~mino~ carbamoyloxy, N-(Cl-C~)-al~yl-
c~rbamoyloxy) ~ di-(Cl-CG)-~lkylc~rb~moyl, ~-tC3-C~)-
cycloalkylcarbamoyl, N-(c~-c~)-a~yl~mi~o~ ~-(C7-c~
~ralkylamino, N-alkyl-aralkylamlno/ ~ ~lkyl-aryl ~ no,
(C3~C8)~Cycloalk~noylamlno~(cl-c~)-alkanoylRmino~(c~-c~)~
aroyl~mino, ~C7-C~ aralkanoylamino, (Cl-C~)-alkanoyl-
0 (Cl~c2)-alkylaFino, ~C3-C~) -cyaloalk~noyl-(C~-C~)-alkyl-
amino, lC~-C~)-aroyl-(Cl C8~-alky}amino, (~rCl~)-ar
alkanoyl-~C1 C~)-alkylamino, tCl-Ca)-alkylmercapto, ~Cl-C8~-
alkyloul~inyl, (Cl-Ca) ~lkyl~ulfonyl, (C 8)-
~lkylcarbonyl, ~C3-Ca)-~yc}o lkylcarbonyl, nitro, tri-
fluoromethyl, phenylmercapto, phenylsulfonyl~ phe~yl-
~ 3ll1finyl, ~ulfamoyl, N-(Cl-C6)-alkyl~ulfamoyl, ~ di-
- (Cl-C6)-al~ylsulfamoyl, ~CI_C~ alkyl-sulfon~mido ~nd
arylsulfonamido, where the aryl and alkyl radi~al~ in the
a~ove ~ub~tituents o~n al00 haYe a heterocycli~ nature
and~or, like ~lkyl, oan be ~ub~t~tut~d b~ 1~ 2, 3, 4 or
5 identical or different ~ubstituent~ from the ~eri~
comprising halogen, ~yano, nitro, trifluoromethyl,
( C~_CB )-alkyll hydroxyl, (C~-C~3-hydroxyalkyl or (C~-C6)-
alkoxY r
or by a ~ub~tituted ~C6-Cl2)-aryloxy radical, (C7--Cll)-
aralkyloxy radical or hetero~ryloxy radical, ~ach of
which ha~ 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 identi¢al or differe~t ~ub-
~tituents selected ~rom the ~eriea ~o~pri~ing hydroxyl,
halogen, cyan~, nitro, trifluoromethyl, tCl-C6)-
hydroxyalkyl, (C1-C8)-alkoxy~ 2-33~5
~OCF2-C~FClr tC~ alkylmercapto, (Cl-C6)-allcyl~ul~inyl~
(Cl-Ca)-alkylsulfonyl, tCl-C0)-alkylcarbonyl, tCl-C6)-
alkoxycarbonyl, carb~moyl, N-(Cl-C~) alkylcarbamoyl,
N,N-di-(Cl-C~)-alkylcarbamoyl, (Cl-C~)-alkylcarbonyloxy,
(C3-C5)-cycloalkyl, carboxyl, phenyl, benzyl, phenoxy,
benzyloxy, NR'-R", phenylmercapto, phenyl~ulfonyl,
phenylsulfinyl, sulfamoyl, N-(Cl-C~)-alkylsulfamoyl,
2~82~
-- 6 --
N,N-di-(CI-C4)-alkylsulfamoyl, aminoalkyl, N-~C1-C8)-
alkylamino-(Cl-Cl2)-alkyl or N-di-(Cl-Ca)-alkylamino-
(Cl-Cl2)-alkyl and which i9 optionally ~ubstituted by up
to 3 o~ the abovem~ntioned identical or dif~erent ~ub-
~titllent~, and one CH2 group of the alkyl chain i~ option-
ally replaeed by O, S, SO, 52 or NR',
or by a radical of the formula II
~5 (II)
in which
R5 is an amino acid bonded via it~ acyl radical, or a
derivative of this amino acid, or an alcohol protec-
tive group,
B a substituted ~C6-C12)aryl radical, (C7-C1l)aralkyl
radical or heteroaryl radical, each of which i~ monosub
stituted or polycub~titutedJ pre~erably mono- or
disubntituted,
by hydroxyl, amino ~C~-C8)-alkoxycarbonyl, (Cl-C8)-alkyl~
carbonyloxy, ~ Cl-c8 ) -alkylamino, di-( Cl-C8 )-alkylamino,
~:: (C1-C6)-hydroxyalkyl, -O-~CH2-]XcfH(2~ )F3~ -OCF2C1,
-OCF2-CHFCl, carbamoyl, N-~Cl-C8)-alkylcarbamoyl,
N,N-di-(Cl-C8)-alkylcarbamoyl, (Cl-C8)-alkylcarbonyloxy,
(C3-Ca)-eycloalkyl, phenyl, benzyl, phenoxy, benzyloxy,
amLnoalkyl, N-(Cl-C8)-alkylamino (Cl-Cl2)-alkyl or N,N-di-
. (cl-ca)-alkylamino-(cl-cl2)-alkyl, (Cl-C8)-alkoxycarbonyl-
oxy, (cl-c8)-alkoxy-(cl-c8)-alkoxycarbonyloxy~ (C6-C12)-
aryloxycarbonyloxy, (C7-C1l) aralkyloxycarbonyloxy,
tC7-Cl1)-aralkylearbonyloxy, cinnamoyl, einnamoyloxy,
(Cg-Cl2)-arylearbonyloxy, (C3-Ca)-alkenylearbonyloxy,
(C3-C8)-alkynylaarbonyloxy,(C3-Ca)-eyeloalkylcarbonyloxy,
(C1-C1z)-alkoxy-(C~-Cl2)-alkoxy, (Cl-Cl2)-alkoxy-amino,
(Cl-Cl2)-alkoxy-N (Cl-C6)-alkylamino, (C~-C~2)-alkoxy-N,N
(Cl-C6)-dialkylamino, earbamoyloxy, N-tC1-Ca)-alkylcarbamo-
2~82~7~
7 --
yloxy, ~, N-di- (C~-C~ alkyl~ 0yl, N- ~C3-C6 ) -cyclo~lkyl-
ca~bamoyl~ N-(C~ ryl~lno, N~t~r~ ral~ylamino,
N-alkyl-arallcylamino, N~ o, ~C~-Ca)-c:yclo-
alkanoylamino, ~Cl-CO) -~lkanoyl~m~no~ ~C~,-C~ royl~no,
(C7-C~ aralk~noyl ~ no, (Cl-Ca)A~Llkanoyl-(Cl-C~,)-~lkyl-
amino, ~ E9-C~ ycloalkanoyl- (Cl-COJ -ell~c3rla~no t (C3-e~
aro~rl-(Cl-C81-alkylamino, (C7~C~ ralk~oyl-(C~ CO)-nlkyl-
A~n~no, ~C1-C8)-a}kylmercapto~ (c~l-c~ k3rl~ulfinyl~
(Cl-~a)-alkyl~lul~onyl~ ~C~-~8)~ carbolly~ 3-C~
10 cyclo~lkylc~rbonyl, nitro, tr~luo~omethyl, ph~nyl-
:~ ~er~:apto, phenyl~ulfonyl, phenylsuli~i~yl, 3ulfæmoyl,
N-(C1-C6)-alkylaulfamoyl, ~9~ di-~C~-C~ alkyl~ulfamoyl,
(Cl-Ct) -alkyl-E~uliEonami do or ~LrylsuliEon2mido,
.
C a substituted (Cl-Cl2) ~lkoxy radical, ( 3-C~ cyclo-
15 alkoxy, (C6-C~2)-aryloxy rAdical or ~ (C~-C~a)-aral~yloxy
radical, each of which i~ ~onosub~itu~ed or polysub~ti-
tuted, pre~erably ~OAO- or di~ubstituted,
~y halogen, tri~luoro~ethyl, (C1-C~ alkoxy, hydroxyl~
( Cl-C~ ) -hydroxyalkyl, ~R ' R ~' or cyano
20 where in each ca~e
R' and R" are identical or different and are hydrog2n,
DC12) -aryl, ( C1-CB) -a ~ C~-C5) -,alkylcarbonyl,
(C~-Cl1~-aralkylcar~onyl or tC6-C~ rylcarbonyl, or
together with the nitrogen, form a saturated heterocyclic
25- ring, pref~rAbly a 5- or 6-m~ r~d ring,
and the abovementioned r~dia~l0 R19 p~2, ~3 ~nd R4 e~ occur
` in combination
with n (C~-C12~-alkyl radical whi~h i~ mc~no~ubsti~uted or
poly~ubetituted, pre~erably mono- or di~ubstituted, }~y
hydrogen, halogen, hydroxyl, cyano, ~mino~ carboxyl,
(C1-Cj)-alkoxy, (C1~C~ lkoxyc~rbonyl f (Cl C4)-alkyl-
carbonyloxy, (Cl C~)-slkyl~ o~ (Cl-C~)-di~lkylamino or with
2~82~7~
- 8 -
a phenyl ring which i~ ~ono-, di- or txi~ub~tituted by
the r~dical~ halogen, n~tro, (C1-C~)-alkyl or ~Cl-C4~-
alkoxy, or in ~mbination
with an aryl or het~roaryl radiaall ~ach of which ~a~
S turn, optionally be mono-, di- or trisub~tituted by
halogen, nitro, cyano, ~Cl-C~ lkyl, ( C~-C4)~ alk9Xy~
including all deri~a~ivas which have a zuitable prot~c-
tive group in ~heir ~mino or hydroxyl group~,
and the phy~iolo~ically active ~alt~ d
n i~ O or 1,
f is 1 to 8, preferably 1 to 5,
g i~ 0, 1 to (2f+1), ~hd
x i~ 0, 1, 2 ox 3, preferably 0 or 1.
Aryl, aryloxy, heter~aryl or heteroa~yloxy ~ompounds are
: 15 -~nderstood as meaning, in particular, phenyl and naphthyl
rin~8~ or unsub~tituted 5- and 6-~embered heteroaromatic
ring~ having l, 2 or 3 ni~rogen and/or oxygen and/or
~ulfur atoms, such a~ pyridyl, pyridazyl, pyrimldyl,
pyrazyl, imidazolyl, triazolyl, thienyl, oxazolyl and
thiazolyl ~eri~atives, nd their benzo-fused derivative~.
