Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
~37~
-- 1
59340.559
Benzimidazoles
The present invention relates to new benzimidazoles,
processes for their preparation and pharmaceutical
compositions containing them.
EP-A-468470 discloses benzimidazoles which are valuable
angiotensin-antagonists.
It has been found that certain novel benzimidazoles have
particularly valuable pharmacological properties as
angiotensin-II-antagonists.
Thus, viewed from one aspect, the present invention
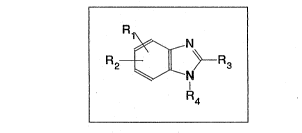
provides compounds of formula I:
...~
(I)
(wherein
R1 denotes a hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine or bromine atom
or a fluoromethyl, difluoromethyl, trifluoromethyl or
alkyl group;
R2 denotes an imidazol-2-yl group optionally substituted
in the l-position by the group Ra, wherein
Ra denotes a phenyl or phenylalkyl group, in which
the phenyl nucleus may be mono- or disubstituted by
alkyl, hydroxy or alkoxy groups and the
. . .
. , :.
. 2~1~37~
-- 2
substituents may be identical or different, a C3 7-
cycloalkyl group or a C16-alkyl group in which the
alkyl moiety may additionally be substituted by a
group metabolically convertible in vivo into a
carboxy group, by a trifluoromethyl, carboxyl,
alkoxycarbonyl, aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl
or dialkylaminocarbonyl group or from position 2 by
a hydroxy, alkoxy, amino, alkyIamino, dialkylamino,
pyrrolidino, piperidino or morpholino group,
a 5,5-spiro-cyclopentano-dihydro-imidazol-4-on-2-yl
group,
an imidazolium-2-yl group substituted in the 1- and 3-
positions by groups Rb, which groups may be identical or
different, wherein ~ :
Rb denotes a phenylalkyl group in which the phenyl
nucleus may be mono- or disubstituted by alkyl,
hydroxy or alkoxy groups and the substituents may
be identical or different, or Rb denotes a C16-alkyl
:~ group in which the alkyl moiety may additionally be~ substituted by a group metabolically convertible ln- vivo into a carboxy group, or by a trifluoromethyl,
~. car~oxyl, alkoxycarbonyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkylaminocarbonyl or dialkylaminocarbonyl group,
an oxazol-2-yl or thiazol-2-yl group,
whilst in the above mentioned imidazol-2-yl,
imidazolium-2-yl, oxazol-2-yl or thiazol-2-yl moieties,
the 4-, 5-positions may be substituted by a C15~alkyl
group or by a phenyl group, wherein the substituents may
be identical or different, or an n-propylene or n-
- butylene bridge may be added via the 4-, 5-positions,
an oxazolin-2-yl or imidazolin-2-yl group substituted in
.
' ' '' ' ` ` ' '` - :.:
- ` 2~3~ -- 3 --
the 4-position by the groups R9 and R1o and in the 5~
position by the group R8, wherein an imino group may
additionally be substituted by Ra or by an R8CO-(R9CR1o)~
NRa-CO- group, wherein
Ra is as hereinbefore defined, and
R8, R9 and R10, which may be identical or different,
denote hydrogen atoms, C1s-alkyl groups or phenyl
groups;
R3 denotes a C1s-alkyl group, a C3s-cycloalkyl group, a
C14-alkoxy or Cl4-alkylthio group; and
R4 denotes a hydrogen atom or a group of formula
.
R5
_CH2 ~r ~ ~ \
wherein
Rs denotes a group metabolic:ally convertabla in vivo
into a carboxy group, or de:notes a carboxy, cyano,
- 2,5-dihydro-5-oxo-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl, lH-
tetrazolyl, l-triphenylmethyl-tetrazolyl or 2-
triphenylmethyl-tetrazolyl group;
whilst unless otherwise specified any alkyl or alkoxy
group contains l to 3 carbon atoms, and
the phrase "a group metabolically convertable in vivo
into a carboxy group" as used herein denotes the esters
thereof of formulae
- CO - OR',
- Co - O - (HCR") - O - CO - R"' and
2~37~
~,
- CO - O - (HCR" ) -- O - CO - OR" '
wherein
R' denotes a straight-chained or branched C16-alkyl
group, a Cs7-cycloalkyl group, a benzyl, 1-phenylethyl,
2-phenylethyl, 3-phenylpropyl, methoxymethyl or cinnamyl
group,
R" denotes a hydrogen atom or a methyl group and
R"' denotes a straight-chained or branched C16-alkyl
group, a Cs7~cycloalkyl group, a phenyl, benzyl, 1-
phenylethyl, 2-phenylethyl or 3-phenylpropyl group)
'
and the 3-isomers, the 1-, 3-isomer mixtures and the
salts thereof.
Examples of the definitions of groups R1, R2, R3 and Rs
mentioned above are as follows:
R1 may denote a hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine or bromine
atom or a fluoromethyl, difluoromethyl, trifluoromethyl,
methyl, ethyl, n-propyl or isopropyl group;
~ R2 may denote the 5,5-spiro-cyclopentano-dihydro-
imidazol-4-on-2-yl, 1-methyl-5,5-spiro-cyclopentano-
dihydro-imidazol-4-on-2-yl, 1-ethyl-5,5-spiro-
cyclopentano-dihydro-imidazol-4-on-2-yl, 1-n-propyl-5,5-
spiro-cyclopentano-dihydro-imidazol-4-on-2-yl, 1-
isopropyl-5,5-spiro-cyclopentano-dihydro-imidazol 4-on-
2-yl, 4,5-dimethyl-oxazol-2-yl, 4-methyl-5-ethyl-oxazol-
2-yl, 4-methyl-5-n-propyl-oxazol-2-yl, 4-methyl-5-n~
butyl-oxazol-2-yl, 4-methyl-5-n-pentyl-oxazol-2-yl, 4-
methyl-5-phenyl-oxazol-2-yl, 4,5-diethyl-oxazol-2-yl, 4-
ethyl-5-n-propyl-oxazol-2-yl, 4-ethyl-5-n-butyl-oxazol-
2-yl, 4-ethyl-5-n-pentyl-oxazol-2-yl, 4-ethyl-5-phenyl-
oxazol-2-yl, 4,5-di-n-propyl-oxazol-2-yl, 4-n-propyl-5-
', : ~ ' , ,,
: '' ' " ' .:
,, ,
.
~37~
.
-- 5 --
n-butyl-oxazol-2-yl, 4-n-propyl-5-n-pentyl-oxazol-2-yl,
4-n-propyl-5-phenyl-oxazol-2-yl, 5-methyl-4-ethyl-
oxazol-2-yl, 5-methyl-4-n-propyl-oxazol-2-yl, 4,5-
diphenyl-oxazol-2-yl, 5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzoxazol-2-
yl, 4,5-dimethyl-thiazol-2-yI, 4-methyl-5-ethyl-thiazol-
2-yl, 4-methyl-5-n-propyl-~hiazol-2-yl, 4-methyl-5-
phenyl-thiazol-2-yl, 4,5-diethyl-thiazol-2-yl, 4-ethyl-
5-n-propyl-thiazol-2-yl, 4-ethyl-5-phenyl-thiazol-2-yl,
4,5-di-n-propyl-thiazol-2-yl, 4,5-di-n-isopropyl-
thiazol-2-yl, 4-n-propyl-5-phenyl-thiazol-2-yl, 4,5-
diphenyl-thiazol-2-yl, 5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benz-thiazol-
2-yl, 4-methyl-oxazolin-2-yl, 4-ethyl-oxazolin-2-yl, 4-
n-propyl-oxazolin-2-yl, 4-isopropyl-oxazolin-2-yl, 4-n-
butyl-oxazolin-2-yl, 4-isobutyl-oxazolin-2-yl, 4-benzyl-
oxazolin-2-yl, 4-phenyl-oxazolin-2-yl, 4,4-dimethyl-
oxazolin-2-yl, 4-methyl-5-phenyl-oxazolin-2-yl, 4,4-
dimethyl-5-n-propyl-oxazolin-2-yl, 4,5-tetramethylene-
oxazolin-2-yl, 4-methyl-imidazolin-2-yl, 4,5-dimethyl-
imidazolin-2-yl, 4,5-tetramethylene-imidazolin-2-yl, 4-
methyl-imidazol-2-yl, 4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1,4,5-
trimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-ethyl-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-
2-yl, 1-n-propyl-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-
isopropyl-4,5-dimethyl-imidaz~1-2-yl, 1-n-butyl-4,5
dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-isobutyl-4,5-dimethyl-
imidazol-2-yl, 1-cyclopropyl-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl,
l-cyclobutyl-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, l-cyclopentyl-
4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-cyclohexyl-4,5-dimethyl-
imidazol-2-yl, 1-cycloheptyl-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl,
1-benzyl-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-phenyl-ethyl)-
4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl-, 1-carboxymethyl-4,5-
dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 3-methoxycarbonylmethyl-4,5-
dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-ethoxycarbonylmethyl-4,5-
dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-n-propoxycarbonylmethyl-4,5-
dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-isopropoxycarbonylmethyl-4,5-
dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-aminocarbonylmethyl-4,S-
dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-methylaminocarbonylmethyl-4,5-
dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-ethylam.inocarbonylmethyl-4,5-
~37~
6 --
dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-n-propylaminocarbonylmethyl-
4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, l-isopropylamino-
carbonylmethyl-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-
dimethylaminocarbonylmethyl-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl,
1-diethylaminocarbonylmethyl-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl,
l-di-n-propylaminocarbonylmethyl-4,5-dimethylimidazol-2-
yl, l-diisopropylaminocarbonylmethyl-4,5-dimethyl-
imidazol-2-yl, 1-N-methyl-ethylaminocarbonylmethyl-4,5-
dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-carboxy-ethyl)-4,5-
dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-4,5-
dimethy].-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-ethoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-4,5-
dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-n-propoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-
4,5~dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-isopropoxycarbonyl-
ethyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-~2-aminocarbonyl-
ethyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-
methylaminocarbonyl-ethyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl,
1-(2-ethylaminocarbonyl-ethyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-
yl, 1~(2-n-propylaminocarbonyl-ethyl)- 4,5-dimethyl-
imidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-isopropylaminocarbonylethyl)-4,5-
dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-dimethylaminocarbonyl-
ethyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-
diethylaminocarbonyl-ethyl)-4,5-climethyl-imidazol-2-yl,
1-(2-d1-n-propylaminocarbonyl-ethyl)-4,5-dimethyl-
imidazol-2-yl, 1.-(2-diisopropylaminocarbonyl-ethyl)-4,5-
dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-N-methyl-ethylamino-
carbonyl-ethyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1~(3-
carboxy-propyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(3-
methoxycarbonyl-propyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-
(3-ethoxycarbonyl-propyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-
(3-n-propoxycarbonyl-propyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl,
1-(3-isopropoxycarbonyl-propyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-
yl, 1-(3-aminocarbonyl-propyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-
yl, l-(3-methylaminocarbonyl-propyl)-4,5-dimethyl-
imidazol-2-yl, 1-(3-ethylaminocarbonyl-propyl)-4,5-
dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(3~n-propylaminocarbonyl-
propyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(3-
isopropylaminocarbonylpropyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-
.
:.
2~3~8~
-- 7
yl, l-(3-dimethylaminocarbonyl-propyl)-4,5-dimethyl-
imidazol-2-yl, 1-(3-diethylaminocarbonyl-propyl)-4,5-
dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(3-di-n-propylaminocarbonyl-
propyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(3-
diisopropylaminocarbonyl-propyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-
2-yl, 1-(3-N-methyl-ethylaminocarbonyl-propyl)-4,5-
dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-4,5-
dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, l-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4,5-dimethyl-
imidazol-2-yl, l-(3-hydroxypropyl)-4,5-dimethyl-
imidazol-2-yl, l-(4-hydroxybutyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-
2-yl, 1-(2-methoxyethyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-
(3-methoxypropyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, l-(4-
methoxybutyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-
ethoxyethyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(3-
ethoxypropyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, l~
ethoxybutyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-
isopropoxyethyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(3-n-
propoxypropyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(4-
isopropoxybutyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-
pyrrolidinoethyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(3-
pyrrolidinopropyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, l-(4-
pyrrolidinobutyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-
piperidinoethyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2~yl, 1-(3-
piperidinopropyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(4-
piperidinobutyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidaæol-2-yl, 1-(2-
morpholinoethyl~-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(3-
morpholinopropyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(4-
morpholinobutyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, l-phenyl-
4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-benzyl-4,5-dimethyl-
imidazol-2-yl, 1-(1-phenylethyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-
2-yl, l-(2-phenylethyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-
(1-phenylpropyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-
phenylpropyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(3-
phenylpropyl)-4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-methyl-4,5-
diethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1,4,5-triethyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-
ethyl-4-isopropyl--5-methyl-imidazol-2-yl, l-ethyl-4-
isobutyl-5-methyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-n-propyl-4-isopropyl-
2~37~
-- 8
5-methyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-n-propyl-4-isobutyl-5-methyl-
imidazol-2-yl, 1,4-diisopropyl-5-methyl-imidazol-2-yl,
1-isopropyl-4-isobutyl-5-methyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-
dimethylamino-ethyl)-4-isopropyl-5-methyl-imidazol-2-yl,
1-(2-dimethylamino-ethyl)-4-isobutyl-5-methyl-imidazol-
2-yl, 1-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-4-isopropyl-5-methyl-
imidazol-2-yl, 1-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-4-isobutyl-S-
methyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1,5-dimethyl-4-ethyl-imidazol-2-
yl, 1,5-dimethyl-4-n-propyl imidazol-2-yl, 1,5-dimethyl-
4-isopropyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1,5-dimethyl-4-isobutyl-
imidazol-2-yl, 1,5-dimethyl-4-phenyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-
methyl-4,5-diphenyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-ethyl-4,5-diphenyl-
imidazol-2-yl, 1-n-propyl-4,5-diphenyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-
isopropyl-4,5-diphenyl-imidazol-2-yl, l-carboxymethyl-
4,5-diphenyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-methoxycarbonylmethyl-4,5-
diphenyl-imidazol-2-yl, 1-ethoxycarbonylmethyl-4,5-
diphenyl-imidazol-2-yl, 4,5-trimethylene-imidazol-2-yl,
1-methyl-4,5-trimethylene-imidazol-2-yl, 5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-methyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-ethyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-n-propyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-benzimidaæol-2-yl, 1-isopropyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-n-butyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-isobutyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-n-pentyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-benzimidazol 2-yl, 1-n-hexyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-cyclopropyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-cyclobutyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-cyclopentyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-cyclohexyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-cycloheptyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-carboxymethyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, l-methoxycarbonylmethyl-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-
ethoxycarbonylmethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-
yl, l-n-propoxycarbonylmethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-isopropoxycarbonylmethyl-5,6,7,8-
- .
