Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
- 2126612
EAT 0122 PUS 92-rTRN-344
AUXILIARY TRANSl\IISSION SECTION
Terhnil ~l Field
The present invention relates to an auxiliary
transmission section for a compound transmission and,
more particularly, to an improved auxiliary transmission
section including a countershaft clutch arrangement.
Ba~k~round Art
Compound change gear transmissions of the type
having one or more auxiliary sections connected in
series with a main transmission section are well known
in the prior art. Briefly, by utilizing main and
auxiliary transmission sections connected in series,
assuming proper sizing of the ratio steps, the total of
available transmission ratios is equal to the product of
the main and auxiliary section ratios. By way of
example, at least in theory, a compound change gear
transmission comprising a four (4) speed main section
connected in series with a three (3) speed auxiliary
section will provide twelve (4x3=12) available ratios.
Auxiliary transmission sections are of three
general types: range type, splitter type or combined
range/splitter type.
In compound transmissions having a range type
auxiliary section, the ratio step or steps may be
greater, equal or less than the total ratio coverage of
the main transmission section and the main section is
shifted progressively through its ratios in each range.
`- 2126612
- EAT 0122 PUS -2- 92-rTRN-344
Examples of compoundtransmissions having range type
auxiliary sections may be seen by reference to U.S.
Patent Nos. 3,105,395; 2,637,222 and 2,637,221.
In compound transmissions having a splitter
type auxiliary section, the ratio steps of the splitter
auxiliary section are less than the ratio steps of the
main transmission section and each main section ratio is
split, or subdivided, by the splitter section. Examples
of compound change gear transmissions having splitter
type auxiliary sections may be seen by reference to U.S.
Patent Nos. 4,Z90,515; 3,799,002; 4,440,037 and
4,527,447.
In a combined range and splitter type auxilia-
ry section, or sections, both range and splitter type
ratios are provided allowing the main section to be
progressively shifted through its ratios in at least two
ranges and also allowing the main section ratios to be
split in at least one range.
One Example of a compound transmission
having a single combined range/splitter type
auxiliary section may be seen by reference to U.S.
Patent Nos. 3,283,613; 3,648,546 and to publication
Small Scale Print No. 016-AD; Fuller~ Transmissions;
Models RT-14613, RTO-14613, RTO0-14613, published
March 1981 by Eaton Corporation, assignee of this
invention. Another example is the "Ecosplit"~ model
of transmission sold by
TM-Trade-mark
2126612
EAT 0122 PUS -3- 92-rTRN-344
Zahnradfabrik Friedrichshafen Aktiengeseushaft of
Friedrichshafen, Federal Republich of Germany which
utilizes a separate splitter auxiliary section in front
of, and a separate range auxiliary section behind, the
main transmission section.
It should be noted that the terms main and
auxiliary sections are relative and that if the designa-
tions of the main and auxiliary sections are reversed,
the type of auxiliary section (either range or splitter)
will also be reversed. In other words, given what is
conventionally considered a four-speed main section with
two-speed range type auxiliary section, if the normally
designated auxiliary is considered the main section, the
normally designated main section would be considered a
four-speed splitter type auxiliary section therefor. By
generally accepted transmission industry convention, and
as used in this description of the invention, the main
transmission section of a compound transmission is that
section which contains the largest (or at least no less)
number of forward speed ratios, which allows selection
of a neutral position, which contains the reverse
ratio(s) and/or which is shifted (in manual or semiauto-
matic transmissions) by manipulation of a shift bar or
shift rail or shift shaft/shift finger assembly as
opposed to master/slave valve/cylinder arrangements or
the like.
A conventional auxiliary transmission section
such as that disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 4,754,665
includes an auxiliary section input shaft and an output
shaft cooperably forming a mainshaft assembly, and an
auxiliary countershaft assembly. A two-way clutch is
2126612
EAT 0122 PUS -4- 92-rTRN-344
provided on the mainshaft assembly and clutching occurs
on the ma1nshaft to drive the countershaft assembly.
Disclosure Of Invention
Accordingly, an object of the present inven-
tion is to provide a new and improved auxiliary trans-
mission section wherein an auxiliary countershaft is
drivable through engagement with a mainshaft or coun-
tershaft.
Another object of the present invention is to
provide a new and improved three-layer, four-speed
auxiliary transmission section of the range and splitter
type for a compound change gear transmission which has
a simpler and less costly mounting of the center layer
input gear.
A further object of the present invention is
to provide a new and improved auxiliary transmission
section of the combined range/splitter type having a
shorter length through the use of one engaged position
splitter clutch assembly on the input shaft and a second
one engaged position clutch assembly on the counter-
shaft.