The radical ~C7-C~ aralkyloxy ie preferably u~der~tood
as meaning a ~ubstituted phenylalkyloxy radical o~ the
; . formula III
R6 R7
-O -[CH2-lr ~ R~ (III)
Rl R9
in which
2t)82~7~
g
R8, ~7~ R8 ~nd RlQ are identical or di~fer0nt and ar~
hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro, txifluorumethYl, (I~ C5~-
alkyl, (Cl-C~ alkoxy, -O-t~2~ CyH~2~ s)F3~ -OCF2Cl~
-O-CF2-CEIFCl, ~ Cl C~ ) -alkylmers~apto, ~ Cl-C~ ~ ~alkylsulf ir~yl,
S (C~-C~ alkylsul~onyl, ~C,-Ca)-alkylcarbonY~ G~-
alkoxyc:arbonyl, carbaDJoyl, N- t Cl C4 ) -alkylc:arlbamoyl,
Il,~-di- ~C~-C~ ~ alkylcarbamoyl, (5~1 C6~ -~lkglcarbonyloxy,
C3-C8 ) -~ycloalkyl, phenyl, benzyl, pherloxy, benzyloxy,
~R'-R", suQh as ~mino, anil~no, ~-methylanilino, phenyl-
10 mer;:apto, phenyl~ul~onylg ph~yls~ Einyl, ~ulf~moyl,~-~C~-C")~alkylsulf~oyl or N,~-di-ICl-C~3-allcylsulfamoyl,
or two adjac~t subst~tuen~r~ together are ~I chain -~CEI2-~n
or -CE~-C~-CB~C~-, where a C~2 group of th~ chain i~
optionally rep}aed ~ O, S, SO, SO2 or NR', Y i3 1, 2~
15 3 or 4 ) pref~rably O and 1, and the remaining o~ the
substituents R6, R7, R8~.R~ and Rl are a8 de~ined above.
o acids which are preferred fxom among~t those
mentioned above are~ in particular, the natural ~-amino
~cid~.
Amino proteative group~ are under~tood ~ aning, in
particular, ~u~h group~ aB are de~cribed in R. ~eiger and
W. ~nig "The Peptides" Volume 3, "Protection of Func
tional Group~ i~ Peptide Synthesi~, B.~. Gro~s,
J. Meienhofer ~dit, AGademic Press, ~ew York (1981l, in
particular pages 7-4~.
Such groups are also deacribed in ~. ~ubbu~h, S~hutz-
gruppen in der Peptidsynthese [ProtectiYe Group~ in
Peptide Synth~Eis], Rontakte 3/791 pag~o 14-23.
Particularly pre~erred amlno protective group~ are the
~oll~wing:
Aoetamidomethyl,
l-Adamantyloxycarbonyl,
l-tl-Adamantyl)-l-methyl-ethoxycarbonyl,
~)82~7~
-- 10 --
Allyloxycarbonyl,
tert-Butyloxycarbonyl,
1~4-Biphenylyl)-l-methylethoxycarbonyl,
Dicyclohexylaarbodilmlde,
~,~-DLmethyl-3,5-dimethoxybenzyloxycarbonyl,
4-Dihydroxyborylbenzyloxycarbonyl,
9-Fluorenylmethyloxyc~rbonyl
l-~ydroxybenzotriazole,
3-Hydroxy 4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-1,2,3-benz~triazine,
I~obornyloxycarbonyl,
l-~ethyl-cyclobutylo~yc~rbonyl r
4-Methoxybenzyloxyc~rbonyl~
~ethyl~ulfonylethyloxycarbonyl,
4~Pyridylmethyloxycarbonyl,
lS 2,2,~-Trichloro-tert-butyloxycarbonyl,
~enzyloxycarbo~yl,
halogen-sub~tituted b~n~yloxycarbo~yl,
4-Nitro-benzyloxycarbonyl J
2-Phosphonoethyloxyc~rbonyl,
: 20 Phenyl~ulfonylethoxyG~rbonyl,
Toluenesulfonylethoxycarbonyl,
~,3,5 Trimethyl-4-methoxy-phenyl~ul~onyl,
Benzotriazol-l-yl-oxy-tri~(dimethylamino)phosphonium
hexafluoropho~phate.
2~ Preferred compound~ ~rom amongst tho~e o~ the ~ormula I
who~e amino groups are protected are those whose pro-
tected amino group i~ part of this amino acid R5.
Suitabls alcohol protective groups axe, in pa~ticular,
~ub~tituted or unsub~tituted ~ethyl ethere, ethyl ethers,
benzyl ether~, silyl ether~, e~ters, carbonates or
~ulfonate~.
rhey embra~e the ollowing compounds:
., .
~ .
:~.
8 ~
A~ ~ubstituted methyl ~thers:
~ethoxymethyl, methylthiomethyl, t-butylthiomethyl,
(phenyld ~ethyl~ilyl)methoxymethyl, benzyloxymethyl,
p-methoxybenzyloxymethyl, ~4-methoxypheno~y)~methyl,
guaiacolmethyl, t-butoxymethyl, 4-pentenylo~ymethyl,
~iloxymethyl, 2-methoxye~hoxymethyl~ 2,2,2-tri~hloro-
ethoxymekhyl~ bia~2-chloroe~hoxy)m~thyl, ~-~trLmethyl-
3ilyl )ethoxymethyl,tetrahydropyranyl~3-bromotetrahydro-
pyranyl, tetrahydrothiopy~anyl~ 1-methoxy~yclohexyl,
4-methoxytetr~hydropyrar,yl, 4-m~thoxytetrahydrothio
pyranyl, 4-methoxytetrahydrothiopyrAnyl-S,S dioxo,
1-~2-chloro-4-me~hyl)-phenyl]-4-methoxypiperidin-4-yl,
1,4-dioxan-20yl, tetrahydrofuranyl J tetrahyfirothio-
furanyl.
As sub titut~d ethyl ethers:
1-Ethoxyethyl, 1-(2-chloroethoxy)ethyl, l-methyl-
l-methoxyethyl, 1-methyl l-benzyloxy~thyl, l-methyl-
1 benzyloxy-2-fluoroethyl, 2,2,~-trichloroethyl, 2-tri-
methylsilylethyl, 2-[phenyl~elenyl)ethyl, t butyl, allyl,-
p-chlorophenyl, p-methoxyphenyl, 2,4-dinitrophenyl,
benzyl.
As ~ubstituted benzyl ethern:
p-Methoxybenzyl, 3,4-dimethoxybenzyl, o nitrobenzyl,
p-nitrobenzyl, p-halogenobenzyl, 2,6-dichloxobenzyl,
p cyanobenzyl, p-phenylbenzyl, 2- and 4-pioolyl,
3-methyl-2-picolyl-N-oxido, diphenylmethyl, p,p'-di-
~itrobenzhydryl, triphenylmethyl, ~-naphthyldiphenyl-
methyl, p-methoxyphenyldiphenylmethy~, di(p-methoxy
phenyl~-phenylmethyl, tri(p-methoxyphenyl)~thyl,
4~(4'-bromophena~yloxy)phenyldiphenylmethyl,
4,4',4"--tris(4,5-dichlorophthalimidophenyl)methyl,
4,4'4"-tris(levulinooxyphenyl)methyl, 4,~4 n -tri8-
(benzoyloxyphenyl)methyl, 3-(imldazole-1,4~-methyl)bis-
(4'4"-dimethoxyphenyl)-methyl, l t 1-bi~(4-me~hoxyphenyl)-
1'-pyrenylmethyl, 9-anthryl, 9-(9-phenyl)x~nthenyl,
9-(9-phenyl-10-oxo)anthryl.
~2~
- 12 -
AB ~ilyl ether~-
Tr ~ethylsilyl; triethyl~ilyl, trii~opropylsilyl,
dim~thyli~opr~pyl~ilyl~ diethyli~opropyl~ilyl, dLm~thyl-
thexyl~ilyl, t butyldLmethyl~ilyl, t-butyldiphenyl~ilyl,
tribenzyl~ilyl, ~ri-p-xylyl~ilyl, triph~nyl~ilyl,
diphenylmethylsilyl, t-butylmethoxyph~enyl~ilyl.
As e~r~:
Formate~, benzoyl fo~mate~ acat~t~, ch~oroa~etate,
dichloroaaet~te, trichlo~oacetate, trif luoroacet~te,
10 Dnethoxya~:etate, triphenylmæthoxyac~etate~ phenoxyacetate,
: p-chloroph2noxyacetate, p-P-phenyla~et~te, 3-phenyl-
propiorlate, 4-oxoperltanoate t l~vul inate ),
4,J.-(ethylenedithio)pentanoate, pivaloate, adamantoate,
cxotonate, 4-1nethoxycrotonate, b~rlzoate,
15 p-phenylbenzoate, 2,4,6-tr~me~thylb~nzoate (m~itoate)~
A~ ~arbonates:
~ethyl, 9-fluorenylmethyl, ~thyl, 2,2,2-tri¢hloroethyl,
2-~trL~ethyl~ilyl)ethyl,2-~ph~nyleulfonyl)ethyl,2-~tri-
phenylpho~pho~io)~thyl, isobutyl, vinyl, allyl, p-nitro-
phenyl, benzyl, p-methoxybenzyl, 3,4-dim~thoxyb~nzyl,
o-nitrobenzyl, p-nitrobenzyl, S-ben~yl thiocarbonates,
4-ethoxy-1-naphthyl, methyl dithiocarbonate~.
Other e~ters:
2,6-Dichloro-4-methylphenoxyacetate, 2,6-Dichloro-
4- ( 1,1, 3, 3 tetramethylbutyl )phenoxyacetate, 2,4-bi~-
(1,1-dLmethylpropyl)phenoxyaoetate, chlorodiph~nyl-
acetate, isobutyrate, monosuGcinate, (~)-2-~ethyl-
2-butenoate (tigloate), O-(methoxycarbo~yl)benzoate,
p P-benzoate, ~-naphthoate, nitrate, alkyl
N~N,N',N'-tetramethylpho~phorodiamid~te, N-phenyl-
carbamate, borate~, dimethylphosphinothioyl, 2,4-dinitro-
phenylsulfenate.
:.
- 2~:~2~7~
~ 13 -
As ~ulfonat0s:
Sulfatss, methanesulfonate (mesylate), benzyl~ulfonate,
tosyl~tee.
