Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
21 ~ 9244
2
STRUCTURAL ELEMENT
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
This invention relates in general to the structural support for light weight
panels.
More specifically it relates to structural elements which comprise preforms of
any
moldable, deformable or laminar material like paper, cardboard, plastics,
reinforced
resins, metals, alloys, compound materials, agglomerates, asbestos, gypsum,
ceramic,
glass or any other similar material, any of which is formed in such a way as
to have a
very high structural resistance to compression and to flexure, maintaining a
low
weight and having a configuration which allows to comprise support points to
which
other preforms or sheets of any material can be affixed to construct the
structural
elements.
The technical aspects and advantages of structural sandwich panels are well
known,
because they have been used for structures that require a very high resistance
and a
very low structural weight. The so called honeycomb sandwich panels are well
known among this type of panels. In this type of structures, the panel is
constructed
by means of strips of the material used that are fixed together at some points
in such a
way that the hexagonal honeycomb is established, in which such honeycombs
extend
perpendicularly to the sheet or sheets with which the sandwich is constructed.
The
strips that form the honeycomb extend longitudinally in a cross sectional way
to the
sheet or sheets that form the sandwich. This means that the strips forming the
215924
3
honeycomb extend perpendicularly to the sheets that form the sandwich panel.
Other
configurations different to hexagonal can be used like triangular, pentagonal,
etc.
Different materials can also be used for the construction of sandwich panels,
both for the
core as well as for the sheets that form the walls of the sandwich. Such
materials can be
for example, paper, cardboard, plastic, metal and composite materials. The
basis of the
sandwich panels rest in keeping a core that work as a perpendicular structure
support for
the panel, while other configurations adopted throughout the time, allow to
distribute the
effort applied all over the panel in a more or less homogenous manner, which
allow to
decrease up to ten times the weight of the structural element in comparison
with
traditional structural elements formerly used, keeping under the same
conditions the
under load support capacity. This type of structures have had huge advantages
by
supporting the same loads at a fraction of the weight and cost of prior
structural elements.
Different methods to build sandwich panels by diverse techniques have been
discussed.
A notable example could be found in US patent 5,028,474 dated July 2, 1991,
granted to
Ronald M. Czaplicki entitled Cellular Core Structure providing Gridlike
Bearing
Surfaces on Opposing Parallel Planes of the Formed Core.
Among the inventions made to give structural cores to sandwich panels is US
patent
3,865,679 dated February 11, 1975, granted to Jesse R. Hale, entitled Sandwich
Panel
having Cellular Core Structure with Reinforcing Elements, which teaches a core
structure
that has nodes, shown in essentially circular manner, that project in opposed
directions
form a mid plane with apices of said nodes abutted against the face sheets of
the panel,
comprising first reinforcing bar means running along to the sides of a first
row of said
nodes, wherein said bar means are bonded to the sides of said nodes of said
center and
4
to the surface of one of the face sheets of the panel and a second reinforcing
bar means
that run along of a second row of said nodes, wherein said second reinforcing
bar means
are bonded to the surface of one of the face sheets. This patent comprises as
improvement the addition of reinforcing bars that are bonded to the face
sheets of the
nodes along two different rows of nodes and are bonded by the ends to the face
sheets of
the sandwich panel. It is evident that the structure used in this invention,
requires an
additional reinforcement to support the stress that will be applied to the
panel and will
not be discussed in more detail.
In US patent 5,028,474 above described, in a three dimensional structure that
comprises
ridges and essentially lineal valleys which establish spaced rows of adjacent
inclined
rectangular shaped facets connected by intermediate rows of adjoining
parallelogram-
shaped facets, wherein said structure is made by folding of a continuous
unbroken sheet
material, wherein said laminate material has a superficial area and said
superficial area
is filled of a repetitive path of cellular units. The central structure
provides support
surfaces of the grid type in two support plan parallel opposed to which the
plates or
sheets can be fixed as faces to form the panel in the form of a sandwich.
From the prior description and the accompanying drawings to the patent of
Czaplicki, it
should be appreciated the problem to establish the actual way in which the
plate or sheet
is folded, which finally constitutes a three dimensional figure but with
different
geometric figures. This relative obstacle to fold the plate or sheet does not
allow to
adequately appreciate the value of this invention.
