Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
` - - 21S2025
A DEVICE AND METHOD FOR ARRESTING A FALL
Field of the Invention
This invention relates generally to devices for
arresting the fall of an individual and more particularly
to the use of webbing wound on the drum of a fall
arresting device to arrest the fall.
Backqround of the Invention
There are many devices in the marketplace for
arresting the fall of an individual. These range from
lanyards with no shock absorbing device to lanyards with
shock absorbers that are made by the stitching of layers
of a safety harness together so that a fall is arrested
by the breakinq of the stitching to elaborate devices
using retractable lanyards to limit free fall distance
and clutches or other braking devices to slow down and
stop the rotation of the lanyard drum. While all of
these devices have proved to be effective in various
degrees, there still exists a need for a relatively
simple, inexpensive but effective device for arresting
the fall of an individual.
215202S
Brief Description of the Invention
This invention provides a device and a method for
arresting the fall of an individual using an elongated
webbing wound on a rotatable drum in a housing so that,
when a fall occurs and the rotation of the drum is
stopped, the fall arresting force is absorbed by the
compaction of a plurality of layers of the elongated
webbing and in some instances by the compaction of a
resilient means between the drum and the first layer of
the elongated webbing and when necessary, by the
elongation of the portion of the elongated webbing
located outside of the housing.
In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the fall
arresting device comprises a housing having an opening
formed therein. A drum is rotatably mounted in the
housing and has an axis of rotation. An elongated
webbing is wound on the drum and has one end secured to
the drum and the other end thereof passing out through
the opening. A connecting device is secured to the other
end of the elongated webbing for connecting the other end
where desired, such as to a harness on a worker. Force
applying means, such as a falling body, apply a force on
the connecting device to rotate the drum. Stop means are
provided for preventing rotation of the drum when a
predetermined rotational velocity thereof has been
reached. Arresting means are provided for absorbing the
fall arrest energy and reducing the deceleration forces
applied to the load supporting device.
2 1 5 2 0 2 5
The stop means comprise at least a portion of the
drum having an outer surface having at least one cam
thereon. At least one pawl is pivotally mounted at a
fixed location on the housing and has a surface in
contact with the outer surface. At least one catch is
mounted on the drum for rotation therewith. Resilient
means are provided for urging the surface of the pawl
into contact with the outer surface. The cam is located
on a first radian of the axis of rotation of the outer
surface spaced in a circumferential direction from a
second radian of the axis of rotation of the outer
surface passing through the at least one catch in the
direction of rotation of the drum. The cam moves the
pawl into the engagement zone above the catch at lower
than locking speeds and requires the normal action of the
spring and pivot pin to pull the pawl out of the
engagement zone before the tip of the sperrad catch
engages it, thus providing a fail safe system. At a
predetermined rotational velocity of the drum, the cam
applies sufficient force on the pawl to overcome the
resilient means and move the at least one pawl into
contact with the at least one catch to prevent rotation
of the drum. In a preferred embodiment, there are a
plurality of cams, pawls and catches.
Resilient means are provided to act on the drum to
apply a resilient force on any portion of the elongated
webbing extending out of the housing and to rotate the
drum to rewind the extended webbing. The resilient means
2ls2o2s
comprise a coiled spring having a plurality of layers
with all but a few of the layers having a diameter at
least twice the diameter of the central body portion of
the drum. The coiled spring has one end secured to the
housing at a fixed location and another end secured to
the drum for rotation therewith.
The fall arresting means comprise a plurality of
layers of the elongated webbing wound on central body
portion of the drum. When a fall occurs, the plurality
of layers wound on the central body portion of the drum
are compressed when the rotation of the drum is stopped.
The fall may further be arrested by the elongation of the
portion of the elongated webbing unwound from the drum.
In another embodiment of the invention, resilient means
are located between the outer surface of the central body
portion of the drum and the first layer of the elongated
webbing to provide for additional compaction of the
layers of the elongated webbing.
A method is provided for arresting a fall of an
individual using a housing having a rotatable drum
mounted therein by winding a plurality of layers of an
elongated webbing on the drum; securing an inner end
portion of the elongated webbing on the drum; mounting a
connecting device on an exposed end portion of the
elongated webbing; placing a weight on the connecting
device due to the fall to move the connecting device in a
downward direction and rotate the drum; stopping the
rotation of the drum and compressing a plurality of the
21~2025
`' ~
plurality of layers of the elongated webbing on the drum
to arrest the downward movement of the connecting device.
