Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
~1 4225 t
HOECHST AKll~SELLSCHAFT HOE 94/F 033 Dr.ST
DESCRIPTION
Water-soluble azo compounds, preparation thereof, and use
thereof as dyes
The present invention relates to the field of the fiber-
reactive azo dyes.
Fiber-reactive azo dyes with 2-A inonAphthalenedisulfonic
acids as diazo component are known in large numbers, for
example from Japanese Patent Application Publications
Sho-59-133 261 and Sho-60-23 453 and from European Patent
Application Publications Nos. 0 128 034, 0 239 847 and
0 292 955. Further~ore, European Patent Application
Publication No. 0 502 893 and PCT Patent Application
Publications WO 91/09913 (U.S. Patent 5 268 458) and
WO 91/09914 (U.S. Patent 5 310 886) describe fiber-
reactive azo dyes having 1-sulfo-6-carboxy-2-amino-
naphthalene as diazo component. The increasing expec-
tations of the quality, the economics and the brilliance
of the dyeings have made it necessary to develop novel
azo dyes which have improved properties in these respects
and, what is more, have simple application properties.
The present invention now provides novel azo compounds
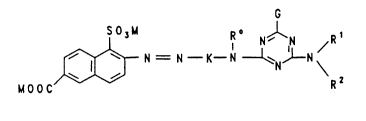
which conform to the formula (1)
SO~U R~ N~N /R1
MOOC N = N--K--N--~NJ--N~ ( 1 )
21~225~
where
M is hydrogen or a salt-forming metal, in particular
an alkali metal, such as sodium, potassium or
lithium;
5 K is the bivalent radical, being free of the group of the formula
--N(R)-, of a water-soluble coupling component containing said
amino group;
R is hydrogen or alkyl of 1 to 4 carbon atoms, such as
methyl or ethyl, or is alkyl of 1 to 4 carbon atoms,-
for example ethyl, which is substituted by sulfo,
carboxy , sulfato, phosphato, hydroxy , methoxy,
ethoxy, phenyl, monosulfophenyl or disulfophenyl,
and preferably is hydrogen;
G is halogen, such as fluorine or chlorine, preferably
fluorine;
Rl is hydrogen or alkyl of 1 to 4 carbon atoms, such as
ethyl or methyl, or is alkyl of 1 to 4 carbon atoms
which is substituted by sulfo, carboxy , phosphato,
sulfato, hydroxy , cyano, phenyl or sulfophenyl, or
is phenyll or is phenyl substituted by sulfo,
carboxy , alkyl of 1 to 4 carbon atoms, alkoxy of 1
to 4 carbon atoms, chlorine and/or nitro;
R2 is hydrogen or alkyl of 1 to 4 carbon atoms, such as
ethyl or methyl, or alkyl of 1 to 4 carbon atoms
which is substituted by sulfo, carboxy , phosphato,
sulfato, hydroxy , cyano, phenyl or sulfophenyl, or
is phenyl unsubstituted or substituted by 1, 2 or 3
substituents selected from the group of the follow-
ing substituents: 2 alkyl groups of 1 to 4 carbon
atoms, such as ethyl and in particular methyl,
2 alkoxy groups of 1 to 4 carbon atoms, such as
ethoxy and methoxy, 1 bromine atom, 2 chlorine
atoms, 3 sulfo groups, 2 carboxy groups, 1 nitro
group, 1 alkylsulfonyl group of 1 to 4 carbon atoms
unsubstituted or substituted by hydroxy (for example ~-
hydroxyethylsulfonyl), 1 alkylamino group of 1 to 4
carbon atoms and 1 alkylamino group of 1 to 4 carbon
atoms unsubstituted or substituted in the alkyl radical
by hydroxy , sulfato, sulfo, phosphato, Al kAnoyloxy
21~225i
of 2 to 5 carbon atoms or by carboxy -substituted
alkanoylamido of 1 to 4 carbon atoms in the alkylene
radical, such as succinamido, or R2 is monosulfo-
naphthyl, disulfonaphthyl or trisulfonaphthyl, or
R1 and R2 form together with the nitrogen atom a hetero-
cyclic radical made up of an alkylene group of 3 to
8 carbon atoms, preferably 4 to 6 carbon atoms, or of
a further hetero group, such as an -NH- or -O-
group, and two alkylene groups of 1 to 4 carbon
atoms, for example N-piperidino, N-piperazino or
N-morpholino.
