Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02136182 2005-08-04
SPECIFICATION
Time Diversity Receiver
Technical Field
This invention relates to receivers which perform time diversity
reception to facilitate the transmission of high-quality signals in radio
communications which are subject to fading. It can be utilized for receivers
in selective radio paging and other mobile radio communication systems.
Background Technology
FIG. 1 shows the constitution of a conventional receiver which
performs time diversity reception using the receiving level. At the
transmitting side, a signal comprising the same symbols will be transmitted a
plurality of times. FIG. 1 will be explained for the case where binary code
is being received.
The signal received via antenna 1 is input to receiver/demodulator
2 and receiving level detector 3. The detector output signal that is output
from receiver/demodulator 2 is subjected to symbol decision as binary data (0
or 1) in symbol decision circuit 4, and is then input to signal processor 6
which performs the time diversity processing. The receiving level signal that
is output from receiving level detector 3 is also input to signal processor 6
after it has been sampled by A/D converter 5. Signal processor 6 compares,
for each symbol, the sampled value of the receiving level of the signal that
has just been received, and the sampled value of the receiving level of a
signal received up to and including the previous time, which is stored in
memory 7, and performs time diversity processing whereby the binary data
corresponding to the higher sampled value of the receiving level is selected.
After the completion of this time diversity reception processing, signal
processor 6 stores in memory 7 said sampled value and the binary data
corresponding to it, and also outputs the binary data to terminal 8. By
repeating these operations, high-quality signal transmission can be achieved
in mobile radio communication channels subject to fading.
However, a problem that has been encountered with conventional time
diversity receivers of this sort is that because receiving level detector 3
is necessary in order to perform time diversity reception processing whereby
high-quality signal transmission can be achieved, the circuitry becomes
complex and power consumption increases.
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a time diversity
receiver which eliminates the increase in circuit complexity and power
consumption that result from the use of a receiving level detector, and which
therefore has lower power consumption.
CA 02136182 2004-11-02
0 - 2 -
Disclosure of the Invention
According to one aspect of the invention, there is
provided a time diversity receiver comprising: a detector that
receives a radio signal comprising the same symbols
transmitted a plurality of times and that outputs an analog
detector signal corresponding thereto; a sampling circuit
which samples said analog detector signal and outputs sampled
digital detector signals, each of said sampled digital
detector signals being indicative of an amplitude of said
analog detector signal; a memory which stores said sampled
digital detector signals; a time diversity processor which
compares, for each symbol of associated received signals, an
absolute value of a first sampled digital detector signal and
an absolute value of a second sampled digital detector signal
corresponding to a previously received signal which is stored
in said memory, and which selects one of said first and said
second sampled digital detector signals having a larger
absolute value as a time diversity processor output signal;
and a symbol decision circuit that receives said time
diversity processor output signal and performs a symbol
decision function thereon.
According to a further aspect of the invention there is
provided a time diversity receiver comprising: a detector that
receives a radio signal comprising the same symbols
transmitted a plurality of times and outputs an analog
detector signal; a sampling circuit which samples said analog
detector signal and outputs sampled digital detector signals,
each of said sampled digital detector signals being indicative
of an amplitude of said analog detector signal; a memory which
stores said sampled digital detector signals output by said
sampling circuit; a time diversity processor which is
adaptable to receive a plural number of said sampled digital
detector signals and adds, for each symbol of associated
CA 02136182 2004-11-02
0 - 2A -
received signals, a first sampled digital detector signal and
a second sampled digital detector signal corresponding to a
previously received signal which is stored in said memory to
produce a time diversity processor output signal; and a symbol
decision circuit that receives said time diversity processor
output signal and performs a symbol decision function thereon
to produce a symbol decision circuit output signal wherein
said symbol decision function is performed after the addition
by said time diversity processor is performed.
According to yet a further aspect of the invention, there
is provided a time diversity receiver comprising: a detector
that receives a signal comprising the same symbols transmitted
a plurality of times and that outputs a detector signal
corresponding thereto; and a time diversity processor which
performs time diversity reception processing using a first
detector signal corresponding to a received signal and a
second detector signal corresponding to a previously received
signal, wherein said detector is adapted to receive frames
comprising n fixed-length subframes repeatedly, where n is a
natural number equal to or greater than 2, each frame
including a paging signal for each receiver, said frames being
constituted so that a new paging signal is inserted in the
subframe arranged at one end of a frame a first time that
frame is transmitted, While a subsequent time that frame is
transmitted, said paging signal is inserted into a subframe of
that frame at a position corresponding to the number of
transmissions.
