Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
~149344
METHOD AND DEVICE FOR COLLECTING AND REMOVING
DUST SEPARATED FROM A WEB IN A PAPER MACHINE
BACRGROUND OF THE lNv~N,lON
The present invention relates to a method in a paper machine
or in a finishing device of a paper machine, in particular in a
slitter-winder, for collecting and removing dust and other
particles that is separated from a web. In the method, an air
blowing is directed at the web in order to separate dust from the
web and suction is applied to the web to remove the separated dust
out of connection with the web.
Further, the present invention relates to a device in a paper
machine or in a finishing device of a paper machine, in particular
in a slitter-winder, for collecting and removing dust and other
particulate matter that is separated from the web. The device
comprises a pressurized chamber space in which there is a nozzle
opening for the application of a directed air blowing to the web
and a suction opening/openings for removing the dust separated from
the web by the directed air blowing.
After the manufacture of paper in a paper machine, dust and
impurities adhere to the face of the paper web, such as debris and
fibers derived from the dryer section of the paper machine.
Another, and perhaps the most important, source of dust is the
slitting process itself in which component webs of desired width
are slit out of a web of full width and then wound by means of a
winder into customer rolls. This dust and these impurities cause
problems in the further processing of the paper, in particular in
printing, because keeping the printing rolls clean is of essential
2149344
importance in order to maintain an adequate printing quality.
Also, dust spreads into the environment both in the paper mill
and in the further processing of the web, and the dust may induce
health risks at work, because it contains various filler particles.
With respect to the prior art, reference is made to Finnish
Patent Nos. 78,944 and 82,105, in which devices and methods for
dust removal are described for use in particular in the manufacture
of tissue paper.
In FI 78,944, a method and a device are described for
collecting and removing dust that is separated from the web in a
paper machine. In this reference, it has been considered the
principal novelty of the method that blowings are applied to the
web to both support the moving paper web free from contact and
separate dust from the web and, moreover, at least partly carry the
dust to its site of collecting. The device for carrying out the
method comprises one or more dust suction boxes in which there are
two nozzle boxes separated by an intermediate space and coanda
nozzles or equivalent blowing means in opposite directions being
placed at the sides of the nozzle boxes, that the intermediate
space communicates with a suction space subjected to a vacuum, and
that at the rear side of the dust suction box, there is a rear
suction space which is open against the by-passing web and which
communicates with a suction space subjected to a vacuum.
In FI 82,105, a method is described for removing dust that is
separated in connection with the detaching-creping of a soft-tissue
web by means of the creping doctor from a yankee cylinder. In
~14~3 1g
connection with the yankee cylinder, part of the dust is carried
along with a boundary layer consisting of air and which is caught
by the effect of the running of the web from the yankee cylinder
toward the reel-up and follows along with the web. In the method,
the dust removing device is provided with an interior space and
with a unified plane that stabilizes the web and is placed directly
against the path intended for the creped web so that during its
running, the web obtains a specified position tightly against the
unified plane, and that, exclusively by sucking into the interior
space, at least a substantial proportion of the boundary layer that
contains dust is removed. In this Finnish patent, a device is also
described for carrying out the method and comprises a path of a
width equal to the width of the web in which there is, in the
running direction of the web, a forward side edge and a rear side
edge, a solid plane covering plate, which are arranged
substantially to enclose the path while defining an interior space
and to form a slot between the covering plate and at least one of
the side edges, and members for producing a vacuum in the interior
space so that air is sucked in through the slot. The device is
intended for installation in a position in which the covering plate
is placed directly against the path of transfer of the creped web,
whereby the plane, unified covering plate produces an effect
stabilizing the web, so that during its running, the web obtains a
precise position tightly against the covering plate and the slot is
placed in the boundary layer that contains dust.