Substituted alkylamino groups as substituents in a phenyl
radical of R2 are for example ~-sulfatoethylamino and ~-
succinamidoethylamino.
Preferably -K-N(R)- is a radical of the formula (2a),
(2b) or (2c)
HO NH HOV--NH--
( 2 ~ ) ( S 03M )m ( S 0~ )m
R
{~ N--
( 2 C ) ( S3~ )m
where
M and R are each as defined above,
m is 1 or 2, and
V is a direct, covalent bond or a radical of the
2142251
formula
-NH-CO-phenylene, -NH-CO-NH-phenylene, -N(CH3)-CO-
phenylene, -N(CH3)-CO-NH-phenylene or -NH-phenylene;
in the formula (2a) in the case of m being 2,one of the
sulfo groups is preferably disposed meta to the
hydroxy group and the other is preferably disposed
para or meta to the amino groupJ and in the
formulae (2b) and (2c) the free bond which leads to
the azo group is preferably disposed on the naph-
thalene nucleus in a position ortho to the hydroxy
group, the hydroxy group is preferably attached to
the naphthalene nucleus in the 8-position, one sulfo
group i6 preferably attached to the naphthalene
nucleus in the 6-position, the group -V-NH- or
-N(R)- is preferably attached to the naphthalene
nucleus in the 2- or 3-position and in the case of
m being 2 the second sulfo group is preferably
attached to the naphthalene nucleus in the
3-position and particularly preferably in the
4-position.
Hereinbefore and hereinafter, "sulfo", "carboxy ",
"sulfato" and "phosphato" include not only the acid form
of the groups but also their salt form. Accordingly,
sulfo groups are groups conforming to the formula -SO3M,
carboxy groups are groups conforming to the formula
-COOM, phosphato groups are groups conforming to the
formula -OPO3M2 and sulfato groups are groups conforming
to the formula -OSO3M, where M has in each case the
abovementioned meaning.
30 In the formulae (2b) and (2c), the hydroxy group and the
free bond are attached ortho to each other to the same
aromatic nucleus. Preferably the hydroxy group is
attached to the naphthalene radical in the ~-position.
Preference is further given to compounds of the
formula (1) in which -NRlR2 is an above-defined
heterocyclic radical, preferably N-morpholino.
2142251
-- 5
Preferred azo compounds of the formula (1) are further
those in which -R-N(R)- is a radical of the formula (3a)
or (3b)
HO NH--Z HO
~ ( 3 c ) ~N H--Z
UO,S SO,I~ IJO,S (SO3~),o
where
M is as defined above,
Z is a radical of the formula (3A)
G
N
~`N~N~ (3A)
where G, R1 and R2 have the meanings mentioned
above, in particular the preferred meanings, and
p is zero or 1 (if zero, this group being hydrogen);0 in the formula (3a) one of the sulfo groups is disposed
meta or para relative to the -NH-Z group and in the
formula (3b) the -NH-Z group i8 attached to the 8-
hydroxynaphthalene radical in the 2-, 3- or 4-posi-
tion, preferably in the 2- or 3-position, and in the
case of p being equal to 1 this sulfo group is
attached to the 8-hydroxynaphthalene radical in the
3- or 4-position, preferably in the 4-position.