- : .
.' ~ ~. ' ' - " .
2~3~
g
tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, l-aminocarbonylmethyl-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-
methylaminocarbonylmethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-ethylaminocarbonylmethyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, l-n-
propylaminocarbonylmethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl, l-isopropylaminocarbonylmethyl-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-
dimethylaminocarbonylmethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-diethylaminocarbonylmethyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, l-di-n-
propylaminocarbonylmethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-diisopropylaminocarbonylmethyl-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, l-N-methyl-
ethylaminocarbonylmethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-carboxy-ethyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-methoxycarbonyl-
ethyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-
ethoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-
yl, l-(2-n-propoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-isopropoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazol-:2-yl, 1-(2-
aminocarbonyl-ethyl)~5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-
yl, l-(2-methylaminocarbonyl-ethyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-ethylaminocarbonyl-ethyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-n-
propylaminocarbonyl-ethyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-t2-isopropylaminocarbonyl-ethyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-
dimethylaminocarbonyl-ethyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-diethylaminocarbonyl-ethyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-di-n-
propylaminocarbonyl-ethyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-diisopropylaminocarbonyl-ethyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-N-methyl-
ethylaminocarbonyl-ethyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(3-carboxy-propyl)-5,6,7,8-
2 ~
-- 10 --
tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(3-methoxycarbonyl-
propyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(3-
ethoxycarbonyl-propyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazol-
2-yl, 1-(3-n-propoxycarbonyl-propyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(3-isopropoxycarbonyl-propyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(3-
aminocarbonyl-propyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-
yl, 1-(3-m~thylaminocarbonyl-propyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro
benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(3-ethylaminocarbonyl-propyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(3-n-
propylaminocarbonyl-propyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-.
benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(3-isopropylaminocarbonyl-propyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(3-
dimethylaminocarbonyl-propyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(3-diethylaminocarbonyl-propyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(3-di-n-
propylaminocarbonyl-propyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(3-diisopropylaminocarbonyl-
propyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(3-N-
methyl-ethylaminocarbonyl-propyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-phenyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-benzyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(1-phenylethyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-phenylethyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(1-phenylpropyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-(2-
phenylpropyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl, 1-
(3-phenylpropyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazol-2-yl,
1,3-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazolium-2-yl,
1,3-diethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazolium-2-yl,
1,3-di-n-propyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazolium-2-yl
or 1,3-dibenzyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzimidazolium-2-yl
group;
R3 may denote a methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl,
isobutyl, n-butyl, 1-methyl-n-propyl, tert.butyl, n-
.: . . . :
- - ~ ,
' ,'
'
' - .
. .
~3~
-- 11 --
pentyl, 1 methyl-n-butyl, 2-methyl-n-butyl, cyclopropyl,
cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, methoxy, ethoxy, n-propoxy,
isopropoxy, n-butoxy, isobutoxy, methylthio, ethylthio,
n-propylthio, isopropylthio, n-butylthio or isobutylthio
group; and
R5 may denote a carboxy, cyano, lH-tetrazolyl, 1-
triphenylmethyl-tetrazolyl, 2-triphenylmethyl-
tetrazolyl, methoxycarbonyl, ethoxycarbonyl, n-
propyloxycarbonyl, isopropyloxycarbonyl, n-
butyloxycarbonyl, isobutyloxycarbonyl,
tert.butyloxycarbonyl, n-pentyloxycarbonyl,
isoamyloxycarbonyl, n-hexyloxycarbonyl,
cyclopentyloxycarbonyl, cyclohexyloxycarbonyl,
benzyloxycarbonyl, l-phenylethyloxycarbonyl, 2-
phenylethyloxycarbonyl, 3-phenylpropyloxycarbonyl,
methoxymethoxycarbonyl, cinnamyloxycarbonyl,
acetoxymethoxycarbonyl, propionyloxymethoxycarbonyl, n-
butyryloxymethoxycarbonyl, isobutyryloxymethoxycarbonyl,
n-pentanoyloxymethoxycarbonyl, isopentanoyloxy-
methoxycarbonyl, pivaloyloxymethoxycarbonyl, n-
hexanoyloxymethoxycarbonyl, cyclopentanoyloxy-
methoxycarbonyl, cyclohexanoyloxymethoxycarbonyl,
phenylacetoxymethoxycarbonyl,
1-phenylpropionyIoxymethaxycarbonyl,
2-phenylpropionyloxymethoxycarbonyl,
3-phenylbutyryloxymethoxycarbonyl,
benzoyloxymethoxycarbonyl, 1-acetoxyethoxycarbonyl,
l-propionyloxyethoxycarbonyl, l-n-
butyryloxyethoxycarbonyl, 1-isobutyryloxyethoxycarbonyl,
l-n-pentanoyloxyethoxycarbonyl, 1-isopentanoyloxy-
ethoxycarbonyl, 1-pivaloyloxyethoxycarbonyl, 1-n-
hexanoyloxyethoxycarbonyl, l-cyclopentanoyloxy-
ethoxycarbonyl, l-cyclohexanoyloxyethoxycarbonyl, 1-
phenylacetoxyethoxycarbonyl, 1-(1-phenylpropionyloxy)-
ethoxycarbonyl, l-(2-phenylpropionyloxy)-ethoxycarbonyl,
1-(3-phenylbutyryloxy)-ethoxycarbonyl, 1-
2~3~5
- 12 -
benzoyloxyethoxycarbonyl, methoxycarbonyloxy-
methoxycarbonyl, ethoxycarbonyloxymethoxycarbonyl, n-
propyloxycarbonyloxymethoxycarbonyl,
isopropyloxycarbonyloxymethoxycarbonyl, n-
butyloxycarbonyloxymethoxycarbonyl,
isobutyloxycarbonyloxymethoxyearbonyl,
tert.butyloxycarbonyloxymethoxycarbonyl, n- :
pentyloxyearbonyloxymethoxyearbonyl,
isoamyloxycarbonyloxymethoxyearbonyl, n-
hexyloxycarbonyloxymethoxyearbonyl,
eyclopentyloxycarbonyloxymethoxycarbonyl,
cyclohexyloxycarbonyloxymethoxycarbonyl,
benzyloxycarbonyloxymethoxycarbonyl, 1-
phenylethoxycarbonyloxymethoxyearbonyl, 2-
phenylethoxycarbonyloxymethoxycarbonyl, 3-
phenylpropyloxycarbonyloxymethoxycarbonyl,
einnamyloxycarbonyloxymethoxycarbonyl, 1-
(methoxycarbonyloxy)-ethoxycarbonyl, 1-
(ethoxycarbonyloxy)-ethoxycarbonyl, l-(n-
propyloxycarbonyloxy)-ethoxycarbonyl, 1-
(isopropyloxycarbonyloxy)-ethoxyearbonyl, l-(n-
butyloxyearbonyloxy)-ethoxyearbonyl, 1-
(isobutyloxyearbonyloxy)-ethoxyearbonyl, 1-
(tert.butyloxycarbonyloxy)-ethoxycarbonyl, l-(n-
pentyloxycarbonyloxy)-ethoxycarbonyl, 1-
(isoamyloxycarbonyloxy)-ethoxycarbonyl, 1-(n-
hexyloxycarbonyloxy)-ethoxycarbonyl, 1-
(cyclopentyloxy-carbonyloxy)-ethoxycarbonyl, 1-
(cyclohexyloxycarbonyloxy)-ethoxycarbonyl, 1-
(benzyloxycarbonyloxy)-ethoxycarbonyl, 1-(1-
phenylethoxycarbonyloxy)-ethoxycarbonyl, 1-(2-
phenylethoxycarbonyloxy)-ethoxycarbonyl, 1-(3-
phenylpropyloxycarbonyloxy)-ethoxycarbonyl, 1-
(cinnamyloxycarbonyloxy)-ethoxyearbonyl, aminocarbonyl,
methylaminocarbonyl, ethylaminocarbonyl, n-
propylaminocarbonyl, isopropylaminocarbonyl,
dimethylaminocarbonyl, diethylaminocarbonyl, di-n-
.
. . . . .
.
'' , ' : '' .
'
2~37~
propylaminocarbonyl, diisopropylaminocarbonyl, N-methyl-
ethylaminocarbonyl, N-ethyl-isopropylaminocarbonyl or
2,5-dihydro-5-oxo-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl group.
Pre~erred compounds according to the invention include
thos of formula I wherein
R1 denotes a hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine or bromine
atom, a trifluoromethyl group or a C13-alkyl group;
R2 denotes an imidazol-2-yl group optionally substituted
in the 1 position by the group Ra, wherein
Ra denotes a phenyl group, a phenyl(C~3-alkyl)
group, a Cs7-cycloalkyl group or a C15-alkyl group
in which the alkyl moiety may additionally be
substituted by a group metabolically convertable ln
vivo into a carboxy group, or by a trifluoromethyl,
carboxyl, methoxycarbonyl, ethoxycarbonyl,
aminocarbonyl, methylaminocarbonyl or
: dimethylaminocarbonyl group or from position 2 by a
hydroxy, methoxy, ethoxy, amino, methylamino,
dimethylamino, pyrrolidino, piperidino or
morpholino group,
' ~'.
a 5,5-spiro-cyclopentano-dihydro-imidazol-~-on-2-yl
group,
an imidazolium-2-yl group substituted i.n the 1- and 3-
position by groups Rb, which may be identical or
different, wherein
Rb denotes a C13-alkyl or phenyl(C13-alkyl) group,
an oxazol-2-yl or thiazol-2-yl group,
whilst in the above-mentioned imidazol-2-yl,
:
2~7~
- 14 -
imidazolium-2-yl, oxazol-2-yl or thiazol-2-yl moieties,
the 4-, 5-positions may be substituted by a C14-alkyl
group or by a phenyl group, wherein the substituents may
be identical or different, or an n-butylene bridge may
be added via the 4-, 5-positions,
an oxazolin-2-yl or imidazolin-2-yl group substituted by
the groups R8, R9 and R10, wherein an imino group may
additionally be substituted by Rar wherein R8, R9, R10 and
Ra each represent a hydrogen atom or a C14-alkyl group;
,
R3 denotes a C2s-alkyl group, a C3s-cycloalkyl group, a
C24-alXoxy or C24-alkylthio group; and
R4 denotes a 4-biphenylylmethyl group subsituted in the
2'-position by the group Rs/ wherein
Rs denotes a group metabolically convertable in vivo
i.nto a carboxy group, or denotes a carboxy, cyano,
lH-tetrazolyl, l-triphenylmethyl-tetrazolyl or 2-
triphenylmethyl-tetrazolyl group;
whilst the expression "a group metabolically convertable
in vivo into a carboxy group" as used hereinbefore
denotes, for example, the esters thereof of the formulae
- CO - OR',
- CO - O - (HCR") - O - CO - R"' and
- CO - O - (HCR") - O - CO - OR"'
wherein
R' denotes a straight-chained or branched Cl4-alkyl
group or a Cs7-cycloalkyl group,
R" denotes a hydrogen atom or a methyl group, and
R"' denotes a straight-chained or branched C14-alkyl
group or a C57-cycloalkyl group;
' : . ' '
. .
. .
2~3~8~
- 15 -
and the 3-isomers, the 1-, 3-isomer mixtures and the
salts thereof.
Particularly preferred compounds according to the
invention include those of formula I above wherein
R3 and R4 are as hereinbefore defined;
R2 is in the 6-position and has the meanings given above;
and
.
R1 in the 4-position denotes a fluorine, chlorine or
bromine atom, a trifluoromethyl group or a C13-alkyl
group;
and the 3-isomers, the 1-, 3-isomer mixt-lres and the
salts thereof.
More particularly preferred compounds according to the
invention include those of formula I above wherein R2 in
the 6-position denotes one of the imidazolyl groups
mentioned above;
and the 3-isomers, the 1-, 3-isomer mixtures and salts
thereof.
The present invention particularly relates to the
following compounds of formula I:
(a) 4'-[~2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid;
(b) 4l-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-methyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid;
2~7~
- 16 -
(c) 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-methyl-5,6,7,8-
te~rahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-
methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl;
(d) 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-benzyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid;
(e) 4'-[[2-ethyl-4-methyl-6-(1-phenyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid;
(f) 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-carboxymethyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid;
(g) 4'-[[2-ethyl-4-methyl-6-(1-ethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-2-(lH-
tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl;
~h) 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4,4-dimethyl-oxazolin-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic
acid;
(i) 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(1,5-dimethyl-4-phenyl-
imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid; and
(k) 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4-isopropyl-1,5-
dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid;
and the salts thereof.
Viwed from a further aspect, the invention provides a
process for the preparation of compounds of the
invention, said processing comprising at least one of
.- '' ' :.
.. . . . .
2~37~
- 17 -
the following steps:
a) (to prepare compounds of formula I wherein R2 denotes
an oxazol 2-yl, thiazol-2-yl or imidazol-2-yl group, in
which an n-butylene bridge is added via the 4,5-
positions and additionally the imino group in the
imidazole ring may be substituted by a C16-alkyl group,
by a phenyl(C13-alkyl~ group or by a phenyl group)
reacting a compound of formula II
(II)
(wherein
R1, R3 and R4 are as hereinbefore defined and
X denotes an oxygen or sulphur atom or an imino group
optionally substituted by a C16-alkyl group, by a
phenyl(C13-alkyl) group or by a phenyl group) with an ~-
haloketone of formula III
(III)
(wherein
Z1 denotes a halogen atom such as a chlorine atom)i
b) (to prepare compounds of formula I wherein R2 denotes
one of the imidazol-2-yl groups mentioned hereinbefore
optionally substituted in the l-position by the group Ra)
reacting a compound of formula IV
2 ~
- 18 -
(IV) . .