The method further comprises pulling a portion of the
elongated webbing out of the housing and stretching the
portion of the elongated webbing pulled out of the
housing to aid in arresting the downward movement of the
connecting device in the event of a fall.
In another preferred embodiment of the invention,
means are provided for attaching a fall arresting device
to a harness of the type described in United States
Patent No. 4,712,513. The attachment means comprise a D-
ring attached to the harness and secured to a nozzle
secured between the front and rear cover plates with a
portion of the nozzle extending through the D-ring.
Locking means are provided on the nozzle for permitting
movement of the D-ring over the portion of the nozzle but
preventing removal of the D-ring after the D-ring has
passed over the portion of the nozzle. Abutment means
are provided on another portion of the nozzle for
preventing movement of the D-ring over the another
portion.
In another preferred embodiment of the invention,
additional locking means are provided for urging the D-
ring into contact with the locking means.
Brief Description of the Drawings
Preferred embodiments of the invention are
illustrated in the drawings in which:
215202~
Fig. 1 is a rear elevational view of the invention
with the cover removed;
Fig. 2 is a cross-sectional view taken on the line
2-2 of Fig. 1 with some parts removed;
Fig. 3 is an elevational view of the stop means of
this invention;
Fig. 4 is an elevational view of a cover of this
invention;
Fig. 5 is an elevational view of the housing of this
invention;
Fig. 6 is a cross-sectional view taken on the line
6-6 of Fig. 5;
Fig. 7 is an elevational view of the spring mounting
of this invention;
Figs. 8 and 9 are elevational views of the nozzle
assembly of this invention;
Figs. 10 illustrates the drum attachment end of the
webbing;
Fig. 11 illustrates one embodiment of the invention
with a portion of the webbing in contact with the drum;
Fig. 12 illustrates another embodiment of the
invention with a steel spring between the drum and a
portion of the webbing;
Fig. 13 illustrates another embodiment of the
invention with a strip of an elastomeric material between
the drum and a portion of the webbing;
215202~
Fig. 14 is an elevational view with parts in section
illustrating another preferred embodiment of the
invention;
Fig. 15 is a side elevational view of Fig. 14;
Fig. 16 is a top plan view of Fig. 14;
Fig. 17 is a perspective view of Fig. 14;
Fig. 18 is a top plan view of a D-ring;
Fig. 19 is an elevational view with parts in section
illustrating a double action single locking attachment of
the invention with the D-ring in a locked position;
Fig. 20 is an elevational view with parts in section
illustrating the D-ring before it is moved into the
locked position; and
Fig. 21 is a top plan view of Fig. 19.
Detailed Description of the Invention
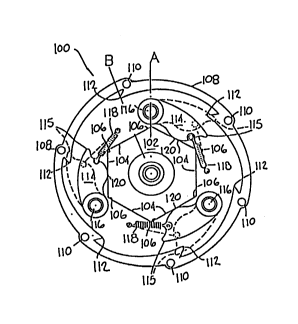
In Figs. 1 and 2, there is illustrated a fall
arrester 2 of this invention having an anchorage mount
configuration. The fall arrester 2 has a housing 4
having an arcuate extent, Fig. 5, of about 290 degrees so
as to provide for an opening 6. The housing 4 has a
plurality of circumferentially spaced apart threaded
openings 8 for purposes described below. A front cover
plate 10 and a rear cover plate 12, Figs. 2 and 4, each
have a plurality of circumferentially spaced apart
openings 14 so that headed threaded bolts 16 may pass
through the openings 14 and be threadedly secured in the
2152025
threaded openings 8 to secure the front 10 and rear 12
cover plates to the housing 4.
A drum 20 is mounted for rotation about an axis of
rotation in the housing 4 and has a central body portion
22 having generally cylindrical inner surfaces 24 and 26
on either side of a central radially inwardly extending
flange 28. Bearings 30 and 32 are mounted on the
generally cylindrical surfaces 24 and 26. A fixed shaft
34 has a generally cylindrical surface 36 which is in
contact with the other side of the bearings 30 and 32 to
allow for rotation of the drum 20. The ends of the shaft
34 fit into recesses 38 and 40 in the front 10 and rear
12 cover plates and are secured therein by headed
threaded bolts 42 and 44.