Particular preference is given to compounds of the
formulae (lA), (lB), (lC' and (lD)
21~2251
-- 6
~ N = N ~N H~N H ~ R
MOOC11035
( S O ~ ~ ) p ( 1 A )
SO,~,I HO N~N/(CH2)c\
~ N = N ~ I~N \ X
IIOOC ~03S ( CH2)~
( S s ~
N~N R 3
SO3~ HO NHJ~N~NH~R~
N = N ~
~IOOC \103S SO,I~/ ( I C )
G
N~N /( CH2 ) o~
SO3~ HO NHI~N~N X
N= N$~ (CH2)b
~lOOC ~OsS SO3~ ( 1 D)
where
M, G and p have the meanings mentioned above, in particu-
lar the preferred ^An;ng8,
a iB 1, 2 or 3, preferably 2,
b iB 1, 2 or 3, preferably 2,
X is oxygen or -NH-,
R3 is hydrogen, ~ulfo, carboxy , alkyl of 1 to 4 carbon
atoms, such as ethyl and in particular methyl,
alkoxy of 1 to 4 carbon atoms, such as ethoxy and in
particular methoxy, or hydroxy , and
R4 is hydrogen, sulfo, carboxy , alkyl of 1 to 4 carbon
atoms, such as ethyl and in particular methyl, or
alkoxy of 1 to 4 carbon atoms, such as ethoxy and in
particular methoxy;
21~22~1
in the formulae (lA) and (lB) the triazinylamino radical
is attached to the 8-hydroxynaphthalene radical in
the 2- or 3-position and in the case of p being
equal to 2 this sulfo group i8 attached to the
8-hydroxynaphthalene radical in the 3- or 4-
position, preferably in the 4-position.
The present invention further provides processes for
preparing the azo compounds of the formula (1) according
to the present invention, which comprise coupling the
diazonium compound of an amine of the formula (4)
S o 3 M
~NH2 ( 4 )
M O O C
where M i~ as defined above, with a compound of the
formula (5)
G
I N l N / R (5)
where K, R, G, Rl and R2 are each as defined above, or
reacting a compound of the formula (6)
SO3M R
~3~ N= N--K--N--~1 ( 6 )
I/OOC
where M, K and R are each as defined above, with a
compound of the formula (7)
21~2251
NlN ~R1
G ~N~L N ~ ( 7 )
where G, R1 and R2 are each as defined above, or reacting
a compound of the formula (8)
G
S o3~ I N~N
~ N=N--K--N--~ ~G ( 8 )
llOOC
where M, K, R and G are each as defined above, with an
amino compound of the formula HNR1R2 where R1 and R2 are
each as defined above.
The diazotization and coupling reactions of the process
according to the present invention are carried out in a
conventional manner, for instance the diazotization
generally at a temperature between -5C and +15C and at
a pH below 2 by means of a strong acid and sodium nitrite
in a preferably aqueous mediumland the coupling reaction
generally at a temperature between 0 and 30C and at a pH
between 1 and 4.5 in the case of an amino-contA;n;ng
coupling component and at a pH between 3 and 7.5 in the
case of a hydroxy -contA;n;ng coupling component, prefer-
ably in aqueous medium.
The condensation reaction of an amino starting compound
of the formula (6) with a compound of the formula (7) is
effected in the usual manner of reacting an amino com-
pound with a triazine compound containing a reactivehalogen atom, for instance in an organic or preferably
aqueous-organic medium, particularly preferably in an
21q2251
aqueous medium, in the presence of an acid-binding agent,
as of an alkali metal or alkaline earth metal carbonate,
an alkali metal or alkaline earth metal bicarbonate or
hydroxide or alkali metal acetate, the alkali metals and
alkaline earth metals preferably being sodium, potassium
or calcium, or of a tertiary amine, for example pyridine,
triethylamine or quinoline. If these condensation reac-
tions are carried out in an organic or agueous-organic
medium, the organic solvent (proportion) is acetone,
dioxane or dimethylformamide. More particularly, this
condensation reaction takes place at a temperature
between -10C and +60C, preferably between 30 and 45C,
and at a pH between 2 and 7, preferably between 2 and
4.5. The reaction with a compound (7) where G is fluorine
is particularly preferably carried out at a pH between 3
and 5 and at a temperature between 0C and 30C.