The following protective groups are parti~ularly
preferred:
(C1-C~-Alkanoyl, (Cs-C~)-alkylcarbamoyl, d~-(C~-Ca)-alkyl~
~arb~moyl, N-( C3-C~ ~-ayclo~lkylcarbamoyl, (Cl-C5)-alkoxy-
carbonyl, ( C6-Clz ) -a~yloxycarbonyl, (C~ aralkyl
oxycarbcnyl, in part~cular benzyloxycarbonyl, (C8-C~
arylcarbonyl, (C~-C~ aralkylcarbonyl, (C1-CB)-alkyl,
(Cl~C~)~alkoxy-(C1-C~)-alkyl, ~arb~oyl-~C1-C~)-alkyl e~ter,
(Cl-C1O)-acyloxy-(C~-C6)-~lkyl, pr~ferably (Cl-C10)
alkanoyloxy-(Cl-C6 ~; alkyl, benzyloxy-( Cl-C6 ) a~kyl,
benzyloxycarbonyloxy-~Cl-C~ alkyl, ~Cl-C~)~
alkoxycarbonyloxy-(Cl CB)-Alkyl, ~mino acid e~ter~ or
tetrahydropyranyl.
Preferred compound~ of the formula I are tho~e in whi~h
Rl and/or R3 Pre hydrogen or m~thyl and R2 and~or R4 have
the abovementioned ~eanings.
Other preferred ~ompound~ of th~ formula I are those in
which Rl and~or R3 are hydrogen and R2 nd/or Rb are
A a branched or unbranched ~Cl-C12)-alkyl radi~al which
is monosubetituted or poly~ub~tituted
by ( cl-c8 ) -alkoxycar~onyloxy~ (C~-C8)-alkoxy (Cl-Ca)-
alkoxycarbonyloxy, ~C8-Cl2)-aryloxycarbonyloxyl (C~-C11)-
aralkyloxycarbonyloxy, (C7 C ~ aralkylcarbonyloxy,
(C7-Cll)-arylcarbonyloxy, (C3-C8)-cycloalkylc:arbonyloxy,
(Cl-C~2~-alkoxy-~e1-Cl2)-alkoxy, carbamoyloxy, ~-(Cl-C~)-
alkylcarbamoyloxy, ~ di-( C1_CA1-alkyloarb~moyl~
~-(C3-C~ cycloalkylcarbamoyl, ~-~C~-Cl~)~
ar~lkylcarbamoyloxy or N-(C6-Cl2)-arylcarbamoyloxy, where
the aryl and aralkyl radical~ in the above ~ub~tituent~
can al80 h~ve a heterocyclic nature and/or, like ~lkyl,
are sub~tituted by l or 2 identical or different
- 14 - 2~82~7~
~uh~tituent~ selected from the ~erie~ comprising halogen,
trifluoromethyl, hydroxyl, (C1-Ca)~al~Y~ 3 ) -
hydroxyalkyl, (C~-C~)-alkoxy, ~ ~2- ] ~C~2~+~ ~)F6 ~ -OCF2Cl ~
-0-CF2-C~FCl, -(C1-C~-alkoxycarbonyl, sarbdmoyl, ~Cl- C3 ) -
alkylcarbonyloxy, (C3Ca~-~ycloalkyl~ phenyl, benZYlr
phenoxy or ~enzylo~y,
or by a sub&tituted (C8-C~2)-aryl radical or het~roaryl
radi~al which h~8 on~ or two iden~ical or diferent
substituent~ sel~ct~d ~rom the seri~ c4mpri~ing
hydroxyl, trifluoromethyl, [Cl-C3)-hydroxyalkyl, (Cl-C3)-
alkoxycarbonyl, ~arbamoyl, NR'R", ~-~Cl-C~ yl
carbamoyl, ~ di-( C~-c4 )-alkylcarbamoyl, (Cl-C3)-alkyl-
carbonyloxy, A~; noalkyl or N-(C1-C~)-alkylamln-tCl-c~)-
alkyl, whare R' and R~ are identical or differen~ ~nd Are
hydrogen, ~C~-Clz) aryl or (Cl-C4)-alkyl,
or by a substituted (C6-C10)-aryloxy radical or ~C~-C~
aralkyloxy radical which has 1 or 2 identical or dif-
fer~nt substituents s~lected ~r~ the nerie~ comprising
hydroxyl, halogen, trifluoromethyl, (Cl-C3)-alkyl, (~ a)~
hydroxyalkyl, ( Cl-c3 ) -alkoxy, (Cl-C3)-alkylmercapto,
(Cl-C3)-alkyl~ul~inyl, (Cl-C3)-alkylsul~onyl, (Cl-C3)-
alkylcarbonyl t ( C1-C3) alkoxycarbonyl, carbamoyl,
~-(C1~C4)-alkylcarbamoyl, N,N-di-~C1-C~)-alkylcarbamoyl,
(Cl-C3)-alkylcarbonyloxy or ~R'R~ where R' and R" are
identical or dif~er~nt and are hydrogen, (C~-C1O)-~ryl or
~Cl-C4) alkyl,
or by a radic21 of the formula II
R5 (II)
in which
R5 i8 an amino acid bonded via it8 ~cyl radical, or a
derlvative of thi~ am1no acid,
~ ~ 2 ~ 7&
B i~ a ~C6-Cl2) aryl or (C7-C~ aralkyl radical, pre-
ferably phenyl, benzyl and phenethyl, each o~ which i~
monosub~tituted by hydroxyl, (C~ C4)-alkylaarbonyloxy,
(cl-c~)-alkoxycarbonyl~ tCl-C~)-hydroxyalkyl, ~mino,
(Cl-C5)-alkylAmino, di- (C~-C5) -alkyl~mino, (Cl~~s)~
alkanoylamino, carbam~yl, N-(Cl-C~)-alkylcarbamoyl,
N,N-di-(Cl C~ lkyl~arbamoyl t ~rbamoyl, N-(Cl~C4)-alkyl-
carbamoyloxy, N,N~ (Cl-C~)-alkylcarbamoyloxy, or
C iB a tCl-C6)-alkoxy radical, ~C3-C~)-cy~loalkoxy
radical, (CB_C1~ ) -aryloxy radical and ( C7-C~ aralkyloxy
radical,
: n i~ O or 1,
is 1 to 8, preferably 1 to 5,
g is 0, 1 to l2~
x i~ 0, l, 2 or 3J pr~f~rably O or 1, and
wher~ the a~ovementioned radical~ Rl, R2, R3 and R4 can
occur in combination
with a (~-Cl2)-alkyl radioal which i5 monosubstituted or
poly~ub~tituted, pr~ferably mono- or disubstituted, by
hydrogen, haloge~, hydroxyl, amino, (Cl-C4~-alkoxy,
(Cl-C4)-alkoxycarbonyl, (Cl-C~)-alkyl- or (C~-C~)-
dialkylamino or a phenyl ring which i~ ~on~-, di- or
trisubstituted by the radl~als halogen, nitro, (Cl-C4)-
alkyl or (Cl-C4)-alkoxy, and also in ~ombination with a~
: 25 aryl or heteroary.l radi¢~l which, ~n turn, can optionally
be mono~ub~t~tuted or di~ub~tituted by halogen, (Cl-C4)~
alkyl or (C~-C4)-alkoxy, including all derivatives which
have a protective group in the respective amino or
hydroxyl group, and the phy~iologically active aalts.
- ~6 - 2~8~
Particularly preferred compound~ of the formula I are
those ~n which R1 nnd/or ~9 are hydrog~n and R2 and/or Rh
are
: A an unbranched (C~-C~)-41kyl r~dical which i~ ~ono-
~ubstitut~d
by ICl-C~)-alkoxyc~rbonylo~y, ~C1-C~-alkoxy-(Cl-C~)-
alkoxycarbonyloxy, (C~-C~)raryloxycarbonYlO~Y, (C~-C~
aralkyloxycarbonyloxy, ~ C7~ r~lkyl~rbonyloxy,
~C6-Cl2)-arylcarbonyloxy, ~ C3-CB )-cycloalkylcarbonyloxy,
~cl-cl2~-alkoxy-(cl-c~)-alkoxy~ (cl-cl2~ kox~-~mino~
(C1~Cl2)-alkoxy-~-(Cl-c6)-alkylamlno~ (Cl-C12~-alkoxy-N,~-
(C1-C6)-dialkylamino, ~ di-lCl-C~-alkylcarbamoyl,
N-( C3_C~ )-cycloalkylcarbamoyl, ~-(C7C~ aralkylcarbonyl-
oxy, N-(C6-Cl23-arylcarbamoyloxy, (~1-C5~-alkanoylamino,
(C3-C6~-cycloalkanoylamino, (C5-Cl2)-~roylamino or (C7-Cll)-
~: aralkanoylamino, where alkyl, aryl, aryloxy, aralkyl or
aralkyloxy, in turn, are ~ub3tituted by h~droxyl or
halogen, in particular fluorine, (Cl-C3)-alkyl or (Cl-C3)-
alkoxy,
or by a phenyl radical which i~ m~nosub~tituted by a
hydroxyl group, or a ~ub~tituted phenoxy or benzyloxy
radiaal which i~ ~ubstituted by hydroxyl, halogen or
~; (Cl-C~)-alkoxy,
or by a radical of the formula II
-0-~3 (II)
.:
;: in which R5 i~ an d no ~cid bond~d via it~ acyl radical, or a derivative o~ this amino acid which i~ ~ub~tituted
on the amino group,
B a (C6-CI2)-aryl or (C7_C~ ara1kY1 radi~al, pre~erably
phenyl, b~nzyl and phenethyl, which i8 mono~ubstituted by
hydroxyl, and
2~82~ ~
- 17 -
C methoxy.
The invention further~or0 rel~te~ to a proce~s for the
preparation of compound~ of the ~ormul~ I which ~omprises
reacting
a comp~u~d of the ~or~ul~ IV
o
~ - C
; ~ (IV)
C - Y
Il
O
with a compound of the for~ulae V
H - N .~ or ~ V)
R 2 R 4
: ~'
~: where Rl, R2 or R3, R4 are as defined in formula I and Y i8
halogen or hydroxyl or together with ths carbonyl group
form~ an ~ctive ester or a ~ixed ~nhydride, and, if
appropriate, ~onverting the reaction products into their
~ physiologically acceptable ~alts.
- The preparation of oompound~ of the formula I and the
preparation of the st~rting material~ raquired therofor,
unle~ they ar~ com~ercially available, will b~ described
hereinafter in greater detail.
