Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
` 21 1-U222
- BAYERA~l~(~ CHAFT 51368 I~V~
Patente K~mem Bu/AB/SP
Use of quinoxalines in coml~ lion with protease inhibitors as medic~ for treating
S AIDS and/or HIV infections
The present invention relates to the use of quinoxalines in co~ lion with protease
inhibitors as medicaments for treating AIDS andlor HIV infections.
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) causes a persistent, progressive, chronicdisease. HIV destroys the immlme system (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome,
AIDS) and the central and peripheral nervous system. In addition to this, a large
number of other clinical ll~~ lions encompassed within the ARC/AIDS syndrome
are caused by the human immlmodeficiency virus - in particular opportunistic infections
(O.I.) which are elicited by other viruses, such as, for example, herpes viruses (HSV I
and II) and cytnm~lovirus (CMV), or O.I. which are elicited by bacteria, fungi or
parasites.
HIV belongs to the retrovirus family; one of the important enzyme activities of these
viruses, which is essential for the replication cycle, is that of the protease (Huff, J.R,
J. Med. Chem. (1991), 34, 2305-2314). Small molecular weight analogues, of a peptide
or non-peptide nature, of the natural s~ les of the protease inhibit HlV replication
(Roberts, N.A. et al., Scienoe (1990) 248, 358 - 361; Lam, P.Y.S. et al., Science
(1994), 263, 380-384).
Analogues of the natural s~ l~ of the reverse transcriptase such as, for example,
azidothyrnidine (AZT), dideoxycytidine (DDC), dideoxyinosine (DDI) and 3'-
thiacytidine (Lamivudine) inhibit HlV replication in vitro and in vivo. AZT is used, for
Le A 30 844 - Foreign Countries
21 70222
example, for treating ARC/AIDS patients. However, the longterm therapeutic tre~trn~nt
of HlV-infected patients with AZT is accompanied by bone marrow toxicity; in
addition to this, AZT-resistant virus isolates develop. Intolerances, such as, for
exarnple, a peripheral ne~lhy, are reported by some patients who have been treated
5 with DDC or DDI. There is, therefore, a need for new inhibitors which will provide a
well-tolerated and effective therapy.
The co,l,~ ion of quinoxalines and protease inhibitors which has now been found is
novel, and the synergistic effect of these compounds on HlV replication, when they are
used in controlling AIDS or H~V infections, represents a considerable improvement as
compared with the state of the art. - -
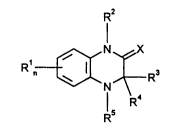
It has now been found that quinoxalines of the general formulae (I) and (Ia)
R'
and also their tautomeric fo~ns of the general formula Ia
R n~ ~R3
Rs R4
in which
1) n is zero,
one,
two,
three
or four,
Le A 30 844 - Forei_n Countries - 2 -
2 1 7U222
- the individual substituents R' are, independently of each other,
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, hydroxyl,
Cl-C8-alkyl, C5-Cg-cycloalkyl, C,-C6-alkoxy, (C,-C6-alkoxy}(C,-C4-alkoxy), C,-
C6-alkylthio, C,-C6-alkylsulphinyl, C,-C6-alkylsulphonyl, nitro, amino, azido, C,-
S C6-alkylamino, di(C,-C6-alkyl)amino, piperidino, morpholino, 1-pyrrolidinyl, 4-
methylpiperazinyl, thiomorpholino, imidazolyl, triazolyl, tetrazolyl, C,-C6-acyl,
C,-C6-acyloxy, C,-C6-acylamino, cyano, carbamoyl, carboxyl, (C,-C6-alkyl}
oxycarbonyl, hydroxysulphonyl or sulphamoyl,
or
a phenyl, phenoxy, phenoxycarbonyl, phenylthio, phenyl~lllphinyl,
phenylsulphonyl, phenoxysulphonyl, phenylsulphonyloxy, anilinosulphonyl,
phenylsulphonylamino, benzoyl, 2-pyridyl, 3-pyridyl or 4-pyridyl radical which
is substituted by up to five R6 radicals which are independent of each other,
where R6
can be fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, cyano, trifluoromethyl,
trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino, azido, C,-C6-alkyl, C3-C8-cycloalkyl, C,-C6-
alkoxy, C,-C6-alkylthio, C,-C6-alkylsulphinyl, C,-C6-alkylsulphonyl, C,-C6-