(wherein
- R1, R3 and R4 are as hereinbefore defined and
R2' denotes one of the above-mentioned oxazol-2-yl
groups) with an amine of formula V
: H2N - R6 ( V )
:
: (wherein
R6 has the meanings given for Ra hereinbefore or denotes
a hydrogen atom);
c) (to prepare benzimidazoles of formula I wherein R4
: denotes a group of the formula:
Rs
CH2~--
reacting a compound of~formula VI
(VI)
~37~
-- 19 --
(wherein
R1, R3 and R4 are as hereinbefore defined and
R2" has the meanings given for R2 hereinbefore, with the
exception of the imidazol-2-yl and imidazolin-2-yl
groups unsubstituted in the l-position) with a biphenyl
compound of formula VII
\
Z2-CH ~ \
(VII)
(wherein
Rs is as hereinbefore defined and
Z2 denotes a nucleophilic leaving group such as a halogen
atom, e.g. a chlorine, bromine or iodine atom, or a
substituted sulphonyloxy group, e.g. a
methanesulphonyloxy, phenylsulphonyloxy or p-
toluenesulphonyloxy group);
d) (to prepare a compound of formula I wherein Rs denotes
a carboxy group) converting a compound of formula VIII
R2- ~ ~ R3
1HZ~ ~ :
(VIII)
(wherein
R1, R2 and R3 are as hereinbefore defined and
Rsl denotes a group which can be converted into a carboxy
group by hydrolysis, thermolysis or hydrogenolysis) into
a compound of formula I by hydrolysis, thermolysis or
hydrogenolysis;
2~3~
- 20 -
e) (to prepare compounds of formula I wherein R2 denotes
a 5,5-spiro-cyclopentano-dihydro-imidazol-4~on-2-yl
group) treating a benzimidazole of formula IX
(IX)
(wherein
`~
R1, R3 and R4 are as hereinbefore defined and
R2"' denotes an imidazol-2-yl group in which an n-
butylene group is attached via the 4,5-position) with a
base in the presence of air and light;
f) (to prepare a compound of formula I wherein Rs denotes
a lH-tetrazolyl group) cleaving a protective group from
a compound of formula X
R2--~C ~R3 r
(X)
(wherein
R1, R2 and R3 are as hereinbefore defined and
R5" denotes a lH-tetrazolyl or 2H-tetrazolyl group
protected in the l- or 2-position by a protecting
group);
g) (to prepare a compound of formula I wherein Rs denotes
a lH-tetrazolyl group) reacting a compound of formula XI
..
,. , ",
: '
R2 ~ ~ R3 CN
CHz~
(XI)
(wher~in
R1, R2 and R3 are as hereinbefore defined) with hydrazoic
acid or a salt thereofi
h) (to prepare compounds of formula I wherein R2 denotes
one of the above-mentioned imidazol-2-yl groups which
may be substituted in the l-position by a phenylalkyl
group twhilst the phenyl nucleus may be mono- or
disubstituted by alkyl, hydroxy or alkoxy groups and the
substituents may be identical or different), or by a
C16-alkyl group, whilst the alkyl group may additionally
be substituted by a group metabo:lically convertable ln
vivo into a carboxy group, or by a trifluoromethyl,
carboxyl, alkoxycarbonyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkylaminocarbonyl or dialkylaminocarbonyl group, or R2
denotes one of the imidazolium-2--yl groups mentioned
hereinbefore) reacting a compound of formula XII
R2~ R3 -
R
(XII)
(wherein
R1 and R3 are as hereinbefore defined,
R2"" represents one of the imidazol-2-yl groups
unsubstituted in the l position mentioned for R2
~3~
- 22 -
hereinbefore and
Rsll' denotes a carboxy group or a group which can be
converted into a carboxy group by hydrolysis,
thermolysis or hydrogenolysis, or a lH-tetrazolyl or 2H- -
tetrazolyl group protected by a protecting group) with a
compound of formula XIII
Z3 - R SXIII)
(wherein
R7 denotes a phenylalkyl group (whilst the phenyl nucleus
may he mono- or disubstituted by alkyl, hydroxy or
alkoxy groups and the substituents may be identical or
dif~erent), or a C16-alkyl group, whilst the alkyl group
may additionally be substituted by a group metabolically
convertable i vivo into a carboxy group, or by a
trifluoromethyl, carboxyl, alkoxycarbonyl,
aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl or
dialkylaminocarbonyl group, and
Z3 denotes a nucleophilic leavig group such as a halogen
atom, e.g. a chlorine, bromine or iodine atom) and
subsequently, if necessary, cleaving any protecting
group used;
i) (to prepare compounds of formula I wherein R2
represents one of the imidazol-2-yl groups mentioned
hereinbefore substituted by the groups R8, R9 and R1o, but
wherein R9 or Rlo must denote a hydrogen atom) reacting
an aminoketone of formula XIV
R~ CO-C N~a'-CO ~
(XIV)
,
... "
... , . . : ~:. . - .
- 23 -
(wherein
R1, R3, R4, R~, R9 and R1o are as hereinbefore defined, but
R9 or R1o must denote a hydrogen atom, and
Ral has the meanings given for Ra hereinbefore or denotes
a hydrogen atom) with an ammonium salt of a lower
aliphatic carboxylic acid;
j) (to prepare compounds of formula I wherein R2 denotes
one of the oxazolin-2-yl or imidaæolin-2-yl groups
mentioned hereinbefore) dehydrating a compound of
formula XV
R~ CN'~R3
(xv)
(wherein
R1, R3, R4, R8, R9 and R10 are as hereinbefore defined and
Y denotes a hydroxy or HNRa group wherein Ra is as
hereinbefore defined~;
k) (to prepare compounds of formula I wherein R2 denotes
one of the imidazolin-2-yl groups mentioned
hereinbefore) reacting a compound of formula XVI
R2" " '--~ ~Ra
R4
(XVI)
(wherein
R1, R3 and R4 are as hereinbefore defined and
- : : . . -. '. . .: . - . :
.: ,
.: . . .
. ~
.. . . .
:. ' , ' .. : ' ~
:
$
- 24 -
R2""' denotes one of the oxazolin-2-yl groups mentioned
for R2 hereinbefore, substituted by groups R8, R9 and R10)
with an amine of formula XVII
H2N-(R8cH)-(R9cR1o)-NH2 (XVII)
(wherein
R8, R9 and R1o are as hereinbefore defined);
l) (to prepare compounds of formula I wherein R2 denotes
one of the oxazol-2-yl groups mentioned hereinbefore
substituted by groups R8, R9 and R10) dehydrating an
aminoketone of formula XVIII
; R3-C-C-NH-C ~ ~ R3
(XVIII)
(wherein
R1, R3, R4, R8, R9 and R1o are as hereinbefore defined, but
~9 or R10 must denote a hydrogen atom);
m) (to prepare compounds of formula I wherein R2 denotes
one of the imidazol-2-yl groups mentioned hereinbefore,
substituted by the groups R8, R9 and R10) dehydrogenating
a compound of formula XIX
N~
R4
(XIX)
. : . .. . . : ~
- . - .. ~ . . -
' ~ :.. . : .
.
:
- : ~
.
: .
.
2 ~
- 25 -
(wherein
R1, R3 and R4 are as hereinbefore defined and
R2""" denotes one of the imidazolin-2-yl groups mentioned
for R2 hereinbefore, substituted by the groups R8, R9 and
R~o~ but R9 or R10 must denote a hydrogen atom);
n) (to prepare compounds of formula I wherein R5 denotes
a 2,5-dihydro-5-oxo-l,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl group) reacting
an amidoxime of formula XX
; 2 { ~ (XX)
NH 2 -C
N -OH
(wherein
R1, R2 and R3 are as hereinbefore defined) optionally
prepared in the reaction mixture, with a compound of
formula XXI
Z4 - CO - OR (XXI)
(wherein
'- Z4 denotes a nucleophilic leaving group such as a halogen
atom, e.g. a chlorine, bromine or iodine atom, and
R11 denotes an alkyl, aryl or aralkyl group, preferably a
lower alkyl group such as a methyl, ethyl, n-propyl or
isopropyl group) and subsequently cyclisizing an
acylated amidoxime thus obtained;
o) converting a compound of formula I thus obtained into
a salt thereof, more particularly for pharmaceutical use
into a physiologically acceptable salt thereof with an
inorganic or organic acid or base, or converting a salt
of a compound of formula I into the free compound; and
. .: ., . : ~ . ,. ~ ,
: ' . , ~ ' .
., ,,, :
7 ~ ~
- 26 -
p) performing a process as defined in any one of steps
(a) to (o) above on a corresponding protected compound
and subsequently removing the protecting group used.
The reaction of step (a) is preferably carried out in
the presence of a suitable solvent such as
dimethylformamide, diethyleneglycoldimethylether,
triethyleneglycoldimethyl-ether or sulpholane,
optionally in the presence of a base such as potassium
carbonate, pyridine, triethylamine, N-ethyl-
diisopropylamine or N-ethyl-dicyclohexylamine, at
temperatures between 0 and 250C.
If X in formula II denotes an oxygen or sulphur atom,
the reaction is preferably carried out in a sol~ent
having a boiling point above 150C or in a melt at
temperatures between 150 and 250C, pre~erably at
temperatures between 175 and 225C.
If X in formula II denotes an optionally alkyl-
substituted imino group the reaction is preferably
carried out in the presence of a corresponding amine as
solvent, e.g. in the presence of liquid ammonia,
methylamine, ethylamine, n-propylamine or
isopropylamine, at temperatures between 0 and 100C,
preferably at temperatures between 20 and 75C.
The reaction of step (b) is expediently carried out in
an excess of the amine used and preferably in the
presence of a corresponding formamide of formula HCONHR6
as solvent, optionally in a pressurised vessel at
elevated temperatures, e.g. at temperatures between 100
and 250C, preferably at temperatures between 175 and
225C.
During the reaction of step (b), any substituted carboxy
group present in the group R4 is simultaneously converted
- . . : ~ - .
,- : ~
2~37g~
- 27 -
into a carboxy group or any substituted tetrazolyl group
present is converted into a lH-tetrazol-5-yl group.
The reaction of step (c) is conveniently carried out in
a solvent or mixture of solvents such as methylene
chloride, diethylether, tetrahydrofuran, dioxane,
dimethylsulphoxide, dimethylformamide or benzene,
optionally in the presence of an acid binding agent such
as sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, sodium
hydroxide, potassium tert.-butoxide, triethylamlne or
pyridine, whilst the latter two may simultaneously also
be used as solvent, preferably at temperatures between O
and 100C, e.g. at temperatures between ambient
temperature and 50C.
The reaction of step (c) preferably produces a mixture
of the 1- and 3-isomers which may subsequently, if
desired, be resolved into the corresponding 1- and 3-
isomers, preferably by chromatography using a carrier
such as silica gel or aluminium oxide.
In step (d) functional derivatives of the carboxy group
such as optionally substituted amides, esters,
thiolesters, orthoesters, iminoethérs, amidines or
anhydrides, a nitrile group or a tetrazolyl group may be
converted into a carboxy group by hydrolysis, esters
with tertiary alcohols, e.g. a tert.butylester, may be
converted into a carboxy group by thermolysis and esters
with aralkanols, e.g. a benzylester, may be converted
into a carboxy group by hydrogenolysis.
The hydrolysis of step (d) is conveniently carried out
in the presence of an acid such as hydrochloric acid,
hydrobromic acid, sulphuric acid, phosphoric acid,
trichloroacetic acid or trifluoroacetic acid, optionally
in the presence of a reaction accelerator such as
hexadecyl-tributyl-phosphonium bromide, in a suitable
.. . . .
.
.
.. . .
.
.. . .
,
,
.
.
3 ~
- 28 -
solvent such as water, water/methanol, ethanol,
water/ethanol, water/isopropanol or water/dioxane, at
temperatures between -10C and 120C, e.g. at
temperatures between ambient temperature and the boiling
temperature of the reaction mixture.
If Rsl in a compound of formula VIII represents a cyano
or aminocarbonyl group, these groups may also be
converted into a carboxy group with a nitrite, e.g.
sodium nitrite, in the presence of an acid such as
sulphuric acid, which may also be simultaneously used as
solvent, at temperatures between 0 and 50C.
~ .
If Rsl in a compound of formula VIII represents, for
example, a tert.-butyloxycarbonyl group, the tert. butyl
group may also be thermally cleaved, optionally in an
inert solvent such as methylene chloride, chloroform,
benzene, toluene, tetrahydrofuran or dioxane and
preferably in the presence of a catalytic amount of an
acid such as trifluoroacetic acid, p-toluenesulphonic
acid, sulphuric acid, phosphoric acid or polyphosphoric
acid, preferably at the boiling temperature of the
solvent used, e.g. at temperatures between 40C and
100 C .
If Rsl in a compound of formulà VIII represents, for
example, a benzyloxycarbonyl group, the benzyl group may
also be hydrogenolytically cleaved in the presence of a
hydrogenation catalyst such as palladium/charcoal, in a
suitable solvent such as methanol, ethanol,
ethanol/water, glacial acetic acid, ethyl acetate,
dioxane or dimethylformamide, preferably at temperatures
between 0 and 50C, e.g. at ambient temperature, and
under a hydrogen pressure of l to 5 bar. During
hydrogenolysis, other groups may be reduced at the same
time, e.g. a nitro group to an amino group, a benzyloxy
group to a hydroxy group, a vinylidene group to the
-: .
.
: . '
2~3~
corresponding alkylidene group or a cinnamic acid group
to the corresponding phenyl-propionic acid group, or
they may be replaced by hydrogen atoms, e.g. a halogen
atom by a hydrogen atom.
The reaction of step (e) is conveniently carried out in
the presence of a base such as sodium hydroxide or
potassium hydroxide, in a suitable solvent such as
water, water/methanol, ethanol, water/ethanol,
water/isopropanol or water/dioxan2, at temperatures
between -10C and 120C, e.g. at temperatures between
ambient temperature and the boiling temperature of the
reaction mixture.
During the reaction of step (e~, any ester group present
in the group R4 is simultaneously converted into a
carboxy group.
Suitable protecting groups for use in step (f) include,
for example, the triphenylmethyl, tributyl tin or
triphenyl tin groups.