According to still yet a further aspect of the invention,
there is provided a time diversity receiver comprising: a
detector that receives a signal comprising the same symbols
transmitted a plurality of times and that outputs a detector
signal corresponding thereto; a sampling circuit Which samples
said detector signal and outputs sampled detector signals; a
CA 02136182 2004-11-02
0 - 2B -
memory which stores said sampled detector signals; and a time
diversity processor which compares, for each symbol of
associated received signals, an absolute value of a first
sampled detector signal, and an absolute value of a second
sampled detector signal corresponding to a previously received
signal which is stored in said memory, and which selects one
of said first and said second sampled detector signal having a
larger absolute value, wherein said detector is adapted to
receive frames comprising n fixed-length subframes repeatedly,
where n is a natural number equal to or greater than 2, each
frame including a paging signal for each receiver, said frames
being constituted so that a new paging signal is inserted in
the subframe arranged at one end of a frame a first time that
frame is transmitted, while a subsequent time that frame is
transmitted, said paging signal is inserted into a subframe of
that frame at a position corresponding to a number of
transmissions.
According to still yet a further aspect of the invention,
there is provided a time diversity receiver comprising: a
detector that receives a signal comprising the same symbols
transmitted a plurality of times and a detector signal; a
sampling circuit which samples said detector signal; a memory
which stores sampled signals output by said sampling circuit;
a time diversity processor which adds, for each symbol of
associated received signals, a first sampled detector signal
and a second sampled detector signal corresponding to a
previously received signal which is stored in said memory,
wherein said detector is adapted to receive frames comprising
n fixed-length subframes repeatedly, where n is a natural
number equal to or greater than 2, frame including a paging
signal for each receiver, said frames being constituted so
that a new paging signal is inserted in the subframe arranged
at one end of a frame a first time that frame is transmitted,
while a subsequent time that frame is transmitted, said paging
CA 02136182 2004-11-02
0 - 2C -
signal is inserted into a subframe of that frame at a position
corresponding to a number of transmissions.
According to this invention, a receiver for time
diversity reception, which achieves high quality reception by
performing time diversity processing on paging signals wherein
a signal comprising the same symbols is transmitted a
plurality of times, performs the time diversity processing by
means of sampled values of the detector output, without having
to carry out receiving level detection. A receiving level
detector is therefore not required.
20
30
y ~ Qc
.. ; _ 3 _ ~.~d~~.~;
,:
Time diversity processing is performed by comparing the absolute values of the
sampled values of the detector output for a signal that has just been
received, and the
absolute values of the sampled values of the detector output for a signal
received up
to and including the previous time, and selecting the larger sampled values.
At the
same time as this, the sampled values after the time diversity reception
processing has
been earned out are written to memory and symbol decision is carried out on
each
symbol.
Time diversity processing can also be performed on the basis of addition,
without comparison of sampled values.
Thus, because time diversity reception processing in this invention is
performed
using only the detector output, there is no need for circuits pertaining to
receiving
level detection and therefore the circuitry becomes simpler. Likewise, because
the
power consumption involved in a receiving level detection circuit is
eliminated, a
receiver according to this invention can have a lower power consumption.
Brief Explanation of the Drawings
Fig.l shows the constitution of a conventional time diversity receiver which
performs time diversity reception processing by means of receiving level
detection.
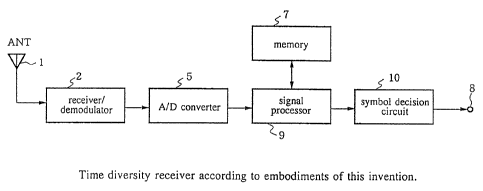
Fig.2 shows the constitution of a time diversity receiver according to a first
and
a second, embodiment of this invention.
Fig.3 serves to explain the working of time diversity processing of detector
output according to the first embodiment, with Fig.3a showing the detector
output for
a signal received for the first time and Fig.3b showing the detector output
for a signal
received for the second time.
Fig.4 shows an example of a frame signal format suited to embodiments of this
invention, with Fig.4a showing the constitution of the time s() frame and
Fig.4b
showing the constitution of the time s0+T frame.
Fig.S is a flowchart showing the working of time diversity processing in the
first embodiment of this invention.
Fig.6 serves to explain the working of time diversity processing of detector
output according to the second embodiment.