~he ~implest way of preparing the compound~ according to
the invention i~ to combine the two co~ponent~, the
pyridine derivative o~ the formula ~IV~ and the amine of
` - 18 - ~$2~
the formula (V~, in equ~s:)lar am:~unts or in up to
~pproximately 5-~old exce~EI of V, ~.nd ~o react them ~t
t~mper4tures of between -3a and 150C, prefarably at
20 to 100C, until th~ reaction i~s QompleteO The end of
the reaction can }:~e determined 3by mean~ of thin~ yer
chromatography ~DC checlc~. In a varian~ o~ thi3 procea3,
the reaction 1~ o~.rriad ou~; ~n a ~3uit~ble solvent ~uch as
sliethyl ~ther or di~ethoxye~h~ne D~C tet:rahydro~ura~
chlorinated hydrocarbon~ ~uch a~ .methyl0ne 3:hloride~
10 ~hloroform, tri- or t~rac:hloroethylen~, benz~ne, toluene
or ~lse po}ar a301vents such a8 diD~ethy~ ~ormamide or
acetone or dimethyl ~ulf oxide .
In thi~ proee~s too, an exceEIY of amine of khe formula
(V), which ean be up ~o approx. 5 fold, can be u0ed. The
15 reaction temperatures ~re between rooDI k~mperature and
the boiling point o~ the E~olv~nt, temperatures in the
range from room temperature o 13û~C being particularly
preferredO
The reaction carl equally be carried out ~ria a m:Lxed
anhydride such as ethyl ~hloroonmate, or via an acti-
vated ~ter ~uch as paranitrophenyl e~ter (Y ~ CIC~2-COO
or NO2-C6~4-O). Suitable ~ethod3 can be found in ~ouben-
Weyl, Methoden der Organi0chen Chem1e ~Methods in Organic
.Chemistry], Volume XV/2, pages 169 to 183 ~mixed anhy-
-25 dride method), or pages 13 et s~q. (active e~ter method),
fourth ed$tion, Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart 1974.
If appropriate, the reaction can al~o be ~arried out in
the presence of base~. 8uitable additional base~ ~re
inorganic a¢id scavenger~ ~uch RB c~rbonates or hydrogen-
car~onates, for example ~odium carbonate, pota3~iumcarbonate, sodium hydrogencarbonate or potassium
hydrogencar~onate, or organic acid ~cavenger~ ~uch a~
tertiary amines, such a~ triethylamine, tributylami~e,
ethyl diieopropylamine or heterocyclic amines ~uch as
N alkylmorpholine, pyridine, quinoline or
2~2~7~
- lg -
dialkyl~niline~ .
The compounds of the formula (IV) are preferably re~cted
with ami~s of the formula (V~ with additio~ of a w~ter-
el~nating agent ~suc:h ~E~ dialkylcarbodli~nidea where the
5 allcyl radical~ have 1 to 8 carbon ~5to~$3 which, in the
casa of the C3-C9-eompound~, can al~o lbe bram:h~d or
cyclic:; dicycloh~$ylc:arbodiimide ~ pref~rably ~mpls~y~d.
A s~litable laethod iE~ da~cribed in Elouben WQY1 Volume
XV/2, pag~ 103 to ~ thoden der Org~ hen Chemit3
10 [Method3 in Organic ChemiE~try~, 4th ~dition, Georg ~hieme
Verlag, Stuttgart, 1974.
I~ appropriate, the product6 can be worked up for ~ample
by extraction or by chromatography, ~Eor example using
silica gel. The i~3olated prodllct ~an be recrystallized
15 and, i~E appropriatet reac:l:ed with a suit~ble acid to give
a physiologioally act:sptable ~alt. 13xamples oiE ~uitable
acids are:
.
Mineral acid~ BUCh a~ hydrochloric ~nd hydrobromic ~cid
a~ well as sulfurit: acid, pho~phoric ~cid, nitric aoid or
perchloric ~cid, or organic acid~ ~uch a~ forn~c acidl
acetic acid, propionic acid, ~uooinic ~oid, glycolic
acid, lactic acid, malic ~cid, tartaric acid, ~:itric
; acid, maleic acid, fumaric acid, phenylacetic acid,
benzoic acid, methanesulfonic acid, toluene~ulfonic acid,
oxalic acid, 4-~minobenzoi~ acid, naphthalene-1,5-di
: ~ulfonic acid or a~corbic ~oid~
If the ~tarting compounds of the fonmula (V) are not
commercially av~ilable, they can be ~ynthe~ized in a
~imple manner (~or example Organikum, organisch
Chemisches Grundpraktikum CPractical Foundation in
Organic Chemistry], 15th ~dition, VEB Deutscher Verlag
der Wissenschaften, 1976; a survey of the various po~si-
bilitie~ can be found in khe methodological regi~ter,
page 822~.
2 ~ 7 6
- 20 -
For exam~le, the ~tarting compound of the fonmula (IV)
can be obtained by reaeting pyridina,-2,4- or -2,5-di-
earboxylie acid to give tha corresponding pyridine-2,4-
or -2,5-dicarboxylic halide, preferably the chloride (by
proce~es ~nown fr~ the litarat,ure, for example
Organikum, Organi~ch Chemi3che~ Grundpraktikum [Practical
Foundation in Organic Chemistry], 15th ~dition, VEB
Deutsch~r Verlag der Wi~sen~chaften, 1976r page 595 et
8eq. ) ~ which i8 then reacted with ~ ~uitable aloohol, ~or
example paranitrobenzyl ~lcohol, to give the aorrespond-
ing active ester. Equal1y, the pyridine-2,4- or -2,5-di-
carboxylic acid ~an also first be con~erted i~to a mixed
anhydride by addition of a ~uitable ~arboxylic acid or
: carboxylate, such as ethyl cbloroformate, and this mixed
anhydride i8 then reacted with the amine6 (V) to gi~e the
product~ accordi~g to the inve~tion. A ~uit~ble methcd i8
described, or example, in ~ouben-Weyl~ ~etho~n der
Organischen Chemie tMethod~ in Organic Chemistry], Volume
XV/2, pages 169 to 183, 4th Edition, 1~74, Georg ~hieme
Verlag Stuttgart.
The ~ompounds of the formula (I) ~ccording ~o the inven-
~; tion have valuable pharmacologic~l propertie~ and are, in
; particular, e~fective a6 inhibitor~ of proline hydroxy-
aBe and lysine hydroxylase, a~ a fibrodepres~ant r
immunodepre~ant and antiathero~clerotic.
;~ The antifibrotic action can be determined with the aid of
~: the carbontetrachloride-induc~d hepatic fibro~is ~odel.
To this end, rat~ are trQated twice weekly with CCl4
(1 ~l/kg) dissolved in olive oil. ~he test sub~t~noe i~
administered daily, if appropxiste even twice daily,
or~lly or intraperitoneally, dissolved in a ~uitable
acceptable solvent- The extent of hepatic fibrosis i~
determined hy~tologically and the amount of oollagen in
the liver i8 analy~ed by hydroxyproline determination as
described by Kivirikko et al. (Anal. Biochem. 19, 249 et
~eq. ~1967)~. The fibrogenetic ~ctivity can be determined
2Q8207~
- 21 -
by radio ~ unological det~r~instion o~ ~oll~gen ~ra~ments
and procollage~ peptides in ~he ~erum. I~ thi~ mode~, the
compounds according to th~ inv~ntion are active at a
concentration of I-100 mg/kg.
5 The fibrogenet~c activity ~an be determined by radio~
unological determi~ation o~ the ~-terminal propeptide
of the type III collagen or th~ N- or Co~ermi~al cro8~-
linking domain of ~he type IV collagen (7~ ~ollagen or
. type IV ~ollagen ~C1~ in the h~rum.
~o this end, the concentration of hydroxyproline,
procollagen III peptide, 7~ collagen ~nd type IV ~ollagen
NC in the liver wer~ measured in
a) untreated rat~ (control),
b) rat~ who had been adminis~red carbon tetrachloride
(CCl; control) and
~) rats who had been administered ~irst CCl~ ~ollowed
by a c~mpound according to the invention
~: ~thi~ te~t method i~ de~erib0d by Rouiller, CO ~ Experi-
mental toxic injury o~ the liver; in The Liver,
C. Rouiller, Vol. 2, page~ 335-476, N~w York, Academi~
Press, 1964).
Another model for evaluating the antibiotic action i8
that of bleo~ycin-induced pul~onary fibrosis ~s described
by Kelley et al. (J. ~ab. Cli~. ~ed. 96, 954, (1980))~
~he ootton ball granuloma ~odel, as de~crib0d by ~eier et
al., ~xperimentia 6, 4S9 (1950), ca~ be u~ed for
evaluating the action of the ¢ompounds according to the
invention on the granulation ti3~ue.
The compounds of the formula I aAn be uned a0 medicam~nt~
in the form of pharmaceutioal preparations which compri~e
the compound3 of the formula I if appropriate together
with acc~ptable pharma~eutical ~xcip;ents. ~he aompounds
oan be u6ed aR drugs, for example in the ~orm o~ pharma-
ceutical preparations, which compri~e these oompound~ in
2~82~7~
-- 22 --
the f orm of ~ mixture with a pharmaceutic:dl, organic or
inorgar~ic excip~ent which i~ 8uitable for enteral, percu-
taneou~ or parenteral admini~tratl on ~uch as, for
example, inter alia, water, gum nrabic:, gelatine,
5 lactose, starch, ~agn~ tearate, t~lc, ~regetab~
oil~, pc:lyalkylene glycc3ls and vaseline.
To thi~; end, they a~n be dmini~atered orally at do~age
rates o~ 0.1-25 mg/kg/day, preferably 1-5 mgrkg/day, or
parenterally at doE~age rates of 0.01-S ~g/kg/d y, pr~fer-
10 ably 0.01-2.5 mg/kg/day, in pa:rticlllar D.5-1.0 mg/lcg/day.
In ~evere c:a8e8 ~ the dosage ra~e~ an ~150 be increa~ed.
In many c:a~es, however, lower do age rate~ ~uf~ice. q~hese
data are based on an ~dl~lt per~3Qn of ~ bcdy w~ight of
approximately 75 kg.
~` 15 ~he invention furthermore compri~e~ the u~e o:E the
compound~ according to the invention in the preparation
of pharmaceutic:als which can be employed for the treat-
me~t and prophylaxi~ o~ the metabo1ic disorder~ :mentioned
~ above.
: 20 A further object of the invention are pharmaceutical3
:compri~inq one or more compound~ o~ the formula I acGord-
ing to the invention and/or phy~iologically acceptable
~alts thereof.
The pharmaceutical~ are prep~red ~y proaesses which ~re
known per ~e ~na ~amiliar to e person skilled in the art.
