Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
- al18972
- 1 - PATENT APPLICATION
28080/MC566
CHAIN SAW WITH COMPACT BRAKE
Field of the Invention
The present invention relates to chain saws,
and more particularly, to a chain braking arrangement for
chain saws.
Bac~ ouud
Chain saws are prone to exhibit a phenomenon
called "kickback." Kickback typically occurs when the
tip of the saw contacts the wood being cut, or another
solid object, resulting in a violent upward motion which
can endanger the operator. The risk of injury can be
m;nlml zed by stopping the saw chain whenever a kickback
occurs or whenever the operator is at risk of coming into
contact with the saw chain.
Various chain braking arrangements have been
discovered and are disclosed in the prior art. Some
devices use a safety handle which actuates the chain
brake when the handle is struck by the operator's hand or
wrist. Other braking devices use an inertial sensor to
actuate the brake when a kickback or other violent motion
of the saw occurs. ~3Oth such devices are disclosed in
Todero, U.S. Pat. No. 4,420,885.
Moore, U.S. Pat. Nos. 3,739,475 and 3,793,727
disclose a braking arrangement which uses a~ake drum
and brake shoes. The brake drum is fixedly connected to
a chain sprocket which drives a saw chain, and the brake
- ' ~118q72
- 2 - PATENT APPLICATION
28080/MC566
shoes make frlctional contact with the outer circumfer-
ence of the brake drum to stop the saw chain.
Hirschkoff, U.S. Pat. No. 4,059,895 discloses
a band brake for a chain saw comprising a flexible
metallic band which is wrapped around a brake drum. One
end of the band is fixed to the chain saw casing or
chassis. The other end is attached to a mechanical
linkage via a biasing means, typically a spring. In a
brake-off condition, the band is loosely wound around the
brake drum, and is not in contact therewith. In a brake-
on condition, the band is tightened around the brake drum
by the biasing means such that the friction between the
band and the brake drum stops the saw chain substantially
instantaneously.
Wieland et al., U.S. Pat. No. 4,662,072
discloses a band brake for a chain saw wherein a brake
drum is located on a motor drive shaft. This patent
alternatively discloses that the brake drum can be
located elsewhere in the drive train of the saw. Other
prior art designs use the outer casing of a centrifugal
clutch as the brake drum. See, e.g., Hirschkoff, U.S.
Pat. No. 4,026,392.
Typically, chain saw brakes are only used in
the event of a kickback or other violent motion of the
saw. In the future, it is anticipated that one or more
regulatory agencies will require that chainr-~w brakes
must be activated whenever the throttle or trigger is
released. Wieland et al., U.S. Pat. No. 4,680,862
discloses a ~hain saw co~prising an electric coastin~
~ 7 2
- 3 - PATENT APPLICATION
28080/MC566
brake in addition to a mechanical safety brake. Such an
arrangement ensures that the operator will not come into
contact with a moving saw chain as the saw chain coasts
to a stop after the throttle or trigger is released.
Further, it may be desirable to use the safety brake
itself as a coasting brake. However, this will require
an extremely durable brake mechanism since the brake will
be applied at least once every time the saw is used.
Many saws, especially those with electric
motors as their means for motive power, use a reduction
gear to ensure that the saw chain is driven at an optimal
speed. In order to produce a saw with a compact design,
chain saws using a cup-shaped or ring-shaped gear have
been developed. Such a gear is generally cylindrical in
shape and has teeth disposed on the inner surface of a
circumferential wall of the gear which are engaged by a
motor-driven pinion. A cup gear is disclosed in Haupt et
al., U.S Pat. No. 3,857,179 and in the above-noted
Wieland et al. '072 patent. A ring gear is disclosed in
Irgens, U.S Pat. No. 3,669,162.
