Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
~o 92/18130 2 1 0 ~ ;1 7 5 PCI`/G892/00647
USE OF GU~NINE DERI\IATIvE OR A PRODRUG THEREOF IN THE TRE~TMENT OF
HIV-l INFECTION
This invention relates to a method of treatment of HIV-1
infection in humans and animals, and to the use of compounds
s in the preparation of a medicament for use in the treatment
of such infection.
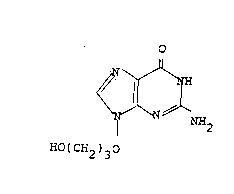
EP-A-242482 ~Beecham Group p.l.c.) discloses BRL 44385, the
compound of formula (A):
o
N.~
N N NH2
HO(CH2)30
(A)
and salts thereof, as antiviral agents.
Pro-drugs of the compound of formula ~A) disclosed
EP-A-242482 are of formula (B):
X
<~ N~
N N NH2
HO(CH2 ) 30
- (B)
and salts and derivatives thereof as defined under formula
(A); wherein X is Cl_6 alkoxy, NH2 or hydrogen. Alternative
pro-drugs are in the form of acetal derivatives of the side
chain, described in EP-A-413544 (Beecham Group p.l.c.),
35 especially 2-amino-9-[3-(isopropoxymethoxy)propoxy)purine,
which is ~L 557a^
.
WO92/18130 PCT/GB92/~K~7
~,~a~ 2- ~`
The compound of formula (A~ and derivatives thereof have
been described as useful i~ the treatment of infections
caused by herpesviruses, such as herpes simplex type l,
herpes simplex type 2, varicella-zoster and Epstein-Barr
s viruses.
It has now been discovered that this compound has potential
activity against the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-l),
in patients also infected with herpesviruses, and are
O therefore of potential use in the treatment of HIV
infections in such patients.
This discovery is related to the ability oî the triphosphate
derivative of BRL 44385 to inhibit the RNA-directed DNA
lS polymerase (reverse transcriptase) activity of human
immunodeficiency virus type l ~HIV-l). The reverse
transcriptase of HIV-l is a virus-encoded enzyme essential
for the conversion of genomic RNA into proviral ds-DNA, and
is therefore an excellent molecular target for antiviral
20 chemotherapy.
The ability of HIV to enter cells previously infected with
herpesviruses is known (for example, B-lymphocytes infected
with EBVl). The presence of both herpes and human
25 immunodeficiency viruses in the same cell has particular
consequences.
1. BRL 44385 would be phosphorylated by herpes
virus-encoded thymidine kinase leading to a high level of
30 BRL 44385 triphosphate. The triphosphate formed is not only
an inhibitor of herpes DNA polymerase, but this work
indicates that it also inhibits HIV reverse transcriptase.
2. HIV replication may be enhanced by herpesvirus
35 transactivating factors. A product of HSV, ICP-4
(infected-cell protein) can increase the initiation of HIV
_ranscription.
. .
. . . ., .... ~ - .
. ' : :
.. ~, ~ ,. .. , . : , . . :
WO92/18130 ~ i PCT/GB92/~7
-3-
3. Double infection of herpesviruses and HIV may result in
phenotypic mixing and the production of 'pseudotype' HIV
particles bearing herpesvirus envelope glycoproteins2. The
packaging of HIV genomic RNA with HSV capsid proteins is
5 also believed to occur. Either situation may lead to the
infection by HIV of CD4-negative, herpesvirus-permissible
cells, previously not susceptible to entry of this virus.
This may also result in doubly-infected cells.
O Accordingly, the present invention provides a method of
treatment of ~IV-l infections in mammals, including humans,
which mammals are infected with herpesviruses, which method
comprises the administration to the mammal in need of such
treatment, an effective amount of a compound of formula (A):
~ N ~ N ~ ~H2
HO(cH2)3O
(A)
2s or a pro-drug, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, of
either of the foregoing.
Examples of pro-drugs, pharmaceutically acceptable salts and
derivatives are as described in the aforementioned European
30 Patent references, the subject matter of which are
0 incorporated herein by reference.
Particular pro-drugs of interest are as described in
EP-A-413544.
