Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
HOECHST AKTIENGESELLSCHAFT HOE 91/F 415 Dr.FI
Substituted pyridine N-oxides, processes for their
preparation, and their use
Compounds which inhibit the enzymes proline hydroxylase
and lysine hydroxylase have the e~fect of a very select-
ive inhibition of collagen biosynthesis by influencing
the collagen-specific hydroxylation re~ctions. In the
course therev, protein-bound pxoline or lysine is
hydroxylated by the enzymes proline hydroxylase or,
respectively, tysine hydroxylase. If this reaction is
suppressed by inhibitors, a non-functional, hypohydroxyl-
ated collagen molecule is formed, which can be released
by cells into ~he extracellular space in only a small
amount. The hypohydroxylated collagen moreover cannot be
incorporated into the collagen matrix, and is very
readily broken down proteolytically. As a consequence of
these effects, the total amount of collagen deposited in
the extracellular space is reduced.
Inhibitors of proline hydroxylase are therefore suitable
substances in the therapy of diseases in which the
deposition of collagen contributes decisively to the
syndrome. These include, inter alia, fibroses of the
lung, liver and skin (scleroderma), as well as
atherosclerosis.
It is known that inhibition of proline hydroxylase by
known inhibitors, such as ~ dipyridyl, leads to an
inhibition of the Clq biosynthesis of macrophages
(W. Muller et al., FEBS Lett. 90 (1978~, 218;
Immunobiology 155 (1978), 47). This results in a failure
of the classical route of complement activation. Inhibit
oxs of proline hydroxylase therefore also act as immuno-
suppressants, for example in cases of immune complex
diseases.
It is known that the enzyme proline hydroxylase is
inhibited effectively by pyridin~-2,4- and
rj
-- 2
-2,5-dicarboxylic acid (K. Majamaa et al., Eur. J.
Biochem. 13B (1984) 239-24$). Elowever, these compounds
are active as inhibitors in the cell culture only in very
high concen-trations (Tschank, G. et al., Biochem. J. 238
(1987) 625-633).
Pyridine-2,4- and -2,5-dicarboxylic acid diesters having
1-6 carbon atoms in the ester alkyl part are described in
DE-A 34 32 094 as medicaments for inhibition of proline
hydroxylase and lysine hydroxylaseO
These lower-alkylated diesters have the disadvantage,
however, that they are split into the acids too quickly
in the organism, and do not arrive at their action site
in the cell in a sufficiently high concentration, and are
therefore not particularly suitable for possible adminis-
tration as medicaments.
DE-A 37 03 959, DE-A 37 03 962 and DE-A 37 03 963 de-
scribe in general form mixed esters/amides, highe:r-alkyl-
ated diesters and diamides of pyridine-2,4- and ~2,5-
dicarboxylic acid which effectively inhibit collagen
biosynthesis in an animal model.
2,4- and 2,5-disubstituted pyridine N-oxides are de-
scribed in German Patent Application P ~0 20 570.3.
It has now been found that substituted pyridine N-oxides
of the following formula I and the physiologically
tolerated salts also effecti~ely inhibit lysine hydroxyl-
ase and proline hydro~ylase.
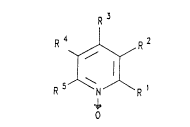
The invention therefore relates to substituted pyridine
N-oxides of the general formula I
_ 3 ~ 5 l~
R 3
R 4 J`-~Y, R ~
5 ~\ ~ (I)
in which
R1 and R3 or R4 are -C(O)-X-R6, in which
X is O or -N(R7)- and
5 R5 and R7 are identical or different, and
A are a branched or unbranched, aliphatic or cycloali-
phatic (C1 C12)-alkyl radical or (C1-C1~3-alkenyl radi-
cal or a (C1-C12)-alkynyl radical,
which is unsubstituted or mono- or polysubstituted,
preferably mono- or disubstituted, by halogen/ in par-
ticular fluorine, chlorine or bromine, hydroxyl, cyano,
carboxyl, (C1-C8)-alkoxy, (C1-C8)-alkoxycarbonyl, (C1-C8)-
alkoxycarbonyloxy, (C1-C8)-alkoxy-(C1-C8)-alkoxycarbonyl-
oxy, (C6-Cl2~-aryloxycarbonyloxy, (C7-Cll~-aralkyloxycar-
bonyloxy, (C7-C11)-aralkylcarbonyloxy, cinnamoyl, cinna-
moyloxy,(C8-C12)-arylcarbonyloxy,( C3 C8 ) - alkenylcarbonyl-
oxy, (C3-C8)-alkynylcarbonyloxy, (C3-C8)-cycloalkylcarbon-
yloxy, ~Cl-Cl2) alkoxy-(Cl-Cl2)-alkoxy, (Cl-Cl2)-alkoxy-
amino, (Cl-Cl2)-alkoxy-N-(Cl-C6)-alkylamino, (Cl-cl2)-
alkoxy-N,N-(C1-C6)-dialkylamino, carbamoyloxy, N-(Cl C8)-
alkylcarbamoyloxy, N,N-di-(Cl-C8)-alkylcarbamoyl, N-
(C3-C8)-cycloalkylcarbamoyl, N-(C8-C12)-arylamino, N-
(C7-C11)-aralkylamino, N-alkyl-axalkylamino, N-alkyl-
arylamino, (C3-C8)-cycloalkanoylamino, (C1-C8)-alkanoyl-
amino, (C8-C12)-aroylamino, (C7-C11)-aralkanoylamino,
(C1-C8)-alkanoyl-(C1-C8)-alkylamino,(C3-C8)-cycloalkanoyl-
(cl-cs)-alkylamino~ (C8~cl2)-aroyl-(cl-c8)-alkylamino~
d, ~ 9 ~ l~
(C,-C~ aralkanoyl-(Cl-C8)-alkylamino, (Cl-C8)-alkylmercap~
to, (Cl-C8)-alkylsulfinyl, (Cl-Ca)-alkylsulfonyl, (Cl-Ca)-
alkylcarbonyl, (C3-C8)-cycloalkylcarbonyl, nitro, tri-
fluoromethyl, phenylmercapto, phenylsulfonyl, phenylsul-
finyl,sulfamoyl,N~(Cl-C6)-alkylsulfamoyl,N,N-di-(C1-C6)-
alkylsulfamoyl, (C1-C8)-alkyl-sulfonamido or a.rylsulfon-
amido, in which the aryl and aralkyl radicals present in
the above substituents can also he hetexocyclic in nature
and/or, as is also the case for alkyl, a.re substituted by
1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 identical or different subs~ituentæ from
the series comprising halogen, cyano, nitro, trifluoro-
methyl, (Cl-C6)-alkyl, hydroxy, (Cl-C6)-hydroxyalkyl,
(Cl-C6)-alkoxy, -O-[CH2-}xCyH(2frl-B)Fg~ -OCF2Cl, -O-CF2-CHFCl,
trifluoromethyl, (C1-C6)-alkylmercapto, (Cl-C6)-alkylsul-
finyl, (C1-C6)~alkylsulfonyl, (C1~C6)-alkylcarbonyl,
(Cl-C6)-alkoxycarbonyl, carbamoyl, N~(Cl-C4)-alkylcar-
bamoyl, N,N-di-(Cl-C4)-alkylcarbamoyl, (Cl-C6)-alkylcar-
bonyloxy~ (C3 Ca)-cycloalkyl, phenyl, benzyl, phenoxy,
benzyloxy, NR'-R", phenylmercapto, phenylsulfo:nyl,
~0 phenylsulfinyl, sulfamoyl, N-(C1-C4)-alkylsulfamoyl and
N,N-di-(C1-C4)-alkylsulfamoyl, in particular by up to 3 of
the abovemen~ioned identical or different substituents,
and a CH2 group of the alkyl chain is optionally replaced
by 0, S, SO, SO2 or NR', or by
an unsubstituted or substituted (C6-Cl2)~aryl radical or
heteroaryl radical which carries 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 identi-
cal or different substituents from the series comprising
halogen, nitro, cyano, carboxyl, hydroxyl, trifluorometh-
yl, (cl-c6)-hydroxyalkyl~ --[cH2~xc~H(2f+l8~F~ -OCF2Cl~
-OCF2-CHFCl, (C1 C6)-alkylmercapto, (C1-C6)-alkylsulfinyl,
(cl-c6)-alkylsulfonyl~ (Cl-C8)-alkoxy, (Cl-Ca)-alkyl,
(Cl-C6)-alkylcarbonyl, (C1-C6)~alkoxycarbonyl, carbamoyl,
N-(Cl-C4)-alkylcarbamoyl, N,N-di-(Cl C4 ) -alkylcarbamoyl,
(Cl-C6)-alkylcarbonyloxy, ~ C3-C8 ) -CyC1 oalkyl, phenyl,
benzyl, phenoxy, benzyloxy, ~R~-R", phenylmercapto~
phenylsulfonyl, phenylsulfinyl, sulfamoyl, N-(Cl-C4)-
alkylsulfamoyl, N,N-di-(C1-C4)-alkylsulfamoyl,
3 'j 9 '3 ~
-- 5
(Cl-CD)-alkoxycarbQnyloxy, (Cl-C~)-alkoxy-(Cl-Ca)-alkoxy-
carbonyloxyr (Ca-Ci2)~aryloxycarbonyloxy, (C7-Cll)-aralkyl-
oxycarbonyloxy, (C7-C1l)-aralkylcarbonyloxy, cinnamoyl,
cinnamoyloxy,(C6-C12)-arylcarbonyloxy,(C3-C~)-alkenylcar-
S bonyloxy, (C3-C8)-alkynylcarbonyloxy, (C3-C8)-cycloalkyl-
carbonyloxy, (Cl-C~2)-alkoxy-(C1-C12)-alkoxy, (Cl~cl2)~
alkoxy-amino, (cl-cl2)-alkoxy-N-(cl-c6)-alkylamino~
(cl-cl2)-alkoxy-N~N-(cl-c6)-dialkylamino~ carbamoyloxy, ~-
(Cl-C8)-alkylcarbamoyloxy, N,N-d.i-(Cl-C~)-alkylcarbamoyl~
N-( C3-C~ ) -cyc.loalkylcarbamoyl, N-( C6-c12 )-arylamino r N-
(C7-Cl1)-aralkylamino, N-alkyl-aralkylam.ino, N-alkyl-