An annular plate 50 is secured on the central body
portion 22 using a plurality of circumferentially spaced
apart headed threaded bolts 52. A flange portion 54
projects radially outwardly from the central body portion
22 and cooperates with the annular plate 50 to define a
first cavity 56. An elongated webbing 58 is wound on a
generally cylindrical outer surface 60 and is located in
the first cavity 56. One end 62 of the elongated webbing
58 is secured to the central body portion by suitable
means described below. The other end 64 passes out of
the housing 4 through a nozzle 66, explained more fully
below. The other end 64 is permanently secured to a
portion 68 of the elongated webbing 58. Other portions
70 of the other end 64 are doubled upon themselves and
2152025
temporarily secured together. A connecting device 72,
such as a D-ring, snap hook or other similar devices, is
located between the other end 64 and the other portions
70 for connecting the other end 64 where desired, such as
to the harness (not shown) of a worker. The inner
surfaces of the other portions 70 are distinctively
colored so that when sufficient force is placed on the
connecting device to arrest a fall, the other portions
will be broken open to reveal the colored portions to
indicate that the fall arrester 2 has been used.
A second cavity 80 is formed between the annular
plate 50 and the front cover plate 10. A coiled spring
82, Figs. 2 and 7, is located in the second cavity 80 and
has one end thereof secured to the nozzle, described
below, by suitable means (not shown). The other end 86
of the coiled spring 82 is secured in the central body
portion 22 so that as the central body portion 22
rotates, the coiled spring 82 is wrapped thereon. The
coil spring 82 exerts a varying force of between about 3
pounds on the outer layer of the elongated webbing 58 and
about 12 pounds on the inner layer of the elongated
webbing 58 on the central body portion 22 tending to keep
the elongated webbing 58 wound on the reel 20. The
coiled spring 82 is attached to ride in the housing, not
the drum, so that in its unwound state substantially all
of the coils thereof are adjacent to the housing 4. By
securing the coiled spring 82 to ride in the housing
rather than the drum, to rotational momentum of the drum
~152025
decreases as the webbing 58 retracts into the drum,
thereby reducing the possibility of damage to the webbing
and the spring should a unit be accidentally released to
retract uncontrollably.
A handle 90 is secured to the housing 4 by suitable
means such as headed threaded bolts 91 passing through
reinforced openings 92 in the housing 4.
Stop means 100 are illustrated in Figs. 1-3. An
axially outer portion 102 of the central body portion 22
is provided with an outer surface having a plurality of
linear extending surfaces 104 separated by a plurality of
cams 106. A sperrad 108 is secured on the flange portion
54 by a plurality of headed threaded bolts (not shown)
passing through circumferentially spaced apart openings
(not shown) in the flange portion 54 and threadedly
secured in the threaded openings 110. The sperrad 108
has an inner surface having a plurality of catches 112.
A plurality of pawls 114 are pivotally mounted on pivot
studs 116 projecting outwardly from the rear cover plate
12. Resilient means 118 urge a surface 120 of each pawl
114 into contact with the linear surfaces 104 of the cams
106. As illustrated in Fig. 3, a radian A passing
through the center point of a cam 106 is located behind a
radian B passing through the tip of a catch 112 in the
direction of rotation of the drums 20. When the surface
120 of the pawl 114 is in contact with the cam 106, the
distance between the axis of the drum 20 and the tip 115
of the pawl 114 is greater than the distance between the
2152025
axis of the drum 20 and the tip of the catch 112 as
indicated by the dashed lines in Fig. 3 and referred to
as the engagement zone. However, as the drum 20 rotates,
the surface 120 of the pawl 114 moves onto the linear
surface 104 so that the distance between the axis of the
drum 20 and the tip 115 of the pawl 114 is less than the
distance between the axis of the drum 20 and the tip of
the catch 112. The cam moves the pawl into the
engagement zone at lower than locking speeds and requires
the normal action of the spring and pivot pin to pull the
pawl out of the engagement zone before the tip of the
sperrad catch engages it, thus providing a fail safe
feature. This permits the normal extension of the
webbing 58 as required by a worker. This is accomplished
by the circumferentially spaced apart locations of the
cams 106 and the catches 112. However, when the drum 20
is rotating at a sufficiently high speed such as when a
fall occurs, the inertial force exerted by the resilient
means 118 will be overcome by the force exerted on the
pawls 114 by the cams 106 so that the pawls 114 remain
extended and will enter into the catches 112 and stop the
rotation of the drum. If something should happen to the
resilient means 118, the pawls 114 would remain as
positioned by the cams 106 so that the pawls 114 would
enter into the catches 112 and prevent rotation of the
drum 20 and thus provide for a fail safe condition.
