Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
21~G~73
_
APPARATUS FOR SYNCHRONIZING MOVEMENT OF A SHIFTABLE MEMBER
Field of the Invention
This invention relates to movement synchronizing apparatus, and will
have application to equalizers used to synchronize end-to-end linear movement
of a shiftable frame.
Background of the Invention
Synchronizing devices, also known in the trade as equalizers, are useful
devices for ensuring corresponding movement of one or more shiftable
members relative to a stationary member. These devices have been used
previously with success in the recreational vehicle field, particularly in the
slide-out room industry. Since it is desirable to synchronize the end-to-end
movements of the sliding frame which supports the slide-out room, various
equalizers have been developed. Several equalizers of this type are shown in
our pending U.S. Patent 5,295,430, which is incorporated herein by reference,
and in the references cited during prosecution of that application.
Most of the prior equalizers are limited in usefulness due to their
elements and their positioning requirements. Our prior invention requires the
use of pulleys and cables which are attached to a protrusion of the slide-out
room support tube. Many of the other equalizers requires complex mechanical
arrangements which limit their versatility and add to the cost of the units.
Summary of the Invention
The equalizer of this invention is of simple, versatile and economical
construction. The equalizer may be adapted for use with almost any
application which includes a sliding member shifting relative to a stationary
member.
The equalizer generally includes a cable or cables and two or more
tensioning members, preferably rotatable grooved pulleys. The tensioning
members are axially fixed to one of the stationary or shiftable members. The
cable or cables extend across the tensioning members and are attached to
~136~73
-
opposite sides of the other of the stationary or shiftable member. In this
fashion, linear movement of the shiftable member is synchronized from side-
to-side due to the constant biasing effect of the fixed length cables and the
axial fixing of the tensioning pulleys.
S The equalizer of this invention is very suitable for use in the recreational
vehicle industry, with particular importance in slide-out room RVs. By
connecting the equalizer to the slidable and stationary frames of the RV, side-
to-side linear movement of the slide-out room is synchronized, thus saving
wear and tear on the RV unit and on the drive train, as well as preventing a
freeze up of the sliding frame.
Accordingly, it is an object of this invention to provide for a novel and
improved equalizer for sliding members.
Another object is to provide for an equalizer which is adaptable for use
in slide-out room RVs.
Another object is to provide for a linear movement equalizer which is of
simple and economical construction.
Another object is to provide for an equalizer which can be easily installed
into either new units or can be adapted to retrofit existing units.
Other objects will become apparent upon a reading of the following
description.
Brief Description of the Drawings
The preferred embodiments of the invention have been depicted for
illustrative purposes only and are not to be considered as limiting the
invention in any way.
Fig. 1 is a top plan view of a first embodiment of the equalizer of this
inventlon.
Fig. 2 is a side elevation view of the equalizer of Fig. 1.
Fig. 3 is a top plan view of a modified equalizer showing stacked
tensioning pulleys.
Fig. 4 is an end elevation view of the equalizer of Fig. 3.
~136673
Fig. S is a top plan view of the equalizer of Fig. 3 showing the tensioning
cable attached directly to sliding tubes that support a slide out room of a
recreational vehicle.
Fig. 6 is a top plan view of another embodiment of the equalizer.
S Fig. 7 is a top plan view of an equalizer similar to that of Fig. S but used
on a tube supported recreational vehicle slide-out room.
Fig. 8 is a top plan view of another embodiment of the equalizer of the
present invention.
Description of the Preferred Embodiments
The preferred embodiments herein described are not intended to be
exhaustive or to limit the invention to the precise forms disclosed. They are
chosen and described to explain the principles of the invention and its
application and practical use to best enable others skilled in the art to followits teachings.
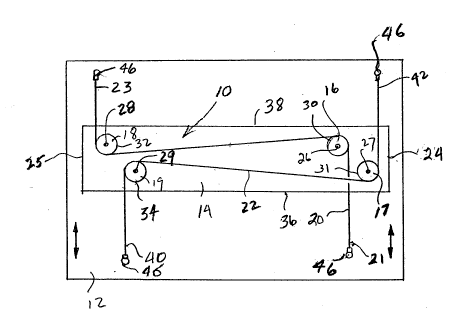
Referring first to Figs. 1 and 2, reference numeral 10 refers generally to
the equalizer or synchronizing apparatus of this invention. Equalizer 10 is
used in conjunction with a frame 12 which is shiftably associated with
stationary frame 14. For purposes of this invention, frames 12 and 14 may be
physically connected to each other, either directly or indirectly, or may be
simply oriented in close proximity with no physical connections therebetween.