arylamino, (C3-C8)-cycloalkanoylamino, (C1-C8)-alkanoyl-
amino, (C6-C12)-aroylamino, ( C7-C 11 )-aralkanoylamino,
(Cl-C8) alkanoyl-(Cl-C8)-alkylamino,(C3-C8)-cycloalkanoyl-
(C1-C8)-alkylamino, (C8-C12)-aroyl-(C1-C8)-alkylam:ino,
(C7-Cll)-aralkanoyl-(Cl-C8)-alkylamino, (Cl~C8)-alkylmer-
cap~o, (cl-c8)-alkylsulfinyl r ( Cl-C8 ) -alkylsulfonyl,
(C1-C8)-alkylcarbonyl, (C3-C8)-cycloalkylcarbonyl, nitro,
trifluoromethyl, phenylmercapto, phenylsulfonyl, phenyl~
sulfinyl, sulfamoyl, N-(C1-C6)-alkylsulfamoyl, N,N-di-
(cl-c8)-alkylsulfamoyl, (Cl-C8)-alkyl-sulfonamido and
arylsulfonamido, in which the aryl and aralkyl radicals
present in the above substituents can also be heterocyc-
lic in nature and/or, as is also the case for alkyl, can
be substituted by 1,2,3,4 or 5 identical or different
substituen~s from the series comprising halogen, cyano,
nitro, trifluoromethyl, (C1-C6)-alkyl, hydroxyl, (C1-C6)-
hydroxyalkyl and (C1-C6)-alkoxy, or by
an unsubstituted or substituted (C6-C12)-aryloxy radical,
(C7-C~ aralkyloxy radical or heteroaryloxy radical,
which carries 1, 2, 3~ 4 or 5 identical or different
substituents from the series comprising hydroxyl, halo-
gen, cyano, nitro, trifluoromethyl, (Cl-C6)-alkyl, (C1-C6)-
hydroxyalkyl, (C1-C6)-alkoxy, ~CH2~~xCfH(2fl1-s)
-OCF2-CHFCl, (C1-C6)-alkylmercapto, (C1-C6)-alkylsulfinyl,
(cl-c6)-alkylsulfonyl~ (cl-c6)-alkylcarbonyl~ (C1-C6)-
alkoxycarbonyl, carbamoyl, N-(C1-C4) alkylcarbamoyl,
-- 6
N,N-di-( Cl-c4 )-alkylc:~arbamoyl, (Cl-C6)-alkylcarbonyloxy,
(C3-Ca) cycloalkyl, carboxyl, phenyl, benzyl, phenoxy,
benzyloxy, NF~'-R, phenylmercapto, phenylsulfonyl,
phenylsulfinyl, sulfamoyl, N-(Cl-C4)-alkylsulfamoyl, N,N~
5 di.-(C1-C4)-alkylsulfamoyl, am.inoalkyl/ ~-(C1-C8)~alkyl-
amino-(Cl-C 12 ) -alkyl and N-di-(Cl-C8)-alkylamin-(Cl-cl2)-
alkyl, is optionally substituted by up to 3 of the
abovementioned identical or di:E:ferent substituent~, and
a C~z group of the alkyl chain is optionally replaced by
lO 0, S, SO, SO2 or NR', or by
a radical of the general formula II
O R8 (II~
in which
R3 is an amino acid bonded via its acyl radica:L, a
derivative of this amino acid or an alcohol-protect-
ive ~roup,
B are an unsubstituted or substituted (C8-C12)-aryl
radical or ( C7 C11)-aralkyl radical or a heteroaryl
radical, which is mono- or polysubstituted, preferably
20 mono- or disubstituted, by
hydroxyl, halogan, cyano, carboxyl, amino, (Cl-C8)-alkyl,
(Cl-C8)-alkoxy, (Cl-C8)-alkoxycarbonyl, tCl-C8)-alkylcar-
bonyl, (C1-C8)-alkylcarbonyloxy, (Cl-C8)-alkylamino, di-
( C1-C8) -alkylamino, ( C1-C6) -hydroxyalkyl,
25 -O-[CH2-]XCfH(2f.t1 ~,F~, -OCF2Cl, -OCF2-CHFCl, ca.rbamoyl, N-
(Cl-C8)-alkylcarbamoyl, N,N-di-(C1-C8) al3cylcarbamoyl,
(cl-c8)-alkylcarbonyloxy~ (C3-C8)-cycloalkyl, phenyl,
benzyl, phenoxy, benzyloxy, aminoalkyl, N-(C1-C8)-alkyl-
amino-(C1-C 12 ) alkyl or N,N-di-(C1-C8)-alkylamino-(C1-Cl2)-
30 alkyl, (C1-C8)-alkoxycarbonyloxy, (C1-C8)-alkoxy-(C1-C8)-
alkoxycarbonyloxy, (C8-C12)-aryloxycarbonyloxy, (C7-C11)-
aralkyloxycarbonyloxy, (C7-C11)-aralkylcarbonyloxy,
- 7 _ ~3 ~j ~
cinnamoyl, cinnamoyloxy, (c6-cl2)~arylcarbonyloxy,
(C3 C8)-alkenylcarbonyloxy, (C3-C8)--alkynylcarbonyloxy,
(C3-C8)-cycloalkylcarbonyloxy, (Cl-~l2)-alkoxy-(cl-c}2)-
alkoxy, (cl-cl2)-alxoxy-aminol (C1-Cl2)-alkoxy-N-(C1-C6)-
S alkylamino, (C1-Cl2)-alkoxy-N,N-(Cl C6)-dialkylamino,
carbamoyloxy, N-(C~-CB)-alkylcarbamoyloxy, N,N-di-(Cl-C8)-
alkylcarbamoyl, N-(C3-C8)~cycloalkylcarbamoyl, N-~C6-C12)-
arylamino, N-( C7 Cll)-aralkylamino, N alkyl-aralkylamino,
N-alkyl-arylamino, (C3-C8)-cycloalkanoyla~ino, (Cl-C6)-
alkanoylamino, (C 6-C12)- aroylamino, ( C7-C~ aralkanoyl-
amino, (C1-C8)-alkanoyl-( C1_CB ) -alkylamino, (c3-C8)-cyclo-
alkanoyl-(Cl-Ca)-alkylamino, (C6-C12)-aroyl--(C1-C8)-alkyl-
amino, (C7-Cll)-aralkanoyl-(Cl-C3)-alkylamino, (Cl-Ca)-
alkylmercapto, (C1-C8)-alkylsulfinyl, (C1-C8)-alkylsul-
fonyl, (C1-C8)-alkylcarbonyl, (C3-C8)-cycloalkylcarbonyl,
nitro, trifluoromethyl, phenylmercapto, phenylsulfonyl,
phenylsulfinyl, sulfamoyl, N-(C1-C6)-alkylsulfamoyl, N,N-
di-(C1-C8)-alkylsulfamoyl, (Cl-Ca)-alXyl-sulfonamido or
arylsulfonamido,
C in the case where X = -N(R7)l are an unsubstituted
or substituted (C1-C12~-alkoxy raclical, (C3-C8)-cycloalkoxy
radical or (C6-C12)-aryloxy radical or a (C7-C11)-aralkyl-
oxy radical, which is mono- or polysubstituted, preferab~
ly mono- or disubstituted, by
halogen, trifluoromethyl, (Cl-C6)-alkoxy, hydroxyl,
(C1-C6)-hydroxyalkyl, NR'R" or cyano,
in which, in each case,
R' and R" are identical or different and are hydrog2n,
(c6-cl2)~aryl~ (cl-cs)~alkyl~ (C1-C8)~alkylcarbonyl,
(C7-C11)-aralkylcarbonyl or (C6-C12)-arylcarbonyl
or form a saturated heterocyclic ring, preferably a 5- or
6-membered ring, with the nitrogen,
~ 13.,~ A
-- 8 --
and
R2, R5 and R4 or R3, if R4 or R3 has not already been
defined above, are identical or different and
D are hydrogen, at least one radical R2, R5 and R4 or
R3 being other than hydrogen, halogen, in particular
fluorine, chlorine or bromine, cyano, nitro, krifluoro-
methyl, (cl-C12)-alkyl, -o-[CH2-]yCyH(2t1-8)F8~ -OCF2Cl~
-O-CF2-C}IFCl,(C1-C8)-alkylmercapto,(C1-C8)-alkylsulfinyl,
(C1-C8)-alkylsulfonyl,(C1-C8)-alkylcarbonyl~carbamoyl,N-
10 ( Cl-C4 ) -alkylcarbamoyl, N,N-di-( Cl-C4 ) -alkylcarbamoyl~
(c3-c8)-cycloalkyl~ phanylmercap~o, phenylsulfonyl,
phenylsulfinyl, (C1~C12)-alkoxycarbanoyl, (C1-C12)-alkyl-
carbanoyloxy, amino, N-lCl-C1O)-alkylamino, di-N,N-
(Cl-C10)-alkylamino, N,N-(C3-C8)-alkanediylamino, such as,
for example, pyrrolidino, piperidino or their hetero-
cyclic derivatives morpholino and thiomorpholîno, N-
( C6-C12 ) - arylamino, N-(C6-Cl2) aryl-N (C1-CIO)-alkylamino, N-
(C7-C11)-aralkylamino, N-( C7 Cll ) -aralkyl-N-(C1-C1O)~alkyl-
amino, (Cl-Cl2)-alkanoylamino, (C3-C6)-cycloalkanoylamino-
( Cl-C 12 ) - hydroxyalkanoylamino, (C1-c8)-alkoxy-(cl-cl2)
alkanoylamino, (C6-Cl2)-arylcarbonylamino, (C7-Cll)-aralk-
ylcarbonylamino, (Cl-C8)-alkoxycarbonyloxy, (Cl-C8)-alkoxy-
(cl-c8)-alkoxycarbonyloxy, (C6-Cl2)-aryloxycarbonyloxy,
(C7-Cll)-aralkyloxycarbonyloxy, (C7-Cll)-aralkylcarbonyloxy,
(C~-C12)-arylcarbonyloxy, (C3-C8)-alkenylcarbonyloxy,
(C3-C8)-alkynylcarbonyloxy,(C3-C8)-cycloalkylcarbonyloxy,
(C1-C12)-alkoxy-(C1-C12)-alkoxy, (C1-C12)-alkoxy-amino,
~Cl-cl2)-alkoxy-N-(cl-c6)-alkylamino~ (Cl-Cl2)-alkoxy-N,N-
(Cl-C6)-dialkylamino, carbamoyloxy, N-(C1~Ca)-alkylcar-
bamoyloxy, N,N-di-(C1-C8)-alkylcarbamoylox~, N-(C3-C8)-
cycloalkylcarbamoyloxy, NR'R", (Cl-C8)-alkylmercapto,
(Cl-C8)-alkylsulfinyl, (cl-c8)-alkylsulfonyl~ (Cl-C8)-
alkylcarbonyl, (C3-C8)-cycloalkylcarbonyl, sulfamoyl,
N-(Cl-C6)-alkylsulfamoyl, N,N-di-(Cl-C6)-alkylsulfamoyl,
(C1-C8)-alkylsulfonamido or arylsulfonamido, in which the
aryl and aralkyl radicals present in the above
9 ~ 5 ~
substituents can also be hete.rocyclic in nature and/or
are substit~lted, as is also the case for alkyl, with 1,
2, 3, 4 or 5 identical or different substituents from the
series comprising halogen, cyanor nitro, trifluoromethyl,
(C,-C6)-alkyl, hydroxyl, (C1-C6)-hydroxyalkyl, (C1-C6)-
alkoxy~ --[CH2-~CfH(2f+~8~F~ -OCF2Cl, -O-CF2-CHFCl, tri-
fluoromethyl, (C~-C6)-alkylmercapto, (C~-C6)-alkylsulfinyl,
(C~-C6)-alkylsulfonyl, (C~-C6)-alkylcarbonyl, ~Cl-C6)-
alkoxycarbonyl, carbamoyl, N-( Cl-c4)-alkylcarbamoyl, N,N-
di-(C1-C4)-alkylcarbamoyl, (Cl-C6) alkylcarbonyloxy,
(C3-C8)-cycloalkyl, phenyl, benzyl, phenoxy, benzyloxy,
NR'-R", phenylmercapto, phenylsulfonyl, phenylsulfinyl,
sulfamoyl, N-(Cl-C4)-alkylsulfamoyl and N,N-di-(C~-C4)-