Cup gears and ring gears have numerous advan-
tages over conventional gears, such as the conservation
of space in the chain saw housing. Cup gears also
protect the gear and pinion mechanisms from cont~m;n~nts~
such as sawdust and dirt. As discussed in the Irgens
'162 patent, cup gears and ring gears can also-~educe the
torque on the drive shaft by ml n ' m; zing the moment arm
acting on the drive shaft. In addition, cup gears and
ring gears have relatively large rotational moments of
- -- ~118472
- 4 - PATENT APPLICATION
28080/MC566
inertia, when compared to conventional gears with
external teeth. As discussed in the Haupt et al. '179
patent, this results in enhanced performance of the chain
saw, especially at low speeds.
Summary of the Invention
According to one aspect of the present inven-
tion, a cup gear is utilized as a braking structure in a
chain saw. More specifically, a pinion driven by a drive
shaft of a motive power means drives a cup gear which in
turn drives a chain sprocket. The cup gear carries a
braking surface which is acted upon by a braking means to
selectively bring the saw chain to a halt.
The braking surface can be an outer circumferential
surface of the cup gear. Alternatively, the braking
surface can be an outer circumferential surface of a
brake drum secured to the outside of the cup gear. An
electric motor can be used as the motive power means in
a chain saw embodying the present invention, and a brake
band can be used as the braking means. The pinion can be
directly driven by the drive shaft for rotation therewith
at all times during operation of the chain saw. Similar-
ly, the chain sprocket can be directly driven by the cup
gear for rotation therewith at all times during the
operation of the chain saw. A mechanical linkage may be
used to activate the braking means.
In an embodiment of the present invention, a
band brake is used in an electric chain saw having a cup
gear as a reduction gear. The band brake comprises a
~118472
- 5 - PATENT APPLICATION
28080/MC566
flexible metallic band having two ends and a brake drum
fixedly attached to the outer surface of the cup gear.
A mechanical linkage is used to actuate the band brake.
The mechanical linkage comprises a pivotally mounted
safety brake lever which carries a pin engaging a cam
follower plate attached to the brake band. During a
brake-on condition, a helical compression spring biases
the brake band in tension tightly around the brake drum.
The present invention allows for significant
weight reduction in the chain saw braking mechanism. The
invention also provides for a compact braking configura-
tion, thereby reducing the width of the chain saw and the
effective moment arm acting on the drive shaft during
braking. Furthermore, a chain saw constructed in
accordance with one embodiment of the present invention
wherein the outer circumference of the cup gear is used
as a braking surface will have fewer parts, thereby
reducing manufacturing costs.
Other features and advantages are inherent in
the apparatus claimed and disclosed or will become
apparent to those skilled in the art from the following
detailed description in conjunction with the accompanying
drawings.
Brlef De~cription of the Drawin~s
Fig. 1 is a perspective view, tak~ from the
rear and above, of a chain saw embodying the present
invention;
` ` 211~72
.
- 6 - PATENT APPLICATION
28080/MC566
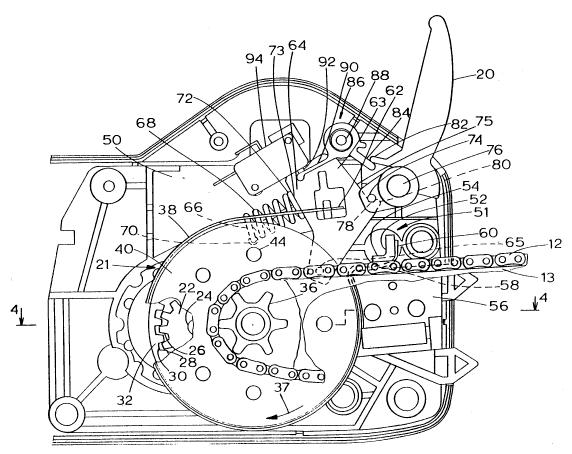
Fig. 2 is a fragmentary elevational view of the
chain saw of Fig. 1 with the gear housing removed and
portions broken away illustrating a chain brake mechanism
in the brake-off position;
5Fig. 3 is a view similar to Fig. 2 illustrating
the chain brake mechanism in the brake-on position;
Fig. 4 is a cross-sectional view taken general-
ly along the lines 4-4 of Fig. 2 of the chain brake
mechanism and pinion together with a motor; and
10Fig. 5 is a view similar to Fig. 4 of an
alternative embodiment of the present invention.