The condensation reaction of a halotriazinylamino com-
pound of the formula (8) with an amino compound conform-
ing to the formula HNRlR2 is likewise carried out
analogously to known procedures for such reactions
between halotriazinylamino compounds and amines, for
instance in the above-indicated reaction media using an
acid-binding agent. Generally this reaction takes place
at a temperature between 0C and 80C and at a pH between
2 and 8, but in the case of starting compounds where Hal
is a chlorine atom the reaction is preferably carried out
at a temperature between 50 and 70C and at a pH between
2 and 4 and in the case of starting compounds where Hal
is a fluorine atom preferably at a temperature between
0C and 10C and at a pH between 6 and 8.
Starting compounds of the formula H-R-N(R)-H are for
example l-amino-3,6- or -4,6-disulfo-8-naphthol, 7-amino-
3-sulfo-1-naphthol, 6-amino-3-sulfo-1-naphthol, 6-amino-
3,5-disulfo-1-naphthol, 2-amino-4-acetyl~m;nohenzene-1-
sulfonic acid, 2-amino-8-naphthol-6-sulfonic acid, 6-methylamino-3-
sulfo-1-naphthol, 6-(4'-aminophenyl)-amino-3-sulfo-1-naphthol and 1-
amino-2,4-disulfo-8-naphthol .
2142251
- 10 -
Starting compounds conforming to the formula HNRlR2 are
for example 2-sulfoaniline, 3-sulfoaniline, 4-sulfoanil-
ine, 2,4-disulfoaniline, 2,5-disulfoaniline, 5-sulfo-2-
methoxyaniline, 4-sulfo-2-methoxyaniline, 5-sulfo-2-
methylaniline, 4-sulfo-2-methylaniline, 3-sulfo-4-
methoxyaniline, 4-sulfo-2-methoxy-5-methylaniline, 4-
sulfo-2,5-dimethoxyaniline, 5-sulfo-2,4-dimethoxyaniline,
4-sulfo-5-methoxy-2-methylaniline, 5-sulfo-2-chloro-
aniline, 3-sulfo-4-chloro-2-methylaniline, 4-sulfo-5-
chloro-2-methoxyaniline, 5- or 6-sulfo-2-amino-
naphthalene, 6,8-disulfo-2 -Am; non~ph thalene, 3,6,8-
trisulfo-2-aminonaphthalene, 8-sulfo-2-aminonaphthalene,
4,6,8-trisulfo-2 -~m; no~Aphthalene, 1,5- orl,6-disulfo-2-
Am;no~Aphthalene, 4~8-disulfo-2-a-m;nonAphthalene~ 6,7-
disulfo-2-aminonaphthalene, 5,7-disulfo-2-amino-
naphthalene, 5- or 6-sulfo-1-aminonaphthalene, 7-sulfo-1-
aminonaphthalene, 1-sulfo-2-aminonaphthalene, 3,6- or
4,6- or 4,8-disulfo-1-aminonaphthalene, ~-sulfoethyl-
amine, ~-hydroxyethylamine, N-methyl-N-(~-sulfatoethyl)-
amine, N-methyl-N-ethylamine, dimethylamine, diethyl-
amine, ~-carboxyethylamine, 4-sulfobenzylamine, 4-sulfo-
penethylamine, benzylamine, 2-methylaniline, aniline, 4-
chloroaniline, N-ethylaniline, N-methylaniline, ammonia,
morpholine, piperidine and piperazine.
The separation and isolation of the compounds of the
formula (1) according to the present invention - herein-
after called compounds (1) - from the aqueous synthesis
solutions can be effected by generally known methods for
water-soluble compounds, for instance by precipitating
from the reaction medium by means of an electrolyte, for
example sodium chloride or potassium chloride, or else by
evaporating the reaction solution itself, for example by
spray drying.