Frame 12 is shiftable in a linear fashion relative to frame 14, which is normally
fixed or stationary.
Equalizer 10 includes a first tensioner including pulleys 16 and 18, a
second tensioner including pulleys 17 and 19, and a pair of cables 20 and 22.
Pulleys 16-19 are connected to stationary frame 14 as by shafts 26, 27, 28 and
29 respectively, with each pulley freely rotatable about its connecting shaft.
Pulleys 16-19 are of similar or identical construction. Each pulley 16, 17, 18,
19 has a continuous circumferential outer groove 30, 31, 32, 34 respectively.
Pulleys 16, 17 are located adjacent to a side edge 24 of stationary frame 14
with pulleys 18, 19 located adjacent the opposite side edge 25 of the stationaryframe. Pulleys 16, 17 and 18, 19 may be longitudinally and transversely
aligned or may be of the offset configuration shown in Figs. 1 and 2.
~131~73
Cables 20 and 22 are formed from any suitable material of sufficient
strength to withstand the forces exerted on the cables during movement of the
shiftable frame 12. Cable 20 is attached at one end 21 to shiftable frame 12
adjacent side edge 24 and end edge 36. Cable 20 extends across pulley 16 and
pulley 18 and rides freely in grooves 30, 32. Cable 20 has its other end 23
attached to shiftable frame 12 adjacent side edge 25 and end edge 38.
Cable 22 is attached at one end 40 to shiftable frame 12 adjacent side
edge 25 and end edge 36. Cable 22 extends across pulley 17 and pulley 19 and
rides freely in grooves 31, 34. The other end 42 of cable 22 is connected to
movable frame 12 adjacent side edge 24 and end edge 38. Cables 20 and 22
may be directly connected to frame 12 in a common manner or may be
connected to the shiftable frame as by tension adjusting devices such as
turnbuckles or threaded cable ends and tensioning nut generally indicated at
46.
When connected to shiftable frame 12, cables 20 and 22 should be taut
with little or no slack in order for the cables to move correspondingly with theshiftable frame. Pulleys 16-19 are axially fixed and are freely rotatable about
their connective shafts 26-29. Common rotation enhancers such as bll~hings,
sleeves or bearings (not shown) may be employed to facilitate free rotation of
the pulleys 16-19.
Shiftable frame 12 is preferably designed for connection to a common
drive means (not shown) and shifts in a linear fashion relative to stationary
frame 14. By virtue of the opposite diagonal corner connections of cables 20,
22 as above described, frame 12 will shift relative to frame 14 in an equalized
or synchronous manner, that is the distance traversed by side edge 25. Should
slack develop in one of the cables 20 or 22, that cable can be tightened by
adjusting turnbuckle 46, or like devices. Of course, the frame 14 upon which
the pulleys 16-19 are mounted may be made the movable frame and the frame
12 upon which the cables are attached made the stationary frame, with the
equalizer 10 functions in the same way as described. While the pulleys have
been described as being mounted on the stationary frame and the ends of the
cables have been described as being secured to the movable frame, one skilled
in the art will recognize that the stationary and movable frames may be
2136673
-
reversed; that is, the pulleys may be mounted on the movable frame and the
cables secured to the stationary frame.
Figs. 3 and 4 illustrate a modified equalizer 50. Equalizer 50 also
operates to synchronize the linear movement of frame 52 relative to stationary
frame 54 as described above. Equalizer 50 includes pulleys 56 and 58 which
are connected to frame 54 as by fixed shafts 60, 62 respectively. Pulleys 56, 58are freely rotatable about shafts 60, 62 and have continuous circumferential
grooves 64, 65 and 66, 67 respectively as shown. For purposes of this
invention pulley 56 may be a single pulley with spaced grooves 64, 65 or may
consist of two grooved pulleys (not shown) stacked on shaft 60. Similarly,
pulley 58 may be a single pulley with spaced grooves 66, 67 or may consist of
two grooved pulleys (not shown) stacked on shaft 62.
Cable 68 is connected at one end 69 adjacent to corner 53 of frame 52.
Cable 68 extends across pulleys 56 and 58 in grooves 64, 66 and has its
opposite end 70 connected to frame 52 adjacent corner 55. Cable 72 is
connected at end 73 to frame 52 adjacent corner 51 and extends across pulleys
56, 58 in grooves 65 and 67. Cable 72 has its other end 74 connected to frame
52 adjacent corner 57. Cables 68, 72 are stretched taut and preferably define
a criss-cross arrangement between pulleys 56 and 58 as shown. The operation
of equalizer 50 is the same as that of equalizer 10.