With further respect to the prior art, reference is made to
2149344
the U.S. Patent No. 4,715,078, in which a method and a device are
described for cleaning the edges of a paper web at a slitter-winder
and for removing dust detached from the edges. In the device shown
in this patent, two cleaning rolls are used which are strategically
placed in the path of running of the paper web. The first cleaning
roll contacts the forward edge of the paper web when the paper web
runs further from the slitter. At the same time as the paper web
runs further, its upper face is also cleaned by the same roll. The
second cleaning roll cleans the rear edge of the paper web as it
runs further. By means of this roll, the lower face of the paper
web is also cleaned. After this, by means of the vacuum system,
the particles that are detached by the cleaning rolls are removed,
and all of the four edges of the paper web are also cleaned. The
pressure system removes the particles from the face of the paper
web so that they can be carried off by means of the vacuum system.
In U.S. Patent No. 3,239,863, a web cleaning device is
described in which a chamber space is employed in which two air
nozzles directed towards the web have been formed. The space
between the nozzles is closed so that it forms an exhaust chamber
for the air discharged from the nozzles and for the dust detached
from the web.
A problem in these prior art devices is how to produce a
sufficiently high air blow velocity to detach dust adhering to the
web, and also the necessity of constructing the devices so that
they are placed quite far from the web, in which case they are
mainly suitable for general dust removal, but not for detaching
214g~44
dust and impurities from the web.
OBJECTS AND SUMMARY OF THE lNV ~ ON
It is an object of the present invention to provide a method
and device for removing dust by means of which it is also possible
to detach dust and impurities adhering to the web and to clean the
environment from dust and/or to prevent spreading of dust into the
environment.
It is a further object of the present invention to provide a
dust removing device that can be operated quite close to the web
without the attendant risk of damage to the paper web.
It is another object of the invention to provide a device that
can be shifted away from the path of the web in the event of a web
break and/or during tail threading.
In view of achieving the objects stated above and others, in
the method in accordance with the invention, a high-pressure air
blowing is directed at the web at a blowing region in order to
separate dust from the web, before the high-pressure blowing region
in the running direction of the web, the dust and other particles
separated from the web are sucked off by the application of a
suction force in a first suction region, and after the high-
pressure blowing region, additional quantities of dust and other
particles separated from the web are sucked off by the application
of a suction force in a second suction region.
The device in accordance with the invention includes a
pressurized air chamber from which a high-pressure blowing is blown
-
2143~ 14
through a nozzle opening therein toward the web, and suction
openings arranged both before and after the nozzle opening in the
running direction of the web.
By means of the device in accordance with the invention, it is
possible to remove the dust and impurities adhering to the face of
the web, which dust and impurities cause problems in the further
processing of the paper. Also, the dust load in the machine hall
is reduced, whereby the working environment is also improved.
According to a preferred exemplifying embodiment of the
invention, the device consists of two blow nozzles, one of which is
a high-pressure dust-detaching nozzle and the other is a low-
pressure air-curtain nozzle by whose means the detached dust is
prevented from being carried into the machine hall. This preferred
embodiment may also include two suction zones into which the dust
and impurities detached from the web are sucked. The device
communicates with an air system which carries the contaminated air
into a wet separator or to some other, equivalent filter, from
which the filtered air is passed either out of the machine hall or
back into the machine hall. In the nozzles in accordance with the
invention, the distance of the air blowing from the web is very
small, from about 2 mm to about 5 mm, preferably just about 2 mm to
about 3 mm, and the pressure used in the air space of the first air
nozzle is from about 20,000 Pa to about 30,000 Pa, preferably from
about 20,000 Pa to about 25,000 Pa, and the pressure in the air
space of the second air nozzle is from about 300 Pa to about 1000
Pa, preferably from about 300 Pa to about 500 Pa, and ideally about
400 Pa. 2149~44
In another preferred exemplifying embodiment, the slot in the
blow nozzle is about 0.5 mm, and the blow velocity employed in it
is about 200 meters per second. In the suction nozzles, a high
duct velocity is used, about 25 m/s to about 50 m/s, preferably
about 30 m/s to about 40 m/s, in order that the contaminations
present in the air should not adhere to the duct walls.
The method and devices in accordance with the invention are
generally usable in the paper machine and in its finishing
equipment, in particular in connection with a slitter-winder. In
a slitter-winder, the dust removing devices are placed after the
slitting as close to the slitting itself as possible, at each side
of the web.
