Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2~~~~62
PCT/EP94/01066 R/Ru-P 3433
Profil-Verbindungstechnik GmbH & Co. KG
New introduction to the specification
The invention relates to a press-in device for the
pressing of fastener parts, such as, for example, nuts,
into plate-like components, comprising an upper housing
part and a lower housing part which are restrictedly
displaceable relative to one another and are biased in
the direction away from one another by a spring force,
wherein the lower housing part has a fastener part
channel to which in each case one fastener part can be
supplied through a lateral supply opening, and a
plunger which is secured to the upper housing part and
extends in the fastener part channel in order, on a
relative displacement between the upper and lower parts
of the housing to displace the fastener part located in
the channel from a starting position adjacent to the
supply opening to a working position adjacent to the
open end of the channel and to press it into the
plate-like component.
Such press-in devices are known. They serve for example
to press self-piercing nuts into sheet-metal parts. The
relative displacement which is necessary for this
purpose between the upper part of the housing and the
lower part of the housing is customarily generated in
that an upper press part to which the pressing device
is secured is moved downwardly whereupon the lower
housing part contacts the plate-like component and,
during the further downward movement of the upper
housing part the plunger presses the fastener component
~m~~sz
- 2 -
into the plate-like component. A cam-controlled holding
device is customarily associated with the plunger and
holds the fastener part in its position during its
downward movement through the fastener part channel.
A press-in device of this kind is for example disclosed
in DE-U-92 05 608.3. The press-in device is hereby
integrated into the upper press part in such a way that
it is secured by centring pins and screws or clamping
means to the upper press part, and in such a way that
the springs which prestress the housing parts are
braced against the press part.
The present invention is based on the object of so
further developing a press-in device of the initially
named kind that the possibilities for use are
increased.
This object is satisfied in accordance with the
invention in that the press-in device is formed as an
integral module which can be connected via a
quick-closure coupling to a machine part in that the
coupling means of the quick-closure coupling are
provided both at the upper housing part (16) and also
at the lower housing part so that the upper or lower
housing part can be selectively attached to the machine
part, in that the lower housing part can be attached by
the quick-closure coupling to an intermediate plate
which is resiliently suspended on the machine part
which is formed as the upper part of a press.
The mounting of press dies to a press through quick
closure couplings is known from FR-A-2 170 532.
The present invention opens up a plurality of
- . ~ ~~~3 ~~
- 3 -
possibilities of use of such a press-in device which
represents a considerable enrichment of the prior art.
Thus, the invention makes it possible to exchange one
press-in device for another press-in device in simple
manner in order for example to process fastener parts
of different kinds or of different dimensions. A
further possibility lies in forming the press-in device
as the exchangeable tool of a tool-changing system of a
machine tool. It is also possible to mount the press-in
device - directly or indirectly - on a robot arm. The
press-in device formed in accordance with the invention
thus represents a mobile unit which can be transported
to any working positions that are desired, which makes
it suitable for use in NC-machines, transfer lines and
the like.
In order to supply the fastener parts, a hose connected
to the press-in device is customarily provided which
leads to a sorter or to another source for the fastener
parts. In a particularly advantageous layout of the
invention, a magazine for receiving a restricted number
of fastener parts is however associated with the
pressing-in device and has a magazine channel which
stands in communication with the supply opening of the
press-in device. This offers a completely free
movability of the press-in device in space and, for
example, makes it possible to press a predetermined
number of nuts or other fastener parts into a switching
plate.
The quick-closure coupling provided in accordance with
the invention naturally also makes it possible to
rapidly exchange the press-in device for service and
repair purposes.
- . ~ V ~1~3:~'~~
- 4 -
The press-in device cannot only be used for the
pressing of self-piercing fastener parts into solid
material, but rather also for the pressing of fastener
parts into pre-bored holes. Apart from nuts, other
fastener parts such as, for example, bolts and rivets
can also be processed.
