Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
-- 2161079 -2-
Backqround of the invention
This invention relates to ventilators for windows and doors.
The construction of windows and doors to reduce heat loss is
desirable to conserve energy and reduce heating costs This has led to
designs with improved sealing to eliminate draughts with the result that
there is a need to provide adequate ventilation in a controlled manner to
prevent condensation and ensure safe operation of gas fires.
One type of known ventilator is mounted on the frame of a door or
window and controls the flow of air through a passageway formed in the-
frame. Typically, the passageway is formed by cutting a hole such as an
elongate slot through the frame. Cutting a hofe through the frame adds to
the cost of fitting the ventilator and weakens the frame.
Another type of known ventilator is mounted between the glazing and
the frame of a door or window in which the glazing is received. This avoids
cutting a hole through the frame but results in more complex constructions,
especially where the ventilator is adjustable to accommodate different
widths of glazing.
The present invention has been made from a consideration of the
problems and disadvantages of these known types of ventilator.
Summarv of the invention
According to the present invention a ventilator is provided for
mounting along an outer edge of a frame of a door or window.
By this invention, the ventilator is provided as an add-on to the frame
of the door or window. As a result, fitment is very simple and does not
involve cutting holes through the frame or adjustment for different glazing
thicknesses as required by the known types of ventilators above-discussed.
Advantageously, the ventilator comprises an elongate housing
provided with a longitudinal flap mounted for pivotal movement between
open and closed positions for controlling the flow of air through the housing
Preferably, the housing comprises two members separated by a pair
of spacer blocks to form an air passageway through the housing with the flap
being mounted for pivotal movement on one of the members and being
engageable with the other member in the closed position.
Advantageously, the housing members and flap are of substantially
uniform cross-section along the respective lengths. For example, the
housing members and flap may be extrusions that can be cut to any desired
- . 2l6ln7~-3-
length for producing different sizes of ventilator. The extrusions may be
metal, for example aluminium, or plastics. The use of plastics having a low
coefficient of thermal conductivity may prevent condensation by reducing
heat transfer when there is a large difference between inside and outside
5 temperatures.
Preferably, the housing members are secured in parallel and spaced
apart positions by engagement with the spacer blocks to provide a desired
ventilation area for a given length of ventilator. For example, the housing
members and spacer blocks may be provided with inter-engageable
10 formations for assembly of the housing. The inter-engageable formations
may be arranged to engage with a snap action to interlock the parts to
provide a rigid assembly without additional fittings.
Advantageously, the flap is mounted on said one housing member by
means of complementary hinge formations extending along the respective
15 lengths. The complementary hinge formations may comprise a part-circular
bead received within a part-circular recess to form a continuous hinge
having a neat appearance for assembly of the flap to the housing.
Preferably, the flap is adjustable to provide any desired level of
ventilation between closed and fully open, and the spacer blocks are
20 conveniently adapted to hold the flap in any selected position. For example,
the flap may be engageable with a resiliently deformable portion of each
spacer block which acts as a spring element providing frictional resistance
to pivotal movement of the flap.
Advantageously, the housing is closed at each end by a respective
25 end cap. By this arrangement, the length of the ventilator can be varied by
sizing the lengths of the housing members and flap with the end caps being
fitted to give the assembled ventilator a neat appearance.
Preferably, the housing is provided with a filter element to prevent
entry of insects or detritus and, where required, sound insulation. For
30 example, the filter element may comprise a foam strip.
Advantageously, the ventilator is chosen to have a length
substantially equal to that of the edge of the frame on which the ventilator is
mounted. In a preferred arrangement, the ventilator is adapted for
horizontal mounting, preferably at the top of the frame, and said other
35 housing member provides an external hood forming a downwardly opening
air inlet that prevents rain penetration and reduces draughts.
~161079 -4-
Preferably, the said other housing member provides an internal hood
having a seating face that is engaged by a sealing face of the flap in the
closed position. One of the faces may be provided with a seal member, for
example a strip of rubber or foam or a pile faced fabric.
According to another aspect of the invention a door or window
comprises a frame for mounting in an opening in a surrounding structure and
a ventilator mounted on an outer side edge of a horizontal rail member of
the frame between the frame and the surrounding structure when the frame
is installed in the opening, the ventilator comprising an elongate housihg
extending lengthwise of the rail member and a flap mounted on the housing
for pivotal movement between open and closed positions to control the flow
of air through the housing.