alkylsulfamoyl, in particular by up to 3 of the abovemen-
tioned identical or different substituents, and a CH2group of ~he alkyl chain is optionally replaced by O~ S,
SO, SO2 or NR',
or
E are an alkyl, alkenyl or alkynyl radical having up
to 9 carbon atoms~ which i5 optionally substitu~ed by
1, 2, 3, 4 or S identical or dif~erent substituents from
the series comprising hydroxyl, halogen, cyano, nitro,
trifluoromethyl, ~C1-C6)-hydroxyalkyl, (C1-C6)-alkoxy,
[CH2~]xcfH(2ftl-B)Fs~ -OCF2CHFCl, (C1-C6)-alkylmercapto,
(Cl-C6)-alkylsulfinyl, (C~-C6)-alkylsulfonyl, (Cl C6)-
alkylcarbonyl, (C1 C6)-alkoxycarbonyl, carbamoyl, N-
(Cl-C4)-alkylcarbamoyl, N,N-di-(Cl-C4)-alkylcarbamoyl,
(C1~C6)-alkylcarbonyloxy, (C3-C8)-cycloalkyl, carboxyl/
phenyl, benzyl, phenoxy, benzyloxy, phenylmercapto,
phenylsulfonyl, phenylsulfinyl, sulfamoyl, N-(C1-C4~-
alkylsulfamoyl, N,N-di-(C1-C4)-alXylsulfamoyl, amino, N-
(C1-C10)-alkylamino, di-N,N-(C1 C10)-alkylamino, N,N-
(C3-C8)-alkanediylamino, such as, for example, pyrroli-
dino, piperidino or their het~rocyclic derivatives
morpholino and thiomorpholino, N-(C6 Cl2)-arylamino,
- lO ~ J~
N-(C~-C~2)-aryl-N-(Cl-C~O)-alkyl~nino, N-(C7-Cll)-aralkyl-
amino~ N-(c7-cll)-aralkyl-N-(cl-c~ alkylamino~ (C~-Clz)-
alkanoylamino, (C3-C8~-cyclo-alkanoylamino, (Cl-cl2)-
hydrQxyalkanoylamino, (C~-C8)-alkoxy-(C,-C~2)-alkanoyl-
amino, (C6-C12)-arylcarbonylamino and (C7-C11)-aralkyl-
carbonylamino, in particular by up -to 3 of the above-
mentioned identical or different substituents, and a CH2
group of the alkyl chain is optionally replaced by 0, S,
SO, SO2 or NR',
or by
an unsubstituted or substituted (C6~C12)-aryl radical,
tC7-C~l)-aralkyl radical or heteroaryl radical, which
carries 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 identical or different substitu~
ents from the series comprising hydroxyl, halogen, cyano,
nitro, trifluoromethyl, (C1-C6)-hydroxyalkyl, (C1-C8)-
alkyl r ( Cl-C6 ) -alkoxy, [CH2~]xc~H~2f+l-8)F~ -OCF2C~IFCl,
(Cl-C6)-alkylmercapto, (Cl-C6)-alkylsulfinyl, (Cl-C6)-
alkylsulfonyl, (C1-C6)-alkylcarbonyl, (C1-C6)-alkoxycar~
bonyl,carbamoyl,N-(C1-C4)-alkylcarbamoyl,N,N-di (C1--C4)-
~0 alkylcarbamoyl, (C1-C6)-alkylcarbonyloxy, (C3-C8)-cyclo-
alkyl, carboxyl, phenyl, benzyl, phenoxy, benzyloxy,
phenylmexcapto, phenylsulfonyl, phenylsul~inyl, sul-
famoyl, N-(C1-C4)-alkylsulfamoyl, amino, N-(C1~C10)-alkyl-
amino, di-N,N-(Cl-C10)-alkylamino, N,~-~C3-C8)-alkanediyl-
am.ino, such as, for example, pyrrolidino, piperidino ortheir heterocyclic derivatives morpholino and thiomor-
pholino, N-(C6-C12)-arylamino, N-(C6-Cl2)-aryl-N-(C1-ClO)-
alkylamino, N-(C7-C~ aralkylamino, N-(C7-C~ aralkyl-N-
(C1-C1O)-alkylamino, (Cl-C12)-alkanoylamino~ ( C3 -C8)-cyclo-
alkanoylamino, (C1-Cl2)-hydroxyalkanoylamino, (Cl-C8)-
alkoxy-(Cl-Cl2)-alkanoylamino, (C6-Cl2)-arylcarbonylamino
and (C7-C~1)-aralkylcarbonylamino, in particular by up to
3 of the abovementioned identical or different substitu-
ents, and a CH2 group of the alkyl chain is optionally
replaced by 0, S, SO, SO2 or NR',
or
F denote a substituted or unsubstituted (c6-cl2)-ar
radical, ~C7-C~ aralkyl radical or heteroaryl radical,
in which the aryl and heteroaryl radical mentioned is, .in
particular, phenyl, naphthyl, thienyl, furyl, pyrrolyl or
pyridine, and which furthermore
carries in the aryl part 1, 2, 3, 4 or S iden~ical or
different substituents from the series comprising hydrox-
yl, halogen, cyano, nitro, tC1--C8)-alkyl, (C1-Cb)-alJcoxy,
carboxyl, trifluoromethyl, (C1-C63-hydroxyalXyl,
--[CH2~]xC~H(2f~ 8)F8/ -OCF2Cl, -OCF2CHFCl, (C~-C6)- lkylmer-
capto, (cl-c6)-alkylsulfonyl~ (C1-c6)-alkYlsulfinyl~
(C1-C6)-alkylcarbonyl, (C1-C6)-alkoxycarbonyl, carbamoyl,
N-(C1-C4)-alkylcarbamoyl, N,N-di-(C1-C4)-alkylcarbamoyl,
(C1-C6)-alkylcarbonyloxy, (C3-Ca) cycloalkyl r phe:nyl,
benzyl, phenoxy, benzyloxy, amino, N-(Cl-CIo) alkylamino,
di-N,N-(C1-C1O)-alkylamino, N,N-( C3_CB )-alkanediylamino,
such as, for example, pyrrolidino, piperidino, morpho-
lino, thiomorpholino, (cl-clo)-alkanoylaminol (C6-C12)-
arylcarbonylamino, (C7-C11)-aralkylcarbonylclmino, phenyl-
mercapto, phenylsulfonyl, phenylsulfinyl, sulfamoyl, N-
(C1-C4)-alkylsulfamoylorN,N-di-(C1-C4)-alkylsulfamoyl,in
particular up to 3 of the abovementioned identical or
different substituents, and in which a CH2 group of the
aryl chain is optionally replaced by O, S, SO, SO2 or NR',
or
G are a substituent of the formulae -OR9 or ~M(R9)2l in
which
R9 is hydrogen, alkyl, alkenyl or alkynyl, in each case
having up to 9 carbon atoms, a (C6-Cl2)-aryl radical or a
heteroaryl radical, which
carries in the aryl part 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 identical or
different substituents from the series comprising hydrox-
yl, halogen, cyano, nitro, carboxyl, (C1-C6)-alkyl,
(Cl-C6)-alkoxy, trifluoromethyl, (C~-C6)-hydroxyal}cyl,
--[CH2-~XCfH(2f+1-B~F8~ -OCF2Cl, -OCF2CHFCl, (Cl C6)-alkylmer-
1 ~ 2 i~
capto, ~C1-C~)-alkylsulfonyl, tCl-C8)-alkylsulfinyl,
(Cl-C6)-alkylcarbonyl, (Cl-C~)-alkoxycarbonyl, carbamoyl,
N-(C1-C4)-alkylcarbamoyl, N,N-di-( Cl-c4 )-alkylcarbamoyl,
(Cl-C6)-alkylcarbonyloxy, ( C3-C~ ) -cycloalkyl, phenyl r
benzyl, phenoxy, benzyloxy, amino, N-(Cl-C10)-alkylamino,
di-N,N-(Cl-C10)-alkylamino, N,N-(C3-Ca)-alkanediylam.ino,
such as, for example, pyrrolidino, piperi.dino, morpho-
lino, thiomorpholino, (C1-C10)-alkanoylaTn.ino, (C5-C12)-
arylcarbonylamino, (C7-C11~-aralkylcarbonylamino, phenyl-
mercapto, phenylsulfonyl, phenylsulfinyl, sulfamoyl, N-
(C1-C4)-alkylsulfamoylorN,N-di-(C1-C4) alkylsulfamoyl,in
particular up to 3 of the abovemen~ioned identical or
different substituents, and in which a CH2 group of ~he
aryl chain is optionally replaced by O, S, SO, SO2 or NR',
and
n = 0 or 1,
f = 1 to 8, preferably 1 to 5,
g = 0.1 to (2f + 1) and
x is 0, 1, 2 or 3, preferably 0 or 1,
plus all derivatives which carry a corresponding protect-
ive group in their amino or hydroxyl groups, and the
physiologically active salts.
~ryl, aryloxy, heteroaryl and heteroaryloxy compounds are
understood as meaning, in particular, phenyl and naphthyl
rings and unsubstituted 5- and 6-memhered heteroaromatic
rings having 1 ,2 or 3 nitrogen and/or oxygen and/or
sulfur atoms, such as pyridyl, pyridazyl, pyrimidyl,
pyrazyl, imidazolyl, triazolyl, thienyl, oxazolyl and
thiazolyl derivatives, and benzo-fused derivatives
thereof. The radical (C7-C~ aralkyloxy is preferably
understood as meaning a substituted phenylalkyloxy
- 13 ~ tr~9 5i
radical of the formula III
~10 Rl I
~''
-o-lCH2~ Rl2 (III)
R 4 Rl3
i hich R10 R11 R12 ~13 and Rl4 are identical or dif-
erent and are hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro, txi-
fluoromethyl, (C1-C6)-alkyl, (C1~C6)-alkoxy,
-~[CH2~]xCfH~2~ B)F8r -OCFzCl, -OCF2CHFCl, (C1~C6)-alkylmer-
capto, (~ 6)-alkylsulfinyl~ ~Cl-C6)~alkylsulfonyl,
(C1-C6) alkylcarbonyl, (Cl-C6)-alkoxycarbonyl, carbamoyl,
N-(C1-C4)-alkylcarbamoyl~ N,N-di~(C1-C4)-alkylcarbamoyl,
(Cl-C6)-alkylcarbonyloxy, (C3-C8)-cycloalkyl, phenyl,
benzyl, phenoxy, benzyloxy, NR'R~, such as amino~ anilino
or N-methylanilino/ phenylmercapto, phenylsulfonyl,
phenylsulfinyl, sulfamoyl, N-(C1-C4)-alkylsulfamoyl or
N,N di-(C1-C4~-alkylsulfamoyl, or two adjacent substitu-
ents togethex are a -[CH2-]n or ~C~=C~-CH=C~- chain, in
which a CH2 group of the chain is optionally replaced by
O, S, SO, SO2 or NR', Y is 1, 2, 3 or 4, preferably 0
or 1, and the other substituents R10, R1lr R12, R13 and R14
are as defined aboYe.