Further advantageous developments of the invention are
set forth in the subordinate claims.
Preferred embodiments of the invention will now be
explained in more detail with reference to the drawings
in which are shown:
Fig. 1 a longitudinal section through a
press-in device in the viewing
direction of the arrow I-I in Fig. 2,
to explain a possible design of a quick
closure coupling and the general layout
of a joining device for fastener parts;
Fig. 2 a plan view of the press-in device of
Fig. 1;
Fig. 3 a longitudinal section through a first
embodiment in accordance with the
invention of a press-in device with a
magazine attached thereto as seen in
the direction of viewing of the arrows
III-III of Fig. 4;
CA 02158562 1999-10-04
rt
- 4A -
Fig. 4 a plan view of the press-in device of
Fig. 3;
Fig. 5 a schematically illustrated possibility of
use for the press-in device of Fig. 3;
Fig. 6, 7 a side view and a plan view respectively
of a modified embodiment of a quick-
closure coupling for the press-in device
of Fig. 3 in a schematic illustration;
Fig. 8 a partially sectioned side view of another
embodiment of a quick-closure coupling in
a schematic illustration;
Fig. 9 a plan view of a supply apparatus with
-
a magazine for the fastener parts;
Fig. 10 a longitudinal section in the direction
of viewing of the arrows X-X in Fig. 9;
Fig. 11 an illustration corresponding to Fig.
of a modified embodiment of the
magazine;
Fig. 12 a schematic illustration of a
tool-changing system with several
press-in devices;
Fig. 13 a C-shaped yoke for mounting the
press-in device of Fig. 1 on a robot
arm in a schematic illustration;
Fig. 14 a side view of a robot with a press-in
device in accordance with Fig. 3
mounted thereon in a schematic
illustration.
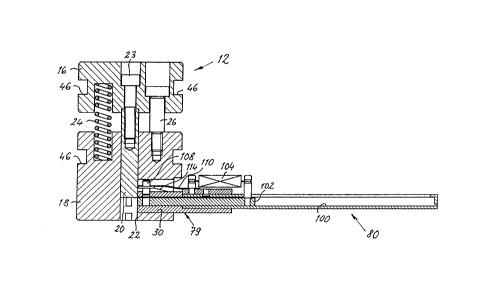
The press-in device 10 shown in Figs. 1 and 2 serves
for pressing a self-piercing nut M into a plate-like
component B. For this purpose, the press-in device 10
is attached by a quick-closure coupling 12 to an upper
press part 14 which can be moved up and down as will be
explained later in detail. The layout of the press-in
device 10 is only described to the extent that is
necessary for an understanding of the present
invention.
The press-in device 10 has an upper housing part 16 and
a lower housing part 18 which is displaceably guided in
a recess 19 of the upper housing part 16. A plunger 20
_ 6 _
secured to the upper housing part 16 extends in a
channel 22 formed in the lower housing part 18 so that
the plunger 20 drives the nut M through the channel 22
on a relative displacement between the upper and lower
housing parts. The two housing parts 16, 18 are biased
in the direction away from one another by coil springs
24 which are braced, at the one end, against a plate 15
which closes the upper side of the upper housing part
16 and, at the other end, in bores of the lower housing
part 18. The relative displacement between the two
housing parts 16 and 18 is restricted by a stroke
limiter 26.
The nuts M are supplied to the channel 22 through a
lateral supply opening 28 which adjoins a cut-out 30. A
magazine or a hose leading to a source can be connected
to the cut-out 30 as will be explained in detail in
conjunction with Figs. 3 and 9 to 11.
For the piercing of the nut M into the component B
supported on a die 34, the upper part l4 of the press
together with the press-in device 12 secured thereto is
moved downwardly until the lower housing part 16
contacts the component B. During the further downward
movement of the upper housing part 16, the plunger 20
drives the nut M from the point of supply adjacent to
the supply opening 28 through the channel 22 out of the
open end of the channel 22 and presses it into the
component B. During the movement of the nut M through
the channel 22, it is held in its position by a -
non-shown - holding means which can, for example,
consist of two cam-controlled holding claws which are
pivotally connected to the lower housing part 18, as is
described in the older patent application
P 42 11 276.1.