In car ying out the above objects, the im-
proved auxiliary transmission section is a combined
range/splitter type auxiliary transmission section for
a compound change gear transmission comprising an
auxiliary transmission section. The auxiliary trans-
mission section comprises a housing, an auxiliary
section input shaft extending into the housing and
driven by the main transmission section and an output
2~26~12
EAT 0122 PUS -5- 92-rTRN-344
shaft extending from the housing. The auxiliary trans-
mission section is characterized by a mainshaft input
gear rotationally fixed to the auxiliary section input
shaft, a mainshaft splitter gear coaxial with and
rotatable relative to the auxiliary section input shaft,
and an output shaft range gear coaxial with and rotat-
able relative to said output shaft.
The auxiliary transmission section also
comprises an auxiliary section countershaft assembly
including an auxiliary countershaft rotationally sup-
ported in the housing, a countershaft splitter gear
coaxial with and rotatable relative to the auxiliary
countershaft and constantly meshed with the mainshaft
input gear, a first auxiliary countershaft gear rota-
tionally fixed to the auxiliary countershaft and con-
stantly meshed with the mainshaft splitter gear, and a
second auxiliary countershaft gear rotationally fixed to
the auxiliary countershaft and constantly meshed with
the output shaft range gear. A first one engaged
position splitter clutch assembly is fixed for rotation
with the auxiliary section input shaft for coupling said
mainshaft splitter gear with the auxiliary section input
shaft and a second one engaged position splitter clutch
assembly is fixed for rotation with the auxiliary
section countershaft for coupling the countershaft
splitter gear with the auxiliary section countershaft
and a control means for alternatively positioning one of
the clutch assemblies for alternatively positioning one
of said clutch assemblies for engagement thereof to
establish a torque flow path from the auxiliary section
input shaft to the output shaft.
- 2126612
EAT 0122 PUS -6- 92-rTRN-344
The above objects and other objects, features,
and advantages of the present invention are readily
apparent from the following detailed description of the
best mode for carrying out the invention when taken in
connection with the accompanying drawings.
Brief Description Of The D~w;..~
FIGURE 1 is a schematic illustration of a
prior art main transmission section of a compound
transmission;
FIGURE 2 is a schematic illustration of an
auxiliary transmission section constructed in accordance
with the present invention for coupling with a main
transmission section of a compound transmission;
FIGURE 3 is a partial assembly cross-sectional
view of a prior art three-layer combined range/splitter
type auxiliary transmission section; and
FIGURE 4 is a partial assembly cross-sectional
view of one embodiment of an auxiliary transmission
section constructed in accordance with the present
invention illustrating a shorter combined range/splitter
type auxiliary transmission section with simpler, lower
cost center layer gear mounting on the input shaft.
Best Mode For Ca~lyi.-~ Out The Il~v~.llion
Certain terminology will be used in the
following description for convenience only and will not
be limiting. The words "upwardly", "downwardly",
212~612
EAT 0122 PUS -7- 92-rTRN-344
"rightwardly", and "leftwardly" will designate direc-
tions in the drawings to which reference is made. The
words "forward" and "rearward" will refer respectively
to the front and rear ends of the transmission as
conventionally mounted in the vehicle, being respective-
ly to the left and right sides of the prior art main
transmission section illustrated in Figure 1.
The term "compound transmission" is used to
designate a change speed or change gear transmission
having a main transmission section and an auxiliary
transmission section connected in series whereby the
selected gear reduction in the main transmission section
may be compounded by further selected gear reduction in
the auxiliary transmission section. The term "upshift"
as used herein shall mean the speed gear ratio is
changed from a lower value to a higher value. The term
~'downshift" as used herein shall means the shifting from
a higher speed gear ratio to a lower speed gear ratio.
The terms "low speed gear" or "low gear" as used herein
shall designate a gear ratio utilized for relatively
lower forward speed operation in a transmission, i.e. a
set of gears having a higher ratio of reduction of
output shaft speed relative to the speed of the input
shaft. "Synchronized clutch assembly" and words of
similar import shall designate a clutch assembly uti-
lized to non-rotatably couple a selected gear to a shaft
by means of a positive clutch in which attempted engage-
ment of said clutch is prevented until the members of
the clutch are at substantially synchronous rotation and
relative large capacity friction means are associated
with the clutch members and are sufficient, upon initia-
tion of a clutch engagement, to cause the clutch members
2126612
EAT 0122 PUS -8- 92-rTRN-344
and all members rotating therewith to rotate at a
substantially synchronous speed.
The auxiliary transmission section 10 herein-
after disclosed is used in combination with a main
transmission section 12 to provide a compound transmis-
sion.