In connection with the device, measurement and guide devices
may be arranged to maintain the distance of the device from the web
at a desired level and by whose means, in the event of a web break
or any other disturbance, the device can be shifted apart from the
web. The device is attached to the frame constructions of the
machine in such a manner that it is displaceable when desired.
In the method in accordance with the invention, the dust is
detached from the web, the dust is removed, and the web is kept far
enough from, but at the same time sufficiently close to, the blow
device.
Also, in the method in accordance with the invention, the
amount of air being directed at the web at the high-pressure
blowing region is regulated relative to the amount of air being
-
~14934~
removed via the suction effect int he first and second suction
regions such that the amount of air that is removed via the suction
effect is about twice the amount of air that is directed at the
web. Preferably, the distance between the web and a respective
point from which each of the high-pressure blowing and a low-
pressure curtain air blowing are directed at the web is measured
and continuously regulated to provide optimum operating conditions.
In its most basic embodiment, the device comprises a frame
including a first, pressurized air chamber, first nozzle means,
i.e., a nozzle opening, for directing a high-pressure air blowing
from the first chamber toward the web, and suction means for
removing dust from the vicinity of the web, the suction means
comprise at least one suction opening arranged before the nozzle
opening in a direction of travel of the web and at least one
suction opening arranged after the nozzle opening in the web travel
direction. The frame may also include a second air chamber, second
nozzle means, i.e., a nozzle opening, for directing a low-pressure
air blowing from the second chamber toward the web, and a third air
chamber having a nozzle opening through which air is blown during
tail threading of the web. The device also includes measurement
and regulation means for measuring and regulating the distance
between the device and the web such that the distance between the
device and the web remains constantly at a desired level.
In the following, the invention will be described in more
detail with reference to the figures in the accompanying drawings.
However, the invention is not strictly confined to the details of
- 2149~44
these illustrations.
BRIEF DE8CRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
The following drawings are illustrative of embodiments of the
invention and are not meant to limit the scope of the invention as
encompassed by the claims.
Figure 1 is a schematic vertical sectional view in the machine
direction of a device in accordance with the invention and which is
used in a method in accordance with the invention.
Figure 2 is a schematic vertical sectional view of a device in
accordance with the invention arranged at a slitter-winder in the
runnlng position.
Figure 3 shows the device of Fig. 2 in the web threading
positlon .
Figure 4 is a schematic illustration of a device in accordance
with the invention in the direction of width of the web.
Figure 5 shows a schematic air diagram for the device in
accordance with the invention.
Figure 6 is a schematic illustration of an exemplifying
embodiment of the arrangement in accordance with the invention at
a slitter-winder.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE lNv~..lON
Referring to the accompanying drawings wherein like reference
numerals refer to the same or similar elements, in the exemplifying
embodiment of the invention illustrated schematically in Fig. 1, a
21~934~
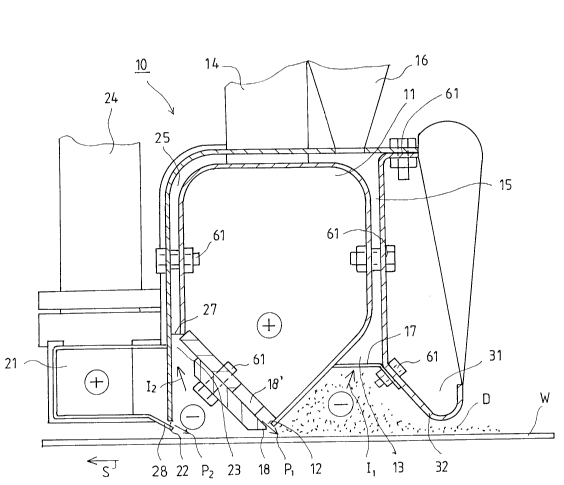
dust removing device 10 is arranged above a web W running in a
direction of travel S. The device 10 comprises a pressurized
chamber 11 into which blow air is introduced through a duct 14.