Of the amino acids mentioned, the naturally occurring ~-
amino acids are particularly preferred.
Amino-protective groups are understood as meaning, in
particular, tho~e groups which are described in R. Geiger
and W. Xonig "The Peptides" Volume 3, ~Protection of
Functional Groups in Peptide Synthesis~, E.G. Gross,
J. Meienhofer Edit, Academic Press, New York (1981), in
particular pages 7 - 46.
- 14 _ 2~5~
Such groups are likewise described in A. Hubbuch,
Schutzgruppen in der Peptidsynthese [Protective Groups in
Peptide Synthesis], Kontakte 3/79, pages .L4~23.
The following amino-protective groups are pa.rticularly
preferred:
acetamidomethyl,
l-adamantyloxycarbonyl,
l-(l-adamantyl~ me-thyl-ethoxycarbonyl,
allyloxycarbonyl,
tert-butyloxycarbonyl,
1-(4-biphenylyl)-1-methyl-ethoxycarbonyl,
dicyclohexylcarbodiimide,
~ dimethyl-3,5-dimethoxybenzyloxycarbonyl,
4-dihydroxyborylbenzyloxycarbonyl,
9-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl,
l-hydroxybenzotriazole,
3-hydroxy-4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-1,2,3 benzot.riazine,
isobornyloxycarbonyl,
l-methyl~cyclobutyloxycarbonyl,
4-methoxybenzyloxycarbonyl,
methylsulfonylethyloxycarbonyl,
4-pyridylmethyloxycarbonyl,
2,2,2-trichloro-tert-butyloxycarbonyl,
benzyloxycarbonyl,
halogen-substitu-ted benæyloxycarbonyl,
4-nitro-benzyloxycarbonyl,
2-phosphonoethyloxycarbonyl,
phenylsulfonylethoxycarbonyl,
toluenesulfonylethoxycarbonyl,
2,3,5-trimethyl-4-methoxy-phenylsulfonyl and
benzotriazol-1-yl-oxy-tris(dimethylamino~phosphonium
hexafluorophosphate.
Preferred compounds of the formula I in which the amino
groups are protected are those in which the protected
amino groups are part of this amino acid Ra.
- 15 ~
Poss.ible alcohol-protec-tive groups are, in particular,
substituted or unsubst.ituted methyl ethers, ethyl ethers,
ben2yl ethers, silyl ethers, esters, carbonates or
sulfonates.
These include the following compounds:
As substituted methyl ethers:
me~hoxymethyl, methylthiomethyl, t-butylthiomethyl,
(phenyldimethylsilyl)methoxymethyl, benzyloxymethyl, p-
methoxybenzyloxymethyl, (4-methoxyphenoxy)-methyl,
guaiacolmethyl, t-butoxymethyl, 4-pentenyloxymethyl,
siloxymethyl, 2-methoxyethoxymethyl, 2,2,2-trichloro-
ethoxymethyl, bis-(2-chloroethoxy)methyl, 2-(trLmethyl-
silyl)ethoxymethyl,tetrahydropyranyl,3-bromotetrahydro-
pyranyl, tetrahydrothiopyranyl, 1-methoxycyclohexyl, 4-
methoxytetrahydropyranyl, 4-methoxytetrahydrothiopyranyl,
4-methoxytetrahydrothiopyranyl-S,S-dioxo, 1-[2-chloro-4-
methyl)phenyl]-4-methoxypiperidin-4-yl, 1,4-dioxan-2-yl,
tetrahydrofuranyl and ~etrahydrothiofuranyl.
As substituted ethyl ethers:
1-ethoxyethyl, 1-~2-chloroethoxy)athyl, 1 methyl-1-
methoxyethyl, 1-methyl-1-benzyloxyethyl, 1-methyl-1-
benzyloxy-2-fluoroethyl,2,2,2-trichloroethyl r 2-trimeth-
ylsilylethyl, 2-(phenylselenyl)ethyl, t butyl, allyl J p-
chlorophenyl, p-methoxyphenyl, 2,4-dinitrophenyl and
benzyl.
As substituted benzyl ethers:
p-methoxy.benzyl, 3,4-dimethoxyben2yl, o-nitrobenzyl, p-
nitrobenzyl, p-halogenobenzyl, 2,6-dichlorobenzyl, p-
cyanobenzyl, p-phenylbenzyl, 2- and 4-picolyl, 3-methyl-
2-picolyl-N-oxido, diphenylmethyl, p,p'-dinitrobenzohy-
dryl, triphenylmethyl, ~-naphthyldiphenylmethyl, p-
methoxyphenyldiphenylmethyl, di(-p-methoxyphenyl)phenyl-
methyl, tri(p-methoxyphenyl)methyl, 4-(4'-bromophenacyl-
oxy)phenyldiphenylmethyl, 4,4',4"'tris(4,5-dichloro~
- 16 - ~J ~ Ll
phthalimidophenyl)methyl, 4,4',4"-tristlevulinooxyphen-
yl)methyl, 4,4',4'l-tris(benzoyloxyphenyl)methyl, 3-
(imidazol-1,4' methyl)bis(4',4"-dLmethoxyphenyl)methyl,
1,1-bis-(4~methoxyphenyl)-1~-pyrenylmethyl, 9-anthryl,
9 (9-phenyl)xanthenyl~ 9-(9-phenyl-lO-oxo)anthryl.
As silyl ethers:
trimethylsilyl, triethylsilyl, triisopropylsilyl, dimeth-
ylisopropylsilyl, diethylisopropylsilyl, dimethylthexyl-
silyl, t-butyldimethylsilyl, t-butyldiphenylsilyl,
triben~ylsilyl, tri-p-xylylsilyl~ triphenylsilyl, diphen-
ylmethylsilyl and t-butylmethoxyphenylsilyl.
As esters:
formates, benzoylformates, acetates, chloroacetate,
dichloroacetate, trichloroacetate, trifluoroacetate,
methoxyaceta~e, triphenylmethoxyacetate, phenoxyacetate,
p-chlorophenoxyacetate, p-P-phenylacetate, 3~phenylpro-
pionate, 4 oxopentanoate ~levulinate), 4,4-(ethylen~3di-
thio)pentanoate, pivaloate, ad~mantoate, crotonate, 4-
methoxycrotonate, benzoate, p-phenylbenzoate and 2,4,6-
trimethylbenzoate (mes.itoate).
As carbonates:methyl, 9-~luorenylmethyl, ethyl, 2,2,2-tri.chloroethyl,
2-(trimethylsilyl)ethyl, 2-~phenylsulfonyl)ethyl, 2-
(triphenylphosphonio)ethyl, isobutyl, vinyl, allyl, p-
nitrophenyl, benzyl, p-methoxybenzyl, 3,4-dimethoxybenz-
yl, o-nitrobenzyl, p-nitrobenzyl, S-ben~yl thiocarbon-
ates, 4-ethoxy-1-naphthyl and methyl dithiocarbonates.
Further esters:
2,6-dichloro-4-methylphenoxyacetate, 2,6-dichloro-4-
(1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutyl)phenoxyacetate, 2,4-bis-(l,l-
dimethylpropyl)phenoxyacetate, chlorodiphenylacetate,
isobutyrate, monosuccinate, (E)-2-methyl-2-butenoate
(tigloate), o-(methoxycarbonyl)benzoa~el p-P-benzoate,
~-naphthoate, nitrate, alkyl N,N,N',N~-tetramethylphos-
- 17 - 2 ~ 2~
phorodiamidate, N-phenylcarbamate, bora-tes, dime-thylphos-
phinothioy:l and 2,4-dinitrophenylsulfenate.
As sulfonates:
sulfates, me-thanesulfonate ~mesylate), benzylsulfonate
and tosylates.
The following protective groups are particularly
preferred:
(Cl-C6~-alkanoyl, (Cl-C~)-alkylcarbamoyl, di~(Cl-C8)-alkyl-
carbamoyl, N-(C3-C8)-cycloalkylcarbamoyl, (C1-C6)-alko~y-
carbonyl, ( C6-cl2 ~ aryloxycarbonyl, ( C7-cll ) -aralkyloxycar-
bonyl, in particular benzyloxycarbonyl, (C6-C12)-arylcar-
bonyl, (C7-C11)-aralkylcarbonyl, (C1-C6)-alkyl, (C1-C6)-
alkoxy-(C1-C6)-alkyl, carbamoyl-(Cl-C6)-alkyl esters,
(C1-C10)-acyloxy-(Cl-C6)-alkyl, preferably (Cl-C10)-alkan-
oyloxy-( Cl-C6 ) -alkyl, ben~yloxy-( Cl-C6 ) -alkyl, benzyloxy-
carbonyloxy-(Cl-C6)~alkyl, (C1-C6)-alkoxycarbonyloxy-
(Cl-C6)-alkyl, amino acid esters and tetrahydropyranyl.
Preferred compounds of the formula I are those in which
Rl and R3 or ~4 are -C(O)-X-R6, in which
X is -N(R7)~.
Compounds of the formula I which are furthermore pre-
ferred are those in which
R6 is hydrogen or methyl and
R7 has the abovementioned meaning,5 R~ and R7 are.hydrogen and/or methyl, if at least one
group R1, R3 or R4 is a radical -C(o)-N(R7) R6,
in which R5 and/or R7 have the abovementioned
meaning.