US patent 5,182,158 dated January 26, 1993, granted to Barnarr C. Shaeffer
titled
Lightweight Sandwich Panel, wherein in a sandwich panel which comprises
external
2~~9Z4~
layers which has projections bonded to the other external layer, wherein the
projections
have relatively flat areas in their edges, in the edges freed to provide
enlarged areas for
bonding, wherein the flat areas are bonded chemically to the other external
layer, the core
layer is a plastic sheet and the projections are formed from the sheet and the
projections
by area would vary in density to provide different resistances to the
deflection in various
parts of the panel, wherein one of the external layers is transparent and the
core layer is
dark to absorb the sun's ray and is open to the passage of air through it. It
can be clearly
appreciated from the prior description that the patent to Schaeffer has been
designed for
its application to aviation in general, wherein it can be appreciated in
figures 2 to 4 that
different cross section sheets are used also bonded to form a honeycomb. In
figure 5 it
could be appreciated a structure with steep projections. The instant invention
differs
from Shaeffer as will be herein further described. From the foregoing it could
be
appreciated that these structures in the form of sandwich are formed by three
or more
pieces, which makes very complex its construction, structure or use. Diverse
geometrical
shape panels with thin metallic sheets have also widely been described, like
in US patents
3,209507; 3,622,430; 3,834,487 and 3,938,963, or there are also inclusive
those patents
which illustrate systems of the multiconical type as US patents 4,672,780 and
4,794,742,
but in none of these cases, these patents have the advantages of the instant
invention.
SUMMARY OF INVENTION
According to the foregoing, it is an object of the present invention to
provide a structural
element in the form of a panel with a simpler design and improved properties
respect to
the prior art panels.
215924
6
It is another object of the present invention to provide a structural element
or structural
panel with outstanding structural features and of relatively easy and very
economic
construction.
It is still another object of the present invention, to provide a panel
element with a three
dimensional structure, which comprises at least a deformable or moldable
continuous
material preform along all of which a plurality of projections are formed in
successive
or simultaneous steps in such a way that the projections can be generally but
not
necessarily symmetrical.
Still a further object of the invention, is to provide a panel that is
susceptible of being
lightened by withdrawing all the unnecessary material to make the functions of
support
and structural reinforcement given by the panel and besides increasing its
possibilities
of application.
It is still an object of the invention, to provide a panel which is
susceptible of being
manufactured by units, lots or continuously, comprising a first piece of a
material and a
second piece of the same or different material.
The present invention comprises a structural element like a panel starting
basically with
two pieces made or formed with a laminate material, projections are made
together or
very close to each other to one or both pieces in a regular or irregular
manner. These
projections can be pyramids, or prisms of square, rectangular, triangular or
hexagonal
base, etc., complete or truncated and with right or rounded edges or of any
other type,
inclusive cones or ovoids, etc. Formed panels are flexible and can be given
any wanted
shape to be flat or curved, but upon fixing the tips of the projections of the
first piece
fixed to the second piece which can have a smooth surface, other preform,
another piece
_ ~ i 5~'~44
that can be prepared to facilitate the fixing, or a mesh, a three dimensional
structure is
built that maintains its given shape with great rigidity and very low weight,
which
structure besides the thickness of the formed panel give to such panel
extraordinary
resistance to flexion and to perpendicular compression. Any material can be
used to
manufacture these structures being the most convenient that which allow a
continuous
massive production like: metals, alloys, plastics, rubber, paper, cardboard,
composite or
agglomerated materials, reinforced resins, concrete, gypsum, ceramic
materials, asbestos,
glass and others. The two pieces that form the panel can be manufactured with
the same
or different material. Any reinforcement can be added within the structure to
increase the
resistance and if convenient any nonconductor or filling material and
externally faces can
be put which complete the finishing and improve the appearance, giving as a
result a
sandwich panel. As in most of the cases it will be convenient to prebuild the
panels for
using them in another place, fixing means can be added to the edges to fix the
panels to
each other and to fix the panels to other portions of a construction, building
or final
product. The structure can have any thickness, though the most common will be
between
and 150 millimeter, nonetheless it is possible to build smaller or bigger
panels to an
extent in which the projections could be arranged in little groups or alone to
be fixed one
to the other and at the same time to the other portion of the structure. This
type of
structure can be lightened by withdrawing the material of the sides of the
projections and
or the faces located between the joining points of the second piece achieving
simultaneously a permeable panel that serves as a support to other materials
as would be
prebuilt elements of construction. It is also possible to use a plurality of
projections of
different shape and size as a preparation for bending before fixing, as it
would be for the
21 5924 4
s
manufacture of beams or other structural elements. Equally it is also possible
to
prepare the sheet of the panel when this embodiment is used to ease the
joining of the
two pieces or to add other features, like adding some projections to make it
antislipping. The flexibility of the instant invention allows a prior
manufacture of the
preform to build the panels thereafter when the application takes place.