Fig.7 is a flowchart showing tl5e working of time diversity processing in the
second embodiment of this invention.
Optimum Configurations for Embodying 'this dnvention
Embodiment 1
The constitution of a first embodiment of this invention will be explained
with
reference to Fig.2. A time diversity receiver according to this embodiment has
antenna 1, receiver/demodulator 2 which receives and demodulates the signal
received
via antenna I, A/D converter 5 which serves as a sampling circuit which
samples the
~ _ ~.~ ri~~.~l
detector output, memory 7 which stores the sampled values, signal processor 9
which
performs time diversity processing, and symbol decision circuit 10. Signal
processor
9 comprises a means which compares, for each symbol of identical received
signals,
the absolute value of the sampled value of the detector output for the signal
received
by retransmission, and the absolute value of tile sampled value of the
aforementioned
detector output for a signal received up to and including the previous time,
which is
stored in the aforementioned memory; and a means which selects the sampled
value
with the larger absolute value; and a means which writes the sampled values
after time
diversity reception processing to the aforementioned memory, and at the same
time
outputs said sampled values to symbol decision circuit 10 for symbol decision.
The operation of a receiver according to this embodiment will now be
explained. Receiver operation will be explained for the case where binary code
is
being received.
Signals received via antenna 1 are input to receiver/demodulator 2. Each
symbol of the detector output signal that is output from receiver/demodulator
2 is
sampled in A/D converter 5 and input to signal processor 9. Signal processor 9
performs time diversity reception processing by calculating, for each symbol,
a value
Z which satisfies the following equation:
~Z~ =znax(~X~, ~Y~) ... (1)
where X is the sampled value of the signal that has just been received and Y
is
the sampled value of an identical signal received up to and including the
previous
time, this latter value being taken from memory 7. After completion of this
time
diversity reception, signal processor 9 stores these sampled values Z in
memory 7 and
also outputs them to symbol decision circuit 10. Symbol decision circuit 10
performs
symbol decision on sampled values Z as binary data (0 or 1) and outputs
this.binary
data to terminal 8. By repeating these operations, high-quality signal
transmission can
be achieved in mobile radio communication channels which are subject to
fading. The
symbol decision performed by symbol decision circuit 10 can be carried out by
signal
processor 9, and in this case it is not necessary to provide a separate symbol
decision
circuit ~ 10.
The operation of this embodiment will be explained in more explicit terms with
reference to Fig.3, which serves to explain the operations whereby time
diversity
processing is performed by sampling the detector output signal and comparing
the
absolute values of the sampled values.
The detector output for a signal received for the first time is assumed to
have
a waveform of the sort shown in Fig.3a. Sampled values Y" Y~, Y3, ... can be
obtained by sampling this waveform with prescribed sampling tlmlngs. These
sampled
values obtained for the first time are stored in memory 7 and are also output
to
CA 02136182 2004-11-02
0 - 5 -
symbol decision circuit 10. Next, the detector output fox a
signal received for the second time is assumed to have a
waveform of the sort shown in Fig. 3b. The sampled values
obtained by sampling this detector output will be X1, X2,
X3,... . Signal processor 9 compares the absolute values of
the sampled values Y1, YZ, Y3, . . . obtained the previous time
and which were stored in memory 7, and the absolute values of
the sampled values X1, X2, X3, ... which have just been
obtained. The sampled values with the larger absolute values
are stored in memory 7 as Z1, Z2, Z3,... and are output to
symbol decision circuit 10. In the present case, comparison
of the absolute values of Y1 and X1 shows that Y1 is larger.
In the case of XZ and YZ, although they are of opposite sign,
X2 has the larger absolute value. Accordingly, the sampled
values Y1, X2, X3, . . . will be stored in memory 7 as the
sampled values Z=, Z2, Z3, ... after time diversity processing.
The inventors have previously presented in corresponding
United States Patent 5,736,934 and United States Patent
5,835,023, a paging signal frame system wherein the number of
times a paging signal has been transmitted can be recognized
at the receiver side. This system serves as a frame signal
format in a radio paging system wherein a signal comprising
the same symbols is transmitted a plurality of times, and it
is suited to a time diversity system according to this
embodiment.
An example of this frame signal format is given in Fig.
4, where it is assumed that a pager which repeatedly receives
a frame of signal length a will first of all receive the time
s0 frame and then receive the time s0+T frame. The
constitution of the time s0 frame is shown in Fig. 4a and the
constitution of the time s0+T frame is shown in Fig. 4b. T is
the frame period.
