Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CLAIMS
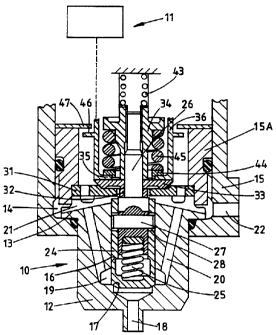
1. An electromagnetically operable fluid control
valve of the ON/OFF type comprising a seating, a valve
member movable between open and closed positions relative
to the seating, an electromagnetic device including a
stator assembly carrying a winding and an armature which
is moved towards the stator assembly when the winding is
energised, a return spring which is stressed during
movement of the armature towards the stator assembly,
means coupling the armature to the valve member, said
means comprising an actuating element operatively
connected to said return spring and a valve member under
travel spring interposed between said actuating element
and the valve member, said under travel spring yielding
to allow continued movement of the actuating element when
the valve member engages the seating, an armature over
travel spring interposed between the armature and said
actuating element and stop means operable to limit the
movement of the valve member away from the seating when
said winding is energised, the armature over travel
spring yielding to permit continued movement of the
armature after said atop means has halted the movement of
the valve member.
2. A fluid control valve according to Claim 1,
including further stop means acting to limit the movement
of the actuating element under the action of the return
spring when the winding is de-energised, said further
stop means being positioned so that the valve member
engages with the seating before the movement of the
actuating element is halted by said further stop means.
3. A fluid control valve according to Claim 2, in
which said stop means and said further stop means are de
fined by a stop plate one face of which is engaged by the
valve member and the other face of which is engaged by a
reaction plate secured to the actuating element.
4. A fluid control valve according to Claim 3,
including a member coupled to the armature and defining
an inturned flange located between said reaction member
and one end of the armature over travel spring, the other
end of the armature over travel spring being engaged with
a spring abutment secured to the actuating element.
5. A fluid control valve according to Claim 4,
including a pin and slot connection between said
actuating element and said valve member.
6. A fluid control valve according to Claim 1,
including a spring abutment mounted on said actuating
element said valve member under travel spring being
located between the valve member and said spring
abutment, said return spring having one end engaging said
spring abutment, and a stop surface defined on a part
movable with the actuating element for limiting the
relative movement of the valve member and the actuating
element under the action of the under travel spring.
7. A fluid control valve according to Claim 6, in
which the other end of said return spring engages a
further spring abutment which is biased by an over travel
spring into engagement with a surface defined on a valve
body, the further spring abutment being engagable by a
flange on the valve member to define the normally open
position of the valve member, and the further spring
abutment being movable away from said surface against the
action of the over travel spring when during the movement
of the valve member away from the seat, the flange
engages the further spring abutment.
8. A fluid control valve according to Claim 7, in
which said actuating element is secured to the armature.