The invention will now be described in more detail, by way of example
only, with reference to the accompanying drawings.
Brief descriPtion of the drawinas
FIGURE 1 is a perspective view of a ventilator embodying the
invention mounted on a window frame;
FIGURE 2 is a perspective view of the ventilator shown in Figure 1
with the end cap removed to show the internal arrangement in the closed
position of the ventilator;
FIGURE 3 is an exploded isometric view of the component parts of
the ventilator shown in Figure 2;
FIGURE 4 is a detail view showing the internal arrangement in the
open position of the ventilator;
FIGURE 5 is a detail view showing the internal arrangement in an
intermediate position of the ventilator; and
FIGURE 6 is a perspective view of a multiple ventilator arrangement.
Detailed descriPtion of the exemPlary embodiments
With reference to the drawings, the ventilator 1 is shown mounted on
top of the outer frame 2 of a timber window 3 having a casement frame 4
supported in the outer frame 2 for outward opening movement about a
horizontal or vertical axis by any suitable hinges (not shown).
The outer frame 2 is fabricated from opposed vertical side members 5
connected at the top and bottom by opposed horizontal rail members ô (one
only shown) to form a rectangular opening 7 with an external rebate 8 in
which the casement frame 4 is received when the window 3 is closed. The
~1610~9 ~5
rebate 8 is provided with a groove 9 in the closing face 10 to receive a
seal (not shown) for engagement with the inner face 11 of -the casement
frame 4 to eliminate draughts and prevent heat loss when the window 3 is
closed .
The ventilator 1 extends the full width of the outer frame 2 and is
secured to the top rail member 6 by screws 12 so that the assembly of outer
frame 2 and ventilator 1 can be fitted in a rectangular opening in the wall of
a surrounding building structure.
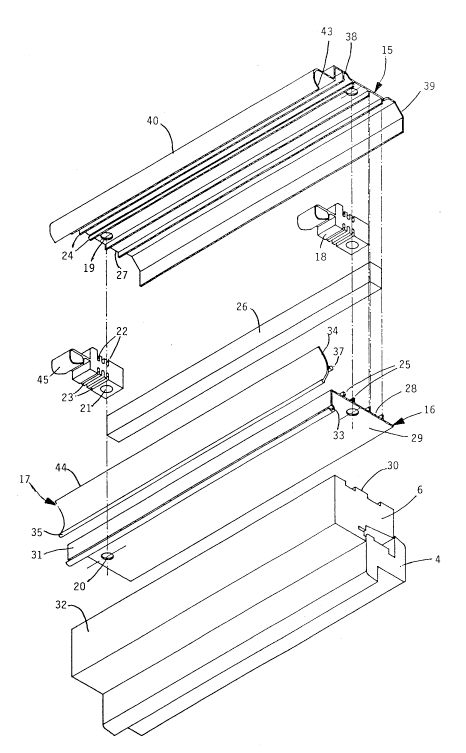
The ventilator 1 comprises an elongate housing 13 defining an air
passageway 14 bounded by upper and lower housing members 15 and 16
respectively, and a flap 17 pivotally mounted on the lower housing
member 16 to control the flow of air through the passageway 14. The
housing members 15,16 and flap 17 are of uniform cross-section along their
length and are cut to the required length from extrusions of alumlnium.
A pair Of spacer blocks 18 are located between the housing
members 15,16 at opposite ends of the housing 13 and the fixing screws 12
extend through aligned holes 19,20,21 in the housing members 15,16 and
blocks 18. The spacer blocks 18 are plastics mouldings. For ventilators of
long length, one or more additional spacer blocks 18 may be provided
intermediate the ends of the housing 13.
Each spacer block 18 is formed with upper and lower pairs of re-
entrant grooves 22,23 respectively for snap engagement by pairs of undercut
ribs 24,25 on the housing members 15,16 respectively. It will be
appreciated that any suitable co-operating formations may be provided for
locating and securing the mounting blocks 18 between the housing
members 15,16.
A filter element 26 of rectangular cross-section is provided between
the housing members 15,16 to act as a screen to prevent entry of insects or
detritus and to provide sound insulation when required. The filter
element 26 is located by channels 27,28 on the housing members 15,16
respectively. The filter element 26 may be a strip of foam selected for the
required air flow.