Depending on
the materials used the panels also can be used as buffer elements, for
isolation,
decoration, stage scenes, reflection diffusion and lots more. It should be
appreciated
that this type of panels is easier to manufacture than normal sandwich panels
lowering
the cost which allows to use its advantages of light weight and rigidity at an
affordable
price.
In one particular preferred embodiment there is provided structural element
which
comprises a first piece and at least a second piece wherein at least said
first piece
comprises a plurality of solid projections which establish a preform and said
second
piece comprises a relatively smooth surface and receives said first piece,
wherein said
projections of said first piece are fixed to said second piece which upon
fixing
establish a very rigid, resistant to flexure and light weight tridimensional
structure,
each of said projections of said first piece having a base, all of said bases
forming a
substantially continuous surface, said first piece and at least said second
piece
comprising an interior component of said structural element of substantially
the same
rigidity as at least one layer of said structural element exterior to said
interior
component, said first piece and at least said second piece comprising said at
least one
layer of said structural element, said at least one layer of said structural
element being
substantially rigid.
In a further particularly preferred embodiment there is provided structural
element
which comprises a first piece and a second piece wherein at least said first
piece
comprises a plurality of projections which comprise different geometric shapes
and
sizes which establish a preform wherein said projections of said first piece
are fixed
to said second piece which upon fixing establishes a very rigid, resistant to
flexure and
21 5924 4
8a
light weight tridimensional structure, at least one of said first piece and
said second
piece being hollowed and having a plurality of open apertures through at least
one
wall of said at least one of said first piece and said second piece to lighten
the element
and to allow the passage of other objects or materials.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
The novel features and advantages of the instant invention should be readily
apparent
for those skilled in the art arising from the teachings of the detailed
description herein
and the accompanying drawings, but it should be understood that the instant
invention
can be embodied in different ways and that the embodiments herein described
are
shown for illustration purposes only, but that they are not restrictive as
referred to the
scope of the invention wherein:
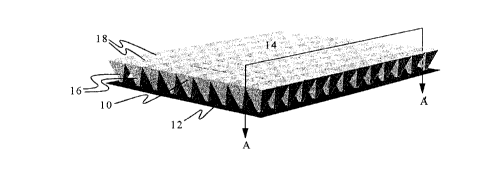
Figure 1 is a perspective view of the preform and sheet type panel,
Figure 2 is a cross cut view along AA' axis of the panel of Figure 1,
Figure 3 is a view of a formed panel,
Figure 4 is a perspective view of an embodiment of the present invention
wherein a
portion of the material of the walls of the projections and of the spaces
between the
joining points is withdrawn to lighten the panel as to form a panel with
modified
2i5~~~~
9
properties,
Figure 5 is a perspective view of another embodiment of the invention wherein
a panel
with two preforms is shown, both preforms are lightened and fixed by the tips
and have
recesses in their solid faces,
Figure 6 is a perspective view of a fourth embodiment of the invention wherein
a panel
is formed with two lightened preforms, and which are joined fixing the tips of
the
projections of one preform with the bottoms of the projections of the other
preform,
Figure 7 is a perspective view of a panel formed with a sheet with recesses
which are
used to fix the preform, wherein said recesses are also used as anti slipping
projections,
and
Figure 8 is a cross cut view along BB' axis wherein the projection tips shown
can be seen
fixing to the sheet in the recesses formed in the plate.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
With reference to figure 1, numeral 10 generally designates a first piece or
preform which
can be fixed to a second piece or sheet 12, which acts as a joining surface of
the tips of
the geometric shapes used in the first piece or preform 10 to fix them in
place. Once the
preform 10 and the second piece or sheet 12 are fixed, they form the panel 14,
which can
be a part of a plurality of articles which can be applied to the building
industry. During
the forming process of preform 10, the relatively flat bottoms of every
geometric shape
formed and the resulting material between them form a face of the structural
elements
which can be added another laminar piece which depends on the desired
finishing for the
particular application.