A~ pharmaceutical~, the pharmacologically active ~om-
pounds ~ e active substance) according to the invention
are employed either as such or, preferably, in combinn-
tion with suitable pharmaceutical adjuvant~ or excipient~
in the form of tablets, coated tablet~, cap~ule~, ~up-
positories, emulsions, ~u3pensions ox solutions, the
active substance content being up to approximately 95%,
advantageou~ly between 10 and 75%~
2~82~76
- 23 -
Suitable adjuvants or excipient~ for the desir~d pharma-
ceutical ~ormulation are ~ be~ides ~olvents, g~lling
agents, bases ~or 8Uppo8itorie8, tableting adjuvant~ and
other aetive sub~tanc~ ~xcipi~nt~ for example ~l~o
antioxidant~, di~persan~r ~mul~l~ier~, dsfoamers, flAvor
improvers, preaervatives, ~olubilizer~ ~r colorant~.
The invention will be illustrat~d in greater detail
hereinafter with the aid of example~.
~xample 1
lQ Bis-N,N'-~3'-benzoyloxypropyl)pyridl~é-2,4 ~ arboxamide
a~ 25 g (128 mmol3 of dimethyl pyridine~ dicarboxylate
are dissolved in 500 ~1 of ethanol and xe~luxed for 4
hour~ together with 22 ml l282 mmol~ of 3-amino-
~ 1-propanol.
; 15 After the mixkure ha~ bean allowed to ~tand ovexnight at
room temperature, the ~olvent i~ distilled off in vacuo,
and the residue i~ ~rystallized from hot ethyl aaetate;
28.7 g m.p. 102-105C.
b) 0.7 g ~2.5 mmol) of the resulting pyridine-
2,4-dicarboxylic bi~-N,N'-(3-hydroxypropyl)~mide are
combined with 100 ml of di~hloro~eth~e and treated with
0.2 g of 4-~,N-dimethylaLlnopyridine, 0.8 ml (6 mmoll of
triethylamine and dropwi~e ~ith 0.6 ml (5 mmol) of
benzoyl ~hloride. After 1 hourt the mixtur~ i8
concentrated and the ~o~centrate i8 ta~en up in water.
After 1 hour, the mixtur~ i~ extracted twice by 3haki~g
with water ~nd ~he organic ph~e i~ concentrated. The
crude product i~ chro~atographed over silica gel using
ethyl acetate, yield: 0.95 g of colorle~ oil.
Bmpirical formula: C27~27N3O8 (489)
MS: m/e G 490 (M ~
- 24 - 2 ~2 ~ 7
~xample 2
~is-N,N~-~2-(2~m~thylbenzoyloxy)propyl3pyridine-2,4-
diaarbox ~ de
The title compou~d i8 obtained analogou~ly to ~xample 1
fro~ 0.7 g ~2.5 mmol~ of pyridine-~4-di~rboxyllc
bis-~N~-(3-hydr~xypropyl)amide A~ 0.66 ml ~5 ~mol~ of
2-methylbenzoyl chloride, yield: 0.9l0 g of colorl~s~ oil.
~mpirical formula: C2~3lN306 ~517)
~S: m/e = 518 tM ~
,
s~ 10 ~xample 3
2-N-~3-Methoxypropyl)-4-N-[3-(2-methylbenzoyloxy)propyl]
pyridine-2,4-di~arboxamide
.3 g (40 mmol) o~ 4~benzyloxy¢arboDylpyxidine-
~: 2-carboxylic acid Ar~ dis~olved in 160 nl of anhydrous
tetrahydrofuran ~nd, at 0C, treated with 6 ml ~43 mmo~
-~ of triethylamine. After lO minutes, 4.1 ml (43 mmol~ of
ethyl chloroformate are ~dded dropwi~e, and the mixture
i8 ~tirred ~or 30 minutes at 0C-
4.4 ml (43 mmol) of 3-methoxypropylam1ne are then added,
the mix$ure i8 ~tirred for 1 hour at 0C and concentrated
: in vacuo at room temperaturet the product i~ t~ken up in
dichloromethane, the ~ xture iB wa~hed with ~aturated
Na~C03 solution, dried ~d ~reed from ~olvent, ~nd 11.2 g
of 4 benzyloxyaarbonyl~ 3-methoxypropyl)pyridi~-
2~ 2-carboxamide are obtai~ed. 6~0 g (18.3 ~mol) of this
compound are combined ~ith 15 ml of 3-amino-1-propanol
and the mixture i~ stirred for 1 hour at 80C. The exce~.
reagent i~ distilled of~ in v~cuo and the residue i~
crystallized ~rom ethyl acetate, yield: 4.8 g o~
2-N-(3-methoxypropyl)-4-N~(3-hydroxypropyl)pyridine-
2,4-dicarboxamide, m.p. 71-73C.
2~82~76
25 -
2 . O g of this c:o~pound are ~cylat~d ~nalogoll~ly to
~xample 1 u~i~g 2-methylbenzoyl chlorl~e7 A:Eter ~ilic~
gel chromatography using ~thyl ac:~tate, 2 . 4 g o~ the
title compound are obtained ;~ a t:olorlsss;, oily prQduct.
S Bmpirical f o~mulal: C~ 2~N305 ( 413 . 5 )
MS: m/e ~ 414 (M ~ ~)
}Sx~mple 4
2 -N- ~ 3-~ydroxypropyl 3 -4-~- l 3- ~ 2-methy:Lbenzoyloxy ) propyl ~ -
pyridine-2, 4-dicarboxamide
1.6 g ~3.86 mmol~of the title compound of ~xample 3 are
con~ined with 50 ml of di~:hlorome~hane, and 4.5 ml ol~ 1 N
boron tribromide solution in hexane ( 4 . 5 ~mol I are a~de :1
dropwise at -25C. After DC eh~k, a further 1.5 ml of
this solution are added dropwl~e, and, aft~r 0.5 hour,
the mixture i~ he~tad to room templ3rature and extracted
.~ by ~haking with ~3atur~ted N~EIC03 ~olutiorl, the organic
pha~3e i8 dried and s:oncentrated, and the oily re3idue i~
chromatographed on silica gel u~ g ethyl acetate /-
methanol . O . 61 g o~ the title c:ompound crys~tallize ~rom
2 0 ethyl acetate,
m.p- 78-80C
Empirical ~ormula: C2l~25N35 (399-4)
~S: m/e ~ 400 (M + ~)
~xampl~ 5
2-N-~3-~ethoxypropyl)-4-N-[3-(N-cyclohexyl~arbamoyloxy~-
propyl]pyridi~-2,4-dicarbox~mide
2.0 g (6.8 mmol~ of ~-N-(3-methoxypropyl)-4-N-(3-hydroxy-
pxopyl)pyridine-2,4-dic~rboxamide (c~0 Bxample 3) are
dissolved in 250 ml of dichlorometha~e, and 1.05 ml
30 (705 mmol) of cyclohexyl isocyanate are added at 0C with
stirring. The mlxture i8 sub3equently refluxed ~or
1 hour, the reaction i~ checked by mean~ of DC, a ~urther
2~8~7~
- ~6 -
1.1 ml o~ cyclohexyl i~ocyanate ar~ added, the mixture i~
heated ~or a further hour, ~ wed to cool ~nd treated
with water, the organic pha~e i~ dried ~nd con~entr ted,
~nd the oily re~due i~ ¢hromato~r~phsd on silic~ gel
u~ing ethyl acet~te.
Suitable fractions are co~centxated and crystallized
using diethyl ether; yield: 1.1 g o~ the colorle~s
crystalline title compound, m.p. 95-98Co
~xample 6
2-N-~2-Methoxyethyl)-4-N ~3~benzoy}oxyethyl)pyridine-
2,4-dicarbox ~ de
a) 150 g of pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylic acid are ~o~bi~ed
with 1.8 1 o~ methanol and 53.5 g of ~ulfuxic a~id (98~)
and heated ~o ~oiling for 3 hour~. ~fter 1 hour, the
pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylic acid i8 largely di~olved. Only
a ~light cloudine~s remain~ in the mixture~ ~he miYture
i8 poured into ice-water and the fi~ely-crystalline
precipitate i~ allswed to settle~ the ~uper~atant i~
decanted off, the re~idue iB ~iltered o~E with ~ùction,
washed with water and then with a very small amount of
ice-cold MeO~. Yield 70-75 g of 2-methyl-
oxycarbonylpyEidine-4~carboxylic acid, m.p. 246-24~C
(decomp.). The filtrate iB extracted 3 time~ u~ing C~2Cl2,
the organic phases are dried and evaporat~d, the re3idue
i~ taken up in ethyl Acstate, and the mlxture i~ ~iltersd
cver ~ilica gel (appro~. 1 kg). The filtrate i8 evapor-
ted in vacuo. Yield 90 95 g of dLm~thylpyridine-2,4~di-
carboxylat~, ~.p. 61-62C.
.
b) 50 g of 2-methyloxycarbonylpyridine-4-carboxylic acid
and lS0 ~1 of 2-methoxyethyl~mine give 32.5 g of
2-N-(2-methoxyethyl)-4-oarboxamidopyridine-4-carboxylic
acid, m.p. 145.5-146C ~from water).
2~8~76
- 27 -
c) 30 g of the ~bove compound ~re co~bined with 10 ml o~
thionyl chlorid~ in lBO ml of toluens and 1 drop of
d ~ethyl~or~mide, the ~ixture i~ heat~d ~or 3 hours.
When cold, 39 ml of triethylam~ne ~re added, iollowed by
~nhydrou3 meth~nol. Filtr~ion wi~h e~hyl ac~tate through
silica gel and recry~tallization :ErQm methanol/water
gives l9.B g of ~-methyloxycarbonyl~N~ ~ethoxy~thyl)
pyridine-2~carboxamide, m.p. 68-68.5'DC.
d~ 5.0 g of tb~ ~bove compound are co~bined with 10 nl of
tha~olaml~e and thè mlxture i~ heatod to ~oil~ng for
30 minutes. 3.0 g of 2-~-[2-me~hoxyethyl)-4-N-[2-hydroxy-
ethyl)-pyridine-2,4-dio~rboxamide, ~.p. 124-125C, are
obtained in the form of ~olorles~ ~rystal~
e) The title c~mpound i~ obtained, analogou~ly to Example
1 from the above compound ~y reaeting it ~ith benzoyl
chloride in the presence of tri~thylamine and 4-NrN-di-
methylaminopyridine, a~ colorle6~ ~ry~tals, m.p. 77-78C
Empirical ~ormula: C1~zlN305 (371)
~s: m/e - 372 !M ~
2Q Bxample 7
2-N-(2-Methoxyethyl)-4-N-(2-benzoyloxypropyl~pyridine-
2,4-dicarboxamlde
Th~ compound i~ obtained analogou~ly to Bxampl~ 6d) ~nd
6e) a~ a colorle~ oil,
~mpirical ~ormula: C20~23~3~S (385l
~S: m/e - 386 ~M + E~)
r
,::
2~2~7~
- 28 -
~xample 8
2-N-(2~ethoxyethyl)-4-N- r 2-(4-hydroxypheny~)ethyll-
pyridine-2,4-dicarboxamide
~ he kitle ~ompound i8 obtained from 0.24 g of 4-methyl-
oxycarbonyl-2-~-~2-methoxyethyl~pyridin~-2~arboxamide
(cf. ~xample 6c)j by ~eltlng it wi~h 2-(4 hydroxyphenyl)-
ethylamine ~tyr~mine3. FiltratîGn with ethyl ~cetate
through 8iliC~ ~el give~ 70 mg of colorle~ ne~dles; m.p.