~~5~~~~
_,-
As shown, the press-in device is formed as an integral
module, which is transported as a unit, is stored and
can be attached by the quick-closure coupling 12 to any
desired machine parts. In the embodiment shown in Figs.
1, 2, the quick-closure coupling 12 has two strips 40
which are secured by screws and centering pins 42 to
the machine part 14. The strips 40 are provided with
laterally projecting latching sections 44 which
confront one another and which are slidingly received
by correspondingly dimensioned grooves 46 in the upper
housing part 16.
The sections 44 of the strips 40 and the grooves 46
thus form a form-fitted connection designed as a
sliding guide between the machine part 14 and the
press-in device 10. A relative displacement in the
sliding guide is restricted at one end by an abutment
48 and at the other end by a releasable lock 50 which
are both provided at one of the strips 40. The
releasable lock 50 consists of a locking lever which is
rotatably journalled at the strip 40 by means of a
spigot 52 and is urged by a spring 54 into its locking
position in which a locking nose of the locking lever
contacts against one side of the upper housing part 16
of the locking device 10.
For the coupling of the press-in device 10 to the
machine part 14, the upper housing part 16 is pushed
into place with its grooves 46 disposed laterally
between the strips 40 until the upper housing part 16
contacts the abutment 48. At this point in time, the
lock 50 is automatically pressed by the spring 54 into
its closed position whereby the press-irk device 10 is
fixed to the machine part 14. For the release it is
- g -
only necessary to pivot the lock 50 into its open
position, whereupon the press-in device 10 can be
pulled off from the strips 40.
A modified embodiment of a press-in device 10 is shown
in the Figs. 3 and 4. The same components or components
which correspond to one another are designated with the
same reference numerals as in Figs. 1 and 2.
The embodiment of Figs. 3 and 4 is distinguished from
that of Figs. 1 and 2 in that the upper and lower
housing parts 16, 18 are vertically spaced from one
another, the plunger 20 takes over the guidance between
the two housing parts and both housing parts have a
cylindrical shape and the same diameter.
The springs 24 are supported directly in bores of the
upper and lower housing parts 16, 18. The plunger 20 is
secured by a screw 23 in an accurately positioned
recess of the upper housing part 16, whereas two screws
which extend parallel to the axis of the press-in
device and which are screwed into the lower housing
part 18 serve as the stroke limiter 26.
As can be seen in Fig. 3, grooves 46 of the
quick-closure coupling 12 are not only provided in the
upper housing part 16, but rather also in the lower
housing part 46. This offers the possibility of
selectively securing the upper housing part 16 or the
lower housing part 18 to a machine part.
As can furthermore be seen in Fig. 4 there are
provided, in addition to the grooves 46, further
grooves 46' which are displaced relative to the grooves
46 by 90° in the peripheral direction. This makes it
~~5~56~-
possible to mount the press-in device in two positions
on the machine part which are displaced by 90° relative
to one another.
Figure 5 shows an application in which the punching
device 10 is not attached to a machine part via the
upper housing part 16, but rather via the lower housing
part 18. As shown, the strips 40 of the quick-closure
coupling 12 are provided on an intermediate plate 60
which is suspended and guided via springs 62 and screws
64 on a machine part 14 in the form of an upper press
part. The manner of operation is in principle the same
as in the embodiment of Figs. 1 and 2.