In the embodiment shown in Fig. 5, support tubes 86, 87 are connected
to a stationary frame (not shown) and underlie movable frame 82. Tubes 88,
89 are telescopically fitted in each tube 86, 87 and are connected in a common
manner to frame 82. Drive means (not shown) is operably connected to either
the frame 82 or the tubes 88, 89 and serves to shift the movable frame 82 and
the room (not shown) between the extended and retracted positions.
Pulleys 56 and 58 are connected to tubes 86, 87 as by shafts 60, 62 as
described above. Cable 68 has its end 69 connected to the inner end of tube
88 and extends across pulley grooves 65, 67 with its opposite end 74 connected
to the inner end of tube 89. A cable 72 has its end 75 connected to end of
tube 88 opposite the bar at which cable 68 is connected at end 69, and cable
72 has its other end 77 connected to the end of tube 89 opposite the end at
which cable 28 is connected. Alternatively, cables 68 and 72 may have their
213~.73
-
ends connected directly to the movable frame 82. Alternatively, pulleys 56, 58
may be connected to the movable frame 82 or the movable tubes 88, 89 with
cables 68, 72 having their ends 69, 74 and 75, 77 connected to the stationary
frame or stationary tubes 86, 87. The sliding of frame 82 relative to frame 76
S and the function of equalizer 50 is as described above.
Returning now to Figs. 6 and 7, elements in Fig. 6 which are the same or
subst~nti~lly the same as those in the embodiment of Fig. 1 and 2 retain the
same reference symbol but increased by 200; elements in the embodiment of
Fig. 7 which are the same or substantially the same as corresponding elements
in the embodiment of Figs. 1 and 2 contain the same reference numerals but
increased by 300. In the embodiment of Fig. 6, the movable frame 212 moves
between the pulleys 216, 217 and 218, 219, which pulleys are arranged in a
quadrilateral arrangement and located respectively at the corners of frame
member 290, 292 which are both secured to the stationary frame 214.
Accordingly, movement of the movable frame 212 is limited by its engagement
with the pulleys. Of course, the pulleys may be mounted on movable frame
212 and the ends 221, 223 and 240, 242 of the cables 220, 222 attached to the
stationary member, with the equalizer 210 functioning in exactly the same way.
In the embodiment of Fig. 7, tubes 390, 392 are secured to the stationary
frame 314, and are telescopically received by slidable tubes 394, 396 which are
slidably mounted on the tubes 390, 392 respectively. The movable frame (not
shown) is secured to the tubes 394, 396. The pulleys 316, 317, 318 and 319 are
mounted on opposite ends of the tubes 390, 392 respectively, with each of the
cables being wrapped around a diagonally opposite pulley and crossing the
other cable at a point between the tubes 390, 392. The embodiment of Fig. 7
operates in the same way that the embodiment of Figs. 1-2 and Fig. 6 operate,
as discussed above.
Referring now to the embodiment of Fig. 8, elements the same or
substantially the same as those of the embodiment of Figs. 1 and 2 retain the
same reference character, but increased by 400. In the embodiment of Fig. 8,
stationary tubes 480, 482 are fixed to stationary frame 414 and slidably
received slide tubes 484, 486, which are connected to a movable frame (not
shown) by connecting plates 488, 490. The end 442 of the cable 422 and the
~13~l~7~
-
end 421 of the cable 420 are both connected to the opposite sides of the plate
490, and the end 423 of cable 420 and the end 440 of cable 422 are both
connected to opposite sides of the plate 488. Thus it can be seen from Fig. 8,
the cable 420 is wrapped around the pulleys 416 and 418 and also is wrapped
about a third pulley 492. Similarly, the cable 422 is wrapped around the
pulleys 417 and 419 and is also wrapped around a third pulley 494. The third
pulleys 492 and 494 wrap their respective cables around the fixed tubes 480
and 482, and also assure that the pulley forces exerted by the cables are
applied along the axis of the tubes 484 and 486. The embodiment of Fig. 8
operates in the same way as the embodiment of Fig. 1 and 2 as discussed
above, wherein equ~li7ing forces are transmitted through the movable frame
through the tubes 484 and 486 as the movable frame is moved.
It should be noted that all embodiments of the equalizer operate in
similar fashion to synchronize linear movement of a movable member relative
to a stationary member. By maintaining constant tension on the cables used in
each equalizer, the pulling effect created by the routing of the cables in each
equalizer serves to apply roughly equal force to both sides of the movable
frame (or both slide tubes) to allow relatively identical travel distances
regardless of the location of the drive means. The equalizers shown represent
only a small cross-section of the configurations and routings possible and are
not to be considered as limiting this invention to any precise structure. Such
limitations on the scope of this invention can only be found by referring to thelanguage of the following claims.