3s
WO92/18130 ~ PCT/GB92tOo~7
The compound of formula (A), pro-drugs, salts and
derivatives may be prepared as described in the
aforementioned European Patent references.
5 The compound may be administered by the oral route to humans
and may be compounded in the form of syrup, tablets or
capsule. When in the form of a tablet, any pharmaceutical
carrier suitable for formulating such solid compositions may
be used, for example magnesium stearate, starch, lactose,
o glucose, rice, flour and chalk. The compound may also be in
the form of an ingestible capsule, for example of gelatin,
to contain the compound, or in the form of a syrup, a
solution or a suspension. Suitable liquid pharmaceutical
carriers include ethyl alcohol, glycerine, saline and water
5 to which flavouring or colouring agents may be added to form
syrups.
For parenteral administration, fluid unit dose forms are
prepared containing the compound and a sterile vehicle. The
20 compound depending on the vehicle and the concentration, can
be either suspended or dissolved. Parenteral solutions are
normally prepared by dissolving the compound in a vehicle
and filter sterilising before filling into a suitable vial
or ampoule and sealing. Advantageously, adjuvants such as a
2s local anaesthetic, preservatives and buffering agents are
also dissolved in the vehicle. To enhance the stability,
the composition can be frozen after filling into the vial
and the water removed under vacuum.
30 Parenteral suspensions are prepared in substantially the
same manner except that the compound is suspended in the
vehicle instead of being dissolved and sterilised by
exposure to ethylene oxide before suspending in the sterile
vehicle. Advantageously, a surfactant or wetting agent is
- ~
WO92/18130 '~ ~IQ~ 7 ~ PCT/GB92/00~7
; -5-
included in the composition to facilitate uniform
distribution of the compound of the invention.
~referred parenteral formulatlons include aqueous
s formulations uslng sterile water or normal saline.
As is common practice, the compositions will usually be
accompanied by written or printed di~ections for use in the
medical treatment concerned.
An amount effective to treat the virus infection depends on
the nature and severity of the infection and the weight of
the mammal.
l5 A suitable dosage unit might contain from 50mg to lg of
active ingredient, for example lO0 to 500mg. Such doses may
be administered l to 4 times a day or more usually 2 or 3
times a day. The effective dose of compound will, in
general, be in the range of from 0.2 to 40mg per kilogram of
20 body wei~ht per day or, more usually, lO to 20 mg/kg per
day.
The present invention also provides the use of a compound of
formula (A) or a pro-drug, or a pharmaceutically acceptable
2s salt of either of the foregoing, in the preparation of a
medicament for use in the treatment of HIV-l infections in
mammals, including humans, which mammals are infected with
herpesviruses.
30 Such treatment may be carried out in the manner as
hereinbefore described.
The present invention further provides a pharmaceutical
composition for use in the treatment of HIV-l infections ir.
3s mammals, including humans, infected with herpesviruses,
WO92/18130 ~~ 6- PCT/GB92/~ ~7
which comprises an e~fective amount of a compound of formula
(A) or a pro-drug, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of
either of the foregoing, and a pharmaceutically acceptable
carrier. Such compositions may be prepared in the manner as
s hereinafter described.
The compound of formula (A~ and its prodrugs show a
synergistic antiviral effect in conjunction with
interferons; and treatment using combination products
0 comprising these two components for sequential or
concomitant administration, by the same or different routes,
are therefore within the ambit of the present invention.
It will be appreciated that the treatment of herpesvirus
5 infected patients may include prophylaxis of herpesvirus
episode attacks (suppressive treatment). In patients with
HSV infection only, suppressive treatment would probably
only be given to those patients with frequent recurrences.
In contrast, the aforementioned finding in relation to HIV-
20 1, indicates the need for continuous suppressive treatmentwith ~RL 44385 or a pro-drug to all HIV-1 infected patients
with herpesvirus recurrences, particularly HSV-1, HSV-2 and
VZV recurrences, even though these recurrences may be
infrequent.
The compound of formula (A) and its prodrugs may also be
administered in combination with other antiviral agents,
especially anti-HIV agents such as AZT.
30 The following biochemical data illustrate the invention.
. . . .. , . .. :
.: .- : -- -
:
. . .
` ~.
