Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
-- P HP/LS/K-20EU C A 2 1 2 4 4 1 7
CABLB MAST AND A TR~VERSE FOR S~ME
The present invention relates to a cable mast, such as
an electricity pylon, and to a traverse therefor. The present
invention relates more particularly to a cable mast which has
lower service costs and a smaller environmental impact.
A known cable mast comprises mast elements made of
angle profile which due to its angled form is difficult to
preserve and therefore requires much maintenance. The
strength of angle profiles is moreover such that the mast
elements must be provided with a large number of shores or
bend shorteners. Such a so-called lattice mast reguires much
maintenance and as a result of galvanized coating being
washed off the environmental impact is relatively great.
The invention has for its object to provide a cable
mast which substantially does not possess the above
drawbacks.
This is achieved with a cable mast according to the
invention which comprises a mast to be placed on a base
structure and at least one traverse supported by the mast for
suspending high-voltage cables therefrom, wherein the rising
mast elements consist of tubular section and are internally
stabilized with stabilizing elements. Because the mast
elements are manufactured from tubular section with a evenly
formed outer surface, such tubular sections are easy to coat.
Because these tubular sections moreover possess a greater
strength, in particular an enhanced bending behaviour, bend
shorteners can substantially be dispensed with and the number
of joints is also reduced. For absorption and conduction of
the loads the cable mast according to the invention must
however be provided internally with tubular diagonals and/or
be stabilized internally.
According to a first embodiment a cable mast according
to the invention comprises meander stabilizing elements
snaking upward in each case between two mutually adjoining
mast elements, wherein preferably the bottom meander
` CA21 2441 7
~ stabilizing element engages onto a torsion bracing coupling
the mast elements. With such a so-called meander mast a
reduction of the surface area (about 478 m2) is obtained
compared to the known 380/110 kV lattice mast (about 990 m2).
According to another embodiment the cable mast
according to the invention comprises stabilizing elements
which are arranged in the shape of a cross running outward
from a cross piece between two mast elements and the cross
piece is connected to a torsion bracing. With this embodiment
the surface area for a 380/110 kV mast is reduced to about
516 m2.
According to another embodiment the cable mast
according to the invention comprises stabilizing elements
which converge between two mast elements to a cross beam
arranged between the two mast elements. With this embodiment
the surface area is reduced to about 630 m2.
According to another embodiment mast elements are
mutually connected by a torsion bracing comprising a cross
beam and the stabilizing elements are connected to adjoining
cross beams. In this case the surface area amounts to about
700 m2.
According to the above described embodiments the cable
masts according to the invention can comprise two or four
mast elements. In the case of two mast elements the lateral
stability transversely of the traverse is substantially
obtained by a good foundation and the tensile load by the
wires hanging thereon, such as high-voltage cables and
lightning conductors.
According to another embodiment the cable mast
according to the invention comprises mast elements which
comprise two foundation mast elements and a floating mast
element which support via shoring elements, and stabilizing
elements which are connected between two torsion bracings to
a foundation mast element and a floating mast element. This
embodiment has a very remarkable and aesthetic appearance.
For a further reduction in the surface area for
maintaining it is further recommended that in accordance with
a first embodiment a traverse comprises two tubular traverse
3 CA212441 7
girders, and in accordance with another embodiment the
traverse comprises a tubular traverse girder.
The cable masts according to the invention are
generally free of climbing devices but service and inspection
can take place using a chair lift which can be fixed for
sideways sliding to the traverse. Optionally the traverse can
also be provided with a walkway.
According to a further aspect of the invention the
traverse consists of one or two tubular traverse girders
which are fixed to the mast elements.
Mentioned and other features of the cable mast and the
traverse according to the invention will be further
elucidated hereinbelow in the light of a number of em-
bodiments given only by way of example, while reference is
made to the annexed drawing.
In the drawing:
figures 1-8 each show a perspective view of a cable
mast according to the invention.
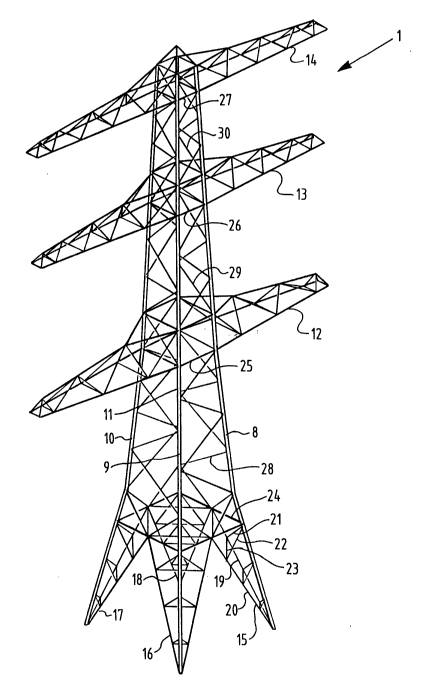
Figure 1 shows a 380/110 kV cable mast 1 according to
the invention. The mast is constructed from four mast
elements 8-11 and three traverses 12-14. The mast elements
are manufactured from tubular section of 220 mm square up to
the traverse 12, of 180 mm square up to the traverse 13 and
120 mm square up to the top. Mast elements 8-11 each form a
leg 15-18 with edge elements 19-20 and shores 21-23. The edge
elements 19-20 are connected to a traverse platform 24.