The portions forming the nozzle 66 are illustrated
in Figs. 1, 8 and 9. The nozzle 66 comprises two V-
2152025
shaped members 122 and 124, having slots 126 and 128
formed therein. The slots 126 and 128 are in alignment
to form an opening for the other end 64 of the elongated
webbing 58 to pass through. Each of the V-shaped members
122 and 124 are provided with passageways 130 extending
therethrough so that headed threaded bolts 132 may be
passed through openings 134 in the front 10 and rear 12
cover plates and be secured in threaded openings in studs
(not shown) located in the passageways 130 and extending
between and in contact with the front and rear cover
plates 10 and 12. Other passageways 138 are formed in
each of the V-shaped members 122 and 124 and extend
therethrough so that bolts 140 may be passed through
openings 142 in the front 10 and rear 12 cover plates and
be secured.in threaded openings in studs (not shown)
located in the passageways 138 and extending between and
in contact with the front and rear cover plates 10 and
12.
The one end 62 of the webbing 58 is illustrated in
Fig. 10. A portion 150 is folded back on another portion
152 and partially stitched together to form a loop 154.
In Fig. 11, there is illustrated one embodiment of the
invention for securing the one end 62 to the central body
portion 22. The central body portion 22 has an inner
portion 156 and a spaced apart outer portion 158 so as to
form a cavity 160. An opening 162 in the outer portion
158 provides access to the cavity 160. The outer portion
158 has threaded openings 164 for receiving the bolts 52.
` 2152025
In securing the webbing 58 to the central body portion
22, the loop 154 is placed around the inner portion 156
and the portions 150 and 152 pass through the opening 162
and are then wound around the outer portion 158.
Another embodiment of the invention is illustrated
in Fig. 12. A steel spring 166 is located between the
outer surface 168 of the outer portion 158 and the first
wrap 150 and 152 of the webbing 58 and is used to provide
for additional compression of the webbing 58 on the drum
20. The steel spring 166 has a plurality of spaced apart
sections 170 in contact with the outer surface 168 and
another plurality of spaced apart sections 172 spaced
from the outer surface 168. The steel spring 166 has
arcuate shaped end portions 174 for securing it to the
outer portion 158. The steel spring 166 provides for
additional compaction of the layers of the elongated
webbing in the event of a fall.
Another embodiment of the invention is illustrated
in Fig. 13. A strip of elastomeric material 176, such as
foamed rubber or other materials having similar
characteristics, is located between the outer surface 168
and the first wrap 150 and 152 and is used to provide for
additional compression o the webbing 58 on the drum 20.
The strip of elastomeric material 176 provides for
additional compaction of the layers of the elongated
webbing in the event of a fall.
In the assembly of the arresting device, the
bearings 30 and 32 are inserted into the central body
2152025
~,
portion 22. The sperrad 108 is secured to the flange
portion 54. The one end 62 of the elongated webbing 58
is secured to the generally cylindrical outer surface 60
and then wound thereon. The annular plate 50 is then
secured to the central body portion 22. A portion of the
elongated webbing 58 prior to the other portions 70 is
located in the slots 126 and 128 and the back cover plate
12 is placed in position. One end of the coiled spring
82 is secured to the nozzle 122 or 124 and the other end
86 is secured in a notch in the central body portion 22.
At least one wrap of the coil spring 82 is used to retain
the other end 86 in the notch in the central body portion
22. The front cover plate 10 is then positioned on the
housing 4 and the various bolts are used to secure the
arresting device 2 in an assembled condition. A force is
applied to the load supporting member 72 to pull all of
the elongated webbing 58 out of the housing 4 and then
the spring 82 is used to retract the elongated webbing
58.
In use of the anchorage mount configuration, the
handle 90 is secured to a fixed support or a life line
(not shown) and the connecting device 70 is secured to
the safety harness (not shown) on a worker. The
elongated webbing 58 has a length of about twenty-one
feet to allow for ordinary movement of the worker. In
the event of an accident or other reasons, if the worker
starts to fall, a greater force is applied to the
connecting device 72 so as to accelerate the rotation of
14
2152025
the drum 20. The acceleration of the drum 20 is rapid so
that, when five to seven inches of the elongated webbing
58 have passed through the nozzle 66, the pawls 114 have
moved into the catches 112 to prevent rotation of the
drum 20. The deceleration force of the fall is then
reduced by the fall arresting energy being absorbed by
the compaction of the elongated webbing 58 on the drum 20
and, when necessary, the elongation of the portion of the
elongated webbing 58 passing through the nozzle 66.