If R5 or R7 is not hydrogen or methyl according to the
above preferred embodiment, the following compounds are
preferred, in which the radicals
2,)(~5~1
- 18 ~
~ are a branched or unbranched (cl-cl~)-alkyl radical,
which is unsubstituted or mono- or polysubstituted by
halogen, in particular fluorine, chlorinel bromine,
hydroxyl, cyano, carboxyl, (Cl-C4)-alkoxy, (cl-c4~-alk
carboxyl, (C1-C~)-alkoxycarbonyloxy, (Cl-c8)-alX
(Cl-C8)-alkoxycarbonyloxy, (C6-Cl2)-aryloxycarbonyloxy,
(C7-Cl1)-aralkyloxycarbonyloxy, (C7-C~ aralkylcarbonyloxy,
( C7 -Cll ) -arylcarbonyloxy, (C3-C8)-cycloalkylcarbonyloxy,
(C1-C12)-alkoxy-(C1-C12)-alkoxy, carbamoyloxy, N-(C1-C8)-
alkylcarbamoyloxy, N,N-di-(Cl-C8)-alkylcarbamoyl, N-
( C3 -C 8 ~ -CyC loalkylcarbamoyll N-( C7~C 11 )-aralkylcarbamoyloxy
or N-~C6~C12)-arylcarbamoyloxy, in wh.ich the aryl and
aralkyl radicals present in the above substituents can
also be heterocyclic in nature, and/or, as is also the
case for alkyl, are substituted by 1 or 2 identical or
different substituents from the series comprising halo-
gen, trifluoromethyl, hydroxyl, (C1-C3)-alkyl, (C1--C3)-
hydroxyalkyl, (C1-C9)-alkoxy, -O [CH2-]xcfH(2f~l-B)F8l -OCF2Cl~
-O-CF2-CHFC1, (C1-C3)-alkoxycarbonyl, carhamoyl, (C1-C5)-
alkylcarbonyloxy, (C3-C8)~cycloalkyl, phenyl, benzyl,
phenoxy, benÆyloxy, or by
an unsubstituted or substituted (C6-C12)-aryl radical or
heteroaryl radical, which carries 1 or 2 identical or
different substituents from the series comprising halo-
gen, nitro, cy~no, carboxyl, hydroxyl, trifluoromet:hyl,(Cl-C3)-hydroxyalkyl, (Cl-C3)-alkoxycarbonyl, carbamoyl,
NR'R", N-~Cl-C4) alkylcarbamoyl, N,N-di-(Cl-C4)-alkylcar-
bamoyl, (Cl-C8)-alkoxy-(Cl-C8) alkyl, (Cl-C3)-alkylcarbon-
yloxy, aminoalkyl and N-(C1-C4)-alkylamino-~C1-C6) alkyl,
in which R~ and R~ are identical or differen~ and are
hydrogen, (C6-Cl2)-aryl or (C1-C4)-alkyl, or by
an unsubstituted or substituted (C5-C10)-aryloxy radical
or (C7-C11)-aralkyloxy radical, which carries 1 or 2
identi.cal or different substituents from the series
comprising hydroxyl, halogen, trifluoromethyl,
- 19 ~ 5~
( C l-C3 ) -alkyl, ~Cl-C3 )-hydroxyalkyl, (Cl-C3)-alkoxy,
(Cl-C3)-alkylmercapto, (Cl-C3)-alkylsulfinyl, (
alkylsulfonyl, ~C1-C3)-alkylcarbonyl, (C1-C3)-alkoxycar-
bonyl,carbamoyl,N-(C1-C4)-alkylcarbamoyl,N,N~di-tCl-C4)-
alkylcarbamoyl/ (Cl-C3)-alkylcarhonyloxy and NR'R", in
which R' and R~ are identical or different and are
hydrogen, (C6-ClO)-aryl or (Cl-C,,)-alkyl~ or by
a radical of the formula II
o Ra (II)
in which
R8 iS an amino acid bonded via its ~cyl radical, or is
a derivative thereof,
B denote a (C~-Cl2)-aryl or (c7-cll)-aralkyl radical~
preferahly phenyl~ benzyl or phene~hyl, which are unsub-
stituted or monosubstitu~ed by halogen, cyano, carboxyl,hydroxyl, ~Cl-C8)-alkyl, (Cl-C8)-alkoxy, (C1-C8)-alkylcar-
bonyl, (Cl-C4)-alkylcarbonyloxy, (Cl-C4)-alkoxycarbonyl,
(Cl-C4)-hydroxyalkyl, amino, (Cl-C5~-alkylamino, di-
1Cl-Cs)-alkylamino, (Cl-C5)-alkanoylamino, carbamoyl, N-
(Cl-C4)-alkylcarbamoyl, N,N-di-(Cl-C4)-alkylcarbamoyl,
carbamoyl, N-(Cl-C4)-alkylcarbamoyloxy or N,N-di-(Cl-C4)-
alkylcarbamoyloxy or
C are an unsubstituted (C1-C6)-alkoxy radical, (C3-C8)-
cycloalkoxy radical, (C6-Cl2)-aryloxy radical or
(C7-Cll~-aralkyloxy radical.
Particularly preferred compounds of the formula I are
those in which R6 and R7, if these are not hydrogen or
methyl, as described above, are
A an unbranched (Cl-Cl2)-alkyl radical, which is unsub-
stituted or monosubstituted by
2f~
hydroxyl, halogen, (C1-C8)-alkoxy r (C1-C~)-alkoxycarbonyl,
(Cl-C8)-alkoxycarbonyloxy, (C~-C8)-alkoacy-(Cl-C8)-alkoxy-
carbonyloxy, (C6-C12)-aryloxycarbonyloxy, (C7-C~ aralkyl-
oxycarbonyloxy, (C7-Cll)-aralkylcarbonyloxy, (C6-cl2)-
S arylcarbonyloxy, (C3-C8)-cycloalkylcarbonyloxy, (Cl-C,2)-
alkoxy-(Cl-Cl2~-alkos~y, (Cl-Cl2)-alkoxy-amino, (Cl-Cl2~-
alkoxy-N-(Cl-C6)-alkylamino, (Cl-Cl2) alkoxy-N,N-(Cl-C6~-
dialkyl~mino, N,N-di-(C1-C8)-alkylcarbamoyl, N-( C3-C~ ) -
cycloalkylcarbamoyl, N-(C7-Cll)-aralkylcarbonyloxy, N-
10 (C8-Cl2)-arylcarbanoyloxy, (Cl-C5)-allcanoylamino, (C3-C6)-
cycloalkanoylamino,(C6-C12)-aroylaminoor(C7-Cll)-aralkan-
oylamino, in which alkyl, aryl, aryloxy, aralkyl or
aralkyloxy in turn are substituted by hydroxyl, halogen,
in particular fluorine, (Cl-C3)-alkyl or (Cl-C3)-al~oxy, or
by
a phenyl radical which is unsukstituted or monosubstitut-
ed by a hydroxyl group, ~ phenoxy or benæyloxy radical
which is unsubstituted or subskitu~ed by hydroxyl,
halogen or (Cl-C4)-alkoxy/ or by
a radical o:E the formula II
o Ra (II)
in which Ra is an amino acid bonded via its acyl radical,
or its derivative subs~ituted on the ~mino group, or
B are a (C6-Cl2)-aryl or ~C7-C11)-aralkyl radical,
preferably phenyl~ benzyl or phenethyl, which is unsub-
stituted or monosubstituted by hydroxyl.
In respect of the substituents R2, Rs and R4 or R3, if R3
or R4 is not already defined as above, compounds in which
not more than two of the three radicals are pre~erably
other than hydrogen, particularly preferably not more
than one of the radicals is other than hydrogen, are
preferred.
2 1 f d ~ ~? ~
-
Compounds which are furthermore preferred are those in
which, independently of one another, R2, Rs and R4 or R3
are other than hydrogen if these are directly adjacent to
not more than one other substi~.u4nt R1 and R3 or R4.
S R2, R5 and R4 or R3, lf R4 and R3 are not already defined
above and are not to be hydrogen, are preferably
D halogen, in particular fluorine, chlorine or brom-
ine, cyano, nitro, trifluoromethyl, tC1-C12)-alkyl,
--[CH~-]xC~H(2ft1-8)Fg~ -OCF2Cl, -O-CF2-CHFCl, (Cl-C8)-alkyl-
carbonyl, carbamoyl, N-(Cl-C4)-alkylcarbamoyl, N,N-dl-
(Cl-c4?-alkylcarbamoyl~( C3-CB ) -cycloalkyl~(C1-C12)-alkoxy-
carbonyl, ~Cl-Cl2)-alkylcarbonyloxy, amino, N-(C1-Clo)-
alkylamino, di-N,N-(C1-C10)-alkylamino or NIN ( C3-~C~ ) -
alkanediylamino, such as, for example/ pyrrolidino,
piperidino or their heterocyclic derivatives morpholino
and thiomorpholino, N-(C6-Cl2)-arylamino, N-(C6-Cl2)~-aryl-
N-(C1-C8)-alkylamino, N-(C7-C11) aralkylamino; N-(C7-C11)-
aralkyl-N-~Cl-C10)-alkylamino, (C6-Cl2~-arylcarbonylamino,
(C7-Cll)-aralkylcarbonylamino, (Cl-C6)-alkoxycarbonyloxy,
(C6-C12)-aryloxycarbonyloxy, (C7-Cl1)-aralkylcarbonyloxy,
(C6-Cl2)-arylcarbonyloxy, (C3-C8)-alkenylcarbonyloxy,
(C3-Ca)-cycloalkylcarbonyloxy, (Cl-Cl2)-alkoxy-(cl~cl2)
alkoxy, (Cl-Cl2)-alkoxy-amino, (C1-Cl2)-alkoxy-N-(C1-C6)
alkylamino, ( Cl-Cl2 ) -alkoxy-N,N-( Cl-C6 ) -dialkylamino,
carbamoyloxy, N-(Cl-C6)-alkylcarbamoyloxy, N,N-di-(Cl-Ca)-
alkylcarbamoyloxy, N-(C3-C8~-cycloalkylcarbamoyloxy,
NR'R", (Cl-C8)-alkylmercapto, (Cl-C6)-alkylsulfinyl,
(C1-C8)-alkylsulfonyl, (C1-C8~-alkylcarbonyl or (C3-C8)-
cycloalkylcarbvnyl, in which the aryl and aralkyl radi-
cals present in the above substituents can also be
heterocyclic in nature and/or, as is also the case for
alkyl, are substituted by 1, 2 or 3 identical or dif-
ferent substituents from the series comprising halogen,
trifluoromethyl, (Cl-C6)-alkyl, hydroxyl, (Cl-C6)-hydro~y-
alkyl, (C1-C6)-alkoxy, -o-[cH2-]xcfH(2f~l-6)FBl (C3_CB)_CYC1O_
alkyl, phenyl, benzyl, phenoxy, benzyloxy, NR'R",
r~ S ~9 ~ ~
- 22 -
phenylmercapto, phenylsulfonyl, phenylsulfinyl, sul-
famoyl, N-(Cl-C4)-alkylsulfamoyl or N,N-di-(C~-C4)-
alkylsulfamoyl,
or
E an alkyl or alkenyl radical having up to 5 carbon
atoms, which is optionally substituted by l, 2 or 3
identical or different substi.~uents from the series
comprising hydroxyl, halogen, cyano, nitro, trifluoro-
methyl, (cl-c6)-hydroxyal]cyl~ (cl-c6)-alkoxy~
10 ,[cH2-]xc~H(2f~l-8~F8r -OCF2-CHFCl, (C~-C6)--alkylcar}:)onyl,
(Cl-C6)-alkoxycarbonyl, carbamoyl, N-(C1~C4)-alkylcar-
bamoyl, N,N-di-(C1-C~)-alkylcarbamoyl, (Cl-C6)-zlkylcar-
bonyloxy, (C3-C8)-cycloalkyl, carboxyl, phenyl, benzyl,
phenoxy, benzyloxy, amino, N~(C1-C6)-alkylamino, di-N,N-
(C1-C6)-alkylamino or N,N-(C3-C8)-alkanediylamino, such as,
for example, pyrrolidino or piperidino, N-(C6-C12)-aryl-