WO92~18130 ~ ~ ~ 7 3 PCT/GB92/~ ~7
--7--
BIOCHEMICAL DATA
Materials and Methods
s Chemicals [3H]dGTP was purchased from Amersham
International, Aylesbury, U.K. Template primers Poly
(rC). p(dG)12 18 and Poly (dC)- P(dG)l2-l8 were obt
from Pharmacia Ltd., Milton Xeynes, U.K. BRL 44385
triphosphate (BRL 44385-TP) was prepared in the laboratories
o of SmithKline Beecham Pharmaceuticals, Great Burgh, United
Kingdom.
Reverse transcriPtase Purified, E. coli expressed HIV-l
reverse transcriptase (RT) was supplied by the Protein
15 Biochemistry Department of SmithKline Beecham
Pharmaceuticals, Upper Merion, U.S.A. The enzyme was stored
and diluted in a buffer containing 50mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0),
lOmM Hepes, llOmM NaCl, 5.7mM DTT, 0.3mM EDTA, 0.06% Triton
X-100, 50% glycerol.
Assav for reverse transCriPtase activity The reaction
mixture for the HIV-l RT assay contained in a volume of
120~1: 33mM Tris HCl (pH 8.0), lOOmM KCl, 3.3mM MgC12, 3.3mM
dithiothreitol, 0.2mM glutathione, 0.33mM EGTA (ethylene
2s glycol-bis-(~-aminoethyl ether) N,N-tetra acetic acid),
0.033% Triton X-100, 4.0~M [3H]dGTP (4.16 Ci/mmol,
16.7~Ci/ml) 0-50~M BRL 44385-TP, 0-3 A260 units/ml Poly
(rC). p(dG)12_18 or Poly (dC)- P(dG)12-18 and 167ng/ml RT
(equivalent to 1.43nM for an equimolar mixture of p66 and
30 pSl polypeptides). The reaction mixtures without RT were
prepared in the microwells of a 96-well plate and
preincubated at 37C before the reactions were started by
the addition of 20~1 of the enzyme solution. The plates
were then incubated for 95-100 minutes at 37C. The
3s reactions were terminated by the addition of 40~1 of EDTA
WO92/18130 PCT/GB92/~ ~7
~ '?~ 5 -8- ~^
solution (0.2M, pH6.5). The individual reaction mixtures
were transferred to a DEAE filter mat (1205-405, LKB Wallac,
Finland), prewetted with 0.3M NaCl/0.03M Na citrate, using a
cell harvester (1295-001, LKB Wallac). The filter mat was
s washed three times in the NaCl/Na citrate buffer and then
once in 95% ethanol. Scintillation fluid (Beta Plate Scint,
LKB Wallac) was added to the dried filter, and the reaction
mixtures assayed for incorporation of radioactive dGMP in an
LKB 1205 Beta Plate Liquid Scintillation Counter.
Results
From the plot of % inhibition against concentration of
inhibitor approximate IC50 values were obtained for
15 BRL 44385-TP as follows.
Experiment 1
y ( C). P(dG)12-18 temPlate - primer used:-
IC50 BRL 44385-TP - 3.7~M.
Experiment 2
25 Poly (rC). ptdG)12-18 template - primer used:-
IC50 BRL 44385-TP = l.9~M.
y (dC). p(dG)12-18 template - primer used:-
IC50 BRL 44385-TP = 1.2~M.
', ~ .: , ~
WO92~18130 ~-~J~ PCT/GB92/~ ~7
" ,:~
_9_
Conclusion
These results indicate that the concentration of BRL 44385
triphosphate required to give 50% inhibition of HIV-1
5 reverse transcriptase using a RNA template is in the range
1.9 - 3.7~M. When DNA was used as the template for the
reverse transcriptase, the IC50 was 1.2~M. These levels of
BRL 44385-TP should be obtained in the herpes-infected cell.
References
1. Complement Receptor 2 Mediates Enhancement of Human
Immunodeficiency virus infection in Epstein-Barr
virus-carrying B cells.
Tremblay et al., J. Exp. Med. 171, 1791 (1990).
20 2. Phenotypic mixing between human immunodeficiency virus
and vesicular stomatitis virus or herpes simplex
virus.
Zhu et al., J. of AIDS, 3, 215 (1990).