The cleaving of a protective group used in step (f) is
preferably carried out in the presence of a hydrohalic
acid, preferably in the presence of hydrochloric acid,
in the presence of a base such as sodium hydroxide or
alcoholic ammonia, in a suitable solvent such as
methylene chloride, methanol, methanol/ammonia, ethanol
or isopropanol, at temperatures between 0 and 100C, but
preferably at ambient temperature or, if the reaction is
carried out in the presence of alcoholic ammonia, at
elevated temperatures, e.g. at temperatures between 100
and 150~C, preferably at temperatures between 120 and
140~C.
The reaction of step (g) is preferably carried out in a
solvent such as benzene, toluene or dimethylformamide,
:. . . .
.: . . . . .
.
- : .:
3 ~ ~ ~
- 30 -
at temperatures between 80 and 150C, preferably at
125C. Conveniently, either the hydrazoic acid is
liberated during the reaction from an alkali metal
azide, e.g. from sodium azide; in the presence of a weak
acid such as ammonium chloride, or a tetrazolide salt
obtained in the reaction mixture during the reaction
with a salt of hydrazoic acid, preferably with aluminium
azide or tributyl tin azide, which is also preferably
produced in the reaction mi~ture by reacting aluminium
chloride or tributyl tin chloride with an alkali metal
azide such as sodium azide, is subsequently libsrated by
acidification with a dilute acid such as 2N hydrochloric
acid or 2N sulphuric acid.
The reaction of step (h) is conveniently carried out in
a solvent or mixture of solvents such as methylene
chloride, diethylether, tetrahydrofuran, dioxane,
dimethylsulphoxide, dimethylformamide or benzene
optionally in the presence of an acid binding agent,
such as sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, sodium
hydroxide, sodium hydride, potassium tert.butoxide,
triethylamine or pyridins, whilst the latter two may
simultaneously be used as solvents, preferably at
temperatures between 0 and 100C, e.g. at temperatures
between ambient temperature and 50C.
If the reaction of step (h) is carried out in the
presence of an excess of the compound of formula XIII
used, a corresponding imidazolium-2-yl compound of
formula I is obtained at the same time.
The subsequent cleaving of a protecting group is
preferably carried out by hydrolysis, thermolysis or
hydrogenolysis.
The hydrolytic cleaving of a protecting group used is
preferably carried out in the presence of an acid such
- :
.' .: ' ' . '~
~3~
- 31 -
as hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid, sulphuric acid,
phosphoric acid, trichloroacetic acid or trifluoroacetic
acid, optionally in the presence of a reaction
accelerator such as hexadecyl-tributyl-phosphonium
bromide in a suitable solvent such as water,
water/methanol, ethanol, water/ethanol,
~ater/isopropanol or water/dioxane at temperatures
between -10C and 120C, e.g. at temperatures between
ambient temperature and the boiling temperature of the
reaction mixture.
The thermolytic cleaving of a protecting group such as
the tert.butyloxycarbonyl group is preferably effected
in an inert solvent such as methylene chloride,
chloroform, benzene, toluene, tetrahydrofuran or dioxane
and preferably in the presence of a catalytic amount of
an acid such as p-toluenesulphonic acid, sulphuric acid,
phosphoric acid or polyphosphoric acid, preferably at
the boiling temperature of the solvent used, e.g. at
temperatures between 40C and 100C.
The hydrogenolytic cleaving of a protecting group such
as the benzyloxycarbony] group is effected in the
presence of a hydrogenation catalyst sUch as
~- palladium/charcoal in a suitable solvent such as
methanol, ethanol, ethanol/water, glacial acetic acid,
ethyl acetate, dioxane or dimethylformamide, preferably
at temperatures between 0 and 50~C, e.g. at ambient
temperature, and a hydrogen pressure of 1 to 5 bar.
The reaction of step (i) is conveniently carried out
with an ammonium salt of a lower aliphatic carboxylic
acid such as ammonium acetate or ammonium propionate,
preferably in the presence of a solvent such as glacial
acetic acid or propionic acid at elevated temperatures,
but preferably at the boiling temperature of the
reaction mixture, e.g. at temperatures between 100 and
- ,: '
. :- . : -: ........................... : . : .
,
2~3~
150C.
The dehydration of step (j) is conveniently carried out
in the presence of a dehydrating agent such as
phosphorusoxychloride, sulphuric acid, polyphosphoric
acid or thionyl chloride, tha latter preferably being
used as solvent at the same time, at elevated
temperatures, e.g. at the boiling temperature of the
dehydrating agent used, e.g. at temperatures between 105
and 150C.
The reaction of step (k) is conveniently carried out in
a solvent such as toluene, dimethylformamide or
dimethylsulphoxide, but preferably in an excess of the
amine of formula XVII used, at elevated temperatures,
e.g. at temperatures between 100 and 150C. However,
the reaction is preferably carried out without a
solvent.
The dehydration of step (1) is conveniently carried out
in the presence of a dehydrating agent such as
phosphorusoxychloride, phosphoric: acid or sulphuric
acid, which is preferably used as solvent at the same
time, at elevated temperatures, e.g. at the boiling
temperature of the dehydrating agent used, e.g. at -
temperatures between 105 and 150C. During the reaction
with phosphorus-oxychloride any tert.butylester present
can simultaneously be cleaved.
The dehydrogenation of step (m) is conveniently carried
out in the presence of a dehydrogenating agent such as
palladium/charcoal, barium manganate or selenium
dioxide, in a suitable solvent such as toluene or
methylene chloride at elevated temperatures, e.g. at the
boiling temperature of the solvent used, e.g. at
temperatures between 110 and 150C.
~37~
The reaction of step (n) is conveniently carried out in
a solvent such as methylene chloride, chloroform,
tetrahydrofuran, dioxane or acetonitrile preferably in
the presence of an inorganic base, such as sodium or
potassium carbonate, or an organic base such as
triethylamine or pyridine whilst the latter two may
simultaneously also be used as solvent at temperatures
between 0 and 20C.
The subsequent cyclization of a thus obtained acylated
amidoxime is conveniently carried out in an organic
solvent such as benzene, toluene, xylene,
tetrahydrofuran or dioxane at elevated temperatures,
e.g. at temperatures between 50 and 100C, preferably at
the boiling temperature of the solvent used.
The necessary starting amidoxime is conveniently
prepared by reaction of a corresponding nitrile of
formula XI with hydroxylamine in the presence of a
solvent such as methanol, ethanol, methylene chloride,
chloroform, dimethylformamide, tetrahydrofuran or
dioxane in the presence of a suitable base such as
sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, sodium hydroxide,
triethylamine, sodium methoxide, sodium ethoxide or
sodium hydride at temperatures between 50 and 100C.
In the reactions described hereinbefore, any reactive
groups present such as hydroxy, amino or alkylamino
groups may be protected during the reaction by
conventional protecting groups which may be cleaved
after the reaction.
Examples of suitable protecting groups for a hydroxy
group include trimethylsilyl, acetyl, benzoyl, methyl,
ethyl, tert.butyl, benzyl and tetrahydropyranyl groups
and suitable protecting groups for an amino, alkylamino
or imino group include acetyl, benzoyl, ethoxycarbonyl
'
.. . . .
2~7~5
- 3~ -
and benzyl groups.
The optional subsequent eleaving of a proteeting group
used is preferably earried out by hydrolysis in an
aqueous solvent, e.g. in water, isopropanol/water,
tetrahydrofuran/water or dioxane/water, in the presenee
of an aeid sueh as hydroehlorie aeid or sulphurie aeid
or in the presenee of an alkali metal base sueh as
sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide, at temperatures
between o and 100C, preferably at the boiling
temperature of the reaetion mixture. However, a benzyl
group is preferably split off by hydrogenolysis, e~g.
with hydrogen in the presence of a eatalyst sueh as
palladium/eharcoal in a solvent sueh as methanol,
ethanol, ethyl acetate or glaeial aeetie aeid,
optionally with the addition of an aeid sueh as
hydroehlorie aeid at temperatures between O and 50C,
but preferably at ambient temperature, under a hydrogen
pressure of 1 to 7 bar, preferably 3 to 5 bar.
An isomer mixture of a eompound of formula I thus
obtained may, if desired, be separated, preferably by
ehromatography using a earrier sueh~as siliea gel or
aluminium oxide.
.. .
The eompounds of formula I obtained may be converted
into the acid addition salts thereof, more particularly
for pharmaeeutieal use into the physiologically
aeeeptable salts thereof with inorganie or organie
aeids. Suitable acids for this purpose include, for
example, hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic aeid, sulphuric
aeid, phosphoric acid, fumarie aeid, suecinic acid,
lactie acid, citric acid, tartaric acid and maleic acid.
Furthermore, the new eompounds of formula I thus
obtained, if they contain a carboxy or lH-tetrazolyl
group, may if desired subsequently be converted into the
2~r~
~ 35 -
salts thereof with inorganic or organic bases, more
particularly for pharmaceutical use into the
physiologically acceptable salts thereof. Suitable
bases for this purpose include, for example, sodium
hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, cyclo~exylamine,
ethanolamine, diethanolamine and triethanolamine.
The compounds of formulae II to XXI used as starting
materials are known from the literature in some cases or
may be obtained by methods known from the literature.
Thus, for example, compounds of formulae II, IV, VI,
VIII, IX, X, XI and XII may be obtained by acylation of
a corresponding o-phenylenediamine and subsequent
cyclisation or by acylation of a corresponding o-amino-
nitro compound, subsequent reduction of the nitro group
and cyclisation, whilst an NH-benzimidazole can
optionally be converted by alkylation with a
corresponding biphenyl derivative into a compound which
is correspondingly substituted in the l-position, with
optional subsequent cleaving of any protecting group
used.
The conversions of oxazol-2-yl compounds of formula IV
into imidazol-2-yl compounds substituted in the 1-
position, as described in this application, may be
carried out analogously to the synthesis of lH-imidazole
described in Angew. Chem. 71: 761 (1959) (conversion of
oxazoles into lH~imidazoles using formamide/ammonia).
The oxazoles of formulae IV, VI, VIII, X and XI may be
prepared by acylation of a corresponding ~-aminoketone
with a corresponding carboxylic acid chloride or
carboxylic acid anhydride followed by cyclisation
analogously to J. Chem. Soc. 95: 2167 (1909) and
Synthesis 1970, 6~8, using as condensation agents strong
acids such as sulphuric acid, phosphoric acid,
' ~ '; , ' '
..
,'., ,
2~3~
- 36 -
hydrofluoric acid or POC13.
A starting compound of formula XV is conveniently
obtained by acylation of a corresponding ~-amino-alcohol
and a compound of formula XVI is obtained by cyclisation
of a compound of formula XV thus obtained.
The acylated ~-aminoketones mentioned above can also be
converted directly into the corresponding substituted
imidazoles by treatment with ammonium acetate in glacial
acetic acid analogously to Chem. Ber. 106: 2~15 (1973).
.~ .
Starting compounds of formulae XIV and XVIII may be
obtained by acylating a corresponding ~-amino-acetone
with a corresponding activated benzimidazole carboxylic
acid, to obtain thé desired ~-amino-acetone from the
corresponding ~-amino acids according to Dakin/West (see
Chem. Soc. Rev. 17: 91 (19g8)).
A starting compound of formula XIX may be obtained by
acylating a corresponding ~-amino-alcohol with a
corresponding activated benzimidazole carboxylic acid,
the resulting compound subsequent.ly being cyclised and
then reacted with a corresponding ethylenediamine.
.... .
The compounds of formula I and the physiologically
acceptable salts thereof have valuable pharmacological
properties. They are angiotensin-antagonists,
particularly angiotensin~ antagonists.
Those compounds of formula I wherein Rs denotes a group
metabolically convertable in vivo into a carboxy group,
or denotes a carboxy or lH-tetrazolyl group, have
particularly valuable pharmacological properties, since
they are angiotensin-antagonists, more particularly
angiotensin-II-antagonists. The other compounds of
formula I wherein R4 denotes a hydrogen atom or Rs
.
~3~J~
- 37 -
denotes a cyano, 1-triphenylmethyl-tetrazolyl or 2-
triphenylmethyl-tetrazolyl group are valuable
intermediates for preparing the compounds mentioned
above.
By way of example, the following compounds:
= 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid;
B = 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-methyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl~2-carboxylic acid;
C = 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-methyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]- .
methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl;
D = 4'-~[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-benzyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidaæol-2-yl)--lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid;
E = 4'-[~2-ethyl-4-methyl-6-(1-phenyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)--lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid-hydrate;
F = 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-carboxymethyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid-semihydrate;
G = 4'-[[2-ethyl-4-methyl-6-(1-ethyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzlmidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl-hydrate;
H = 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4,4-dimethyl-oxazolin-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
.
,, . - . : .
'
.
,
- 38 -
carboxylic acid-di-trifluoroacetate;
I = 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(1,5-dimethyl-4-phenyl-
imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-
biphenyl~2-carboxylic acid-hydrate; and
K = 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4-isopropyl-1,5-
dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid x 1.2S water
were tested for their biological effects as follows:
.
Descri~tion of method: Angiotensin II-receptor bonding
The tissue (rats lung) is homogenised in Tris-buffer
(50 mMol Tris, 150 mMol NaCl, 5 mMol EVTA, pH 7.40) and
centrifuged twice for 20 minutes at 20,000 x g. The
finished pellets are resuspended in incubating buffer
(50 mMol Tris, 5 mMol MgCl2, 0.2~ BSA, pH 7.40) 1:75,
based on the moist weight of the tissue. Each 0.1 ml of
homogenate is incubated for 60 minutes at 37C with
50 pM [125I]-angiotensin II (NEN, Dreieich, FRG) with
increasing concentrations of the test substance in a
total volume. of 0.25 ml. Incubation is ended by rapid
filtration through glass fibre filter mats. The filters
are each washed with 4 ml of ice cold buffer (25 mMol
Tris, 2.5 mMol MgCl2, 0.1% BSA, pH 7.40). The bound
radioactivity is measured using a gamma-counter. The
corresponding ICso value is obtained from the dose-
activity curve.
In the test described, substances A to K show the
following ICso values:
2~3~$~
- 39 -
Substance IC50 [nM]
_ .-
A 12.0
B 3.8
C 2.6
D 6.0
E 46.0
F 38.0
G 1.6
H 37.0
I 3.2
K 19.5
Moreover, when the above-mentioned compounds were
administered in a dose of 30 mg/kg i.v. no toxic side
effects, e.g. no negative inotropic effects and no
disorders in heart rhythm, were observed. The compounds
are therefore well tolerated.