amino, N-(C6-C1z)-aryl-:N-(Cl-C6~-alkylamino, N-(C7-~
aralkylamino, N~( C7-C~ )-aralkyl-N-(Cl-C10)-alkylamino,
(C~-C6)-alkanoylamino, (C1-C8)-alkoxy-(C1-C6)-alkanoylamino,
(C6-C12)-arylcarbonylamino and (C7-C1~)-aralkylcarbonyl-
amino,
or by
an unsubstituted or substituted (C6-C~z)-a.ryl radical,
( C7-C~ ) -aralkyl radical or heteroaryl radical, which
~5 carries 1, 2 or 3 identical or different substituents
from the series comprising hydroxyl, halogen, cyano,
nitro, trifluoromethyl, (C1-C6)-hydro~yalkyl, (C~-C6)-
alkoxy, (cl-c6)-alkoxy~ [cH2-]xcfHt2~+l-8)F8~ (C1-C6) alky
bonyl, (C~-C6)-alkoxycarbonyl, carbamoyl, N-( C~-C4 )-alkyl-
carbamoyl, N,N-di-(Cl-C4)-alkylcarbamoyl, (Cl-C6)-alky.lcar-
bonyloxy, (C3-C8)-cycloalkyl, carboxyl, phenyl, benzyl,
phenoxy, benzyloxy, amino, N-(C1-C6)-alkylamino, di N,N-
(Cl-C6)-alkylamino or N,N-(C3-C8)-alXanediylamino, such as,
for example, pyrrolidino or piperidino, N-(C6~C12)-aryl-
35 amino, N-(C6-C12)-aryl-N-(C1-C6)-alkylamino, N-~C7-C11)-
~ 3
- 23 -
aralkylamino, N-~C7-C~ aralXyl-N-~C1-C10)-alkylamino,
(Cl-C6)-alkanoylamino, (c3-c3)-cycloalkanoylamino~ (Cl-C6)-
hydroxyalXanoylamino, (Cl-C6)-alko~y-(Cl C~)-alkanoylamino,
(Cg-Cl2)-arylcarbonylamino and (C7-C11)-aralkylcarbonyl-
amino,
or
F an unsubstituted or substituted (C6-Cl2~-aryl radi-
cal, (C7-C1l)-aralkyl radical or het~roaryl radical, in
which the aryl and heteroaryl radical mentioned is, in
particular, phenyl, naphthyl, thienyl, furyl, pyrrolyl or
pyridine, and which furthermore carries 1, 2 or 3 identi-
cal or differsnt substituents from the series comprising
hydroxyl, halogen, cyano, nitro, (Cl-C6)-alkyl, (Cl-C6)-
alkoxy, carboxyl, trifluoromethyl, (C1-C6)-hydroxyalkyl,
--~CH2-]xCfH~2~+1-g)F6~ (C1-C6)-alkylcarbonyl, (C1-C6)-alkoxy-
carbonyl, carbamoyl, N-(C}-C4)-alkylcarbamoyl, N,N-di-
(C1-C4)-alkylcarhamoyl, (C1-Cg)-alkylcarbonyloxy, (C3-C~)~
cycloalkyl, phenyl, benzyl, phenoxy, benzyloxy, amino, N-
(C1-C10)-alkylamino, di-N,N-(C1-C10)-alkylamino or N,N-
(C3-C3)-alkanediylamino, such as, for example, pyrrolidino
or piperidino, (C1-C10)-alkanoylamino, (C6~C1z)-aryl-
carbonylamino and (C7-Cll)-aralkylcarbonylamino,
or
G a substituent of the formula -OR9 or -N(R9)2, in
which
R9 is hydrogen, alkyl or alkenyl having in each case up
to 6 carbon atoms, a (C6-C12)-aryl radical or a heteroaryl
radical, which carries 1, 2 or 3 identical or different
substituents from the series comprising halogen, hydrox-
yl, cyano, nitro, carboxyl, trifluoromethyl, (C1-C6)-
alkyl, (C1-C6)-hydroxyalkyl, (Cl-C6)-alkoxy,
--[CH2-]xCfH(2f+1-g)F6/ (C1-C6)-alkylcarbonyl, (C1-C6)-alkoxy-
carbonyl, carbamoyl, N-(Cl-C4)-alkylcarbamoyl, N,N-di-
(C1-C4)-alkylcarbamoyl, (C1-C6) alkylcarbonyloxy, (C3-C6)-
5 1~
- 24 -
cycloalkyl, phenyl, ben~yl, phenoxy, benzyloxy, amino, N-
(Cl-C~ alkylamino, di-N,N-(Cl-C10)-alkylamino or N,N-
(C3-C8)~alkanediylamino r such as, ~or example, pyrrolidino
or piperidino, (Cl-C10)-alkanoylamino, (C6-Cl2~-aryl-
carbonylamino and (C7-C11)-aralkylcar~onylamino.
Of these, compounds of the formula I which are preferred
are those in which
R2, R5 and R4 or R3, if R4 and R3 are not already defined
above and are not to be hydrogen, are
D halogen, in particular flllorine, chlorine or brom-
ine, trifluoromethyl, (C1-C12)-alkyl, -O-[CH2-3xC~H~2~+l-~)F8
-OCF2Cl, -O-CF2-CHFCl, (Cl-C8)-alkylcarbonyl, ~ C3 C8)~
cycloalkyl, amino, N-(Cl-C1O)-alkylamino, di-N,N-(C1-C,o)-
alkylamino,N-~C6-Cl2)-arylamino,N-(C6-Cl2)-aryl-N-(Cl~Ca)~
alkylamino, N-( C7-cll)-aralkylamino or N-( C7-cll )-aralkyl-
N-(C~-C1O)~alkylamino, in which the aryl and aralkyl
radicals present in the above substituents can also be
heterocyclic in nature and/or, as is also the case -for
alkyl, can be substituted by 1 or 2 identical or dif-
ferent substituents from the series comprising halogen,trifluoromethyl, (C1-C6)-alkyl, hydroxyll (C1-C6)-hydroxy-
alkyl, (C1-C6)-alkoxy, -O [CH2-~XC~H(2~18,F~ and NR -R, or
E an alkyl or alkenyl radical having up to 5 carbon
atoms, which is optionally substituted by 1 or 2 identi-
cal or different substituents from the series comprisinghydroxyl, halogen, trifluoromethyl, tCl-C6)-hydroxyalkyl,
(Cl-C6)-alkoxy, (C1-C6)-alkylcarbonyl, (Cl-C6)-alkoxycar-
bonyl, ~C1-C6)-alkylcarbonyloxy, phenyl~ benzyl, phenoxy,
benzyloxy, amino, N-~Cl C5)-alkylamino and di-N,N-(C~-C6)-
alkylamino, or by
an unsubstituted or substituted (C6-C12)-aryl radical,
(C7-Cll)-aralkyl radical or heteroa.ryl radical, which
carries 1 or 2 identical or different substituents from
_ ~5 _ ~~
the series comprising hydroxyl, halogen, trifluoromethyl,
(Cl-C6)-alkyl, (Cl-C6)-hydroxyalkyl, (Cl-C6)-alkoxy,
--[CH2-]xCfH~2f~l-8)F~ (C1-C6)-alkylcarbonyl, (Cl-C6)-alkoxy-
carbonyl, phenyl, benzyl, phenoxyl ben~yloxy, amino, N-
(Cl-C6)-alkylamino, di-N,N-(C1 C6)-alkyl~lino or N,N-
(C3-C~)-alkanediylamino, such as, for example, pyrrolidino
or piperidi.no, or
F an unsubstituted or substituted ~C6-Cl2)-aryl radi-
cal, ( C7 C11)-aralkyl radical or hetero ryl radical, in
which the aryl and heteroaryl radical mentioned is, in
par~.icular, phenylr naphthyl, th.ienyl, furyl~ pyrrolyl or
pyridine, and which fur~hermore carries 1, 2 or 3 identi-
cal or different substituents from the series comprising
hydroxyl, halogen, (Cl C6)-alkyl, (C1-C6~-alkoxy, carbo~yl,
trifluoromethyl, (Cl -C8 )-hydroxyalkyl, --[CH2 ]XCfH(2f+1~,Fg,
(Cl-C63-alkylcarbonyl, (Cl-C6)-alkoxycarbonyl, amino, N-
(C~-C10)-alkylamino and di-N,N-(Cl-C10)-alkylamino, or
G a substituent of the formula -oR9 or -N(R~)2, in
which
R9 is hydrogen or alkyl having in each case up ~o
6 carbon atoms, a (C6-Cl2)-aryl radical or a heteroaryl
radical, which contains 1 or 2 identical or different
substituents from the series comprising halogen, tri-
fluoromethyl, (Cl-C6)-alkyl, (Cl-C6)-alkoxy,
-O-~CH2-]xCfH(2f+~8~F~, amino, N-(C,-C10)-alkylamino and di-
N,N-(Cl-C10)-alkylamino.
Particularly preferred compounds of the formula I are
those in which
R2, R5 and R4 or R3, if R4 and R3 are not already defined
above and are not to be hydrogen, are
D halogen~ in particular fluorine, chlorine or brom-
ine, trifluoromethyl, (Cl-Cl2)-alkyl/ --[CH2-]xCfH(2f~l-g)Fg~
-- 2 6 ~ h ~ ) r3 9 ~
-OCF2Cl, -O CF2~CHFCl, (Cl-C~)-alkylcarbonyl, (C3-C8)-
cycloalkyl, amino, N-(Cl C10)-alkylamino, di-N,N-(Cl-Clo)-
alkylamino~N-(c6-cl2)-arylamino~N-(c6-cl2)~aryl-N-(cl-c~)-
alkylamino, N-(C7-Cl,)-aralkylamino or N (C7--Cl1)-aralkyl-
N-(C1-C10)-alkylamino, or:
E an alkyl or alkenyl radical having up to 5 carbon
atoms, which is optionally substituted by 1 or 2 identi-
cal or different substituents from the series comprising
hydroxyl, halogen, trifluoromethyl, (Cl-C6)-alkoxy,
10 (Cl-C6)-alkylcarbonyl, (Cl-C6)-alkoxycarbonyl, (Cl-C6)-
alkylcarbonyloxy, phenyl, phenoxy, benzyloxy, amino, N-
(Cl-C6)-alkylamino and di-N,N-(Cl-Cs)-alkylamino/ or by an
unsubstituted or &ubstituted (C~-C~-aryl radical,
(C7-Cll)-aralXyl radical or heteroaryl radical, which
carries 1 or 2 identical or different substituents from
the series compxising hydroxyl, halogen, trifluoromethyl,
(Cl-C6)-alkyl, (Cl-C6)-hydroxyalkyl, (Cl-C6)-alkoxy,
(Cl-C6)-alkylcarbonyl and (Cl-C6)-alkoxycarbonyl, or
F an unsubstituted ox substituted (C6-C12~-aryl radical
or (C7-C11)-aralkyl radical, in which the aryl radical
mentioned is, in particular, phenyl or naphthyl and which
furthermore carries 1 or 2 identical or different substi-
tuents from the series comprising hydroxyl, halogen,
(Cl-C6)-alkyl, (Cl-C6)-alkoxy, carboxyl, trifluoromethyl,
(C,-C6)-hydroxyalkyl, (C1~C6)-alkylcarbonyl and (C1-C6)-
alkoxycarbonyl, or
G a substituent of the formula -O~9 or -N(R9)2, in
which
R9 is hydrogen ox alk~l having in each case up to
6 carbon atoms, a (C6-C12)-aryl radical or a heteroaryl
radical, which contains 1 or 2 identical or different
substituents from the series comprising halogen, tri-
fluoromethyl, (C1-C6)-alkyl, (Cl-C6)-alkoxy, amino, N-
~Cl-C10)-alkylamino and di-N,N-(Cl-C10)-alkylamino.