Torsion bracings 25-27 are also situated at the level of
traverses 12-14. Meander stabilizing elements 28-30 are
arranged snaking upward in each case between two mutually
adjoining mast elements 8 and 9. The number of components
amounts to 478, the number of connections to 846 and the
weight to 35,600 kg.
In the cable mast 2 according to figure 2 the edge
elements 19 extend as far as an intermediate platform 31 and
likewise consist of tubular section (diameter 355 mm, 244 mm
and 152 mm respectively), whereby the shores 21-23 can also
be dispensed with.
The traverses 32-34 consist of two tubular traverse
girders 35 and 36 held at a mutual distance by cross pieces
` ` CA2124417
~ 37 and 38 on which rests a walkway. Stabilizing elements 42
and 43 are connected to the ends 40 and 41 of the traverse.
The number of components amounts to 344, the number of
connections to 585 and the weight to 39,400 kg.
Figure 3 shows a cable mast 3 according to the
invention wherein the four legs of the mast 3 are formed only
by the tubular mast elements 44-47 which are each divided
into three sections 48-50 (diameter dimensions 356 mm, 216 mm
and 193 mm). Stabilizing elements 51-54 are arranged in the
shape of a cross running outward from a cross piece, in each
case between two mast elements 44 and 45. The cross piece 55
is connected to a torsion bracing 56. The stabilizing
elements 51-54 are all under tension. The stabilizing
elements 51 and 52 end at the height of a torsion bracing 57
which is provided with internal stabilizing elements 58 and
59. Traverse 60 is a single tubular section resting in a
torsion bracing 61 and is further connected to the mast
elements 44 and 45 via stabilizing elements 62 and 63.
Suspended from the traverse 60 is an insulator 64 which is
joined via a connecting element 65 to a high-voltage cable to
be suspended thereon.
The number of components amounts to 220, the number of
connections to 458 and the weight to 36,880 kg.
The cable mast 4 according to the invention shown in
figure 4 once again comprises four mast elements 66-69 of
tubular section (diameter 356 mm) and a number of torsion
bracings 70 formed from cross beams 71 arranged between two
mast elements 66-67.
Stabilizing elements 72 and 73 are under tensile strain
and are connected to a mast element 66, 67 and on the other
side to the centre of a cross beam 71. Stabilizing elements
77, 78 are arranged between adjoining cross beams 71, 74-76.
The number of components amounts to 95, the number of
connections to 194 and the weight to 41,475 kg.
In the cable mast 5 shown in figure 5 only the torsion
bracings 70 are now retained, with therebetween the
transverse and lateral stabilizing elements 77, 78
respectively. The diameter dimension of the mast elements 79-
~ ~` 5 ~A2124417
~ 82 is 508 mm, the number of components amounts to 55, the
number of connections to 114 and the weight to 58,400 kg.
In the cable mast 6 according to figure 6 the two mast
elements 83 and 84 consist of a profile that is oval-shaped
in section and bent (largest dimension 1200 mm, smallest
dimension 600 mm) having cross beams 85, 86 therebetween.
Cross beam 85 is joined to the mast elements 83 and 84 via
stabilizing elements 87 and 88 and 89 and 90. The tubular
traverse 60 is provided with only one stabilizing element 91.
The number of components amounts to 88, the number of
connections to 74 and the weight to 56,025 kg.
Figure 7 shows a cable mast 7 according to the
invention of exceptionally aesthetic form. Cable mast 7
comprises two foundation mast elements 92 and 93 (diameter
609 mm) and a floating mast element 94 (diameter 298 mm).
Mast elements 92 and 93 support via the shores 95 and 96 and
the mast element 94 supports via shores 97 and 98. A torsion
bracing 99 consists of cross beams 100-102. Stabilizing
elements 104 and 105 are arranged between two torsion
bracings 99 and 103. A tubular traverse 106 is suspended via
stabilizing elements 107 and 108.
- Stabilizing elements 109, 110 are further arranged at
the height of the torsion bracing 103 between the foundation
mast elements 92 and 93 and the floating mast element 94.
The number of components amounts to 38, the number of
connections to 93 and the weight to 42,350 kg.
Finally, figure 8 shows a cable mast 115 according to
the invention which is constructed from four mast elements
111-114 manufactured from a tubular section with a diameter
of about 320 mm up to the traverse 116, with a diameter of
219 mm up to traverse 117 and a diameter of 139 mm up to
traverse 118.
The cable mast 115 comprises four legs 119-122 which
are assembled from a mast element and two edge elements 123
and 124 which extend as far as the first intermediate
platform 125. At the height of crossing edge elements 123 and
124 is situated a junction 126 which, with the other three
junctions, forms part of the traverse platform 127.
` 6 CA2124417
~ Torsion bracings 128, 129 and 130 are likewise situated
at the height of the traverses 116, 117 and 118.
The traverses 116, 117 and 118 have a construction
corresponding with the traverses of figures 3-6.
It will be apparent that for types of mast other than
the described 380/110 kV mast equivalent advantages are
obtained.
*****