Also, the deformation of the steel spring 166 or the
elastomeric material 176 will also provide for additional
compression of the webbing 58 on the central body portion
22. In some instance, an external shock absorber, such
as that illustrated in United States Patent No.
4,618,026, which is incorporated herein by reference
thereto, may be secured to the load supporting device 72.
The following table lists various parameters that
must be met by any fall arresting device.
Table 1
Test ParameterANSI Z359.1OSHA 1910. 66 CSA
Z259.2 CEN
Test Weight (lbs.)220* 220 220**
220
Free Fall (ft.) 0* 0 2**
Freq. Filter (hz.) 100 120* No
spec. 60**
Cable Extraction (ft.) 3* No spec. 2
Allowables:
Force (lbf.) 1,800 1,260* 2,700
1,350**
2152025
Extension (in.) 54 42* 40**
78
220 The ANSI and OSHA are United States
requirements; the CSA is Canadian requirements and the
CEN is European requirements. A series of tests were
conducted using various materials as the webbing 58. The
parameters indicated by the single asterisk were used to
determine whether or not a material passes a O free fall
and the parameters indicated by the double asterisks were
used to determine whether or not a material passed at 2
feet of free fall. In addition to the test at three feet
of initial webbing extraction, tests were conducted at
eight, thirteen and eighteen feet of initial webbing
extraction. Two materials that passed the tests were a
nylon webbing marketed by the Elizabeth Webbing Company
under the trade designation N-7649 which had a width of
1.0 inch and a thickness of 0. 085 inch and a nylon
webbing marketed by the Murdock Webbing Company under the
trade designation No. 11210 which had a width of 0. 9375
inch and a thickness of 0. 076 inch.
In Figs. 14-16, there is illustrated a back pack
configuration for attaching the fall arrester 2 to the
rear plate of the safety harness illustrated in United
States Patent No. 4,712,513 which is incorporated herein
by reference thereto or any other similar safety harness.
A D-ring 180, Fig. 18, is used instead of the ring
illustrated in the ' 513 patent.
16
2152025
A nozzle 182, Fig. 17, comprises two members 184 and
186 which have passageways 188 and 190 similar to the
passageways 130 and 128 so that the members 184 and 186
may be secured to the front and rear cover plates 10 and
12 in the same manner as the members 122 and 124. When
joined together, the members 184 and 186 have a
rectangular portion 192 and a cylindrical portion 194. A
recess 196 is formed in the member 184 and a recess 198
is formed in the member 186 so that when the members 184
and 186 are joined together they form a slot for the
passageway of the elongated webbing 58. Two spaced apart
openings 200 and 202, Fig. 16, are formed in the member
184 and two spaced apart openings 204 and 206 are formed
in the member 186. A pivot pin 208 is located in the
openings 200 and 204 and another pivot pin 210 is located
in the openings 202 and 206. Two spaced apart recesses
212 and 214 are formed in the member 184 and two spaced
apart recesses 216 and 218 are formed in the member 186.
A locking lever 220 is located in the recesses 212 and
216 and is mounted for pivotal movement on the pivot pin
208 and is urged outwardly by a spring 222 located in
recesses (not shown) in the members 184 and 186. Another
locking lever 224 is located in recesses 214 and 218 and
is mounted for pivotal movement on the pivot pin 210 and
is urged outwardly by a spring 226 located in recesses
(not shown) in the members 184 and 186.
A recess 230 is formed in the member 184 and a plate
232 is located in the recess 230. A portion 234 projects
2152025
from the plate 232 and is located in a recess in the
cylindrical portion 194 and has an arcuate hook portion
236 for purposes described below. The plate 232 has two
abutment surfaces 238 and 240. A recess 242 is formed in
the member 186 and a plate 244 is located in the recess.
A portion 245 of the plate 244 projects from the plate
244 and is located in a recess in the cylindrical portion
194. The plate 244 has two abutment surfaces 246 and
248. The plates 232 and 244 are secured in the recesses
230 and 242 by headed threaded bolts 250 passing through
openings in the front and rear cover plates 10 and 12 and
secured in threaded openings 252 in studs 254 located in
passageways 256 and 258 formed in the members 184 and 186
and in contact with the plates 232 and 244.