In view of their pharmacological properties, the new
compounds and the physiologically acceptable salts
thereof are suitable for the treatment of hypertension
and cardiac insufficiency and also for treating
ischaemic peripheral circulatory disorders, myocardial
ischaemia (angina), for the prevention of the
progression of cardiac insufficiency after myocardial
infarction and for treating diabetic nephropathy,
glaucoma, gastrointestinal diseases and bladder
diseases.
The new compounds and the physiologically acceptable
salts thereof are also suitable for treating pulmonary
diseases, e.g. lung oedema and chronic bronchitis, for
preventing arterial re-stenosis after angioplasty, for
preventing thickening of blood vessel walls after
.~ - -
.: . . . .
: . , . : . .
.. . ..
. ~ ., ~ , ' ~ . '
- 2~3~
- 40 -
vascular operatlons, and for preventing arteriosclerosis
and diabetic angiopathy. In view of the effects of
angiotensin on the release of acetylcholine and dopamine
in the brain, the new angiotensin-antagonists are also
suitable for alleviating central nervous system
disorders, e.g. depression, Alzheimer's disease,
Parkinson syndrome, bulimia and disorders of cognitive
function.
Thus, viewed from a further aspect the present invention
provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising a
compound of formula I or a physiologically acceptable
salt thereof together with at least one physiologically
acceptable carrier or excipient.
Viewed from a still further aspect the invention
provides the use of a compound of formula I or a
physiologically acceptable salt thereof for the
manufacture of a therapeutic agent having an
angiotensin-antagonistic activity.
In particular, the invention provides the use of a
compound of formula I or a physiologically acceptable
salt thereof for the manufacture of a therapeutic agent
for the treatment of hypertension and cardiac
insufficiency, for treating ischaemic peripheral
circulatory disorders, myocardial ischaemia (angina),
for the prevention of the progression of cardiac
insufficiency after myocardial infarction and for
treating diabetic nephropathy, glaucoma,
gastrointestinal diseases and bladder diseases, in
particular for treating pulmonary diseases, for
preventing arterial re-stenosis after angioplasty, for
preventing thickening of blood vessel walls after
vascular operations, and for preventing arteriosclerosis
and diabetic angiopathy.
~3'~
- 41 -
More particularly, the invention provides the use of a
compound of formula I or a physiologically acceptable
salt thereof for the manufacture o~ a therapeutic agent
for alleviating central nervous system disorders.
Viewed from a yet still further aspect the invention
provides a method of treatment of the human or non-human
animal body to combat hypertension and cardiac
insufficiency, for treating ischaemic peripheral
circulatory disorders, myocardial ischaemia (angina),
for the prevention of the progression of cardiac
insufficiency after myocardial infarction and for
treating diabetic nephropathy, glaucoma,
gastrointestinal diseases and bladder diseases, in
particular to combat pulmonary diseases, arterial re-
stenosis after angioplasty, for preventing thickening of
blood vessel walls after vascular operations, and for
preventing arteriosclerosis and diabetic angiopathy,
said method comprising administering to said body a
compound of formula I or a physiologically acceptable
salt thereof.
More particularly, the invention provides a method of
treatment of the human or non-human animal body to
alleviate central nervous system disorders, said method
comprising administering to said body a compound of
formula I or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof.
. .
The dosage required to achieve these effects in adults
is appropriately, when administered intravenously, 0.5
to 100 mg, preferably 1 to 70 mg, and, when administered
orally, 0.1 to 200 mg, preferably 1 to 100 mg, 1 to 3
times a day. For this purpose, the compounds of formula
I prepared according to the invention, optionally in
conjunction with other active substances, such as
hypotensives, ~CE inhibitors, diuretics and/or calcium
antagonists, may be incorporated together with one or
- .
. ~ ~ . .. .
. ~ . . .
2 ~
- 42 ~
more inert conventional carriers and/or diluents, e.g.
with corn starch, lactose, glucose, microcrystalline
cellulose, magnesium stearate, polyvinylpyrrolidone,
citric acid, tartaric acid, water, water~ethanol,
water/glycerol, water/sorbitol,
water/polyethyleneglycol, propyleneglycol, cetylstearyl
alcohol, carboxymethylcellulose or fatty substances such
as hard fat or suitable mixtures thereof, in
conventional galenic preparations such as plain or
coated tablets, capsules, powders, suspensions or
suppositories.
Additional active substances which may be included in
the combinations mentioned above include, for example,
bendroflumethiazide, chlorothiazide, hydrochloro-
thiazide, spironolactone, benzothiazide, cyclothiazide,
ethacrinic acid, furosemide, metoprolol, prazosine,
atenolol, propranolol, (di)hydralazine-hydrochloride,
diltiazem, felodipin, nicardipin, nifedipin, nisoldipin,
nitrendipin, captopril, enalapril, lisinopril,
cilazapril, quinapril, fosinopril and ramipril. The
dosage for these active substances is appropriately 1/5
of the lowest recommended dose up to 1/1 of the normally
recommended dose, i.e., for example, 15 to 200 mg of
hydrochlorothiazide, 125 to 2000 mg of chlorothiazide,
15 to 200 mg of ethacrinic acid, 5 to 80 mg of
furosemide, 20 to 480 mg of propranolol, ~ to 60 mg of
felodipine, 5 to 60 mg of nifedipin or 5 to 60 mg of
nitrendipin.
The following non-limîting Examples are provided to
illustrate the invention. All percentages and ratios
are by weight, other than eluant or solvent ratios which
are by volume.
~37$~
- 43 -
Example 1
Methyl 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4~methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-
biphenyl-2 carboxylate
a) Methyl 4'-[(2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-amidino-lH-
benzimidazol-1-yl)-methyll-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Hydrogen chloride gas is piped into a solution of 6.2 g
(14.6 mMol) of methyl 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-cyano-
lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate in
750 ml of absolute methanol for 3 hours at ambient
temperature and the mixture is stirred for a further 2
hours at ambient ternperature. After removal of the
solvent the mixture is evaporated down in vacuo, the
residue is taken up twice with 50 ml of methanol and
50 ml of ether and evaporated down once more. Then the
residue is dissolved in 750 ml of absolute methanol and
mixed with 30 g of ammonium carbonate. After 12 hours
at ambient temperature, 50 g of silica gel (parti~le
size: 0.06-0.3 mm) are added. Ater filtration and
evaporation of the filtrate the residue is
chromatographed on silica gel (particle size
0.032-0.063 mm) using as eluant mixtures of methylene
chloride and methanol of increasing polarity (9:1, 4:1,
3:1 and 1:1). The uniform fractions are combined and
evaporated down.
Yield: 4.3 g (57% of theory),
Foam, Rf value: 0.14 (silica gel; methylene
chloride/ethanol = 9:1)
b) Methyl 4'-[(2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-
methyll-bi~henvl-2-carboxylate
0.5 g (1.0 mMol) of methyl 4'-[(2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-
amidino-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylate, 0.13 g (1.0 mMol) of 2-chloro-cyclohexanone
and 10 ml of liquid ammonia are heated to 60C in a bomb
. , - . ~ . '
'
,
- . .
~ $ ~ $ 3
- 44 -
for 15 hours. After cooling and evaporation of the
ammonia the residue is dissolved in methanol/methylene
chloride (2:1) and chromatographed on silica gel
(particle size: 0.032-0.063 mm), using as eluant
mixtures of methylene chloride and ethanol of increasing
polarity (19:1 and 9:1). The uniform fractions are
combined and evaporated down.
Yield: 0.1 g (19% of theory),
Foam, R~ value: 0.50 (silica gel; methylene
chlGride/ethanol = 9:1)
Example 2
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(s,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
0.1 g (0.2 mMol) of methyl 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-
(5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-
yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and 10 mg (0.02 mMol)
of hexade~yl-tributylphosphonium bromide are taken up in
lO ml of (48%) hydrobromic acid and heated to llO~C for
15 minutes. After cooling, 20 ml of ether are poured
over and the mixture is diluted with lO ml of water.
After extraction the organic phase is separated off.
The aqueous phase is adjusted to pH 7 with ammonia, the
precipitate thus formed is suction filtered, washed with
water and taken up in methylene chloride/ethanol (4:1).
The solvent is evaporated off, the residue is triturated
with ether and dried. The crude product is
chromatographed on silica gel ~particle size:
0.032-0.063 mm), using as eluant methylene
chloride/ethanol (9:1). The uniform fractions are
combined and evaporated down. The residue is triturated
with ether and dried.
Yield: 64 mg (64% of theory),
Melting point: 231-235C (decomp.)
C32H32N402 (504-64)
~3,~
- 45 -
Mass spectrum: (M + H)~ = 505
Example 3
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(5,5-spiro-cyclopentano)-
dihydroimidazol-4-on-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid-semihydrate
0.05 g (0.1 mMol) of methyl 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-
(5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-
yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate are dissolved in 4 ml
of ethanol, mixed with 2 ml of 1 N sodium hydroxide
solution and stirred for 4 days at ambient temperature.
After the addition of 4 ml of water the pH is adjusted
to 6 using glacial acetic acid, the precipitate formed
is suction filtered, washed with water and dried over
potassium hydroxide. The crude product is
chromatographed on silica gel (particle size:
0.032-0.063 mm), using as eluant methylene
chloride/ethanol/glacial acetic acid (50:1:0.1 and
30:1:0.1). The uniform fractions are combined and
evaporated down. The residue is triturated with ether
and dried.
Yield: 30 mg (59% of theory),
Melting point: 310-311C (decomp.)
C32H32N4O3 (520.64)
Mass spectrum: (M + H)+ = 521
Examp]e 4
Tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6 (5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzoxazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
. . _ . _ .
a) 2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzoxazol-2-yl~-lH-benzimidazole
2.17 g (10 mMol) of 2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-aminocarbonyl-
lH-benzimidazole and 10.25 g (77 mMol) of 2-chloro-
- ~ .' ' ' ' .
.
'
,. . .
~37~
~ 46 -
cyclohexanone are heated to 190C for one hour. After
cooling to ambient temperature the reaction mixture is
triturated with ether and suction filtered. The residue
is taken up in water and mixed with concentrated
ammonia. Then it is extracted with methylene chloride,
the organic phase is washed with water, dried over
magnesium sulphate and evaporated down~ The residue is
chromatographed on silica gel (particle size:
0.032 0.063 mm) using as eluant mixtures of methylene
chloride and ethanol of increasing polarity (50:1, 25:1
and 20:1). The uniform fractions are combined and
evaporated down.
Yield: 1.9 g (64% of theory),
Foam, Rf value: 0.20 (silica gel; ethyl acetate)
b) Tert.butyl 4i-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzoxazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-
methvl]-biphen~1-2-carboxylate
3.3 g (11 mMol) of 2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzoxazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazole are
dissolved in 15 ml of dimethylformamide and at 5-10C
1.5 g (13.2 mMol) of potassium tert.butoxide are added
in batches. After 15 minutes at 5C 4.6 g (13.2 mMol)
of tert.butyl 4'-bromomethyl-biphenyl-2-carboxylate are
added. After a further 45 minutes at 5C the reaction
mixture is stirred into 200 ml of water. The
precipitate formed is suction filtered, washed with
water and taken up in 200 ml of ethyl acetate. The
solution is washed with water and with saturated sodium
chloride solution, dried over magnesium sulphate and
evaporated down. The residue is chromatographed on
silica gel (particle size: 0.032-0.063 mm) using as
eluant methylene chloride/ethanol (50:1). The uniform
fractions are combined and evaporated down.
Yield: 4.8 g (78% of theory),
Foam, Rf value: 0.23 (silica gel; methylene
chloride~ethanol = 49:1)
2~3785
- 47 -
_xample 5
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylate
2.0 g (3.56 mMol) of tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-
methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzoxazol-2-yl)-lH-
benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate, 16 ml
(40 mMol) of formamide and 40 ml of ammonia (liquid) are
heated to 200C in the bomb for 14 hours. After
cooling, the reaction mixture is diluted with wàter, the
precipitate thus formed is suction filtered. The
filtrate is adjusted to pH 6 with glacial acetic acid,
the precipitate formed is removed by centrifuging and
washed with water. The residue is taken up in 50 ml of
2 N hydrochloric acid. By the addition of concentrated
ammonia the pH is adjusted to 6 and the precipitate thus
formed is suction filtered, washed with water and dried.
Yield: 1.3 g (72% of theory),
Melting point: from 235C (decomp.)
Example 6
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(1,3-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazolium iodide-2-ylj-lH-benzimidazol-
l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
0.85 g (1.7 mMol) of 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-
(5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-
yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid are dissolved in
9 ml of dimethylsulphoxide, mixed with 420 mg (3.7 mMol)
of potassium tert.butoxide at 5C and stirred for 10
minutes. After the addition of 570 mg (4.0 mMol) of
methyliodide the reaction mixture is heated to 70C for
25 minutes. After cooling, it is poured onto ice, the
precipitate formed is suction filtered and washed with
water. The residue is taken up in 50 ml of ethanol,
2~378~
- 48 -
combined with 12 ml of 1 N sodium hydroxide solution and
stirred for 5 days at ambient temperature. The solvent
is evapor~ted off ln vacuo, the residue is mixed with
ice and acidified with aqueous citric acid (5%). The
preci,pitate thus formed is suction filtered, washed with
water and dried.
Yield: 470 mg (42% of theory),
Melting point: 240-242C (decomp.)
C34H37N4O2I (660.61)
Calculated: C 61.82 H 5.65 N 8.48
Found: 61.69 5.88 8.72
~ .
Example 7
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-methyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid-hydrate
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzoxazol-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and N-methylformamide/methylamine.
Yield: 27% of theory,
Melting point: 183-186C
C33H34N4o2 x H20 (536.68)
Calculated: C 73.85 H 6.76 ~ 10.44
Found: 74.22 6.97 10.48
Example 8
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-2-(lH-
tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-semihydrate
a) 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzoxazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-
methYll-2-(l-triphenylmethyl-tetrazol-5-vl)biphen
Prepared analogously to Example 4b from 2-n-propyl-4-
2~37~
methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzoxazol-2-yl)-lH-
benzimidazole and 4'-bromomethyl-2-(1-triphenylmethyl-
tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl.