181-181.5C ~rom ethyl ~cetate~;
Empirical ~ormula: C1B~21N30~ (343)
MS: m/e = 344 (M +
Example 9
Bi~-N,N'-~2-~4-methylben~oyloxy)-ethyl]pyridine-2 r 4 -di-
carboxamide
~he title compound i~ obtained analogou31y to ~xampLe lb)
~rom bis(N f N'-(2-hydroxyethyl)pyridine-2,4-diaarboxamide
and 4-methylbenzoyl chloride a~ ¢olorle8s ~ry8tal powder,
.p. 1~5-16~C.
Empirical formula: C27~2~N3O6 ~489)
MS: ~/e - 490 ~M + B~)
Example 10
Bi~ 2-ben~oyloxyethyl)pyridine-2~4-dicarboxa~ide
analogou~ly to ~ample lb)
colorle~ needl~s, ~.p. 13g-140C
~mpirical ~ormula: C25~23N3O6 (461)
MS: m/e ~ 462 (M ~ ~t)
The meanings in the tables below are as follow~:
Ph phenyl
Me methyl
30 ~t ethyl
- 29 2~82~
Pr propyl
Bu butyl
~n benzyl
Pen p~ntyl
S ~ex hexyl
T~P tetrahydropyr~noyl
n unbranched ohain
c cycl~
i i~o.
Rl/R2 and R3/R~ ~eans that aither Rl or R2 and R3 or R4,
r~peetivsly, i~ the rad~cal ~entioned. The sub~tituent
which remain~ in each case i~ hydrogen.
The ~ompQunds are in each ca~e 2,4-di~ubstituted pyridine
derivatives.
_ 3~ - 2~2 ~ 7 ~
r~ ----
E~ . Rlt~2 R~
11 CH2 C:H2 0 CO Ph U~, CH~ O CC~ ~h
12 CH2 CH2 0 CO ~h ~ ~a C~Ha O CO NH Et
. . ___ _
13 CH2 Ctl2 0 CO Ph CH2 CH2 0 CO NH-n~u
. . .
14 ~H2 CH2 O CO OEt CH2 ~ 2 0 Cl:) Ph
. . _ _
CH, CH, ~ Ct~ O~ OH, OH, O C:O NH
16 C;H2 CH2 0 CO NH n-8u :;H2 CH2 0 CO Ph
. _ __
. 17 CH, CH, O CO NH ~I~u C--~ CH, O Cc NR n-~u
18 CH2 CH2 O CO NH CH2 CH2 OH CH2 Cl 12 CO NH n Bu
__
. CH2 CH2 0 CO Ntl CH2 CH2 OH CH2 CH~ O C:O NH CH2 CH2 OH
CH2 CH2 0 THP CH2 CH2 0 THP
, ~ ~
21 t:;H2 CH2 0 THP CH2 CH2 0 CO Ph
. ~
22 CH2 CH;, CH2 0 CO Ph CH2 CH2 t:H2 0 ::O Ph
_ . _ .
23 CH2 CH2 CH2 O CO Ph CH2 CH2 t;H2 0 GO NH Et
~ ~--
24 CH2 CH2 CH2 C) CO Ph CH2 CH2 CH2 0 CO NH n-Bu
__ . _ , . , , __
CH2 CH2 CH2 0 CO O Et Ctl2 OH2 CH2 0 C:O Ph
_ ~ __ _ , _ _
26 OH2 CH2 CH2 O O:~ O l~t C~~ CH, CH, l~ CD n~
27 CH2 Cl~2 CH2 0 CO NH n-Bu CH2 CH2 CH2 0 CO Ph
_ . . ~ . , . , _
28 CH2 CH2 CH2 0 ~O NH n-Bu CH2 CH2 CH2 0 CO NH n-Bu .
_ ~
2~2~7~
- 31 -
_~
E ~ . R-~2 ~3/R4
29 CH2 CH2 CHa O t;O NH CH2- C~ C::Ha C:H2 C:tl,2 0 C 0 NH n-Bu
OH
. , . _____
CH2 CH2 CH2 O C :) NH CH2- C H2 CH2 C:H2 CH2 O I C) NH ~C~2
OH C:H2 OH
...... .. _ . _ _ _ _ _ . ~ 11
31CH;~ CH2 CH2 ~P OH2 GHa CH2 0 TllP
~ _ . ~
32CH, C--, CH, O ll ll' CH2 Cl~ CH, O CO I'h
33CH2 CH2 O CH3 CH2 t::H2 C:H2 0 CO c-H~x
34CH2 t: H2 0 CH3 CH2 CH2 C;H2 0 CO ~-Pen
_ , , , . . . _ _ ~
35CH2 CH2 t:) CH3 C:H2 C:H2 CH2 0 C:O O Et l
_ . _ ,_
36CH2 CH2 0 CH3 CH2 CH2 CH~ O CO O n-Bu
.. _ ~ ~
37 CH2 CH2 O OH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 O GO O G Hex
_ .
38 CH2 CH2 0 ~H3 CH2 C:H2 C:H2 0 CO Ph
_
39 CH2 CH2 C) CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 t:~ CO i-Pr
_ . . . . . _ ~_ _. - ~- I
40CH2 CH2 0 Ct 13 C:H2 C:H2 CH2 0 CO O Ph
~_ . _ _.
41C H2 CH2 0 ~H3 CH2 ~H2 CH2 O CH2 CH2 0 Me ¦
~ . . __ . __
42 CH2 CH2 0 ~ H3 C;H2 CH2 CH2 O CH2 9;;H2 0 Et
~_
43CH2 CH2 0 CH3 GH2 CH2 CH2 Q CH2 CH2 0 Ph
1 - - - - - . , . ... ... ~
44~H2 CH2 O CH~ ~;Hz C;H2 CH2 O Ph
I _ _ ._ . ""_
CH2 CH2 0 CH3 ~ CH2 CH2 CH2 0 THP
~_ . . _ . - , ........ ... .__
46 CH2 CH2 0 CH3 CH2 C:H2 CH2 O CO NH Et
_ _ _ _ . , , l
47 CH2 CH2 0 CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 0 CO NH Pr
~ __ _ ___ _ _ . ~ , .
48 CH2 CH2 0 CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 0 C~ N~l ~ Bu
2~82~76
-- 32 --
.
~_ ~ .__I
E x . Rl/R2 R~/R~
_~ ~ ~ I
49 CH2 CH2 O CH3 CH2 GH;, CH2 0 CC) NH c-Hex
, . ,~ . . . ~ I
CH2 CH2 OH CH2 CH;~ CHa O CO c-Hex l
. ._ . _ ~
51 CH2 CH2 0~1 CH2 GH2 CH2 1 ) CO c-P~nt
_ , _ , , .
52 CH2 CH2 OH CH2 t::H2 CHi Q C;O O Et
,,, . ,, , _
53 CH2 CHa OH GH~ CHa CH2 O CO O n-Bu
,., ~
54 CH2 CH2 OH CH2 ~H2 CH2 0 CC) O c-H~x
CH2 CH2 OH O~, CH, CH, O CO (~ Ph
56 CH2 CH2 OH C~l2 CH2 CH~ C) CO ~2-Me Ph)
CH, CH, OH CH2 C:H2 CH2 0 CO Ph
~8 CH2 CH2 OH C:H2 CH2 CH2 0 CH2 CH2 CH
O- lUle
~ ~ .. . , . . .. _ _
59CH2 CH2 OH CH2 CH2 CH2 O CH2 CH2 CH
~:~ ~ O- Et
60CH2 CH2 OH ~2 ~ t~2 CH2 O CH2 CH2 C:H
O Ph
~ _ . _
61CH2 CH2 ~ CH2 CH2 CH2 O Ph l
I
62O--, CH, 011 CH, C--, CH, O T--P
63CH2 CH2 OH CH2 C:H2 C:H2 CO NW Et l
_ _ .. . I
64 CH2 CH2 OH C~12 CH2 CH2 0 CO NH Pr
.. _ _ _ . .. _ _ . ....... ._~._. . --l
65 . CH2 CH2 OH CH2 CH2 CH2 0 ~ 0 NH n-Bu
66 CH2 CH2 OH CH2 CH2 CH2 0 C:O NH c-Hex. . _ -. . _ I
67 CH2 CH2 OH ___ CH2 CH2 CH2 O CO NH Ph l
2~2~7~
-- 33 --
.
_ ~ I
E ,~ R1/R~ R3/R4
I ~__ ~ , ._ ~ I
68 C ~2 C~H2 CH2 ~ CH3 ~H2 ~H2 ~Ha t O C-HBX
._v____ - _ ~ I
69 - C H2 C~H2 ~H2 ~ HJ ~H2 ~H2 ~;H2 CO C- P~n
. . .__ . I
~H2 ~ i i2 C H2 O CH3 CH2 CH~ CH2 C ) CC) O Eth
_ , ~--~
71 CH2 CH2 CH2 0 CH~ . 5;H2 ICH2 CHa O CO t) n-8u
. ~ _~
72 CH2 t~H2 ~H2 ~ HJ ~H2 CH2 CH2 C ) CO O c-Hex
, ~ . ~ _~
73 CH2 ~ H2 ~; H2 O CH3 CH2 CHa Cl'l2 CO Ph
I . ~.
7~ CH;2 CH2 C::H2 0 CH3 CH2 ~H2 CH;~ C) CO i-Pr
_ ~
1 75 CH2 Ct12 CH2 O CH3 CH~ C H2 C H2 O Ce) O Ph
I ~,
I76 CH2CH2CH2O~H3 CH2CH2CH2OCH2~H2M@
.