Detalled Description of the Drawin~s
Referring to Fig. 1, a chain saw 10 includes a
saw chain 12, a guide bar 13, a rear handle 14, a front
15handle 16, a motor housing 18, a gear housing 19, and a
safety brake lever 20.
Figs. 2 and 4 show a braking and drive mecha-
nism 21 of the present invention in a first or brake-off
position or configuration. A pinion 22 is fixedly
attached to a motor drive shaft 24 which is driven by a
motor 25. A plurality of pinion teeth 26 disposed on the
pinion 22 engage a plurality of cup gear teeth 28
disposed on an inner surface 30 of a cylindrical wall 32
of a cup gear 34. A chain sprocket 36 is fixedly
attached to the cup gear 34. The chain s~rocket 36
drives the saw chain 12 as it moves along the guide bar
13. It should be noted that the bottom side of the saw
chain 12 moves toward the chain sprocket 36. Thus the
~118472
- 7 - PATENT APPLICATION
28080/MC566
chain sprocket 36, cup gear 34, and pinion 22 all rotate
in a clockwise direction as indicated in Fig. 2 by an
arrow 37.
Although a chain saw powered by an electric
motor 25 is depicted in the drawings, the present
invention is also applicable to chain saws powered by
internal combustion engines.
Referring to Fig. 4, the braking and drive
mechanism 21 comprises a brake band 38 disposed around a
brake drum 40. The brake drum 40 is rigidly attached to
the cup gear 34 by a plurality of stamped bosses 42 which
extend into a plurality of corresponding bores 44 in the
cup gear 34. Each boss 42 includes an enlarged head 46
which, together with an axial face 48 of the brake drum
40, capture the cup gear 34 therebetween. Alternatively,
the brake drum 40 could be secured to the cup gear 34 by
another means of attachment, such as bolts, screws, or
rivets.
A motor housing partition 50 separates the
motor 25 from the braking and drive mechanism 21. As
seen specifically in Fig. 2, an angle bracket 51 having
a vertical portion 52 and a horizontal portion 54, and a
guide bar support 56 protrude from the motor housing
partition 50 and form a channel 58 therebetween. A fixed
end 60 of the brake band 38 is bent at approximately a
right angle so that it fits in the channel 5~and bears
against the vertical portion 52 of the angle bracket 51.
Other means of securing the fixed end 60 of the brake
band 38 may alternatively be used. A moveable end 62 of
Z11847~
- 8 - PATENT APPLICATION
28080/MC566
the brake band 38 is secured by any suitable means to a
cam follower plate 63.
One suitable means of attachment comprises the
following arrangement. The moveable end 62 of the brake
band 38 may be twisted 90 degrees so that it aligns with
an outward facing surface 64 of the cam follower plate
63. The moveable end 62 of the brake band 38 may be
attached to the cam follower plate 63 by a post (not
shown) extending from the cam follower plate 63 which
engages a hole (not shown) in the moveable end 62 of the
brake band 38.
The cam follower plate 63 is pivotally mounted to
the motor housing partition 50 by a cam follower plate
mounting pin 65.
A fixed end 66 of a helical compression spring
68 is fixed within a retaining hole 70 in the motor
housing partition 50. A moveable end 72 of the helical
compression spring 68 bears against a rearward side 73 of
the cam follower plate 63, and may also be attached
thereto by any suitable means. A roller pin 74 carried
by the safety brake lever 20 engages a forward side 75 of
the cam follower plate 63. The safety brake lever 20 is
pivotally mounted to the motor housing partition 50 by a
safety brake lever mounting pin 76.