21 ~ 9~ ~-~
In figure 2, a cross cut along AA' axis of panel 14 can be seen, wherein the
geometric
shapes of preform 10 can be clearly seen, sheet 12 fixed to preform 10 by tips
20 and how
it is firmly supported by projections 16 and how bottoms 18 of projections 16
establish
a relatively flat continuous surface, wherein it can be appreciated that
another sheet 12
is unnecessary on the opposite side to that which sheet 12 is fixed to preform
10, because
the particular system formed by bottoms 18 which are formed longitudinally and
transversely to preform 10, give enough rigidity to panel 14 so any additional
support is
unnecessary.
In figure 3, a panel 22 is shown to illustrate the different shapes that this
type of panel
can have.
In figure 4, it is shown a hollowed preform 24 to which a portion of the
material of sides
26 of projections 16 and material between the joining points of sheet 28 has
been
withdrawn. This embodiment allows to lighten the structure to apply it to such
articles
or building applications that require a strict control of the total weight
while maintaining
the rigidity of the whole structure, or when it is desired to have a permeable
panel which
allows the passage of other objects or filling materials.
Figure 5 shows another embodiment of the invention wherein two hollowed
preforms are
fixed by their tips as to form a panel by a first piece or preform 24 and a
second preform
24', which form panel 30. This type of panel can also be formed with other
shapes and
sizes to maintain an adequate ratio to allow the tips of both preforms 24, and
24' to
register in place to establish the joining points to fix the preform and form
the panel even
though such panel has a different to flat shape.
Figure 6 shows other embodiment of the invention, wherein a first hollowed
preform 24
2 i 5~~~-4
11
is fixed to a second hollowed preform 24' as to fix the tips of first preform
24 to the
recesses in the inner portion between projections 28' of second preform 24'
while fixing
the tips of second preform 24' to the recesses in the inner portion between
projections 28
of first preform 24 to form panel 32. This configuration allows to fix to some
points the
sides of projections 28 and 28' of both preform to give an increased
resistance to the
structure. In this figure hollowed preforms were used that were lightened by
withdrawing
a portion of material to the sides of the projections, but in the case in
which preforms
were complete continuous surfaces they could establish closed spaces between
every four
projections two of every preform, wherein faces can be applied to both sides
of the panel
giving a plurality of closed spaces adjacent one to the other with superb
isolating and
buffering features besides its properties of light weight, resistance and ease
of
manufacture derived from the main principle of the invention.
Figure 7 shows a view of another embodiment of the invention, wherein a first
piece or
preform 10 is fixed to a second piece 34, which has recesses 36 comprised on
the inner
face of second piece 34, which comprise a plurality of projections 38 in the
external face
of said second piece 34, once fixed the first piece 10 to second piece 34 they
form panel
40, which has special characteristics because of the projections which can
give the
surface an antislipping property when the construction element is used for
floors or the
like.
Figure 8, shows a cross cut along BB' axis of panel 40 in figure 7, wherein
recesses 36
can be readily appreciated comprised in the inner face of second piece 34, and
the way
in which said recesses are used to receive inside them the tips of projections
of first pies ;,
or preform 10 to fix both pieces and to form panel 40. Projections 38 can also
be
2 ~ 5924
12
appreciated as established on the exterior face of second piece 34 and which
give to the
panel improved properties over the panels of prior art.
From the foregoing description it should be appreciated that multiple changes
and
modifications can be made to both first and second pieces and to the whole
panel once
it is formed as to make a plurality of panels adapted to different uses and
based on their
structural rigidity, light weight and also on their structural shape which
allows to make
precise bendings which also can be used for decoration. It should be
understood that the
foregoing description and the different embodiments of the invention are used
herein for
illustration purposes but are not limitative and that this modifications are
within the
scope and spirit of the invention.