If the last-mentioned form of isolation is chosen, it is
21422~
frequently advisable, prior to the evaporation, to remove
any sulfate present in the solutions by precipitation as
calcium sulfate and separation by filtration.
The compounds (1) have fiber-reactive properties and very
useful dye properties. They can therefore be used for
dyeing (including printing) hydroxy -containing and/or
carboxamido-containing materials. For this purpose it is
also possible to use the as-synthesized solutions of the
compounds (1) directly in dyeing in the form of a liquid
preparation, with or without prior addition of a buffer
substance and with or without prior concentrating.
The present invention therefore also provides for the use
of the compounds (1) for dyeing (including printing)
hydroxy_ and/or carboxamido-contAi n; ng materials or
processes for their application to these substrates.
Preferably the materials are employed in the form of
fiber materials, in particular in the form of textile
fibers, such as yarns, for example in the form of hanks
or packages, and fabrics. This can be done analogously to
known procedures.
Hydroxy -containing materials are those of natural or
synthetic origin, for example cellulose fiber materials
or their regenerated products and polyvinyl alcohols.
Cellulose fiber materials are preferably cotton but also
vegetable fibers thereof, such as linen, hemp, jute and
ramie fibers; regenerated cellulose fibers are for
example staple viscose and filament viscose rayon.
Carboxamido-containing materials are for example 6yn-
thetic and natural polyamides and polyurethanes, in
particular in the form of fibers, for example wool and
other animal hairs, silk, leather, nylon-6,6, nylon-6,
nylon-11 and nylon-4.
The compounds (1) can be applied to and fixed on the
substrate6 mentioned, in particular the fiber materials
21~22~1
- 12 -
mentioned, in accordance with the use provided by the
present invention by the techniques known for water-
soluble, fiber-reactive dyes, for example by applying the
compound (1) to the substrate in dissolved form or
incorporating it therein and fixing it thereon or therein
by the action of heat or by the action of an alkaline
agent or by both measures. Such dyeing and fixing methods
are numerously described in the literature (for example
in European Patent Application Publication
No. 0 181 585). The compounds (1) are notable for high
degrees of exhaustion and fixation. Especially in the
exhaust processes they yield even at from 40 to 80C
dyeings of high color strength with a high degree of
fixation.
The dyeings of the present invention, in particular on
cellulose fiber materials, have good light fastness
properties not only in the dry state of the dyeing but
also in the wet state, moistened for example with a
perspiration solution, and also good wet fastness prop-
erties, for example good wash fastness properties at 60to 95C, even in the presence of perborates, acid and
alkaline fulling, cross-dyeing and perspiration fastness
properties, good acid and alkaline perspiration fastness
properties, a high ste~m;ng resistance, good acid, water
and seawater fastness properties, further good pleating
fastness, hot press fastness and rub fastness. They
similarly have good acid fading resistance when stored in
the moist, dyed state with acetic acid still present.
The Examples which follow serve to illustrate the inven-
30 tion. The part~ and percentages are by weight, unless
otherwise stated. Parts by weight relate to parts by
volume as kilogram to the liter.
The compounds described in the Examples by means of a
formula are indicated in the form of the free acid;
generally they are prepared and isolated in the form of
their alkali metal salts, such as lithium, sodium or
21~2~5~
potassium salts, and used for dyeing in the form of their
salts.
Similarly, the starting compounds and components men-
tioned in the Examples which follow, especially in the
Table Examples, in the form of the free acid can be used
in the synthesis a~ ~uch or in the form of their salt~,
preferably alkali metal salts.
The absorption maxima (AmaX) in the visible region report-
ed for the compounds of the present invention were
determined on their alkali metal salts in aqueous sol-
ution. In the Table Examples the AmaX values are given in
brackets in the hue column; the reported wavelength i6
given in nm.