In the brake-off configuration (as depic~ed in
Fig. 2), the safety brake lever 20 is dis~sed in a
substantially upward or vertical position and the roller
pin 74 engages an indentation 78 and a lobe 80 on the cam
follower plate 63 such that the cam follower plate 63 is
~1 1847~
- g - PATENT APPLICATION
28080/MC566
prevented from rotation about the cam follower plate
mounting pin 65. Thus, the helical compression spring 68
is in a compressed state and the brake band 38 is loosely
wrapped around the brake drum 40 such that the brake band
38 is not in contact therewith.
As seen in Fig. 2, an arm 82 on the safety
brake lever 20 engages a first arm 84 of a brake switch
actuator 86 pivotally mounted on the motor housing
partition 50 at a brake switch actuator mounting pin 88.
A second arm 90 of the brake switch actuator 86 engages
a spring-loaded plunger 92 of a microswitch 94. The
microswitch 94 is configured such that electrical power
is supplied to the motor 25 (Fig. 3) when the plunger 92
is depressed. The plunger 92 is pushed outward from the
microswitch 94 by a spring (not shown) such that the
plunger 92 is extended and the microswitch 94 is open in
the absence of pressure on the plunger 92.
- A second or brake-on position or configuration
is depicted in Fig. 3. When the safety brake lever 20 is
pushed forward tto the right in Figs. 2 and 3), for
example by a user's hand during a kickback condition, the
roller pin 74 moves upwardly, releasing the cam follower
plate 63 for clockwise rotation under the influence of
the force applied by the helical compression spring 68.
The brake band 38 thus is pulled tightly around the brake
drum 40 and the friction between the brake b~d 38 and a
cylindrical flange 96 (Fig. 4) of the brake drum 40
brings the saw chain 12 (not shown in Fig. 3) quickly to
a halt.
~il8472
- 10 - PATENT APPLICATION
28080/MC566
In addition, in the brake-on position, the
plunger 92 of the microswitch 94 is extended and the
microswitch 94 is open. Thus, electrical power is cut
off from the motor 25 when the safety brake lever 20 is
in the brake-on position.
As seen in Fig. 4, the brake drum 40 surrounds
the cup gear 34 and the cylindrical flange 96 of the
brake drum 40 provides a braking surface 97 with which
the brake band 38 comes into frictional contact during
braking. Although not necessary, the cylindrical flange
96 of the brake drum 40 may be radially spaced outwardly
from an outer cylindrical surface 98 of the cup gear 34.
This separation facilitates air flow around the cylindri-
cal flange 96 of the brake drum 40 for better cooling.
Also, it helps m;nlmlze heat transfer from the brake drum
40 to the cup gear 34. As a result, the cup gear 34 can
be made of a less durable, more inexpensive material,
such as plastic.
Fig. 5 shows an alternative embodiment of the
present invention wherein elements common to Figs. 2-4
are assigned like reference numerals. In this
embodiment, an outer surface 198 of a cup gear 134 is
utilized as a braking surface. In such a design, the cup
gear 134 must be manufactured from a durable material,
such as steel. Although this design results in more
weight in the cup gear 134, the absence of~.~a separate
brake drum (40 in Fig. 4) simplifies the manufacture of
the chain saw. Also, the additional inertia of a heavier
~ 7 2
- 11 - PATENT APPLICATION
28080/MC566
cup gear 134 improves performance of the saw at low
speeds.
Numerous modifications and alternative embodi-
ments of the invention will be apparent to those skilled
in the art in view of the foregoing description.
Accordingly, this description is to be construed as
illustrative only and is for the purpose of teaching
those skilled in the art the best mode of carrying out
the invention. The details of the structure may be
varied substantially without departing from the spirit of
the invention, and the exclusive use of all modifications
which come within the scope of the appended claims is re-
served.