alkylamino, di(C,-C6-alkyl)amino, (C,-C6-alkyl)-oxycarbonyl, phenyl, phenoxy
or 2-, 3- or 4-pyridyl,
R2 and R5 are identical or di~r~lll and are, independently of each other,
hydrogen, hydroxyl, C,-C6-alkoxy, aryloxy, C,-C6-acyloxy, cyano, amino, C,-C6-
alkylamino, di(C,-C6-alkyl)amino, a~ylamino, C,-C6-acylamino, C,-C8-alkyl,
optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, cyano, amino,
mercapto, hydroxyl, C,-C6-acyloxy, benzoyloxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy, C,-C6-
alkoxy, C,-C6-alkylamino, di(C,-C6-alkyl)amino, C,-C6-alkylthio, C,-C6-
alkylsulphonyl, phenylsulphonyl, oxo, thioxo, carboxyl or carbamoyl;
Le A 30 844 - Foreign Countries - 3 -
2 1 70222
C2-C8-alkenyl,
which is optionally substituted by
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, cyano, amino, mercapto, hydroxyl, C,-C6-
acyloxy, benzoyloxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy, C,-C6-alkoxy, C,-C6-alkylarnino, ~
di(C,-C6-alkyl)arnino, C,-C6-alkylthio, Cl-C6-alkylsulphonyl, phenylsulphonyl,
oxo, thioxo, carboxyl or carbarnoyl;
C3-C8-allenyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine or hydroxyl,C,-C4-alkoxy, oxo or phenyl;
C3-C8-alkinyl,
which is optionally sllbstitllte(l by
fluorine, chlorine, brornine, iodine, cyano, amino, mercapto, hydroxyl, Cl-C6-
acyloxy, benzoyloxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy, C,-C6-alkoxy, C,-C6-alkylarnino,
di(CI-C6-alkyl)amino, C,-C6-alkylthio, C~-C6-alkylsulphonyl, phenylsulphonyl,
oxo, thioxo, carboxyl or carbamoyl;
C3-C8-cycloalkyl
which is optionally substituted by
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, cyano, amino, mercapto, hydroxyl, C,-C6-
acyloxy, benzoyloxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy, C,-C6-alkoxy, Cl-C6-alkylamino,
di(C~-C6-alkyl)amino, Cl-C6-alkylthio, C,-C6-alkylsulphonyl, phenylsulphonyl,
oxo, thioxo, carboxyl or carbamoyl;
C3-C8-cycloalkenyl
which is optionally substituted by
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, cyano, amino, mercapto, hydroxyl, C,-C6-
acyloxy, benzoyloxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy, Cl-C6-alkoxy, Cl-C6-alkylamino,
di(CI-C6-alkyl)amino, Cl-C6-alkylthio, Cl-C6-alkylsulphonyl, phenylsulphonyl,
oxo, thioxo, carboxyl or carbarnoyl;
(C3-C8-cycloalkyl)~(C,-C4-alkyl)
which is optionally substituted by
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, cyano, amino, mercapto, hydroxyl, C,-C6-
Le A 30 844 - Foreign Countries - 4 -
- - 21 70222
acyloxy, benzoyloxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy, C,-C6-alkoxy, C~-C6-alkylamino,
di(C,-C6-alkyl)amino, C,-C6-alkylthio, C,-C6-alkylsulphonyl, phenylsulphonyl,
oxo, thioxo, carboxyl or carbamoyl;
(C3-C8-cycloalkenyl~(C,-C4-alkyl)
which is optionally substituted by
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, cyano, arnino, mercapto, hydroxyl, C,-C6-
acyloxy, benzoyloxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy, C,-C6-alkoxy, Cl-C6-alkylamino,
di(C,-C6-alkyl)amino, C,-C6-alkylthio, C,-C6-alkylsulphonyl, phenylsulphonyl,
oxo, thioxo, carboxyl or carbamoyl;
C,-C6-alkylcarbonyl
which is optionally substituted by
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, cyano, amino, mercapto, hydroxyl, Cl-C6-
acyloxy, benzoyloxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy, Cl-C6-alkoxy, Cl-C6-alkylamino,
di(CI-C6-alkyl)amino, Cl-C6-alkylthio, Cl-C6-alkylsulphonyl, phenylsulphonyl,
oxo, thioxo, carboxyl or carbamoyl;
C2-C8-alkenylcarbonyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine or
hydroxyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy, oxo or phenyl;
(C3-C8-cycloalkyl)carbonyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorineor hydroxyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy, oxo or phenyl;
(C5-C8-cycloalkenyl)carbonyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine,