In the embodiment of the quick-closure coupling 12
illustrated in Figs. 1 to 5, the movement in and out
takes place by a relative movement between the machine
part and the press-in device in a direction which
extends perpendicular to the axis of the press-in
device 12 and thus perpendicular to the direction of
the relative displacement between the upper and lower
housing parts 16, 18. It will however be understood
that a plurality of other embodiments of the
quick-closure coupling exist. In the quick-closure
coupling 12' which is only schematically illustrated in
Figs. 6 and 7, the inward and outward movement likewise
takes place in a plane which stands perpendicular to
the axis of the press-in device 10. In this case, a
ring groove 70 is however provided as the coupling
means on the press-in device 10. Two coupling jaws 72
which are rotatable about the spigot 74 can be moved
into and out of engagement with the ring groove 70.
In the quick-closure coupling 12" schematically
illustrated in Fig. 8, the inward and outward movement
- 10 - ~~,~
takes place in a direction which extends parallel to
the axis of the press-in device 10. In this case, the
upper housing part 16 is provided with a central spigot
76 which insertable into a bore of a ring 78 fixed to
the machine part. The spigot 76 is fixed in the ring 78
by a latching device with a spring-loaded latching
ball.
As already mentioned, the nuts M or other fastener
parts can be supplied to the channel 22 through a hose
which is fixedly or releasably connected to the lower
housing part 18. Another possibility lies in supplying
the fastener parts from a magazine 80 for receiving a
restricted number of fastener parts. As is shown in
Figs. 3 and 9 to 11, the magazine 80 forms a part of
the supply device 79 which is interchangeably mounted
to the lower housing part 18 of the press-in device 12.
The supply device 79 can, apart from the magazine 80,
have the same layout as the supply device of the German
patent application P 42 il 278.8. It has a mouthpiece
82 with a throughgoing supply channel 83. A
cross-sectionally enlarged portion of the supply
channel 83 receives the magazine housing 84 so that a
magazine channel 100 formed in the magazine housing 84
merges smoothly into the supply channel 83. The
magazine housing 84 is fixed in the mouthpiece 82 by a
clamping plate 86, pins 88 and screws 90.
The mouthpiece 82 is provided with a formation 92 which
can be inserted into the recess 30 of the lower housing
part 18 of the press-in device 10 (see Fig. 3). For the
coupling of the mouthpiece 82 to the housing part 18
two levers 94 are provided which are pivotable about
pins 76 and are biased into their locking position in
- ~~a~aG~
- 11 -
which their hook-like ends engage around the housing
part 18 by the springs 98.
A slider 102 is longitudinally displaceably journalled
in the magazine channel 100 of the magazine housing 84
formed by the two parts 100a, 100b. In the embodiment
of Fig. 9 the slider 102 is biased by a tension spring
104 in a direction in which it drives the nuts lying in
the magazine channel 100 in the direction towards the
discharge end of the formation 92 of the mouthpiece 82.
The tension spring 104 is suspended at the one end on a
pin 108 fixed to the mouthpiece 82 and at the other end
on a pin 106 secured to the slider 102, with the pin
106 extending through a longitudinally extending
aperture 109 of the upper magazine part l0ob.
In order to prevent the nuts falling out of the
mouthpiece channel 100 and thus out of the magazine 80
in the decoupled state of the supply device 79, a
blocking device in the form of a pin 110 is provided
which is biased by a leaf-spring 112 secured to the
supply device into a position which blocks the
mouthpiece channel 82 and is automatically pressed into
a released position during the coupling-on.
The magazine 80 is filled in the decoupled state with a
preset number of nuts (for example 10 nuts) so that the
slider 102 moves from its left-hand end position in
Fig. 10 into its right-hand end position in which the
nuts are prevented from falling out by the pin 110.
During the coupling of the supply apparatus 79 onto the
pressing-in device 10 the bolt is automatically moved
into its releasing position (Fig. 3) by an inclined
surface 114. The slider 102 which is preloaded by the
spring 104 can then supply the nuts one after the other
,,
- 12 -
to the channel 22 in the lower housing part 18.