Oil, Rf value: 0.67 (silica gel; ethyl acetate)
b) 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-t5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl~-2-
(lH-tetrazol-5-vl)biphenyl-semihydrate
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from 2-n-propyl-4-
methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzoxazol-2-yl)-lH-
benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-2-(1-triphenylmethyl-
tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl and formamide/ammonia.
Yield: 70% of theory,
Melting point: from 230C (decomp.)
C32H3zN8 x 0 5 H2O (537.68)
Calculated: C 71.48 H 6.19 N 20.84
Found: 71.43 6.46 21.20
Example 9
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4~methyl-6-(1-methyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-semihydrate
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from 4'-[[2-n-propyl-
4-methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzoxazol-2-yl)-lH-
benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-2-(1-triphenylmethyl-
tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl and N-methyl-
formamide/methylamine.
Yield: 63% of theory,
~elting point: from 240C (decomp.)
C33H34N8 x 0-5 H2O (551.71)
Calculated: C 71.84 H 6.40 N 20.31
Found: 71.63 6.45 20.64
- 5~ -
Example lo
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzoxazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-
2-carboxylic acid
-
1.2 g (24 mMol) of tert.butyl 2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-
(5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzoxazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-
yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate are dissolved in
25 ml of methylene chloride, mixed with 8.5 ml of
trifluoroacetic acid and stirred for 3 hours at ambient
temperature. Then the solvent is evaporated off in
vacuo, the residue is mixed with ice and made alkaline
with conc. ammonia. After one hour the pH is adjusted
to 5 by the addition of citric acid. The precipitate
thus formed is suction filtered, washed with water and
dried. The crude product is purified on silica gel
(particle size: 0.032-0.063 nm) using ethyl acetate as
eluant. The uniform fractions are combined and
evaporated down.
Yield: 33% of theory,
Melting point: 229-232C (decomp.)
C32H31N303 (505.62)
Mass spectrum: M~ = 505
Example 11
4'-[t2-Ethyl-4-methyl-6-(1-methyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl) lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-2-(lH-
tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl-hydrate
a) 2~ethyl-4-methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzoxazol-2-
Yl)-lH-benzimidazole
Prepared analogously to Example 4a from 2-ethyl-4-
methyl-6-aminocarbonyl-lH-benzimidazole and 2-chloro-
cyclohexanone.
Yield: 60% of theory,
,
.
- .
~: ,: ' ' '
- ' ' ' : ' . ' '
2 ~
- 51 -
Oil, Rf value: 0.17 (silica gel; ethyl acetate)
b) 4'-[[2-Ethyl-4-methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzoxazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl-2-(1-
triphenylmethyl-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl
Prepared analogously to Example 4b from 2-ethyl-4-
methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzoxazol-2-yl)-lH-
benzimidazole and 4'-bromomethyl-2-(1-triphenylme~hyl~
tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl.
Yield: 63~ of theory,
Oil, Rf value: 0.69 (silica gel; ethyl acetate)
c) 4'-[[2-Ethyl-4-methyl-6-(1-methyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methvl-2-flH-tetrazol-5-Yl)-biphenyl-hydrate
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from 4'-[[2-ethyl-4-
methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzoxazol-2-yl)-lH-
benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl-2-(~-triphenylmethyl-tetrazol-
5-yl)-biphenyl and N-methyl-formamide/me~hylamine.
Yield: 51% of theory,
Melting point: from 180C ~decomp.)
C32H32N8 x H2O (546.69)
Calculated x H2O: C 70.31 H 6.27 N 20.50
Found: 70.07 6.55 20.60
- Mass spectrum: M+ = 528
Example 12
4'-[t2-Ethyl-4-methyl-6-(1-methyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid-hydrate
a) tert.butyl 4'-[[2-ethyl-4-methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzoxazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methYll-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Prepared analogously to Example 4b from 2-ethyl-4-
methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzoxazol-2-yl)-lH-
benzimidazole and tert.butyl 4'-bromomethyl-biphenyl-2-
''; ' . ' -' ' - ~:
- ,, : .
',
... :, ~ ' . .
:
~, ., . . . .. ~. .. . .. ~ -
'~
_25~93 ~8
carboxylate.
Yield: 77% of theory,
Melting point: 160-162C
~) 4'-[[2-ethyl-4-methyl 6-(1-methyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyll-bi~henyl-2-carboxylic acid-hydrate
Prspared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-ethyl-4-methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzoxazol-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and N-methylformamide/methylamine.
Yield: 34% of theory,
Melting point: 292-300C tdecomp.)
C32H32N4O2 x H2O (522.66)
Calculated x H2O: C 73.54 H 6.56 N 10.72
Found: 73.3~ 6.76 10.67
- Mass spectrum: M+ = 504
ExamPle 13
4'-[[2-Ethyl-4-methyl-6-(1-phenyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid-hydrat:e
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-ethyl-4-methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzoxaæol-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl3-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and N-formyl-anilide/aniline.
Yleld: 13% of theory,
Melting point: 255-257~C (decomp.)
C37H34N4O2 x H2O (584.73)
Calculated x H2O: C 76.00 H 6.20 N 9.58
Found: 76.36 6.18 9.59
Mass spectrum: M' = 566
:,
: . ............... . . ~ ,. . . .
,. : , -, . .
. . : . : , , ,: : , . .
- 53 -
~xample 14
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-phenyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl3-
biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid-semihydrate
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4 methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzoxazol-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and N-formyl-anilide/aniline.
Yield: 23% of theory,
Melting point: 258-260C (decomp.)
C38H36N4O2 x 1/2 H2O (589.
Calculated x 1/2 H2O: C 77.39 H 6.32 N 9.50
Found: 77.03 6.30 9.39
Mass spectrum: Mt = 580
Example 15
4' [[2-n-Propyl 4-methyl-6-(1-benzyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl 6 (5,6,7,8--tetrahydrobenzoxazol-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and N-benzyl-formamidejbenzylamine.
Yield: 54% of theory,
Melting point: 256-258C (decomp.)
C39H38N4O2 (594.77)
Calculated: C 78~76 H 6.44 N 9.42
Found: 78.50 6.49 9~35
Mass spectrum: M~ = 594
'; . , , '. . . ..
-
~, . :
.: , .
,
. : -
2~3~37~
- 54 -
Example 16
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-ethyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl~-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic a~id-sesquihydrate
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzoxazol-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and N-ethyl-formamide/ethylamine.
Yield: 17% of theory,
Melting point: from 228C (decomp.)
`` C34H36N4O2 x 1-5 H2O (559 7 )
Calc. x 1.5 H2O: C 72.96 H 7.02 N 10.01
Found: 73.04 6.90 9.77
Mass spectrum: M+ = 532
Example 17
4'-[[2~Ethyl-4-methyl-6-(1-isopropyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimldazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.hutyl 4'-
[[2-ethyl-4-methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzoxazol-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and N-isopropyl-formamide/isopropylamine.
Yield: 2% of theory,
Melting point: 197C
C34H36N4O2 (532.69)
Mass spectrum: M+ = 532
''. . ' ' . . : ,' .' : :' :
., . . :
.:
, ' '~ : : '
,
. . . ~ .
7 8 ~
- 55 -
Example 18
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4~methyl-6-(1-isobutyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carbbxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 5 ~rom tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzoxazol-2-
yl~-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl~-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and i 5 obutylaminejwater.
Yield: 5% of theory,
C36H40N4O2 (560.75)
Mass spectrum: ~M+H)+ = 561
Example 19
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(1,3-dibenzyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazolium acetate-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-
l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid-semihydrate
Prepared analogously to Example 6 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(5,6,7,8--tetrahydrobenzimidazol-
2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and benzylbromide/sodium hydroxide
solution/glacial acetic acid.
Yield: 76% of theory,
Melting point: sintering from 80C
C46H44N4O2 x CH3COOH x 1/2 H2O (753-95)
Calc. x CH3COOH x 1/2 H2O: C 76.47 H 6.55 N 7.43
Found: 76.46 6.65 7.76
Mass spectrum: M+ = 684
.
': ' '
' ' .
2~378~
- 56 -
Exampl Q20
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-carboxymethyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid-semihydrate
Prepared analogously to Example 6 from 4'-[[2-n-propyl-
4-methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-
benzimidazol 1-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2 carboxylic acid
and ethyl bromoacetate/sodium hydroxide solution.
Yield~ 34% of theory,
Melting point: 239-242C
C34H34N4O4 x 1/2 H2O (571.69)
Calc. x 1/2 H2O: C 71.43 H 6.17 N 9.80
Found: 71.39 6.19 9.81
Mass spectrum: M+ = 562
Example 21
4'-[[2-Cyclopropyl-4-methyl-6-(1-methyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic ac:id-semihydrate
Prepared analogously to Example '~ from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-cyclopropyl-4-methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzoxazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl~-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and N-methyl-
formamide/methylamine.
Yield: 50% of theory,
Melting point: 285-289C
C33H32N4O2 x l/2 H2O (525.66)
Calculated: C 75.40 ~ 6.33 N 10.66
Found: 75.24 6.44 10.42
Mass spectrum: M = 516
The following compounds may be obtained analogously to
the preceding Examples:
., .
.. , ~ . - .
, . : .
: :
.
2~3~
- 57 -
(1) 4'-[[2-cyclopropyl-4-methyl-6-(1-methyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol~5-yl)biphenyl
(2~ 4'-[[2 ethoxy-4-methyl-6-(1-methyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
(3) 41-[[2-ethoxy-4-methyl-6-(1-methyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl
(4) 4'-[[2-ethyl-4-methyl-6-(1-isopropyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-
methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yljbiphenyl
(5) 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-isopropyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
(6) 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-isopropyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl~biphenyl
(7) 4'-[[2-ethyl-4-methyl-6-(1-i~obutyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-
methyl3-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
(8) 4'-[[2-ethyl-4-methyl-6-(1-isobutyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-
methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl
(9) 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-isobutyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl
(10) 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl 6-(1-carboxymethyl-
.
, . ~ - : . : ,
2~378~
- 58 -
5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-
yl]-methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl
(11) 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-meth~l-6-(1-methyl-4,5-
trimethylene-imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
(12) 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-tl-methyl-4,5-
trimethylene-imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl~-
methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl~biphenyl
Example 22
4'-[[2-Ethyl-4-methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzoxazol-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)-
biphenyl
Prepared analogously to Example 10 from 4'-[[2-ethyl-4-
methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzoxazol-2-yl)-lH-
benzimidazol-I-yl]-methyl]-2-(l-triphenylmethyl-
tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl and hydrochloric acid in
methanol.
Yield: 15~ o~ theory,
Melting point: 140-142C (decomp.)
H29N70 (515.63)
Mass spectrum: (M+H)~ = 516
',
Example 23
4'-[[2-Ethyl-4-methyl-6-(l-ethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
benzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-2-(lH-
tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl-hydrate
Prepared analo~ously to ~xample 5 from 4'-[[2-ethyl-4-
methyl-6-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzoxazol-2-yl)-lH-
benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-2-(l-triphenylmethyl-
te~razo~-5-yl)-biphenyl and N-ethyl-
formamide/ethylamine.
, , :: . .
.
.. . .
.
2~37~
- 59 -
Yield: 25% of theory,
Melting point: from 180C (decomp.)
C33H34N8 x H20 (560.72)
Calculated: C 70.68 H 6.47 N 19.99
Found: 70.46 6.44 19.56
Mass spectrum: M+ = 542
Example 24
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(4,4-dimethyl-oxazolin-2-yl)-
lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
di-trifluoroacetate
-
Prepared analogously to Example 10 from tert.butyl 4'-
[C2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4,4-dimethyl-oxazolin-2-yl)-lH-
benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and
trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 60% of theory,
Melting point: 158-159C
C3~H31N303 x 2 CF3C00~l (709.64)
Calculated: C 57.55 H 4.6g N 5.92
Found: 57.76 4.72 6.02
Mass spectrum: M+ = 481
Example 25
4:-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(1,5-dimethyl-4-phenyl-
imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid-hydrate
a) Tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-[N-(l-benzoyl-
ethyl)-methylaminocarbonyl]-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyll-bi~henyl-2-carboxylate
To a solution of 1.0 g (2.0 mMol) of tert.butyl 4'-[[2-
n-propyl-4-methyl-6-chlorocarbonyl-lH-benzimidazol-l-
yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-carboxylate in 20 ml of methylene
chloride are added 20 ml of toluene and 0.44 g
.
,
.
%~7~
- 60 -
(2.2 mMol) of 2-methylamino-propiophenone. The reaction
mixture is heated to 85C and 10 ml of pyridine are
added dropwise within 4 hours. Then the reaction
mixture ls evaporated down, the residue is mixed with
ice water and extracted twice with methylene chloride.
The combined organic phases are dried over magnesium
sulphate and evaporated down. The crude product is
chromatographed on silica gel (particle size:
0.032-0.063 mm) using as eluant methylene chloride to
start with and later methylene chloride/ethanolfammonia
(50:1:0.25 and 25:1:0.01). The uniform fractions are
combined and evaporated down.
Yield: 1.0 g (79% of theory),
Foam, Rf value: 0.50 (silica gel; methylene
chloride/ethanol = 9:1)
b) Tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(1,5-dimethyl-
4-phenyl-imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyll-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
A solution of 1.0 g (1.5 mMol) of tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-
propyl-4-methyl-6-[N-(1-benzoyl-ethyl)-
methylaminocarbonyl]-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylate and 15 g of ammonium acetate in
80 ml of glacial acetic acid is refluxed for 2.5 hours.
Then the reaction mixture is evaporated down to half,
the residue is mixed with ice water and extracted twice
with ethyl acetate. The combined organic phases are
washed with water, dried over magnesium sulphate and
evaporated down. The crude product is chromatographed
on silica gel (particle size: 0.032-0.063 mm) using as
eluant methylene chloride with increasing amounts of
ethanol (3%, 10% and 20%). The uniform fractions are
combined and evaporated down.
Yield: 0.68 g ~74% of theory),
Foam, Rf value: 0.40 (silica gel; methylene
chloride/ethanol = 19:1)
. . .
2~3~
- 61 -
c) 4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-~1,5-dimethyl-4-phenyl-
imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol~1-yl]-methyl]-
bi~henyl-2-carbox~ c acid-hydrate
Prepared analogously to Example 10 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(1,5-dimethyl-4-phenyl-imidazol-
2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl~-biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 90% of theory,
Melting point: ~rom 152C (decomp.