The lower housing member 16 has a base wall 2~ that seats on the
outer side edge 30 of the top rail member 6 and a flange 31 that extends
from one side of the base wall 29 to overlie the inner face 32 of the top rail
member 6. The flange 31 terminates in a recess 33 of part-circular section.
- 2161079 -6-
The flap 17 has a curved main wall 34 with a lip 35 of part-circular
section on t5~e lower edge to provide a finger grip for operating the flap 17.
A flange 36 extends rearwardly from the main wall 34 and terminates in a
bead 37 of part-circular section complementary to the recess 33 of the lower
5 housing member 16.
The flap 17 is assembled to the lower housing member 16 by locating
the bead 37 in one end of the recess 33 and sliding the flap 17 lengthwise of
the housing member 16 so that the parts are connected for pivotal
movement of the flap 17.
The upper housing member 15 has a main wall 38 that is spaced
above the base wall 29 of the lower housing member 16 with an external
hood 3g one side and an internal hood 40 on the other side.
The external hood 39 forms a downwardly facing air inlet 41 on the
outside of the window 3 to prevent rain penetration and reduce draughts
15 when the ventilator 1 is open. By this feature of the external hood 39, the
top rail member 6 can have the same section as the side members 5 of the
frame thereby reducing manufacturing costs.
The internal hood 40 forms a downwardly facing air outlet 42 on the
inside of the window 3 and the lower edge of the hood 40 provides an
20 internal seating face 43 that is engaged by a sealing face 44 at the upper
edge of the flap 17 to close the air outlet 42.
Each spacer block 18 has an integral hollow leg portion 45 on one
side that is resiliently deformable by wiping engagement with the upper edge
of the flap 17 and acts as a spring element providing frictional resistance to
25 pivotal movement of the flap 17. In this way, the flap 17 is maintained in
the closed position (Figure 2), the fully open position (Figure 4) and any
intermediate position (Figure 5) selected for controlling the flow of air
through the passageway 14.
The housing 13 is closed at each end by a respective end cap 46 so
30 that the assembly of the ventilator 1 and outer frame 2 has a rectangular
external profile. As a result, installation of the assembly in a surrounding
structure, for example a wall, is straightforward and finishing by plastering
etc in the normal manner to provide a neat appearance is facilitated.
It will be understood from the foregoing description that the invented
35 ventilator is designed for mounting between the outer frame of a window or
door and the surrounding structure in which the frame is fixed, for example
216 1079 ~7~
the wall of a building. As a result, the formation of an air passageway
through the frame is avoided and different thicknesses of glazing can be
accommodated without adjusting the ventilator. The ventilator can be fitted
to the frame by the window manufacturer or supplied separately for fitment
5 on site prior to installation of the window.
Doors and windows are typically manufactured in standard sizes
requiring a specific ventilation area, for example 2000, 4000, 6000 or 8000
sq.mm. The invented ventilator may be produced in a range of standard
lengths to match the standard frame sizes and required ventilation areas for
10 selection and fitment of the appropriate ventilator. For non-standard frame
sizes, the ventilator which is longer than the frame size may be selected and
cut to the required length.
For certain applications, it may be desirable to provide the required
ventilation area by the selection and fitment of two o- more ventilators with
15 a suitable connector piece 47 between adjacent ends as shown in Figure 6.
For example, a ventilation area of 12000 sq.mm. may be obtained by fitting
three ventilators each having a ventilation area of 4000 sq.mm. In this way,
large ventilation areas for wide frames, such as may be required above patio
doors, may be obtained in a simple manner by selection and fitment of an
20 appropriate combination of ventilator sizes. As will be appreciated, when
more than one ventilator is fitted, the number and extent to which each
ventilator is opened can be varied to control further the desired level of
ventilation.
The invented ventilator has application to both new and replacement
25 doors and windows constructed from any suitable materials including timber,
plastics, metal or any composite of these. For new doors and windows, the
assembled outer frame and ventilator can be installed in the surrounding
structure during construction or a sub-frame may be installed during
construction to receive the assembly when construction is completed. As a
30 result, the ventilator can be provided as an add-on to the outer frame of
doors and windows of standard size or any other size as desired. For
replacement doors and windows, the outer frame is constructed to allow for
fitment of the ventilator so that the assembled outer frame and ventilator
matches the size of the existing opening.