chlorine or hydroxyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy, oxo or phenyl;
(C3-C8-cycloalkyl)-(CI-C3-alkyl)carbonyl which is optionally substituted by
fluorine, chlorine or hydroxyl, C,-C4-alkoxy, oxo or phenyl;
(Cs-C6-cycloalkenyl~(C~-C3-alkyl)carbonyl which is optionally substituted by
fluorine, chlorine or hydroxyl, C,-C4-alkoxy, oxo or phenyl;
Le A 30 844 - Foreign Countries - S -
- 21 70222
- C,-C8-alkyloxycarbonyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine,
brornine, hydroxyl, C~-C4-alkoxy, C~-C4-alkylamino, di(C~-C4-alkyl)arnino or
C, -C4-alkylthio;
C2-C8-alkenyloxycarbonyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine,
S hydroxyl, C~-C4-alkoxy, oxo or phenyl;
C2-C8-alkinyloxycarbonyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine,
hydroxyl, C,-C4-alkoxy, oxo or phenyl;
C,-C8-alkylthiocarbonyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine,
hydroxyl, C,-C4-alkoxy, oxo or phenyl;
C2-C8-alkenylthiocarbonyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine,hydroxyl, C,-C4-alkoxy, oxo or phenyl;
C,-C8-alkylaminocarbonyl and di(C,-C8-alkyl)aminocarbonyl which are
optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine, hydroxyl, C,-C4-alkoxy, oxo or
phenyl;
pyrrolidin-1-yl, morpholino-, piperidino-, piperazinyl- or~methylpiperazin-1-yl-carbonyl which are optionally substituted by C~-C4-alkyl, C2-C6-alkenyl, C~-C4-
acyl, oxo, thioxo, carboxyl or phenyl;
C2-C8-alkenylaminocarbonyl and di(C,-C6-alkenyl)aminocarbonyl which are
optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine, hydroxyl, C,-C4-alkoxy, oxo or
phenyl;
C,-C6-alkylsulphonyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine,
hydroxyl, C,-C4-alkoxy, oxo or phenyl;
C,-C6-alkenylsulphonyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine,
hydroxyl, C,-C4-alkoxy, oxo or phenyl;
Le A 30 844 - Foreign Countries - 6 -
2l 702?2
- or aryl, arylcarbonyl, aryl(thiocarbonyl), (arylthio)carbonyl,(arylthio)thiocarbonyl, aryloxycarbonyl, arylaminocarbonyl,
(arylamino)thiocarbonyl, arylalkylarninocarbonyl, a~lsulphonyl, arylalkyl,
arylalkenyl, arylalkinyl, arylalkylcarbonyl, arylalkenylcarbonyl,
S arylalkoxycarbonyl or aryl(alkylthio)carbonyl which are substituted by up to
five R6 radicals which are independent of each other, and where the alkyl
radical can in each case contain from 1 to 5 C atoms and R6 is defined as above
or heteroaryl, heteroarylalkyl, heteroarylalkenyl, heteroarylalkylcarbonyl or
heteroarylalkenylcarbonyl, heteroaryloxycarbonyl, (heteroarylthio)carbonyl,
heteroarylaminocarbonyl, heteroarylalkyloxycarbonyl,
heteroaryl(allcylthio)carbonyl or heteroarylalkylaminocarbonyl which are
substituted by up to three R6 radicals which are independent of each other, and
where the alkyl radical can in each case contain from 1 to 3 C atoms,
R3 and R4 are identical or di~e~ and are, independently of each other,
hydrogen, or C~-C8-alkyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine,
hydroxyl, amino, mercapto, C,-C4-acyloxy, benzoyloxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy,
C,-C4-alkoxy, C,-C4-alkylamino, di(C~-C4-alkyl)amino, C,-C4-alkylthio, C,-C4-
alkylsulphonyl, C,-C4-alkylsulphinyl, carboxyl or carbamoyl;
C2-C8-alkenyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine or chlorine, hydroxyl,amino, mercapto, C,-C4-acyloxy, be~zoyloxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy, C,-C4-
alkoxy, C~-C4-alkylamino, di(C,-C4-alkyl)amino, C~-C4-alkylthio, C,-C4-
alkylsulphonyl, C,-C4-alkylsulphinyl, carboxyl or carbamoyl;
C3-C8-cycloalkyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine, hydroxyl,
amino, mercapto, C~-C4-acyloxy, benzoyloxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy, C,-C4-
alkoxy, C~-C4-alkylamino, di(C,-C4-alkyl)amino, C~-C4-alkylthio, C,-C4-
alkylsulphonyl, C,-C4-alkylsulphinyl, carboxyl or carbamoyl;
C3-C8-cycloalkenyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine or chlorine,
