Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
,vo 93/15732 21 2 8 3 r~ ~1 pcI/uss3!ol43l
Treatment of g!auc ma
The term glaucoma cove,rs pathological symptoms of the eye that are attributable eo
elevated intra-ocular pressure. Obstruction of the movement of aqueous humour often
causes an increase in intra-ocular pressure. Chronically increased intra-ocular pressure has
a damaging effect on the op~ic nerve and the re~ina, which can result not only in a
restricted field of vision but also in blindness.
~ccordingly, the search for active ingredients that are able significantly to reduce intra-
ocular pressure is regarded as very important. U.S. Patent No. 5 036 048 describes angio-
tensin-II antagonists as being suitable agents for the treatment of glaucoma
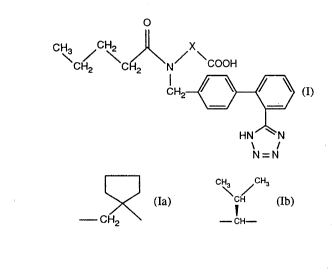
Extensive phannacological studies have shown that the compounds of the formula
CH2 CH)I\N/ COOH
CH2~ (I), wherein
HN N
N=N
X is 5~ ~c/ (Ib) the carboxy group being linked direclly
--CH2 --CH--
to the cyclopentyl rin~ in the case where X = (la~, and their salts are suitable to a
surprising degree for reducing intra-ocular pressure. This effect is achieved not only by the
topical adminis~ration of the active ingredient but also by its systemic administration.
The compounds of formula (I) and their salts were also found to have a surprisin_ly lono
dura~ion of ac~ion when used in lhe treatmenl of male albino rats, in which intra ocular
~,~?,~3~ ~
Wo 93/15732 pcr/us93/ol4
hypertension had been produced, using the glucocor~icoid model.
The compounds of formula (I) or salts thereof are also distinguished by being extremely
well tolerated by the eye, which can be demonstrated in a test model using rabbits' eyes.
For that purpose, eye drops comprising the ac~ive ingredient in different concentrations are
administered to the conjunctival sac of animals of the Himalaya type (pigmented~, for
example over a period of five days. Ophthalmological and ophthalmopathological
examinadons revealed no local or systemic intolerances.
Another surprising effect is that the compounds of formula ~I) and their salts have a
vaso-relaxing èffect on the eye, both when administered topically and when administered
sy.~temically, and can accordingly be used in the treatment of vasospastic constitu~ions of
the eye.
In addition, the compounds of formula (I) a ld the,r salts can be used in the trea~nent of
diabetic retinopathy.
The compounds of formula (I) and their salts are described in the European Patent Applic-
ation having the publication number 443 983 as angiotensin-II antagonists, in particular
specifically in Examples 16 [(S~-N-(l-carboxy-2-methylprop-1-yl)-N-pentanoyl-N-[2'-
( I H-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl-4-ylmethyl~-amine3 and 40 lN-(2-carboxy-2,2-tetra-methylene-ethyl)-N-pentanoyl-N-12'-( 1 H-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl~-ylmethyl)-amine~ .
The present invention relates to the use of the compounds of formula (1) and their salts in
the preparation of pharmaceu~ical compositions for the treatment of glaucoma, for increas-
ing the movement of (retinal) intra-ocular fluid, being the aqueous humour, for the
trea~ment of vasospastic constitutions of the eye and for the treatment of diabetic retino-
pathy.
The present Application relates also to a method of treatin~ glaucoma, increasing the
movement of (retinal) intra-ocular fluid, treatin~ vasospastic constitutions of the eye an
treatin~ diabetic retinopathy, which method comprises administering to patients requiring
such treatment a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I) or of a
pharmaceu~ically acceptable salt thereof.
Compounds (1) and. where appropriate. their tautomers may be in the form of salls.
~'0 93/15732 212 ~3 3 2 ~ PCI/US93/01431
especially phaImaceutically acceptable salts. Because compounds (I) have, for example, at
least one basic centre, they can form acid addition salts. The latter are formed, for
example, with strong inorganic acids, such as mineral acids, for example sulfuric acid, a
phosphoric acid or a hydrohalic acid, with strong organic carboxylic acids, such a~s unsubs-
tituted or substitu~ed, for example halo-substituted, Cl-C4alkanecarboxylic acids, for
example acetic acid, such as saturated or unsaturated dicarboxylic acids, for example
oxalic, malonic, succinic, maleic, fumaric, phthalic or terephthalic acid, such as hydroxy-
carboxylic acids, for example ascorbic, glycolic, lactic, malic, tartaric or citric acid, such
as amino acids, for example aspartic or glu~nic acid, or such as benzoic acid, or with
organic sulfonic acids, such as unsubstituted or substituted, for example halo-substituted,
Cl-C4aLkanesulfonic or arylsulfonic acids, for example methane- or p-toluene-sulfonic
aci5!"Corresponding acid addition salts can also be formed with any additional basic
~entre that may be present. Furthermore, compounds (I), having the acidic 5-tetrazolyl
group, can form salts with bases. Suitable salts with bases are, for example, metal~salts,
such as aL~cali metal or aL~caline earth metal salts, for example sodium, potassium or
magnesium salts, or salts with ammonia or an organic amine, such as morpholine, thio-
morpholine, piperidine, pyrrolidine, a mono-, di- or tri-lower alkylamine, for example
ethyl-, tert-butyl-, diethyl-, diisopropyl-, triethyl-t tributyl- or dimethyl-propyl-amine, or a
mono-, di- or tri-hydroxy-lo~r alkylamine, for example mono-, di- or tri-ethanolamine.