I77 CH2 CH2 C~2 O CH3 ~2 C H2 ~ H2 CH2 CH2 O Et
_ _ . . ,_ ~ _
I78 CH2 ~ H2 CHa C3 ~H3 ~ H2 ~ H2 t~H2 O CH2 CH2 O Ph
~ . - ....... .. __ . . ~
79 CH2 CH2 ~H2 ~H3 CH2 eH2 CH2 Ph
80 CH2 C~H2 ~H2 ~ H3 CH2 CH2 ~ H2 THP
_ . , . , .. . 11
~ R1 CH2 CH2 CH2 0 CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 0 CO NH Et
~ , , , . _ . . , . .... ~
l ~2 CH2 C~2 CH2 0 CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 0 CO NH Pr
- ~ A
83 CH2 ~H2 ~ H2 O C~l3 CH2 CH2 CH2 O CO NH n-Bu
84 CH2 CH2 CH2 0 ~H3 C:H2 CH2 C:H2 0 CO NH c-Hex
, ,
Ctl2 CH2 CH2 OH CH2 C:H2 CH2 0 CO c~tlex
_ _ ~ ~ ~ _ ...... ... ~, _. --
86 CH2 CH2 CH2 OH CH2 CH2 CH2 0 C:O c-Pen
__ _ _ __ , ~ , . ~ _ ~
I 87 t:~H2 ~H2 CH2 OH CH2 ~ :H2 ~H2 CO C-Et
_ _ , " ", " " .. ,
1 88 C;H2 CH2 CH2 OH CH2 C:H2 CH2 0 C:O C n~Bu
_ __ . .__ __ . ~
_CH~ CH2 t::H2 OH _ CH2 CH2 CH2 0 ~O O c-Hex
2~2~7~
-- 34 --
_ I
E~. R /R R3/~4
I . ., ~ I
CH2 CH2 CH2 OH ~ C~ 1`4 ~ CO O Ph
91 t J'12 ~ H2 CH2 OH ~ ~a e H2 C~z ~ CO ~2~Me Ph)
! ~
92 CH2 CH2 CH2 OH C:H2 CH2 C ~2 C~ Ph
. . ~
93CH2 CH2 CH2 OH CH2 CH2 CH2 0 CH2 CH2 CH2
~ Ms
_ _ I
94CH2 CH~ CH2 OH GH2 GH2 t :H2 O CH2 CH2 CH2
O- Et
_
95CH2 CH2 5H2 OH CH2 CH2 CH2 O ~H2 ~H2 CH2
O- Ph
I . .. __ v~_u ~
1 96CH2 ::H2 CH2 OH CH2 CH2 CH2 O Ph
_ ~ ~
97CH2 CH2 CH2 OH CH2 CH2 Ctl2 O THP
. . ....
98CH2 CH2 CH2 OH CH2 CH2 CH2 0 CO NH R
_ _ _ , _,_,_ __, _ _ r . ,_ ::
l 99CH2 C:H2 CH2 OH GH2 CH2 CH2 0 CO NH Pr
_ _ , . ..... .. ~ -- _
1100 CH2 CH2 CH~ OH CH2 CH2 CH2 0 CO NH n-Bu
.. . _ ,, ~ _ .
1 101 CH2 CH2 Ctl2 OH CH2 CH2 CH2 0 CO NH c-Hex
. _ .,
10Z CH2 CH2 CH2 OH CH, C~, CH, O CO N~l Ph
¦ 103 C~2 CH2 CH2 0 CO c-Hex CH2 CH2 0 ~Ae
. . . _ __
104 ~2 ~;H2 CH2 0 CO c-Pen C:H2 CH2 0 M~
_ , . ..... .. _
l 105 CH2 CH2 CH2 O CO O Et CH2 CH2 O Me l
__ _ ~ -- . ~ .. .....
106 CH2 CH2 CH2 0 CO O n-Bu CH2 CH2 M~
_ __. _ _ , _ , _
1 107 CH2 CH2 CH2 0 C :) O c-Hex CH2 CH2 0 Me
. . _ _ - ._ . _
I 108 Cl12 Ctl2 GH, O CO O Ph CH2 CH2 0 Me
2~82~7~
-- 35 --
~--.__~
E x . F~' /R' R'j~'
109 ~H2 ~H2 CH2 O C 2-M~ Ph t~H2 ~H2 O MB
_ ~ .
110 C:H2 CH2 CH2 0 C:O Ph CH2 C;H2 0 Me~
,. _~
111 t::H2 CH2 CH2 0 C:H2 CH2 CHa ~ CH2 ICHa O Me
Me
I ~__
112 C:H2 C:H2 CH2 0 THP CHa CH2 0 M~
,_~
113 C;H2 CH2 C:H2 0 CO NH Et CHa CH2 Q M~
_ -.. ---- ............. _ ___ . ~_ ,
1 1 4 CH2 CH2 C H2 0 CO NH Pr CH2 CH2 ~ M~ -
_ , . _ _
I 1~5 CH2 CH2 CH2 0 C NH n B~ ~H2 CH2 M~
~ ,, _ _ _ _ _ .
I 116 CH2 CH2 t~H2 0 CO NH C-H~X ~;H2 ~H~ O M~
_ ~
¦ 1~7 CH2 CH2 CH2 0 CO NH Ph CH2 CH2 0 Me
r
118 Ctl2 C:tl2 CH2 0 CO c:-H~x GH2 C:Ha C:H2 0 Me
. ~ - ~ _ _ _ ~ ...... _ ~ I
I 119 CH2 CH2 CH2 C ~-Pen ~H2 ~H~7 CH2 Me
~ _ ~
120 CH2CH2CH2OCOOEt C:H2CH2C~2OM~ l
... . ~ .. __ __ , , I
1 121 C:H2 CH2 CH2 0 CO O n-BuCH2 CH2 CH2 0 Me
,_ , . - ._ ~ , ~
122 CH2 CH2 CH2 0 CO O c-HexCH2 CH2 CH2 0 Me
_ , ,_, ..
123CH2 CH2 CH2 C) CO O PA CH2 CH2 CHa O Mi~
r _ -- -- -- -- _ _
124 CH2 Clt2 CH2 0 CO 2-Me Ph CH2 CH2 t H2 0 Me
__ , ,,, _- ~
125 CH2 CH2 CH2 O CO Ph C~2 CH2 C:tl2 0 Me
_ ~ _ _ _ _ I
126 CH2CH2CH20CH2CH2S~H20 CH2CH2~H20Me
Me
_ ~ _ _
127 CH2 CH2 CH2 THP CH2 CH2 CH2 Me
__ . . __
128 CH2 CH2 CH2 0 CO NH Et CH2 CH2 CH2 0 Me
.
- 36 2~8~
~ ~ ~_ I
E~ . R~/~ R3/~
. . . _ . . ~
129 ~ ~2 C~2 C H2 CO NH Pr CH2 CH2 CH2 0 M~
. I
13D CH2 C:H2 OH2 0 GO NH n-Bu g:tl2 CH2 CH2 O M~
, _ . . ... _
131 C;H2 C:H2 t;ll2 0 ~O NH c-H~x C:Ha tCH2 CH2 O Me
.
132 CH2 CH2 C:H2 ~ CO Nl I Ph CH2 CH2 CH2 0 M~
. ~ ~
133 C:H2 CH2 OH2 0 CO e-Hex OHa CH2 CH2 OH
. . ___ ;
134 CH2 CH2 C:i 42 CC) c-~n GH2 CH2 C:H2 OH
. . _ . .
13~ CH2 CH2 CH2 0 CO O Et C:H~ CH2 CH2 C)H
. _ . _ I
136 CH2 CH2 CH2 O eo o n-Bu C;H,2 CH2 CH2 OH
_, .
137 CH2 Ctl2 CH2 O CO O c-l lex C:H2 :::H2 C :H2 OH
~ _
138 CH~ CH2 t;H2 O CQ O Ph OH2 CH2 CH2 OH
139 CH2 CH2 CH2 O CO 2-Me Ph ~ ~2 C:H2 C:H2 OH
. . ~
140 CH2 CH2 CH2 0 CO Ph CH2 CH2 CH2 OH l
~ .~ ~
141 OH2 CH2 CH2 0 Ch2 CH2 CH2 - CH2 Ctl2 1~ OH
Me
~ ~ - ~ - - I
142 Ctt2 CH2 CH2 0 THP GH2 CH2 CH2 OH
~ _ _ _ _ __ _
143 C:H2 CH2 CH2 0 CO Nll Et t::H2 CH2 CH2 OH
_ _ ___ .
144 t::H2 CH2 CH2 0 C:O NH Pr CH2 CH2 CH2 OH l
_ . . , _ _ I
~45 CH2 CH2 CH2 0 CO NH n-Bu CH2 CH2 CH2 C)H
_ _ ~ I
146 ~H2 CH2 CH2 O CO NH c-ttex CH2 CH2 C:H2 OH
._ . ~ __ _ , , _
147 CH2 CH2 CH2 0 CO NH Ph CH2 CH~ CH,2 OH l
_ _ . ~ I
148 CH2 CH2 CH2 O CO c-Hex CH2 CH2 OH l
__ . . . _ . _ . _ _ I
149 CH2 CH2 CH2 0 CO c-Pen CH2 Ctl2 OH
.