One example of a main transmission section 12
is hereinafter disclosed for purposes of describing the
auxiliary transmission 10. Other types of main trans-
mission sections can be connected up to the auxiliarytransmission section 10.
With reference to Figure 1, a prior art main
transmission section is schematically illustrated.
Typically, the auxiliary transmission section 10 and
main transmission section 12 are housed within a single
housing. Main transmission section 12 includes an input
shaft 16 driven by a prime mover such as diesel engine
E through a selectively disengaged, normally engaged
friction master clutch C having an input or driving
section 18 drivingly connected to the engine crankshaft
and a driven portion 22 rotatably fixed to the
transmission input shaft 16.
In the main transmission section 12, the input
shaft 16 carries an input gear 24 for simultaneously
driving a plurality of substantially identical main
section countershaft assemblies 26 and 26a at substan-
tially identical rotational speeds. In the transmission
10 illustrated, two substantially identical main section
countershaft assemblies are provided on diametrically
opposite sides of a mainshaft 28, which mainshaft is
2126612
-
EAT 0122 PUS -9- 92-rTRN-344
generally coaxially aligned with the input shaft 16.
Each of the main section countershaft assemblies 26 and
26a comprises a main section countershaft 30 supported
by bearings 32 and 34 in housing H, only a portion of
which is schematically illustrated.
Each of the main section countershafts 30 is
provided with an identical grouping of main section
countershaft gears 38, 40, 42, 44, 46 and 48, fixed for
rotation therewith. A plurality of main section drive
or mainshaft gears 50, 52, 54, 56 and 58 surround the
mainshaft 28 and are selectively clutchable, one at a
time, to the mainshaft 28 for rotation therewith by
sliding clutch collars 60, 62 and 64 as is well known in
the art. Clutch collar 60 may also be utilized to
clutch input gear 24 to mainshaft 28 to provide a direct
drive relationship between input shaft 16 and mainshaft
28. Preferably, each of the main section mainshaft
gears encircles the mainshaft 28 and is in continuous
meshing engagement with and is floatingly supported by
the associated countershaft gear group.
Typically, clutch collars 60, 62 and 64 are
axially positioned by means of shift forks (not illus-
trated) associated with a shift bar housing assembly
(not illustrated) as well known in the prior art.
Clutch collars 60, 62 and 64 are of the well known non-
synchronized double acting jaw clutch type.
With continued reference to Figure 1, main
section mainshaft gear 58 is the reverse gear and is in
continuous meshing engagement with countershaft gears 48
by means of conventional intermediate idler gears (not
shown). It should also be noted that while main trans-
2126612
EAT 0122 PUS -10- 92-rTRN-344
mission section 12 does provide five selectable forward
speed ratios, the lowest forward speed ratio namely,
that ratio provided by drivingly connected mainshaft
drive gear 56 to mainshaft 28 is often of such a high
gear reduction as to be considered a low or "creeper"
gear which is utilized only for starting of a vehicle
under severe conditions and is usually not utilized in
the high transmission range and/or may not be split in
the low transmission range.
Jaw clutches 60, 62 and 64 are three-position
clutches in that they may be positioned in a centered,
non-engaged position as illustrated or in a fully
rightwardly engaged or fully leftwardly engaged posi-
tion.
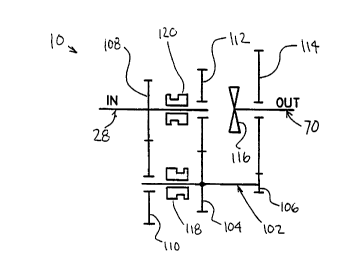
Referring now to Figure 2, auxiliary transmis-
sion section 10 is described with reference to main
transmission section 12 although the auxiliary transmis-
sion section described can be utilized with other type
main transmission sections. Auxiliary transmission
section 10 includes an auxiliary countershaft 102
carrying two auxiliary section countershaft gears
104,106 fixed for rotation therewith. A mainshaft gear
108 i9 constantly meshed with and support~ a splitter
gear 110 which surrounds countershaft 102. Auxiliary
countershaft gear 104 is constantly meshed with and
supports auxiliary section splitter gear 112 which
surrounds mainshaft 28. Auxiliary countershaft gear 106
is constantly meshed with and supports auxiliary section
range gear 114 which surrounds output shaft 70. A two-
way synchronizer assembly 116 is utilized to couple
splitter gear 114 to output shaft 70.
`_ 2126612
EAT 0122 PUS ~ 92-rTRN-344
A sliding one position jaw clutch collar 118
is utilized to selectively couple splitter gear 110 to
the auxiliary countershaft 102 to establish a first
torque flow path between mainshaft 28 and output shaft
70. Alternatively, a sliding one position jaw clutch
collar 120 is utilized to selectively couple splitter
gear 112 to the mainshaft 28 to establish a second
torque flow path between the mainshaft and output shaft
70. Many of the well known synchronized positive clutch
structures are suitable for use in the auxiliary trans-
mission section of the present invention.