Whereas, in the embodiment of Figs. 9, 10 the slider
102 is displaced by spring force, the preloading force
is generated in the embodiment of Fig. 11 by compressed
air. For this purpose, a compressed air connection 118
is provided at the rear end of the magazine channel
100, which is designed in fluid-tight manner, and leads
via a hose connection to a source of pressurised air.
The hose connection can be guided to a compressed air
coupling (not shown) provided at the mouthpiece 82
which automatically establishes a communication to the
compressed air source during the coupling of the supply
device to the press-in device.
With an appropriate construction of the magazine, the
slider 102 can also be omitted so that then the
fastener parts are acted on directly by the compressed
air. In this case, a filling opening could be provided
at the rear end of the magazine.
Since the pressing-in device 10 shown in the Figures
represents an integral module which, through the
quick-closure coupling 12, can be rapidly attached in a
simple manner to any desired machine part, manifold
possibilities of use are open to the press-in device
10. Thus the Figure 12 shows in schematic manner a tool
changing system of a machine tool 150 indicated in
chain-dotted lines in which a plurality of press-in
devices 10 with attached magazines 80 are provided as
exchangeable tools. The press-in devices 10 are stored
together with other tools (not shown) in a store 152
and are transported, depending on the requirement, by a
conveying and changing device indicated by means of a
double arrow 154, to the machine tool 150 to which they
~1~3~~~
- 13 -
can be clamped by means of a correspondingly formed
quick-closure coupling.
Another possibility of use is shown by Fig. 13. A
C-shaped yoke 122 with an upper limb 124 and a lower
limb 126 is attached via an attachment connection 127
to a robot arm (not shown). The upper limb 124 of the
yoke 122 carries an actuating device in the form of a
piston-cylinder unit 128 with a hydraulic piston 130. A
press-in device 10 in accordance with Figs. 1 and 2 is
interchangeably mounted on the hydraulic piston 130
through the quick-closure coupling 12.
The lower housing part 18 carries a magazine 80 which
is interchangeably attached, in accordance with Figs. 9
to 11, to the lower housing part 18. The magazine 80
can, however, also be fixedly attached to the lower
housing part 18 if a possibility for filling the
magazine 80 is provided at the lower housing part 18 or
at another position. As indicated in broken lines, the
straight-line magazine 80 could also be replaced by a
curved magazine 80' in which the fastener parts are
supplied by gravity. Instead of a magazine 80 or 80', a
flexible hose 125 could however also be provided which
stands in connection with a sorter or another source
and is so dimensioned that it does not hinder the
movements of the robot arm and the press-in device
secured thereon.
The lower limb 126 of the C-shaped yoke 122 has a
counter-surface in the form of a die 34 for supporting
a plate-like component (not shown) into which the
fastener parts can be pressed.
The construction shown in Fig. 13 makes~it possible to
~~8~~~
- 14 -
transport the press-in device 10, with the aid of the
(non-shown) robot arm, to any working position
reachable by the robot arm in order to carry out a
press-in procedure there.
In accordance with Fig. 14, the press-in device 10 is
directly secured by the quick-closure coupling 12 to
the arm 134 of the schematically illustrated robot 130
provided with a linkage 132. Likewise schematically
indicated is a stationary support 136 with a mould 138
which contains a correspondingly deformed plate-like
component B. A fastener part (not shown) is to be
pressed into the component B at the position 140. For
this purpose, the robot 130 moves the press-in device
into a position in which the fastener part channel
of the press-in device 12 lies precisely above the
working position 140. For the pressing of the fastener
part into the component B, the robot 130 then moves its
arm 134 vertically downwardly so that the press-in
movement of the plunger 20 is supplied by the robot
itself .
If one is concerned with self-piercing fastener parts,
then the piercing force must necessarily be supplied by
the correspondingly designed robot. A substantially
lower press-in force is necessary when the press-in
device 10 presses the fastener parts into pre-
manufactured holes of the component B.