- 37 - 2 ~82 ~ 7 ~
Es. R /R ~/~
150 CH2 CH2CH2O CO O R CH2C~2 OH
_ __~
151 CH2 Ctl2 C:H2 0 t:O ~ n-E~u CH2 Cl 1~ OH
__ __
1~2 CH2CH2CH2O CO O C Hex CH~ CH2OH
. ~
. 153 CHaCH2CH2O CO O Ph . CH2 C~2 ~H
_ ~
~4 ~H2 CH2 CH2 O CO 2-Me Ph I::H;~ CH2 OH
155 CH2 C:H2 CH2 O CO Ph CHa Cl 12 OH
., _ , . _ ~.. ,, . ,, _ , ~
156 CH2 CH2 CH2 t:) CH2 CH2 CH2 - C;H2 CH2 OH
Me
_ . . . _ ~_
: 157 ~2 ~H2 CH2 O THP CH2 CH2 OH
, ~ ~
158 CH2 CH2 CH2 0 CO NH E~ C:H2 CH2 OH
. _
159 CH2 CH2 Clt2 0 CO NH Pr CH2 C;H2 ~H
_
160 CH2 CH2 CH2 C) CO NH n-Bu CH2 Ct''12 OH
_ ~
161 GH2 C~12 CH2 0 CO NH c-Hex CH2 CH2 OH
162 CH2 ~H2 CH2 0 CO NH Ph CH, Ol l, (~11
~` ~xample 163
Bi~-~,N'-[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-ethyl~pyridine-2 J 4 -di-
carboxamide
Analogously to B~mple 8 from dL~ethyl pyridine-2,4-di-
carboxylate and tyrnminecolorle~s cry~t~l~, m.p. 165-166C
~mpirical formula: C23~23N3O4 ~4D5)
MS: m/e - 40 (M + ~)
2~2~
. - 38 -
-
Example 16~
Bi 8 t~ thoxy--N-methyl~pyridine-2,4-dic~rbox ~ de
5.1 g ~40 mmol) of N-ethylmo~pholene are ~dded ~t 20C
with stirring to 1.67 g (10 mmoll of 2~4-pyridinedi-
carboxylic acid, ~u~pended in 100 ml of diahloromethane,
~.9 ml (20 ~mol~ o~ i~obutyl chloro~ormate are ~ubse-
qu~ntly added dropwi~e ~t -15C, and the ~ixture i~
~tirred for 20 minute~ at lO~C~ 1995 ~lacuna~ (20 mmol)
o~ ~,O-dimethylhydroxyl~mi~e hydrochlorid~ are then
added, the mixture i~ ~tirred for 1 hour ~t -15C and
allowed to come to 20C o~ernight, wat~r i8 add~d, the
mixtur~ i8 extracted with dichloxomethane, a~d, after
puri~ication o-E ~he crude product by column ~hrom~-
tography over silica gel (ethyl acetate/methanol ~ lOJl)~
1.6 g of the ti~le co~pound are obtained a~ a colorl~s
oil,
Empirical formula: C~ 5~304 (253)
MS: m/e - 254 (M + ~+)
Example 165
2-N~ -Methoxyethyl)-4-N-(ethyloxy(N-tert.butyloxy-
carbonylglycyl))pyri~ine-2,4-dicarboxamlde
0.8 g (3 mmol) of ~-N-(2-~ethoxyethyl)o4-N-~2-hydroxy-
ethyl)pyridine-2,4-dic~rbox~mide ~aompound o~.x~mple 6d)
i8 combined with 25 ml of anhydrou3 ~cetonitrile and
~25 mg (3 mmol) of N-butyloxycarbonylglycine, 0.4 ml
(3 mmol) o~ N-ethylmorpholine~ 0O45 g ~3.3 m~ol) of
N-hydroxybenzotriazole and 0.62 g (3 mmol) of ~ di-
cyclohexylcarbodilmide, And the mixture i~ ~tirred for 20
hours ~t 25C. ~he resulting N,N-dicyclohexylurea is
filtered off with suction, washed with acetonitrile ~nd
concentrated, the product i~ taken up in dichloromethane,
the mixture i6 extracted with saturated aqueous Na~CO3
801ution, the extract i~ ~haken with 10~ atrength ~queous
2~82~7~
- 39 -
citric acid, dried ~nd freed from solvent~ and the
residue i8 chromatographed over ~ilica gel.
~mpirical formula: Cl~29N407 (4~4)
~S~ 425 ~
~urther ~xamples are: I ynths~ized ~rom the ~ompound
2-N-(2-mathoxyethyl)-4-~-(2 hydroxyethyl~pyridine-
2,4-carboxamide described in ~x~mple 6d), or from
~nalogou~ ~ompound~, by benzylation)
2-~ (2-Methoxyethyl~-4-~-(2-benzyloxye~hyl)pyridine-
2,4-dicarboxamide
2-N-(2~ydroxye~hyl)-4-N-(2-benzyloxye~hyl~pyridine~
2,4-dicarbox~mlde
2-N-~3-~ethoxypropyl)-4-~-(2-ben~yloxyethyl)pyridine-
2,4-dicarboxamide
2-N-~2-~ydroxypropyl)-4-N-(2-benzyloxyethyl)pyridine-
2,4-dicarboxam~de
Bis-N,N'-[benzyloxyethyl)pyridine-2,4-dioa:rboxami~e
(N,N'-Benzyloxypropyl)pyridine-2~4-dicarboxamid~
2-N-(2-Methoxyethyl)-4-N-[2-~4-fluorobenzyloxy)ethyl3-
pyridi~e-2,4-d~carb~xamide
2-N-~2-~ydroxyethy~)-4-N-l2-(4~fluorobenzyloxy)ethyl]-
pyridine-2,4-dicarboxamide
2-N-(3-~ydroxypropyl)-4 N-[2-(4-fluoro~enzyloxy)ethyl]-
pyridine-2,4-dicarboxamide
2-N-(2-Methoxyethyl)-4 N-~2-(4-methoxybenzyloxy)ethylJ-
: pyridine-2,4-dicarboxamide
2082~ ~6
- 40 -
2-N-~2-~ydroxysthyl)-4-N- r 2-(4-methoxybenzyloxy)ethyl]
pyridine-2,4-dicarboxamlde
2-N-(2-~ydroxypropyl)-4-N-t2-(4-~ethoxybenæyloxy)ethyl]~
pyridine 2,4-dicarbox~mide
2-N-~2-Benzyloxyethyl34-~-(4-hydroxyethyl~pyridine-
2,4-dic2rboxnmlde
2-M-(2-~enzyloxyethyl)-4-N~(4-hydroxypropyl)pyridine-
2,4-dicarboxamlde
2-N-~2-Benzyloxypropyl)-4-N-33-hydroxypropyl)pyridine-
2,4-di~arboxamide
2~ 2-(4-Chlorobenzyloxy)ethyl~-4-~-(2-hydroxyethyl)-
pyridine-2,4-dicarboxamide
2-N-~2~ Chlorobenzyloxy)ethyl]-4-~-(3-hydroxypropyl)-
:~ pyridine-2,4-dicarboxa~ide
2-N-~2-Methoxyethyl)-4-N-t2-benzy~oxypropyl~pyridine-
2,4-dicarboxamide
2-N-(2-~ydroxyethyl) 4-N-~2-benzyloxypropyl)pyridine-
2,4-dicarboxamide
2-N-(3-Methoxypropyl)-4~ 2 benzyloxypropyl)pyridine-
~;~ 20 2,4-di~arboxamide
2~ 2-~ydroxypropyl)-4-~-(2-benzyloxypropyl)pyridine-
2,4-dicarboxamide
2-N-(2-Methoxyethyl)-4-~[2-(4-fluorobenzyloxy)propyl]-
pyridine-2,4-dicarboxamide
2-~-[2-Hydroxyethyl)-4-N-[2 (4-fluorobenzyloxy)propyl]-
pyridine-2,4-diaarboxamide
~08207bj
- 41 -
2-N-(3-~ydroxypropyl~-4-N-[2-(4-fluorobenzyloxy)propyl3-
pyridine-2,4-dicarboxamlde
2-N-(2-~ethoxy~thyl)-4~ 2-~4-msthoxybe~æyloxy)propyl~-
pyridine-2~4-dioarbox~mide
2-N ~2-~ydro~yethyl~-4-~-t2-~4-methoxybenzyloxy)propyl]
pyridine-2,4-dicarboxamide
2-N-~2-~ydroxypropyl)~4-~-t2~(4-methoxybenzyloxy)propyl]-
pyridine-2,4-d~carboxamide
2-N-(2~Benæyloxypropyl)-4-N-t2-hydroxyethyl~pyridine-
2,4-dicarboxamide
2-N-~2-Benzyloxypropyl)-4-~-(3-hydroxypropyl)pyridine-
2,4-dicarboxamide
2-N-[2-t4-Chlorobenzyloxy)propyl]-4-N-~2-hydroxyethylj-
pyridine-2,4-dic~rbox2mide
2-N-1~-(4-hlorobenzyloxy)propyll~4-N-~3-hydroxypropyl)-
pyridine-2,4-dicarboxamide
2-N-(2-~ethoxyethyl)-5-N-~2-benzyloxyethyl)pyridine-
2,5-dicarboxa~ide
2-~-(2-~ydroxyethyl~-5-~-(2-be~zyloxyethyl~pyridine-
2~5-dicarboxamide
2~ 3-Methoxyp~opyl)-5-~-(2-b~nzyloxy~thyl~ pyridin~-
2,5-dicarboxa~ide
2-N-~2-~ydroxypropyl)-5-N-~2-benæyloxyethyl~pyridine-
2,5-dicarboxamide
Bi~-N f ~ benzyloxyethyl)pyridine-2,5-dicarboxamide
2~g~07~
- 42 -
.
(N,N~-Ben~yloxypropyl)pyridi~e-2~5-dioarboxamlde
2~ 2-Methoxyethyl~ N-t2-(4-fluorob~nzyloxy)ethyl3-
pyridine-2,5-dicarboxamide
2-N-~2-~ydroxy~thyl)-5~N-[2 (4-fluorobenzyloxy~et~yl]
pyridi~e-2,5-dicarboxamide
2-N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-5~ 2-(4-~luQrobenzyloxy )ethylJ-
pyr~dine-2,5-dic~rbox~mide
,
:~ 2-N-(2-Methoxyethyl~-S-N-t2-(4-methoxybenzyloxy)ethyl~-
pyridine-~,5-dicarbox~mide
2-N-(2-~ydroxyethyl)-5-N-[2-~4-~thoxyben~yloxy3ethylJ-
pyridine-2,5-dicarboxamide
2-N (2-~ydroxypropyl) o5-N- 1 2- (~-~ethoxybenzyloxy3ethyl]-
~ pyridine-2,5-di¢arboxamide
: 2-N-(~-Benzyloxye~hyl)-5 N-t2-~2-hydroxye~hyl)pyridine-
2,5-dicarbox~ide
~-N-(2-Benzyloxyethyl)-~-N-[2-(3-hydroxypropyl)pyridine-
2,5-dicarboxa~ide
2 -N ( 2 -Ben zyloxypropyl ) ~5~~~ t 2 - ( 3-h~droxypropyl ) pyridine-
2, 5 dicarboxami~e
2-N-[2-~4-Chloroben~yloxy)ethyl~-5-N-( 2 -hydroxyethyl ~ -
pyridine-2,5-dicarboxamide
2-N-[2-(4-Chlorobenzyloxy~ethyl~-5-N-l3-hydroxypropyl)
pyridine-2,5-dicarboxamide