Correspondin~ internal salts can also be formed.
The present Application relates also to pharmaceulical compositions for the treatment of
olaucoma, for increasin~ the movement of (retinal) fluid~ for the treatment of vasospastic
constitutions of the eye and for the treatment of diabetic retinopathy, comprising a thera-
peudcally effective amount of a compound of formula (1) or of a pharmaceu~icallyacceptable salt thereof, and a pharrnaceutically acceptable formulation agent suitable for
ophthalmic and f~)r systemic use.
Corresponding ophthalmic compositions are advantageously administered topically to the
eye, especially in the form of a solution, an ointment, a gel or a solid insert. Such
compositions comprise lhe active inoredient, for example, in a range of from approx-
imately 0.01 to approximately 10.0 % by weight, preferably from approximately 0.5 to
approximately 5.0 % by weioht. Unit dose forms ot ~he aclive ingredient comprise? for
example, from approximately 0.001 to approximately 5.0 % by wei~ht, especially from
approximately 0.05 to approximately 2.0 % by weioht, preferably from approximately 0.1
lo approximately 1.5 % by weioht, more especiallv from approximately 0.1 to approx-
WO 93/lS732 P~US93/014
2 ~ 3 32 ~
- 4 -
imately 1.0 % by weight, of active ingredient. The dose of the active ingredient may
depend on various factors, such as mode of admir~istration, requirement, age and/or
individual condi~ion.
There are used for corresponding ophthalmic compositions customary pha~naceutically
acceptable excipients or additives known tO the person skilled in the ar~, for example those
of the type mentioned below, especially with the addition of isotonising agents, buffers,
complexing age~ts, solubilisers and thickeners. Examples of such excipients and additives
can be found in the PCT Patent Application having the publication number WO 91115206.
Such compositions are prepared in a manner known per ser for example by mixing the
active ingredient with the corresponding excipients andlor additives to form corresponding
o.phthalmic composidons. The active ingredient is preferably administered in the form of
eye drops, ~eing dissolved especially in a sterile, aqueous isotonic solution which, if
necessary. is buffered to the desired pH value.
Accordingly, the invendon relates likewise to systemically administrable pharmaceutical
compositions that comprise a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceudcally acceptable
salt thereof as active ingredie!lt, and to a process for the preparation thereof.
Those pharmaceudcal compositions are for enteral, such as oral, and also recta~ or
parenteral administration to warm-blooded anirnals, the pharmacological active ingredient
being comprised on itS own or together with customary pharmaceutical excipients. The
pharmaceutical composi~ions comprise, for example, approximately from 0.1 % to 100 %,
preferably from approximately 1 % to approximately 60 %, of the active ingredient.
Pharrnaceutical compositions for enteral or parenteral and also for ocular administration
are, for example, compositions in unit dose forms, such as dragées, tablets, capsules or
suppositories, and also ampoules. Ihose composi~ions are prepared in a manner known
se, for example by means of conventional mixing, granulating, confectioning, dissolving
or lyophilising processes. For example, phannaceu~ical compositions for oral adminis-
tration can be obtained by combining the active ingredient with solid camers, optionally
~ranulating a resulting mixture and, if desired, processing the mixture or granules, if
necessary after the addi~ion of suitable excipients, to ~orm tablets or dragée cores.
Suitable carriers are especially fillers, such as sugars, for example lactose, saccharose,
mannitol or sorbitol, cellulose prepara~ions and/or calcium phosphates, for exarnple tri-
calcium phosphate or calcium hydrogen phosphate, also binders, such as starch pastes
,1vO 9~/15732 2 1 2 8 3 2 ~ Pcr/US93/01~31
using, for example, com, wheat, rice or potato starch, gelatin, gum tragacanth, methyl-
cellulose and/or polyvinylpyrrolidone, and, if desired, disintegrators, such as the above-
mentioned starches, also carboxymethyl starch, cross-linked polyvin~lpyrrolidone, agar or
alginic acid or a salt thereof, such as sodium alginate. Excipients are especia ~ flow
conditioners and lubricants, for example silicic acid, talc, stearic acid or salts thereof, such
as magnesium or calcium stearate, and/or polyethylene glycol. Dragée cores are pro~ided
with suitable, optionally enteric, coatings, there being used, inter alia, concentrated sugar
solutions which may comprise gum arabic, talc, polyvinylpyrrolidone, polyethylene glycol
and/or titanium dio~ide, or coating solutions in suitable organic solvents or solvent
mL~tures, or, for the production of enteric coatings, solutions of suitable cellulose prepar-
ations, such as acetylcellulose phthalate or hydroxypropylmethylcellulose phthalate.