C36H33N402 x H20 (572.72)
Calculated: C 75.50 H 6.34 N 9.78
Found: 75.95 6.48 9.92
Mass spectrum: M' = 554
Example 26
4'-~[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-methyl-4,5-diphenyl-
imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1 yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid-sesquihydrate
a) Tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-methyl-4,5-
diphenyl-imidaæol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methvl1-biphenvl-2-carboxYlat:e
Prepared analogously to Example ~Sb from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-[N-(l-berlzoyl-benzyl)-
methylaminocarbonyl3-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylate and ammonium acetate in glacial
acetic acid.
Yield: 27% of theory,
Oil, Rf value: 0.40 (silica gel; methylene
chloride/ethanol = 19:1)
b) 4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-methyl-4,5-diphenyl-
imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid-sesquihvdrate
Prepared analogGusly to Example 10 from tert.butyl 4'~
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-methyl-4,5-diphenyl-imidazol-
2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
2~3r~
- 62 -
carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 60% of theory,
Melting point: 325-328C (decomp.)
C41H36N402 x 1-5 ~2 (643.79)
Calculated: C 76.49 H 6.11 N 8.70
Found: 76.53 6.1S 8.75
Mass spectrum: M+ = 616
Example 27
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4~methyl-6-(5-methyl-4-isopropyl-
imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid-dihydrate-acetate
a) Tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(5-methyl-4-
isopropyl-imidazol~2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-biphenYl-2-carboxylate
Prepared analogously to Example 25b from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-[N-(l-acetyl-2-methyl-n-propyl)-
methylaminocarbonyl]-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylate an~ ammonium acetate in glacial
acetic acid.
Yield: 45% of theory,
oil, Rf value: 0.10 (silica ~el; ethyl acetate/
petroleum ether = 2:1)
: -`
b) 4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(S-methyl-4-isopropyl-
imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid-dihYdrate-acetate
Prepared analogously to Example 10 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(5-methyl-4-isopropyl-imidazol-
2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 75~ of theory,
Melting point: from 155C (decomp.)
C32H34N402 x CH3COOH x 2 H20 (602.74)
Calculated: C 67.75 H 7.02N 9.30
Found: 67.69 7.02 9.53
.'
, . ~ - ,
-
: , :
.
2~78~
- 63 -
Mass spectrum: M+ = 506
Example 28
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(4-methyl-imidazolin-2-yl)-
lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic
acid-di-trifluoroacetate
a) Tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4-methyl
imidazolin-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylate
A mixture of 0.43 g (Q.8 mMol) of tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-
propyl-4-methyl-6-(4,4-dimethyl-oxazolin-2-yl)-lH-
benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and
0.67 ml (5.8 mMol) of 1,2-diaminopropane is heated to
120C for 48 hours. The yellow solid obtained after
cooling to ambient temperatur~ is stirred with water for
1 hour, suction filtered and dried. The crude product
is chromatographed on silica gel (particle size:
0.032~0.063 mm) using as eluant methylene
chloride/ethanol/ammonia (50:1:0.05, 20:1:0.02 and
7:1:0.07). The uniform fractions are combined and
evaporated down.
Yield: 0.26 g (62% of theory),
Foam, Rf value: 0.20 (silica gel; methylene
chloride/ethanol = 9:1 + ammonia)
b) 4'-[[2-n-PropyI-4-methyl-6-(4-methyl-imidazolin-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid-di-trifluoroacetate
Prepared analogously to Example 10 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4-methyl-imidazolin-2-yl)-lH-
benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and
trifluoroacetic acid.
Yield: 72% of theory,
Melting point: 115-118C (decomp., sinters from lOOaC)
C29H30N402 x 2 CF3COOH (694.63)
Calculated: C 57.06 H 4.64 N 8.07
,
2~3'~
- 64 -
Found: 57.02 5.02 8.13
Mass spectrum: M+ = 466
~xam~le 29
4'-[[2-n-~ropyl-4-methyl-6 (4-isopropyl-5-methyl-oxazol-
2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid
3.9 g (6.7 mMol) of tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-
6-[N-(l-acetyl-2-methyl-n-propyl)-aminocarbonyl]-lH-
benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate are
dissolved in 50 ml of phosphorusoxychloride and stirred
for 2.5 hours at 105 D C. Then the phosphorusoxychloride
is removed, the residue is decomposed with water at 80~C
and, after cooling, mixed with conc. ammonia. The pH is
adjusted to 5 by the addition of glacial acetic acid,
the precipitate thus Eormed is suction filtered, washed
with water, taken up in methylene chloride/methanol
(9:1) and dried over magnesium sulphate. The crude
product is chromatographed on silica gel (particle size:
0.032-0.063 mm) using as eluant petroleum ether/ethyl
acetate/glacial acetic acid (1:1:0.002) and methylene
chloride/ethanol/glacial acetic acid (20:1:0.002). The
uniform fractions are combined, evaporated down,
triturated with ether and suction filtered.
Yield- 2.4 g (71% of theory),
Melting point. 222-223OC
C32H33N303 (507.64)
Calculated: C 75.71 H 6.55 N 8.28
Found: 75.61 6.59 8.36
Mass spectrum: M+ = 507
: . ' ' . ' '
. ' , ,
2~3'~8~
- 65 -
Example 30
4'~[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl 6 (4-isopropyl-1,5-dimethyl-
imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl~-biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid x 1.25 water
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4-isopropyl-5-methyl-oxazol-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and N-methyl-formamide/methylamine.
Yield: 38~ of theory,
Melting point: from 150~C (decomp.)
C33H36N402 x 1-25 H2O (543.2 )
Calculated: C 72.97 H 7.14 N10.32
Found- 72.95 7.02 9.94
Mass spectrum: M~ = 520
Example 31
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-ethyl-4-isopropyl-5-
methyl-imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimiclazol-1-yl]-methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4-isopropyl-5-methyl-oxazol-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and N-ethyl-formamide/ethylamine.
Example 32
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-isopropyl-4-isopropyl-5-
methyl-imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4-isopropyl-5-methyl-oxazol-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and N-isopropyl-formamide/isopropylamine.
2~37~
- 66 -
Exam~le 33
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6~ cyclohexyl-4-isopropyl-5-
methyl-imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4-isopropyl-5-methyl-oxazol-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and N-cyclohexyl-formamide/cyclohexylamine.
Yield: 10% of theory,
C38H44N402 (588.80)
Rf value: 0.24 (silica gel; methylene
chloride/ethanol/acetic acid = 9:1:0.01)
Mass spectrum: (M+H)' = 589
Example 34
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-[1-(2-dimethylamino-ethyl)-4-
isopropyl-5-methyl-imidazol-2-yl]-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid-semihydrate
-
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4-isopropyl-5-methyl-oxazol-2-
yl)~lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and M-(2-dimethylamino-ethyl)-formamide/2-dimethylamino-
ethylamine.
Yield: 48% of theory,
Melting point: 192-195C (decomp.)
C36H43Ns02 x 0-5 HzO (586.79)
Calculated: C 73.69 H 7.56 N 11.93
Found: 73.53 7.55 11.94
Mass spectrum: M~ = 577
. .
: ~
-, ~ . .
~3~
- 67 -
Example 35
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(1,5-dimethyl-4-isobutyl-
imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl 6-(4-isobutyl-5-methyl-oxazol-2-
yl) lH-benzimidazol-1-yl~-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and N-methyl-formamide/methylamine.
Yield: 64% of theory,
Melting point 155-157C (decomp.)
C34H3sN4O2 x 0-7S H20 (548.22)
Calculated: C 74.49 H 7.28 N 10.22
Found: 74.45 7.29 10.35
Mass spectrum: M~ = 534
Example 36
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-ethyl-4-isobutyl-5-methyl-
imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid x 0.25 water
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4-isobutyl-5-methyl-oxazol-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and N-ethyl-formamide/ethylamine.
Yield: 62% of theory,
Melting point: 239-241C
~33H3sN33 x 0.25 H2O (526.17)
Calc. x 0.25 H20: C 75.33 H 6.80 N 7.99
Found: 75.35 6.75 7.96
Mass spectrum: M~ = 527
- 68 -
Example 37
4'-[[2-n Propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-tert.butyl-4-isobutyl-5-
methyl-imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]~
biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n propyl-4-methyl-6-(4-isobutyl-5-methyl-oxazol-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and N~tert.butyl-formamide/tert.butylamine.
Example 38
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-benzyl-4-isobutyl-5-
methyl-imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4-isobutyl-5-methyl-oxazol-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and N-benzyl-formamide/benzylamine.
Example 39
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-~1-(2-morpholino-ethyl)-4-
isobutyl-5-methyl-imidazol-2-yl)--lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic ac:id
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4-isobutyl-S-methyl-oxazol-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and N-(2-morpholino-ethyl)-formamide/2-morpholino-
ethylamine.
Yield: 30% of theory,
Melting point: 201-203C (decomp.)
C3sH47N503 (633.85)
Calculated: C73.90 H 7.47 N 11.05
Found: 73.657.45 11.07
.
'::: ' : '.- ' ' ' , ' :
.: :: ~ ': ,.',
~, , - ,: . ::
- . ' .':
- 69 -
Mass spectrum: M~ = 633
Example 40
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-[1-(2-methoxy-ethyl)-4-
isobutyl-5-methyl-imidazol-2-yl]-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid-hydrate
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4-isobutyl-5-methyl-oxazol-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and N-(2-methoxy-ethyl)-formamide/2-methoxy-ethylamine.
Yield: 29% of theory,
Melting point: 135-137C (decomp., sintering from
110 C)
C36H42N4O3 x HzO (596.78)
Calculated: C 72.46 H 7.43 N 9.39
Found: 72.50 7.45 9.77
Mass spectrum: M~ = 578
Example. 41
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-[1-(2-hydroxy-ethyl)-4-
isobutyl-5-methyl-imidazol-2-yl]~lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
E [ 2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4-isobutyl-5-methyl-oxazol-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and N-(2-hydroxy-ethyl)-formamide/2-hydroxy-ethylamine.
Example 42
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-[1-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-
4-isobutyl-5-methyl-imidazol-2-yl]-lH-benzimidazol-l-
yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
~3~
- 70 -
[[2~n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4-isobutyl-5-methyl-oxazol-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-formamide/3-
dimethylamino-propylamine.
Example 43
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-~1-carboxymethyl-4-isobutyl-
5-methyl-imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-
biphenyl 2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogousl.y to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[~2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4-isobutyl-5-methyl-oxazol-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and N-formylglycineethylester/glycineethylesterc
Examele 44
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-aminocarbonylmethyl-4-
i.sobutyl-5-methyl-imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4-isobutyl-5-methyl-oxazol-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and N-formyl-glycinamide/glycinamide.
Example 45
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-[1-(2-carboxy-ethyl)-4-
isobutyl-5-methyl-imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4-isobutyl-5-methyl-oxazol-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
and ethyl 3-formylamino-propionate/ethyl 3-
aminopropionate.
'. ' ' ' : :
- : . . . ' : . :
.
:
2~3~
The following may be obtained analogously:
4'-~[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(1,5~dimethyl-4-isobutyl-
imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl~-methyl]-(lH-
tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl
4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-n-propyl-4-isobutyl-5-
methyl-imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-(lH-
tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl
4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-[1-(2-dimethylamino-ethyl)-4-
isobutyl-5-methyl-imidazol-2-yl]-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl
Example 46
Methyl 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4-methyl-imidazol-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate
-
A solution of 0.35 g (0.7 mMol) of methyl 4'-[[2-n-
propyl-4-methyl-6-(4-methyl-imidazolin-2-yl)-lH-
benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate in
10 ml of toluene is mixed with 0.16 g palladium (10% on
activated charcoal) under nitrogen and the mixture is
refluxed for 66 hours. Then the toluene is evaporated
off, the residue is taken up in methylene chloride,
filtered and evaporated down. The crude product is
chromatographed on silica gel (particle size: 0.032-
0.063 mm) using as eluant methylene chloride to start
with, later followed by methylene chloride/ethanol/
ammonia (50:1:0.05, 20:1:0.02, 10:1:0.01 and 5:1:0.005).
The uniform fractions are combined and evaporated down.
Yield: 0.30 g (9~ of theory),
Mass spectrum: M+ = 478
2 ~
- 72 -
~Example 47
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(1,4,5-trimethyl-imidazol-2-
yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl 2-carboxylic
acid 0.25 x H20
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from t* .butyl 4'-[[2-
n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4,5-dimethyl-oxazol-2-yl)-lH-
benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and N-
methyl-formamide/methylamine.
Yield: 61~ of theory,
Melting point: 217-219C (decomp.)
C31H32N402 x 0-25 HzO (497.13)
Calculated: C 74.90 H 6.59 N 11.27
Found: 74.84 6.58 11.26
Mass spectrum: M' = 492
Example 48
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-ethyl-4,5-dimethyl-
imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert~butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4,5-dimethyl-oxazol-2-yl)-lH-
benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and N-
ethylformamide/ethylamine.
Example 49
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-methyl-4,5-diethyl-
imidazol~2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl3-2-(lH-
tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from 4'-[[2-n-propyl-
4-methyl-6-(4,5-diethyl-oxazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-
yl]-methyl]-2-(2-triphenylmethyl-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl
and N-methyl-formamide/methylamine.
.
.: ,-: , , - :
.
'" ~
,. ' ~'
,
,
2~37~
- 73 -
Example 50
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(l-ethyl-4,5-dimethyl-
imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-2-(lH-
tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from 4'-[[2-n-propyl-
4-methyl-6- (4,5-dimethyl-oxazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-
yl~-methyl]-2-(2-triphenylmethyl-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl
and N-ethyl-formamide/ethylamine.
Example 51
.
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-isopropyl-4,5-dimethyl-
imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl~-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4,5-dimethyl-oxazol-2-yl)-lH-
benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and N-
isopropyl-formamide/isopropylamine.
Example 52
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-[1-(2-dimethylamino-ethyl)-
4,5-dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl]-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Exampl.e 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4,5-dimethyl-oxazol-2-yl)-lH-
benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and N-
(2-dimethylamino-ethyl)formamide/2-dimethylamino-
ethylamine.