The chamber 11 has a nozzle opening 12 from which an intensive,
directed air blowing P1 is blown toward the web at a blowing region
so that any impurities and dust particles D adhering to the web are
detached from the web W. Before the blow opening 12, the device 10
includes a suction opening 13 through which the detached dust and
contamination particles D are removed from a first suction region
by a suction effect in the direction of arrow I1 into a suction
duct 15 and through suction duct 15 further into an exhaust duct
16. The blowing Pl blown out of the nozzle opening 12 constitutes
a high-pressure blow whereas other directed air blowings P2 passed
out of a chamber 21 in the device 10 through a blow opening 22
toward the web is a low-pressure blow and operates as an air
curtain nozzle. Chamber 21 has a lip 28 which forms part of the
blow opening 22. By means of air blowing P2, the detached dust D
is prevented from being carried into the machine hall and from
being carried further along with the air layer moving along with
the web W. Air is passed along a duct 24 into the blow chamber 21.
Between the first blow nozzle 12 and the second blow nozzle 22,
there is a second suction opening 23 which functions to draw or
suck any particles of impurities and dust D that may be present in
the area between the nozzles, i.e., in a second suction region,
into a suction duct 25 and from suction duct 25 further into the
exhaust duct 16. The device also includes a chamber 31 out of
- 21493-~
which, through a nozzle opening 32, blow air is passed toward the
web W when the device is used for tail threading of the web W (Fig.
3).
The blowing P1 detaches the dust from the web W and, at the
same time, keeps the web W far enough from the constructions of the
device 10. The nozzle openings 12,22 are continuous slot nozzles
having a gap width from about 0.2 mm to about 1 mm, preferably for
example about 0.5 mm. The nozzle openings 12,22 extend in the
transverse direction of the web W substantially across the entire
width of the web W. The distance E of the device 10 from the web
is between about 2 mm and 6 mm, preferably from about 2 mm to about
3 mm, during running. The blow velocity of the blowing P1 is, for
example, from about 150 m/s to about 200 m/s, and the pressure
employed in the chamber 11 is from about 20,000 Pa to about 30,000
Pa, preferably from about 20,000 to about 25,000 Pa. The blow
velocity of the blowing P2 is, for example, from about 30 m/s to
about 50 m/s, and the pressure employed in the chamber 21 is from
about 500 Pa to about 1500 Pa, preferably about 500 Pa to about 750
Pa. The suction velocity in the suction openings 13,23 is between
about 25 m/s and about 50 m/s, preferably from about 30 m/s to
about 40 m/s. The gap width of the suction opening 13,23 is about
5 mm to about 20 mm, preferably from about 10 mm to about 15 mm.
It is a goal of the dimensioning of the components of the
device 10 and the applied pressure and air blow velocities that the
amount of air that is sucked from the first and second suction
regions through the suction openings 13,23 is about twice as large
21~9344
as the amount of air that is blown through the nozzle openings
12,22. In this manner, it is substantially assured that the dust
detached from the web is not spread into the environment. The
second blow nozzle 22 produces the blowing P2 which, as stated
above, operates as an air curtain nozzle and prevents any dust that
may have been carried beyond the suction opening 23 from being
carried further along with the web W and also prevents spreading of
the dust into the environment.
The suction openings 13 and 23 are preferably provided with a
perforated plate/net 17,27 which prevents access of any chaffed
paper formed, for example, in connection with a web W break into
the device 10.
The device 10 is constructed from sheet constructions which
are shaped in the forms of the necessary chambers and ducts and
which are assembled together by means of fastening members 61 which
permit disassembly of the parts for the purpose of cleaning of the
device 10. Nozzle plates 18 which form the first nozzle opening 12
are manufactured by machining, in which case the accuracy of the
nozzle opening 12 can be made adequate. The nozzle plates 18,18'
are also interconnected by means of fastening members 61 whereby
cleaning of the chamber 11 and also cleaning of the nozzle opening
12 is easy and uncomplicated, if and when cleaning thereof is
necessary. The device 10 includes a frame formed by the assembly
of several material sheets and the suction ducts 15,25 are formed
between the material sheets, i.e., the sheet defining the chamber
11 and the outer sheet which are held together by the fastening
- 21493 14
members 61.