The D-ring 180 has three straight sides 260, 262 and
264 and an arcuate side 266. A center partition 268
forms a rectangular opening 270 and a circular opening
272 and is thinner than the straight sides 260, 262 and
264 and arcuate side 268.
In use of the back pack configuration, the crossing
portions of the harness as illustrated in the '513 patent
are located in the rectangular opening 270. The arcuate
side 266 is placed under the hook portion 236 and the D-
ring 180 is moved over the cylindrical portion 194. As
the D-ring 180 moves over the cylindrical portion 194, it
pushes the locking levers 220 and 224 inwardly. When the
D-ring 180 has passed the locking levers 220 and 224, the
springs 222 and 226 move the locking levers 220 and 224
18
2152025
outwardly so that the end portions 274 and 276 will be
superposed over the straight sides 260 and 264 to prevent
the accidental removal of the D-ring 180. Portions of
the center partition 268 are in contact with the abutment
surfaces 246 and 248. Since the center partition 268 is
thinner, this results in a slight angle for the D-ring.
If desired, this slight angular relationship can be
changed by raising the abutment surfaces 246 and 248.
Portions of the arcuate side 266 are in contact with the
abutment surfaces 238 and 240. If a fall occurs, the D-
ring 180 applies a force on the abutment surfaces 246 and
248 and pivotal movement of the D-ring 180 is prevented
by the hook portion 236 and the arcuate side 266.
Another preferred embodiment of the invention is
illustrated in Figs. 19-21 and is to be used in
association with the harness in United States Patent No.
4,712,513 or any other similar safety harness. Portions
of the embodiment of Figs. 19-21 are similar to portions
of the embodiment illustrated in Figs. 14-18 and have
been given the same reference numerals. This embodiment
requires a double action to release the D-ring as
required for use with double action single locking snap
hooks.
A pair of spaced apart recesses 280 are formed in
the member 186 and a mating pair of spaced apart recesses
282 are formed in the member 184. Inverted L-shaped
metal plates 284 are located in the recesses 280 and 282.
The pivot pins 206 and 208 pass through openings in the
19
215202S
inverted L-shaped metal plates 284. Threaded metal bolts
286 pass through passageways in the members 184 and 186
and are threaded into opposite ends of a common threaded
nut 288.
Resilient means 290 are provided for urging the
portions 260 and 264 of the D-ring 180 into the locking
levers 220 and 224 or for maintaining the locking levers
in a retracted position. A sleeve having a generally
cylindrical portion 292 and a flange portion 294 is
mounted for sliding movement over the cylindrical portion
194 of the members 184 and 186. A coiled spring 295 has
a first coil 296 secured by a press fit to the
cylindrical portion 194 and a second coil 298 secured by
a press fit to the cylindrical portion 292. Under normal
conditions, the coiled spring 195 will hold the
cylindrical portion 292 at a location to hold the locking
levers 220 and 224 in a retracted position as illustrated
in Fig. 20 wherein the D-ring has been moved into contact
with the flange portion 294.
In use of the back pack configuration, a force is
applied to the portions 260 and 264 of the D-ring 180 to
move them over a portion of the cylindrical portion 194
and moved into contact with the flange portion 294.
Continued movement of the portions 260 and 264 compresses
the coiled spring 295 and the movement of the portions
260 and 264 is continued until the locking levers 220 and
224 are urged outwardly by the springs 222 and 226.
Outward movement of the locking levers 220 and 224 is
2152025
halted when portions thereof contact abutment surfaces
300 and 302. The force is removed from the portions 260
and 264 and the coiled spring 295 urges the portions 260
and 264 in contact with the locking levers 220 and 224.
Since the center partition 268 is thinner, there will be
a slight angular relationship of the D-ring. When it is
desired to remove the fall arrester 2, two distinct and
separate actions are required. First, the D-ring must be
pushed down to disengage the levers 220 and 224. Second,
the levers 220 and 224 must be moved inwardly and then
the D-ring can slide up and over the levers 220 and 224.
The coiled spring 295 moves the portions 260 and 264 and
the cylindrical portion 292 over the cylindrical portion
194 until they reach the location illustrated in Fig. 20.
At that time, the portions 260 and 264 are removed from
the portion of the cylindrical portion 194.
While illustrative and presently preferred
embodiments of the invention have been described in
detail herein, it is to be understood that the inventive
concepts may be otherwise variously embodied and employed
and that the appended claims are intended to be construed
to include such variations except insofar as limited by
the prior art.