~37~
- 74 -
Example 53
4'-[[2 n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-[1-(2-morpholino-ethyl)-4,5-
dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl]-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4,5-dime~hyl-oxazol-2-yl)-lH-
benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and N-
(2-morpholino-ethyl)-formamide/2-morpholino-ethylamine.
Example 54
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-[1-(2-morpholino-ethyl)-4,5-
diethyl-imidazol-2-yl]-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-2-
(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from 4'-[[2-n-propyl-
4-methyl-6-(4,5-diethyl-oxazol-2-yl~-lH-benzimidazol-1-
yl]-methyl]-2-(2-triphenylmethyl tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl
and N-(2-morpholino-ethyl)-formamide/2-morpholino-
ethylamine.
Exam~le 55
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-[1-(2--methoxy-ethyl)-4,5-
dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl]-lH-benzim.idazol-1-yl]-methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4,5-dimethyl-oxazol-2-yl)-lH-
benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and N-
(2-methoxy-ethyl)-~ormamide/2-methoxy-ethylamine.
2~3~
- 75 -
Example 56
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-[1-(2-methoxy-ethyl)-4,5-
dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl]-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-2-
(lH-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl
-
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from 4'-[[2-n-propyl-
4-methyl-6-(4,5-dimethyl-oxazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-1-
yl]-methyl]-2-(2-triphenylmethyl-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl
and N-(2-methoxy-ethyl)-formamide/2-methoxy-ethylamine.
Example 57
,
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-[l-(2-carboxy-ethyl)-4,5-
dimethyl-imidazol-2-yl]-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-2-
biphenyl-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2~n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4,5-dimethyl-oxazol-2-yl)-lH-
benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]~biphenyl-2-carboxylate and
ethyl N-formyl-3-aminopropionate~ethyl 3-
aminopropionate.
E mple 58
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-methyl-4,5-diethyl-
imidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylic acid x 0.25 H20
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4,5-diethyl-oxazol 2-yl)-lH-
benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and N-
methyl-formamide/methylamine.
Yield: 65% of theory,
Melting point: 247-249C (decomp.)
C33H36N4O2 x 0.25 HzO (525.18)
Calculated: C 75.47 H 7.01 N 10.67
Found: 75.43 7.11 10.6
2~7~
- 76 -
Mass spectrum: M = 520
Example 59
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyI-6~ methyl-imidazolin-2-yl)-
lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared by heating tert.butyl 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-
6-[2-(N-methylamino)-ethylaminocarbonyl]-lH-
benzimidazol-l-yl]~methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate in
phosphorusoxychloride and isolating analogously to
Example 10.
Yield: 30% of theory,
C2sH30N42 (466.59)
Rf value: 0.50 (methylene chloride/methanol/acetic acid
= 2:1:0.02)
Mass spectrum: (M+H)+ = 467
Exam~le 60
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-[1-(2-dimethylamino-ethyl)-
4,5-diethyl-imidazol-2-yl]-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid-dihydrate-
trihydrochloride
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl~4-methyl-6-(4,5-diethyl-oxazol-2-yl)-lH-
benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and N-
(2-dimethylamino-ethyl)-formamide/2-dimethylamino-
ethylamine.
Yield: 14% of theory,
Melting point: 210C (decomp.)
C36M43N5O2 x 3 HCl x 2 H2O (723.21)
Calculated: C 59.79 H 6.97 N 9.69 Cl 14.71
Found: 59.28 6.92 9.75 14.26
' ,
... . .
.
. : . ~ ,.
' ' ' ': ' , ' ' :
~37~
- 77 -
Example 61
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-[1-(2-morpholino-ethyl)-4,5-
diethyl-imidazol-2-yl]-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-
biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4,5-diethyl-oxazol-2-yl)-lH-
benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and N-
(2-morpholino-ethyl)-formamide/2-morpholino-ethylamine.
Yield: 41% of theory,
Melting point: from 196C (decomp.)
3sH45NsO3 (619.82)
Mass spectrum: M+ = 619
Example 62
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-[1-(2-methoxy-ethyl)-4,5-
diethyl-imidazol-2-yl]-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-
biphenvl-2-carboxylic acid hydrate
Prepared analogously to Example 5 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(4,5-diethyl-oxazol-2-yl)-lH-
benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-carboxylate and N-
(2-methoxy-ethyl)-formamide/2-methoxy-ethylamine.
C3sH4~N4O3 x H20 (582.76)
Calculated x H20 c 72.14 H 7.27 N 9.61
Found: 71.99 7.19 9.84
Mass spectrum: (M-H) = 563
Example 63
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-~4,5-diethyl-oxazol-2 yl]-lH-
benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyll-biphenvl-2-carboxvlic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 29 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-[N-(l-propionyl-n-propyl)-
aminocarbonyl]-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl~-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and phorusoxychloride.
Yield: 97% of theory,
. , .
' ~ ' . ' .
- ~ ' .' .: -
- . ~ : . .
' ', ' ~ ,' ~ ' '': ' ,
2~3~
- 78 -
Melting point: 250-255C
C32H33N3O3 (507.64)
Calculated: C 75.71 H 6.55 N 8.28
Found: 75.77 6.59 8.46
Mass spectrum: M~ = 507
Example 64
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(4,5-diethyl-lH-imidazol-2-
yl]-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-2-(lH-tetrazol-5-yl-
~phenvl
Prepared analogously to Example 25b from 4'-[[2-n-
propyl-4-methyl-6-[N-(1-propionyl-n-propyl)-
aminocarbonyl]-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-2-(2- -
triphenylmethyl-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl and ammonium
acetate/glacial acetic acid.
Yield: 27% of theory,
Melting point: 221 223C
C3ZH34N8 x H20 (530.69)
Calculated: C 70.05 H 6.61 N 20.42
Found: 70.79 6.98 18.83
Mass spectrum: M~ = 530
Example 65
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl 6-(4,5-climethyl-oxazol-2-yl]-
l benzimidazol-l-yll-methylJ-bi~henyl-2~carboxylic acid
Prepared analogously to Example 29 from tert.butyl 4'-
[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-[N-(1-acetyl-ethyl)-
aminocarbonyl]-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-biphenyl-2-
carboxylate and phosphorusoxychloride.
Yield: 88% of theory,
Melting point: 259-260C (decomp.)
C30H29N3O3 x 0-25 ~l2 (484.09)
Calculated: C 74.44 H 6.14 N 8.68
Found: 74.33 6.14 8.69
Mass spectrum: M+ = 479
.
: .
'
. .
2~37~
- 79 -
Example 66
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-methyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl]-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-2'-(2,5-dihydro-5-oxo-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)-
biphenyl
a) 4' [[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-methyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro~enzimidazol-2-yl]-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-2'-thvdroxycarbamimidoyl)-biphenyl
To a solution of 8.4 g (0.12 Mol) of hydroxylamine-
hydrochloride in 30 ml of dimethylsulfoxide are added
30ml of a sodium methoxide solution (30% in methanol) at
room temperature. ~fter 10 minutes, 4.5 g (10 mMol) of
4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-methyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl]-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-2'-cyano-biphenyl are added to this solution and
the suspension obtained is heated to 90C for 12 hours.
After cooling to room temperature the reaction mixture
is poured into 200 ml of ice water. The precepitate
obtained is suction filtered, washed with water,
dissolved in methylene chloride and chromatographed on
silica gel (particle size: 0.023-0.063 mm) using as
eluant mixtures of ethyl acetate, ethanol and
concentrated ammonia (19:1:0.06, 19:1:0.08, l9:1:o.1 and
9:1:0.2). The uniform fractions are combined,
evaporated, triturated with ether and dried.
Yield: 1.2 g (25~ of theory),
Melting point: 221-224C (decomp.)
b) 4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(1-methyl-5,6,7,3-
tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl]-lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-
methyl]-2'-(2,5-dihydro-5-oxo-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)-
biphenyl
To a solution of 0.5 g (1 m~ol) of 4'-[[2-n-propyl-4-
methyl-6-(1-methyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzimidazol-2-yl]-
lH-benzimidazol-l-yl]-methyl]-2'-(hydroxycarbamimidoyl)-
. . . ~ .,
- - ~
.
.
.' ' :'
,
- 80 -
biphenyl and 0.14 ml (l mMol) of triethylamine in 40 ml
of tetrahydrofuran is added a solution of 0.1 ml (1
mMol) of ethyl chloroformate in l ml of methylene
chloride at 5C. After 2 hours at room temperature, the
precipitate formed is suction filtered. After
evaporation of the filtrate the residue obtained is
dissolved in 5 ml of xylene and refluxed for 90 minutes.
After cooling to room temperature, the reaction mixture
is mixed with 20 ml of ethyl acetate, washed with water
and dried over magnesium sulfate. After evaporating the
organic phase, the Gbtained residue is chromatographed
on silica gel (particle size: 0.032-0.063 mm) using as
eluant methylene chloride with increasing amounts of
ethanol (0 to iO%). The uniform fractions are combined,
evaporated, triturated with ether and dried.
Yield: 80 mg (14% of theory),
Melting point: 199C (decomp.)
R~-value: 0.33 (silica gel; ethyl acetate/methanol =
3:1)
C34H34N62 (558.59)
Mass spectrum: (M-H)- = 557
.
The following compound may be obtained analogously to
Example 66:
4'-[[2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-6-(1,4,5-trimethyl-imidazol-2-
yl]-lH-benzimidazol-1-yl]-methyl]-2'-~2,5-dihydro-5-oxo-
1,2 4-oxadiazol-3-vl)-biPhenyl
In the Examples of Pharmaceutical Formulations which
follow, any suitable compound of formula I, particularly
those compounds wherein Rs denotes a group metabolically
convertable in vivo into a carboxy group, or Rs denotes a
carboxy or lH-tetrazolyl group, may be used as the
active substance:
::
. ' ' .
:
:
2~37~
- 81 -
~xample I
Ampoules containing 50 mg of active substance per 5 ml
Active substance 50 mg
KH2PO4 2 mg
Na2HP04 x 2H20 50 mg
NaCl 12 mg
Water for injections ad5 ml
Preparation:
The buffer substances and isotonic substance are
dissolved in some of the water. The active substance is
added and, once it has been completely dissolved, water
is added to make up the required volume.
Exam~le II
Ampoules containing 100 mg of active ~ubstance per 5 ml
Active substance 100 mg
Methyl glucamine 35 mg
Glycofurol 1000 mg
Polyethyleneglycol-polypropylene-
glycol block polymer250 mg
Water for injections ad5 ml
Pre~aration:
Methyl glucamine is dissolved in some of the water and
the active substance is dissolved with stirring and
heating. After the addition of solvents, water is added
to make up the desired volume.
.
~ ' . " ' ' :' . . ' .: ,
,
.
'
` ~ .
2~3 ~
- 82 -
Example III
Tablets containing 50 mg of active substance
Active substance 50.0 mg
Calcium phosphate 70.0 mg
Lactose 40.0 mg
Corn starch 35.0 mg
Polyvinylpyrrolidone 3.5 mg
Magnesium stearate 1.5 mq
200.0 mg
Preparation:
The active substance, CaHPO4, lactose and corn starch are
uniformly moistened with an aqueous PVP solution. The
mass is passed through a 2 mm screen, dried at 50C in a
circulating air dryer and screened again.
After the lubricant has been added, the granules are
compressed in a tablet making machine.
Example IV
Coated tablets containing 50 mg o F active substance
Active substance 50.0 mg
Lysine 25.0 mg
Lactose 60.0 mg
Corn starch 34.0 mg
Gelatin 10.0 mg
Magnesium stearate 1.0 mq
180.0 mg
Preparation:
The active substance is mixed with the excipients and
2~37~
- 83 -
moistened with an aqueous gelatin solution. After
screening and drying the granules are mixed with
magnesium stearate and compressed to form cores.
The cores thus produced are covered with a coating by
known methods. A colouring may be added to the coating
suspension or solution.
.
- : -' , :
',, ' ' ' :
. .
2~37~
- 84 -
Example V
Coated tablets containing 100 mg of active substance
Active substance 100.0 mg
Lysine 50.0 mg
Lactose 86.0 mg
Corn starch 50.0 mg
Polyvinylpyrrolidone2.8 mg
Microcrystalline cellulose 60.0 mg
Magnesium stearate 1.2 mg
` 350.0 mg
Preparation:
The active substance is mixed with the excipients and
moistened with an aqueous PVP solution. The moist mass
is passed through a 1.5 mm screen and dried at 45C.
After drying, it is screened again and the magnesium
stearate is added. This mixture is compressed into
cores.
The cores thus produced are covered with a coating by
known methods. Colourings may be added to the coating
suspension or solution.
Exam~le VI
Capsules containing 250 mg of active substance
Active substance 250.0 mg
Corn starch 68.5 mg
Magnesium stearate 1.5 mg
320.0 mg
2i~3~
- 85 -
Pre~aration:
The active substance and corn starch are mixed together
and moistened with water. The moist mass is screened
and dried. The dry granules are screened and mixed with
magnesium stearate. The final mixture is packed into
size 1 hard gelatin capsules.
Example VII
Oral suspension containing 50 mg of active substance per
5 ml ;
. ~
Active substance 50.0 mg
Hydroxyethylcellulose50.0 mg
Sorbic acid 5.0 mg
70% sorbitol 600.0 mg
Glycerol 200.0 mg
Flavouring 15.0 mg
Water ad 5.0 ml
Pre~aration:
The distilled water is heated to 70C and the
hydroxyethylcellulose is dissolved therein with
stirring. With the addition of sorbitol solution and
glycerol the mixture is cooled to ambient temperature.
At ambient temperature, sorbic acid, flavouring and
active substance are added. The suspension is evacuated
with stirring to remove any air. One dose of 50 mg is
contained in 5.0 ml.
-: , . :' - '. ' ,'' . ::. '
-- , . ~ , .
, ,, : , :: . . .
,
. . ~ , : .
- . ..
', : . , , .. : .
,
2~g~7~
- 86 -
Exam~e VIII
Suppositories containing 100 mg of active substance
Active substance 100.0 mg
Solid fat 1600.0 mq
1700.0 mg
Preparation:
The hard fat is melted. At 40C the ground active
substance is homogeneously dispersed in the melt. It is
cooled to 38C and poured into slightly chilled
suppository moulds.
, . . . :