CA 02136182 2004-11-02
0 - 5A -
Internally, these frames comprise n fixed-length
subframes following a frame synchronization signal, with one
or more new paging signals being inserted in the first
subframe and a paging signal that is transmitted fox the mth
time being inserted in the mth subframe. Focusing on one
paging signal, it will be seen that its position shifts by one
subframe every frame period. Referring to the examples shown
in Fig. 4a and 4b, if paging signals A, B, C and D have been
inserted in the first subframe of the time s0 frame, these
paging signals A, B, C and D will be inserted in the second
subframe of the time s0+ T frame and in the kth subframe of
the time s0+ (K-1) T frame (where k=1, . . . n) . Transmission for
the nth time will be completed in the time s0+(n-1)T frame.
In other words, because the position of a paging signal in the
frame in successive transmission periods will change in a
regular manner, so that the position of a paging signal being
transmitted for the second or subsequent time can be predicted
at the receiver side, and because identical paging signals are
comprised of identical bits, when time diversity processing is
performed at signal processor 9, identical received signals
can be extracted and compared symbol by symbol.
"~) 6.' S
~~:.~~J~_~;
:--w
An example of the working of time diversity processing in a radio paging
system according to this embodiment, using the frame signals shown in Fig.4,
is
shown as a flowchart in Fig.S. Note that this flowchart relates to subframe
which
contains identical signals,
A time diversity receiver according to the embodiment described above enables
time diversity reception processing to be performed by application of the
detector
output only, without having to carry out receiving level detection.
Embodiment 2
A second embodiment of this invention will now be explained. The constitution
of the receiver is the same as in the first embodiment, but the time diversity
reception
processing in signal processor 9 differs from that employed in the first
embodiment.
It should be noted that the operation of the transmitting side involves
transmitting a signal comprising the same symbols a plurality of times, which
is
similar to a conventional system, and that the receiver will be explained for
the case
where binary code is being received.
Signals received via antenna 1 are input to receiver/demodulator 2. Each
symbol of the detector output signal that is output from receiver/demodulator
2 is
sampled in A/D converter 5 and input to signal processor 9. Signal processor 9
performs time diversity reception processing by calculating, for each symbol,
a value
Z which satisfies the following equation:
Z=X+Y ... (2)
where X is the sampled value of the signal that has just been received and Y
is
the sampled value of an identical signal received up to and including the
previous
time, this latter value being taken from memory 7.
After completion of this time diversity reception processing, signal processor
9 stores these sampled values Z in memory 7 and also outputs them to symbol
decision
circuit I0. Symbol decision circuit 10 performs symbol decision on sampled
values
Z as binary data and outputs this binary data to terminal 8. By repeating
these
operations, high-quality signal transmission can be achieved in mobile radio
communication channels which are subject to fading:
The operation of this embodiment will. now be explained in more explicit terms
with reference to Fig.6. In similar fashion to the first embodiment, the
detector
output for a signal received for the first time is assumed to have had the
waveform
shown in Fig.6a. This waveform is sampled with prescribed sampling timings,
whereupon sampled values Y" Y~, Y3, ,.. are obtained. These sampled values
obtained for the first time are stored in memory 7 and are also output to
symbol
decision circuit 10. Next, the detector output for the signal received for the
second
' ~:~3~~ R~
time is assumed to have the waveform depicted in Fig.6b. The sampled values
obtained by sampling this detector output will be X" Xi, X3, ... . Signal
processing
part 9 performs addition of the sampled values Y" Yz, Y3, ... obtained the
previous
time, which were stored in memory 7, and the sampled values Xl, Xz, X3, ...
that
have just been obtained, and Z,=X,+Y" ZZ=XZ+Yz, Z3=X3+Y3, ... are stored in
memory 7 as the sampled values after time diversity processing, and are also
output
to symbol decision circuit 10.
The working of time diversity processing in a radio paging system according
to this second embodiment, using the frame signals shown in Fig.4, is shown as
a
flowchart in Fig.7. Note that this flowchart relates tda subframe which
contains
identical signals.
A time diversity receiver according to the embodiment described above enables
time diversity reception processing to be performed by application of the
detector
output only, without having to carry out receiving level detection.
Although the working of the first and second embodiments described above has
been explained for the case where binary coda is received, this invention is
similarly
effective in cases where three-valued or higher valued codes are received. In
such
cases, the symbol decision circuit should correspond to the number of values
of the
code being used.