In Fig. 2, an exemplifying embodiment of the device in
accordance with the invention is shown arranged in connection with
a web guide roll 49 after the slitter. The device 10 is in the
running position, in which case it operates in the manner described
above with respect to Fig. 1. The device 10 is attached to the
other frame constructions 100 of the machine in a way in itself
known, and the running of the web W is also guided by an auxiliary
roll 101 arranged in connection with the device 10, e.g., attached
to the same frame construction 100 before the device 10 in the
running direction of the web.
In Fig. 3, the device 10 is shown shifted away from the
vicinity of the web W which is its position during threading of the
tail T of the web W. In the tail threading process, a nip N is
formed between the auxiliary roll 101 and the web guide roll 49,
through which nip the tail end T of the web W is passed. Out of
the blow chamber 31 of the device 10, blowings P3 are blown which
aid in the tail threading of the web W. The displacement of the
device 10 from the position as shown in Fig. 2 to the position as
shown in Fig. 3 is by any known displacement means. For tail
threading, by regulating the air flow of the high-pressure air
blowing P1 and the low-pressure air blowing P2 to decrease until
they cease, only the blowings P3 are directed at the web to aid the
tail threading.
Fig. 4 is a schematic sectional view of a dust removing device
10 arranged on a spread (deflected) web W. The device 10 has been
- -21493~4
divided into a plurality of separate blocks 10' extending in a
direction transverse to the running direction of the web, i.e.,
across the width thereof, whereby the blocks 10' and thus the
blowings provided thereby can be arranged in accordance with the
curve form of the web W. The number of the blocks 10' is from
about 3 to about 5, preferably about 3, depending on the width of
the web W. The distance E' of the blocks 10' from the web W is
measured by means of measurement devices 40', for example, at the
junction points between the blocks 10', and the data on the
distances are conveyed from the measurement devices 40' to a
control device 50.
Fig. 5 shows a schematic air diagram of the inventive method
and device. Dust is sucked out of the web W through the suction
zones 13,23 into the exhaust duct 16 from which the dust-containing
air is passed to a washer 53 into which water is passed through a
valve 54. After the washer 53, the washed air is passed into a
dust separator 55 after which the air is passed through a exhaust
blower 56 to the open air or back into the machine hall.
The clean filtered air is passed through a blow-air blower 52
into the blow-air ducts 14,24, and from the blow-air ducts 14,24
further into the blow chambers 11,21 from which, as shown in Fig.
1, out of the chamber 11 the dust-detaching blowings Pl are blown
toward the web W, and out of the chamber 21, the air-curtain
blowings P2 is formed.
In connection with the device 10, a measurement device 40 is
arranged for measuring the distance E of the device 10 from the web
14
21~-~3~4
W, for example, by means of ultrasonic or laser measurement. From
the measurement device 40, the information on the distance is
passed to the control device 50 which regulates the distance E of
the device 10 from the paper web W to the desired level, i./e.,
from about 2 mm to about 6 mm, preferably about 2 mm to about 3 mm.
The position of the device 10 in relation to the web W is regulated
constantly, because, for example, on the spreader rolls placed
after the slitter, the spreader roll may move up to 150 mm.
The control device 50 controls the movement of the device 10
on the frame constructions 100 of the machine. The arrangements of
transfer of the device 10 can be carried out by means of guide
and/or equivalent arrangements, which are known in themselves to a
person skilled in the art. The control device 50 also controls the
operation of the device so that, for example, in connection with a
web break, the device 10 is shifted apart from the path of the web
W.
Fig. 6 shows devices in accordance with the invention arranged
in connection with a slitter 45. In the slitter 45, component webs
of desired width are slit out of a web W of full width and then
wound by means of a winder 48 into customer rolls. One device in
accordance with the invention is arranged at the wire guide roll 49
placed after the slitter 45, at the opposite side of the web W, the
next device is placed before the spreader rolls 46 at the same side
of the web W, however, at the opposite side in relation to the
former dust removing device. Finally, the web W is passed to the
winder 48.
21~934~
The examples provided above are not meant to be exclusive.
Many other variations of the present invention would be obvious to
those skilled in the art, and are contemplated to be within the
scope of the appended claims.