Col,ourings or pigments may be added to the tablets or dragée coaungs, for example for
identification purposes or to indicate t' ~ferent doses of active ingredient.
Fur~her orally ac; listrable pharmac ~ compositions include dry-f~lled capsules
consisting of geL3~ n, and also soft, s~ ' capsules consisting of gelatin and a plasticiser,
such as glycerol or sorbitol. The dry- .~d capsules may contain the active ingredient in
tne form of granules, for example in .mixture with fillers, such as laeto~e, binders, such
as S~ -~hes, and/or glidants, such as lalc or magnesium stearate, and or nally st. bilisers.
In ~ capsules, the active ingredien~ is preferably dissolved or suspes d in suitaole
liq~.s, such as fatty oils, p raffin oil or liquid polyethylene glycols, ~ which stabilisers
may likewise be added.
Suitable rectally administrable pharmaceutical compositions are, for example,
suppositories that consist of a combination of the active ingredient and a suppository base.
Suitable suppository bases are, for example, natural or synthetic triglycerides, paraffin
hydrocarbons, polyethylene glycols and higher alkanols. It is also possible to use gelatin
rectal capsules that comprise a combination of the active ingredient and a base material.
Suitable base materials are, for example, liquid triglycerides, polyethylene glycqls and
paraffin hydrocarbons.
For parenteral administration there are suitable especially aqueous solutions of an active
ingredient in water-soluble form, for exarnple in the form of a water-soluble salt, and also
suspensions of the active ingredient, such as corresponding oily injection suspensions,
there bei~ ;? used suitable lipophilic solvents or vehicles, such as fatty oils, for example
sesame oll. or synlhetic fatty acid esters, for example ethyl oleate or triglycerides, or
WO 93/15732 P~/US93/014~
21~832~
-- 6 --
aqueous injection suspensions that comprise viscosi~-increasing substances, for example
sodiurn carboxymethylcellulose, sorbitol and/or dextran, and, if desired, also stabilisers.
The dose of the active ingredient may depend on various factors, such as the mode of
administration, species of warm-blooded animal, age andlor individual condi~ion.
The present Application relates also to the use of a compound of formula (I) or a pharma-
ceutically acceptable salt thereof in the preparation of pharrnaceutical compositions for the
treatment of glaucoma, for increasing the movement of (retinal) intra-ocular fluid, for the
treatment of vasospæ~ic constitutions of the eye and for the treatment of diabetic retino-
pathy.
~e following E~xamples illustrate the invention described above; they are not, however,
intended to limit the scope thereof in any way.
Formulation Examples 1. 2 and 3: A solution, comprising 20 mg of active ingredient, for
example (S)-N-( 1 -carboxy-2-methylprop- 1-yl)-N-pentanoyl-N-~2' -( lH-tetrazol-5-yl)-
biphenyl-4-ylmethyl~-amine, can be made up as follows:
Composition:
1)
aclive in~redient 20.00 mg
NaOH.lN 86.00 mg
benzalkonium chloride 0.l0 m~
disodium ethylenediamine
tetraacetate 0.50 mg
sorbitol 10.00 mg
Na2HPO~-2H2o 9.91 mg
K2HPO4 0.44 mg
water (purity: pro inj.j ad 1.00 ml
2)
active in~redient 20.00 mg
NaOH.lN 86.00 mg
Macrogol 400 20.00 mg
benza!konium chloride 0.10 rng
~o 93/15732 ~ ~L 2 ~ PCr/US93/01431
disodium ethylenediamine
tetraacetate 0.50 mg
sorbitol 6.00 mg
Na2HPO2-2H2O 9.73 mg
K2HPO4 0.43 mg
water (purity: pro inj.) ad 1.00 ml
3)
active ingredient 20.00 mg -~
NaOH.lN 86.00 mg
Polyoxyl 35 castor oil 4.00 mg
benzalkonium chloride 0.10 mg
d~isodium ethylenediamine
tetraacetate 0.50 mg
sorbitol 6.00 mg
Na2HPO2-2H2o 9.91 mg
K2HPO4 0.44 mg
water (purity: pro inj.) ad 1.00 ml
For this purpose, the constituents are introduced into wa~r and dissolved.
Formulation Examples 4 and 5 for eve drops:
Vehicle:
Na2HPO4-12 H2O 3.58 g
NaCI 0.29 g
H2O 100 ml
Active ingredient:
N-(2-carboxy-2,2-tetramethylene-ethyl)-N-pentanoyl-N-~2' -~ l H-tetrazol-5-yl~-biphenyl-
4-ylmethyl~-amine
4) 5 % active ingredient solution:
vehicle 0.995 ml
NaOH 2N 0.015 ml
active inaredient (5 %) 50 ml
~H = 6.0
WO 93/15732 PCr/US93/014
2 1~83~ 8-
5) 0.5 % active ingredient solu~ion:
vehicle 0.9 ml
ac~ive ingredient (5 ~o) 0.1 ml
pH=7.0
A compound of forrnula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof can be processed
in an analogous marmer, fvr example as described in the above Examples.