With continued reference to Figure 2, by
selectively axially positioning both jaw clutch collars
118,120 in the forward and rearward axial positions
thereof, four distinct ratios of mainshaft rotation to
output shaft rotation may be provided. For example,
RATIORATIO CLUTCH CLUTCH ~Y~KONIZER
SPLITTER RANGE 118 120 116
OD LOENGAGED DISENG REARWARD
DIR LODISENG ENGAGED REARWARD
OD HIENGAGED DISENG FORWARD
DIR HIDISENG ENGAGED FORWARD
Accordingly, auxiliary transmission section 10
is a 3-layer auxiliary section of the combined range and
splitter type providing four selectable speeds or drive
ratios between the input (shaft 28) and output (output
shaft 70) thereof. In the compound transmission de-
scribed, the main section 12 provides a reverse and five
potentially selectable forward speeds. However, one of
these selectable forward gear ratios (gear 56) is often
a creeper or low gear not intended to be used in the
21~612
EAT 0122 PUS -12- 92-rTRN-344
high range. Thus, the compound transmission is properly
designated as a (4+1)x(2)x(2) type transmission provid-
ing 17 or 18 selectable forward speeds depending upon
the desirability and/or practicality of splitting the
low or creeper gear.
The detailed structure of the preferred
embodiment of auxiliary transmission section 10 is
illustrated in Figure 4. A prior art auxiliary section
10' is illustrated in Figure 3. In the description that
follows, like reference numerals will be used to identi-
fy like structure in both auxiliary transmissions 10,
10 ' .
Referring to Figure 4, the rearward end of
mainshaft 28 extends into the auxiliary transmission
section 10 and is provided with external splines 130
which mate with internal splines 132 on clutch collar
120 for rotationally coupling clutch collar 120 to the
mainshaft 28 while allowing relative axial movement
therebetween. The clutch collar 120 is provided with
clutch teeth 134 for selective axial engagement with
clutch teeth 136 provided on gear 112. The clutch
collar 120 is also provided with a groove 138 for
receipt of a shift fork 140. Gear 112 surrounds main-
shaft 28 and is normally free to rotate relative thereto
and is axially retained relative to the mainshaft 28 by
means of retainers 142 and 143. Gear 112 is in continu-
ous meshing engagement with gear 104 which is fixed for
rotation with countershaft 102. Countershaft 102 is
provided with external splines 144 which mate with
internal splines 146 provided in clutch collar 118 for
rotationally coupling clutch collar 118 to the counter-
shaft 102 while allowing relative axial movement there-
2126612
EAT 0122 PUS -13- 92-rTRN-344
between. The clutch collar 118 is provided with clutch
teeth 148 for selective axial engagement with clutch
teeth 150 provided on gear 110. The clutch collar 118
is also provided with a groove 152 for receipt of a
shift fork 154.
Gear 110 surrounds countershaft 102 and is
normally free to rotate relative thereto. Gear 110 is
in continuous meshing engagement with gear 108 which is
fixed for rotation with mainshaft 28.
Located axially between gears 108 and 114, and
rotationally fixed to output shaft 70 by means of
external splines 158 and internal splines 160, is the
double-acting two position synchronized clutch assembly
116. Many of the well known synchronized positive
clutch structures are suitable for use in the auxiliary
transmission section 10 of the present invention.
Synchronized clutch assembly 116 illustrated is of the
pin type described in U.S. Patent No. 4,462,489.
The prior art auxiliary transmission section
10' of Figure 3 is described in detail in U.S. Patent
No. 4,754,665 assigned to the assignee of the present
in~ention. With reference to Figure 3 herein, the
auxiliary section 10' includes a single clutch collar
162 provided with clutch teeth 164 and 166 for selective
axial engagement with clutch teeth 168 and 170 provided
on gear 112' and on splitter/range gear 172 which is
rotationally supported at the inward end 174 of output
shaft 70~.
By contrasting Figures 3 and 4, it can be
appreciated that the use of the 2 one-engaged position
212~512
EAT 0122 PUS -14- 92-~^TRN-344
clutches 118 and 120 in the auxiliary transmission
section 10 requires less axial displacement for opera-
tion than does the 1 two-engaged position clutch collar
162 of the prior art auxiliary transmission section 10'.
S While the best mode for carrying out the
invention has been described in detail, those familiar
with the art to which this invention relates will
recognize various alternative designs and embodiments
for practicing the invention as defined by the following
claims.