_ ~7 ,~ ,3~
The inven-tion furthermore relates to the use of compounds
of the :Eormula ~ and physiologically tolerated salts
thereof for the preparation of a proline hydroxylasa-in-
hibiting and lysine hydroxylase-inhibiting medicament.
Final.ly, the invention relates to the compounds of the
formula I for use as medicaments.
In particular, the invention relates to the compounds of
the formula I for use as fibrosuppressarlts and Lmmunosup-
pressants and for inhibition of proline hydroxylase and
lysine hydroxylase, and for influencing the metabolism of
collagen and collagen-like substances and the biosyn-
thesis of Clq.
The invention furthermore relates to a process for the
preparation of compounds of the formula I.
The following Equation I applies to the preparation of
2,4-disubstituted pyridine N-oxide derivatives. However,
in pri.nciple, it can also be used to illustrate the
preparation of 2,5-disubstituted pyridine N-o~ide deriva-
tives, and for mixed derivatives (esters/amides)
~ 2û ~ 5 ~1
Equat ion
o
Co~H C_o-R6
XlxEsterif ication\~ o
R S C 9 2 H R ~ C - O - R V
V
Aminolysi~ /
/ Ox.idation
,~ C- O- R 6
C-N ( R7 ) R6
R ~ R 2
~ N ( ~ 7 ) R 6 R S ~ C - O - R
RS li O
Oxidation ~
/ Aminolysis
C-N ( R7 ) R6
R 1~ R 2
5/~N~\ C - N ( R 7 ) R 6
O
- 29 _ 2~ 5~
Substituted pyridine-2,4- and -2,5-dicarboxylic acids of
the formula IV are obtained, for example, by oxidation
from the corresponding dimethylpyridines VII or VIII or
the corresponding methyl-2-hydroxymethylpyridines IX. The
preparation of the dimethylpyridines VII and VIII in turn
is described in R.J. Ife, J. Med. Chem. 32, 1970-1977
(1989) and the literature cited therein. The following
Equation II gives an indication of this. On the basis of
this equation, the substituted pyridine derivatives
according to the invention are accessible to the expert.
A particular example is 2,5-dimethyl-3 r 4-dichloro-
pyridine.
Equation II
~3
;, -----------~ ',s~ ~ ? ` Qu~
o
C L, 1~10 ~ /
O )~
hc~c~ C~3~
~3~C lh 1~ h2 olt
X ~
- 30 - 2 ~5 ~ 5l~
Compounds of the formula VII are converted into compounds
of the formula VIII with alcohols ROH and a base in
dimethylfo.rmamide or dimethylacetamide at ~0 to 150~C.
Compounds of the type IX are prepared by reactions of
VIII with acetic anhydride/ace-tic acid at 120C and
subsequent reaction with NaOH/methanol at 25~C. ~he
oxidation to give compound X with sodium permanganate in
water at 70 to 100C can be carried out starting from
VIII or IX. The dicarboxylic acids X can be either
esterified and oxidized to give the N-oxides I according
to the invention in accordance with Equation I, or - also
in accordance with Equation I - converted into amides and
oxidized.
The preparation of the compounds of type IV is described
in the following literature references. This preparation
is the introduction of the substituents R2, R4 and R5 into
the ~,4- or 2,5~pyri.dine-dicarboxylic acid.
Starting with the compound of the formula IV, the
amide VI can be prepared either directly from IV or via
the ester V.
The reaction of V or VI to give the amides I or esters I
is carried out under conditions analogous to those in
P 40 20 570.3-
For this, an oxidizing agent, such as, for example,
hydrogen peroxide or peracids, such as peracetic acid,perfluoroacetic acid, perbenzoic acid or metachloroper-
benzoic acid, in solvents, such as chlorinated hydrocar-
bons, such as, for example, methylene chloride, chloro-
form, tri- or tetrachloroethylene, benzene or toluene, is
added to the pyridine compounds to be oxidized, which can
likewise be dissolved in the abovementioned solvents, and
the mixture is stirred at a temperature of between -30
and +40C, preferably 0 and 25C, ~or between 30 minutes
and 3 days~ The end of the reaction can be determined,
_ 31 ~ 5~
for example, by means of thin layer chromatography.
Preferably, the compounds according co the invention can
be prepared by employing the pyridine derivative and the
oxidi~ing agent in equimolar ~nounts or with up to an
approximately 5-fold excess o oxidiæing agen-t~
If appropriate, an excess of peracid can also be elimin-
ated, for example, by passing gaseous ammonia into the
reaction solution and separating off the resulting
precipitate from the reaction solution by fil-tration.
If appropriate, the product can be worked up, for ex-
ample, by extraction or by chromato~raphy, for example
over silica gel. The product isolated can be
recrystallized.
General instructions for this oxidation method are also
described, for exampler in "E. Lingsberg, Pyridine and
its Derivatives, Interscience Publishers, New York, 1961,
Part 2, 93".
The oxidation with hydrogen peroxide is described, for
example, in "E. Ochiai, J. Org. Chem. lB, 534 (1953)".
The conditions for an aminolysis of the ester I to give
the amide I correspond to those used for the reaction of
V to give VI.
The preparation and the aminolysis are otherwise reaction
types which are known as such: However, compounds of the
formula I prepared by the above reactions are novel.
The process conditions can be seen in detail in German
Patent Applications P 38 26 471.4, 38 23 140.6,
39 24 093.2 and 40 01 002.3, and DE-A-37 03 959,
37 03 962 and 37 03 963.
32 ~ ) g~j3~
The compounds of the formula I according to the invention
have useful pharmacological proper-ties and exhibit, in
particular, activity as inhibitors of proline hydroxylase
and lysine hydroxylase, and as a fibrosuppressant,
immunosuppressant and antiatherosclerotic.
The antifibrotic action can be determined using the model
of liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride. For
this, rats are treated twice ~eekly with CCl,, (1 mlJkg) -
dissolved in olive oil. The tes-t substance is adminis-
tered daily, if appropriate even twice daily, perorallyor in~raperitoneally ~ dissolved in a sui~able tolerated
solvent. The extent of the liver fibro~is is determined
hi~tologically, and the amount of collagen in the liver
is analysed by hydroxyproline determination - as de-
scribed by Kivirikko et al. (Anal. Biochem. 19, ~49 etseq. (1967)). The fibrogenesis activity can be determined
by radioimmunological assay of collagen fragments and
procollagen peptidas in the serum. The compounds accord-
ing to the invention are active in a concentration o~
1 - 100 mg/kg in this model.
The fibrogenesis activity can be determined by radioim-
munological assay of the N~terminal propeptide of col-
lagen type III or of the N- and C-terminal crosslinking
domains of collagen type IV (7s-collagen or type IV
collagen-NC1) in the serum.
For this purpose, the hydroxypr~line, procollagen III
peptide, 7s-collagen and type IV collagen-NC concentra-
tions wers measured in th~ liver of
a) untreated rats (control)0 b) rats to which carbon tetrachloride had been adminis-
tered (CCl4 control)
c) rats to which first CCl4 and then a compound accord-
ing to the invention had been administered
(this test method is described by Rouiller, C., experi-
mental toxic injury of the liver; in The Liver,
- 33 -
C. Rouiller, Vol. 2, 5. 335-476, New York, Academic
Press, 1964).
Another model for evaluation of the antibiotic action is
that of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis as described
by Kelley et al. (j. Lab. Clin. Med. 96, 954, (1980)).
The model of the cotton-wool swab granuloma as described
by Meier et al., Experimentia 6, 469 (1950) can be used
to evaluate the action of the compounds according to the
invention on granulation tissue.
The compounds of the formula I can be used as medicaments
in the form of pharmaceutical preparations which comprise
them, if appropriate together with tolerated pharmaceuti-
cal excipients. The compounds can be used as medicines,
for example in the form of pharmaceutical preparations
which comprise these compounds as a mixture with a
pharmaceutical, organic or inorganic excipient which is
suitable for enteral, percutaneous or parenteral adminis-
tration, such as, for example, water, gum Arabic, gela-
tin, lactose, starch, magnesium stearate, talc, vegetable
oils, polyalkylene glycols, petroleum jelly and the like.
For this purpose, they can be administered orally in
doses of 0.1 - 25 mg/kg/day, preferably 1 - 5 mg/kg/day,
or parenterally in doses of 0.01 - 5 mg/kg/day, preferab-
ly 0.01 - 2.5 mg/kg/day, in particular 0.5 -
1.0 mg/kg/day. In serious cases, the dosage can also be
increased. However, lower doses are also sufficient in
many cases. These data relate to an adult weighing about
75 kg.
The invention furthermore relates to the use of the
compounds according to the invention in the preparation
of medicaments employed for the treatment and prophylaxis
of the abovementioned metabolic disturbances.
3~ 5 ~I S ~
The invention furthermore relates to medicaments which
comprise one or more compounds of the formula I according
to the invention and/or physiologically tolerated salts
thereof.
The medicaments are prepared by processes which are known
per se and familiar to the expert. As medicaments, the
pharmacologically acti~e compounds according to the
invention (= active compound) are employed either as such
or, preferably, in combination with suitable pharma-
ceutical auxiliaries or excipients, in the form otable~s, coated tablets, capsules, suppo~itories,
emulsions, suspensions or solutions, the active compound
content being up to about 95 %, advantageously between lO
and 75 ~.
Suitable auxiliaries or excipients for the desired
medicament formulation are, for example, in addition to
solvents, gel forming agents, suppository bases,
tablet auxiliaries and other active compound exc:ipientsl
also antioxiflants, dispersing agents, emulsifiers, foam
suppressants, flavor correctants, preservatives, solu-
bilizing agents or dyestuffs.
The following examples are intended to illustrate the
invention.