Example 1
31.9 parts of 1-amino-3,6-disulfo-8-naphthol are con-
densed with 16 part~ of cyanuric fluoride in 200 parts of
water and 100 parts of ice at a pH of 7.5 and at a
temperature between 0C and 10C. Thereafter a solution
of 8.7 parts of morpholine in 200 parts of water is added
and the second condensation reaction is carried out at a
pH of 8.5. A solution of the diazonium salt of 27 parts
of 1-sulfo-6-carboxy-2-aminonaphthalene in about
450 parts of water, conventionally diazotized with sodium
nitrite in a hydrochloric acid medium, is added to the
resulting solution of the coupling component, a pH of 5
to 6 is set, and the coupling reaction is carried out
within that pH range at a temperature of about 20C.
The novel azo compound of the formula (written in the
form of the free acid)
21~ 5t
- 14 -
N~r ~CH2-CH2\
S O ~ H H O N H J~`N~ N ~ ~
)~3~ N = N ~ 2 2
HOOC HO~S SO,H
(~lrnaX = 545 nm)
is salted out with sodium chloride and isolated in the
form of the sodium salt. It has very good fiber-reactive
dye properties. The customary application techniques for
fiber-reactive dyes give strong dyeings and prints in
fast, bluish red shades of high brilliance.
Examples 2 to 25
Further novel dyes conforming to a formula (A)
G
so3~ N l N /R~
~IOOC N N K ~N~ \ (A)
where M is as defined above, are written in the ~able
~xamples which follow by means of the formula (A) and the
symbols indicated in the Table. They can be prepared
according to the present invention, for example analog-
ously to the above Example 1, and likewise have very good
fiber-reactive dye properties. The customary application
and fixing techniques in the art for fiber-reactive dyes
produce in particular on cellulose fiber materials the
strong fast hue indicated for each Table Example.
2~4~51
~x. -K-NH- G -NRlR2 Hue
2 8-hydroxy-3,6-fluorinepiperazinored (546)
disulfonaphth-7-
yl-l-ylamino
3 dittofluorine piperidino red (541)
4 dittofluorine 2-methyl- red (525)
phenyl-
amino
dittofluorine 3-sulfo- red (515)
phenyl-
amino
6 8-hydroxy-4,6- fluorine phenyl- red (510)
disulfonaphth-7- amino
yl-l-ylamino
7 dittofluorine 3-sulfo- red
phenyl-
amino
8 8-11YdLOXY-6-8U1- fluorine morpholino orange
fonaphth-7-yl-2- (483)
ylamino
9 dittofluorine 3-sulfo- orange
phenyl- (480)
amino
dittofluorine N-methyl- orange
phenyl-
amino
11 8-hydroxy-6-sul- fluorine morpholino scarlet
fonaphth-7-yl-3- (490)
ylamino
12 dittofluorine 3-sulfo- scarlet
phenyl- (492)
amino
13 dittofluorine N-methyl- scarlet
phenyl- (495)
amino
14 dittofluorine N-ethyl- scarlet
phenyl- (495)
amino
15 8-hydroxy-4-sul- fluorine 3-sulfo- orange
fonaphth-7-yl-1- phenyl-
ylamino amino
16 ditto chlorine ditto orange
17 8-hydroxy-6-sul- chlorine 2,5-disul- scarlet
fonaphth-7-yl-3-fophenyl-
ylamino amino
1~ dittochlorine 3-sulfo- scarlet
phenyl- (493)
amino
19 8-hydroxy-6-sul- chlorine 2,5-disul- orange
fonaphth-7-yl-2- fophenyl-
ylamino amino
21422~1
- 16 -
Ex. -R-NH- G -NRlR2 ~ue
8-l-ydloxy-3,6-chlorine N-methyl- red
di 8ul fonaphth-7- phenyl-
yl-l-ylamino amino
21 dittochlorine 2-methyl- red
phenyl-
amino
22 ditto chlorine 3-sulfo- red (546)
phenyl-
amino
23 8-hydroxy-4,6-chlorine N-methyl- red
disulfonaphth-7-phenyl-
yl-l-ylamino amino
24 ditto chlorine 4- 8ul fo- red (520)
phenyl-
amino
dittochlorine morpholino red