Example 1
5-Bromo-pyridine-1-oxide-2,4-dicarboxylic acid bis-~3-
methoxypropyl)amide]
a) 5~Bromo-2,4-dimethylpyridine
150 ml of 65 % strength oleum are added dropwise to
28.9 ml of 2,4-dimethylpyridine, while cooling with ice
and stirring, such that the temperature does not rise
above 35C. When the solution has become homogenized,
_ 35 h a ~ ~ 9 ~ ~
6.42 ml of bromine are slowly added dropwise. The mixture
is stirred at 80C for 3~ hours. After cooling, it is
allowed to drip carefully onto 1 kg of ice, and the
resulting mixture is neutralized with solid Na2CO3 and
extracted 3 times with 300 ml of ether each time. ~he
organic layer is separated off and dried over magnesium
sulfate. After remo~al of the sol~en~ by distillation in
vacuol 34.6 g of a pale yellow oil wh:ich comprises the
isomers S-bromo-2,4-dimethylpyridine and 3-bromo-2,4-
dimethylpyridine are obtained. The isomers are separatedby column chromatography on silicon dioxide gel to give
10 g of S-bromo-2,4-dimethylpyridine as a colorless
liquid (13.0 g of 3-bromo-2,4-dimethylpyridine).
Yield: 22 %.
b) 5-Bromo-pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylic *cid
4 g of 5-bromo-2,4-dimethylpyridine from Example 1 are
heated to 70-80C in 200 ml of water and 2.4 g o KOH.
Half of 12.74 g of potassium permanganate is then intro-
duced in portions. The solution is heated to the boiling
point and the remainder of the potassium permanganate is
added. The mixture .i9 s~irred at 70-80nC for 20 hours and
then filtered hot with suction, and the precipitate is
washed 4 times with 50 ml portions of hot water. The
combined filtrates are concentrated to 100 ml in vacuo.
The solution is brought to pH 1 with concentrated hydro-
chloric acid and is left to stand at 0C for 20 hours.
The crystalline solid is filtered off with suction and
dried in vacuo at 100C. The yield is 2.9 g.
Melting point 261-263C.
c) 5-Bromo-pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylic acid bis-~3-
methoxypropyl)amide]
2.46 g (10 mmol) of 5-bromo-pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylic
acid are suspended in 70 ml of toluene and 0.2 ml of
dimethylformamide, and 1.45 ml (20 mmol~ of thionyl
- 36 ~
chloride are added. The reaction mixture is heated at
110C for 5 hours, during which a clear solution forms.
The solution is then allowed to cool to 0Cr and ~
solution of 2.05 ml ~20 mmol) of 3-methoxypropylamine and
2.8 ml of -triethylamine in 10 ml of tolllen~ is added
dropwi 5 e.
The mixture is left to stand at 20~C for 12 hours and
concentrated in ~acuo/ water is addedl the mixture is
extracted with methylene chloride, and the organic phase
is dried and freed from the solvent to give the subst~nce
as a colorless oil, yield 2.2 g.
Empirical formula: C15H2~BrN3O4 (388.26
MS: m/e = 389 (M + H+)
d) The above compound is dissolvad in 80 ml of methylene
chloride, and 5 mg of meta-chloro perbenzoic acid are
added in portions at 10C. After 2 hours, a further 5 g
of peracid are added, the mixture i5 heated at 42C for
3 hours, a further 5 g of peracid are added, and the
mixture is heated at 42C for 5 hours.
Excess peracid and 3-chlorobenzoic acid are precipitated
by passing in ammonia gas ~nd are filtered off with
suction. The solution is concentrated and the residue is
chromatographed o~er silica gel using ethyl acetate/meth-
anol 10:1 The title compound is obtained as colorless
crystals. Melting point 94~.
Empirical formula: Cl5H22BrN304 (404.26)
MS: m/e = 405 (M + H+)
Example 2
Pyridine-1-oxide-2,4-dicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester
- 37 -
7.0 g (35.~ mmol) of pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylic acid
dimethyl ester are dissol~ed in 200 ml of methylene
chloride, and 6.2 g (36 mmol) of 3-chloroperbenzoic acid
are added at 10C. Aftex ~ hours, a further 6.~ g of
peracid are added, the mixture is allowed to stand
overnight, a further 3.1 g of peracid are added, and the
mixtura is heated at 40C for 5 hours (thin layer chroma-
tography control).
Excess peracid and 3-chlorobenzoic acid are precipita-ted
by passing in ammonia gas 3 times, and are filtered off.
The solution i5 concentrated and the residue is crystall-
ized from toluene, 4.5 g.
Melting point 132C; R~ (SiO2, ethyl acetate) = 0.~9
Example 3
Pyridine-l-oxide-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester-4-car-
hoxylic acid (2-benzyloxyethyl)amide and pyr:idine-1-
oxide-2-carboxylic acid t~-benzyloxyalkyl)amide-4-car-
boxylic acid methyl ester
3.1 g (15 mmol) of the title compound from Example 2 are
~0 heated at 100C in 50 ml of N,N-dimethylacetamide with
22.8 g (150 mmol) of 2-benzyloxyethylamine (prepared from
2-aminoethanol, sodium and benzyl chloride) for 1 hour.
The mixture i~ allowed to cool and is concentrated, water
is added, the mixture is extracted with methylene chlor-
ide and concentrated and the oily residue ~4.8 g) iscrys-tallized with ethyl acetate.
Melting point 76-78C (colorless crystals)
Empirical formula: C17H1~N205 (330)
MS: m/e = 331 (M + H+)
The corresponding diamide was to be obtained after
10 hours at 140C.
- 38 - 2 ~ ~ 9
Example 4
4-Methoxy-pyridine-1-oxide-2~5-dicarbo~ylicacidbis-[(2-
hydroxyethyl)~nide]
a) 2-Hydroxymethyl 4-methoxy-5-methyl-pyridine
5.4 g (35 mmol) of 4-methoxy-2,5-dimethyl-pyridine N-
oxida (melting point 102-104C, diisopropyl ether;
prepared from 2,5-dimethyl-pyridine N oxide and sodium
methylate in methanol) are dissolved in 30 ml of glacial
acetic acid, and 40 ml of acetic anhydride are added
dropwise at 80C.
The mixture is heated at 115C for 90 minutes and cooled
to 80C, 75 ml of methanol are added dropwise, the
mixture is concentrated, the residue i5 taken up in
methanol, 200 ml of 1.5 N methanolic sodium hydroxide
lS solution are added dropwise, water is added, the mixture
is extracted with methylene chloride, dried and concen-
trated and the residue is crystalli~ed with cyclohexane,
yield: 4.4 g; melting point 92-94C.
b) 4-Methoxy pyridine-2,5-dicarboxylic acid
2.3 g (15 mmol) of the compound from 4a) are suspended in
a solution of 1 g of XOH in 75 ml of watex, and 7.2 g
(45 mmol) of KMnO4 are added in por~ions at 70C. Ths
mixture is left at 80C for a further hour, the magnesi~n
dioxide which has been filtered off with suction is
washed with water, and the filtrate i5 concentrated and
brought to pH 1 with hydrochloric acid;
Yield: 1.45 g; rnelting point 231C (decomposition).
c) 4-Methoxy-pyridine-1-oxide-2/5-dicarboxylic acid
dimethyl ester
- 39 ~
1.4 ~ of th~ compound from 4b) are heated at the boiling
point in 150 ml of methanol and 2 g of sulfuric acid
(98 % streng-th) for 15 hours. The mixture is allowed to
cool, saturated ammonium chloride solution is added,
while cooling, and the mixture is extracted with methyl-
ene chloride and concentrated to give, analogously to
Example 2 by reaction of the crude product with 3 chloro-
perben~oic acid, 0.8 g of 4-methoxy-pyridine-2,5-dicar-
boxylic acid dimethyl ester N~oxide, melting point
134-136C.
d) The title compound is obtained ~rom the above compound
of Example 4c) by reaction with exces~ 2-aminoethanol,
colorless crystals, melting point 124-127C ~from ethyl
acetate).
lS The following compounds were to be obtained analogously
from the compound of Example 4c) by reaction with the
corresponding amines:
4-methoxy-pyridine 2,5-dicarboxylicacidbis-[(2-methoxy-
ethyl)amide] N-oxide
4-methoxy-pyridin~-2,5-dicarboxylicacidbis-[(3-hydroxy-
propyl)amide~ N-oxide
4-methoxy-pyridine-2,5-dicarboxylicacidbis-[(3-methoxy-
propyl)amide~ N-oxide
4-methoxy-pyridine-2,5-dicarboxylic acid bis-[(2-
benzyloxyethyl)amide] N-oxide
Example 5
Pyridine-l-oxide-2,4-dicarboxylic acid bis-N,N'-[~-(4-
methylbenzoyloxy)ethyl]amide
a) Pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylic acid bis-N,N'-[2-~4-
methylbenzoyloxy)ethyl]amide
-- 4 0 _ h ~
b) 0.2 g of 4-N,N-dimethylaminopyridine and 0.8 ml
(6 ~mol~ of triethylamine are added to 0.7 g (2.5 mmol)
of pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylic acid bis-N,N'-(3-hydroxy-
ethyl)amide in 100 ml of methylene chloride, and 0.6 ml
(5 mmol) of 4 methylbenzoyl chloride are then added
dropwise. After 1 hour, the mixture is concentrated and
~he residue is then taken up in water. After 1 hour, the
mixture is extracted by shaking twice with water and the
organic phase is concentrated. The crude product is
chromatographed over silica ~el using ethyl acetate.
Colorless crystalline powder: melting point 165-166C
Empirical formula: C27H27N3O6 (489)
MS: m/e = 490 (M + H+).
b) 0.31 ml of 30 percent strength H2Oz is added dropwise
to a solution of 0.25 g of the above compound in 5 ml of
96 percent strength formic acid, and the mixture is
heated at 80C ~or 4 hours. It is then evaporated in
vacuo and the crystalline residue is stirred with hot
methanol and filtered off with suct~on. 0.18 g of pyrid-
ine-2,4-dicarboxylic acid N,N'-bis-[2-(4-methylbenzoyl-
oxy)ethyl]amide is obtained as a colorless crystalline
powder, melting point 186-188C.
MS: m/e = 506 (M+ ~ H+).
Example 6
Pyridine-1-oxide-2,4-dicarboxylic acid N,N'-bis-[~2-
benzoyloxyethyl)amideJ
a) Pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylic acid bis-N,N'-[(2-
benzoyloxyethyl)amide]
Analogously to Example Sa)
Colorless needles, melting point 139-140C
Empirical formula: C2sHZ3N3o6 (461)
MS: m/e = 462 IM+ + H+).
- 41 ~
b) 0.31 ml of 30 percent strength H2O2 is added dropwise
to a solution of 0.46 g of pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylic acid
N,N~-bis-[(2-benzoyloxy)ethyl]amide (Example 6a)) in 5 ml
of 96 percent strength formic acid, and the mixture is
heated at B0C for 4 hours, while stirring. After addi-
tion of a further 0.2 ml of H2O2, the mixture is stirred
at this temperature for a further 2 hours and then
evaporated in vacuo, and the residue is purified by
chromatography over silica gel using ethyl acetate as the
eluent. 0.37 g of pyridine-1-oxide-2,4-dicarboxylic acid
N,N-bis-[(2-benzoyloxyethyl)amide] is obtained as color-
less crystals, melting point 159-160C (methanol),
MS: m/e - 478 (Nt ~ H~).