hydroxyl, amino, mercapto, C,-C4-acyloxy, benzoyloxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy,
Le A 30 844 - Forei~n Countries - 7 -
21 7U222
- C,-C4-alkoxy, C~-C4-alkylamino, di(C~-C4-alkyl)amino, C,-C4-alkylthio, C,-C4-
alkylsulphonyl, C,-C4-alkylsulphinyl, carboxyl or carbamoyl;
aryl, arylalkyl, heteroaryl or heteroarylalkyl which are substituted by up to five
R6 radicals which are independent of each other, and where the alkyl radical
can in each case contain from 1 to 3 C atoms and R6 is defined as above,
R3 and R4 or R3 and R5 can, in addition, also be part of a saturated or
unsaturated carbocyclic or heterocyclic ring having from 3 to 8 C atoms which
can optionally be substit~lte~ by fluorine, chlorine, hydroxyl, amino, C~-C6-alkyl,
C2-C6-alkenyl, C2-C6-alkinyl, C,-C6-acyloxy, benzoyloxy, C,-C6-alkoxy, oxo,
thioxo, carboxyl, carbamoyl or phenyl,
X denotes oxygen, sulphur, selenium or substituted nitrogen N-R2, in which R2 can
have the abovementioned me~ning;,
with the exception of the compounds in which R3 and R4 simultaneously denote H and
compounds in which R2 and Rs denote H and R3 and/or R4 denote arylalkyl and
compounds in which X denotes oxygen and R2 and Rs denote hydrogen,
are ver,v well suited, in combination with protease inhibitors, for use as medicaments
in the control of AIDS and HIV infections.
The alkyl groups mentioned in the prec~ling definitions can be straight-chain orbranched. Unless otherwise d~fin~, they pler~l~ly contain 1-8, particularly preferably
1-6, in particular 1~, C atoms. Examples are the methyl, ethyl, propyl, 1-methylethyl,
butyl, 1-methylpropyl, 2-methylpropyl and 1,1-dimethylethyl groups, and the like.
The alkenyl groups mentioned in the prece lin~ definitions can be straight-chain or
branched and contain from 1 to 3 double bonds. Unless otherwise defined, these groups
preferably contain 2-8, in particular 2-6, C atoms. Examples are the 2-propenyl, 1-
methylethenyl, 2-butenyl, 3-butenyl, 2-methyl-2-propenyl, 3-methyl-2-butenyl, 2,3-
dimethyl-2-butenyl, 3,3-dichloro-2-propenyl and pentadienyl groups, and the like.
Le A 30 844 - Foreign Countries - 8 -
- ` 2 1 70222
The alkinyl groups mentioned in the prece~1ing definitions can be straight-chain or
branched and contain from 1 to 3 triple bonds. Unless otherwise defined, they
preferably contain 2-8, particularly preferably 3-6, C atoms. Exarnples are the 2-
propinyl and 3-butinyl groups, and the like.
5 Unless otherwise defined, the cycloalkyl and cycloalkenyl groups mentioned in the
preoerling definitions yler~l~bly contain 3-8, particularly yl~r~ly 4-6, C atoms.
Examples are the cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclopentenyl, cyclohexyl and
cyclohexenyl groups.
The acyl groups mentioned in the prec~ling definitions can be aliphatic, cyclo~liph~tic
10 or aromatic. Unless otherwise defined, they pl~r~,~ly contain 1-8, particularly
uler~l~bly 2-7, C atoms. Exarnples of acyl groups are the formyl, aoetyl, chloroaoetyl,
trifluoroaoetyl, hydroxyaoetyl, propionyl, butyryl, isobutyryl, pivaloyl, cyclohexanoyl
and benzoyl groups.
The aryl groups mentioned in the prec~ling definitions are yler~l~bly aromatic groups
lS having 6-14 C atoms, in particular having 6-10 C atoms, such as, for example, phenyl
and naphthyl.
Examples of suitable heteroatoms in the abovementioned heterocyclic rings or
heteroaryl groups are, in particular, O, S and N, where N-Z, in which Z is H or R5
having the respective, above-described definitions, is present in the case of a N-
20 cont~ining ring which is saturated at this position.
Unless otherwise defined, the heterocyclic rings yler~l~ly have 1-13 C atoms and 1-6
heteroatoms, in particular 3-9 C atoms and 1-4 heteroatoms.
Examples of suitable heteroaromatic radicals for the heteroaryl groups mentioned in the
prece lin~ definitions are radicals such as 2- or 3-thienyl, 2- or 3-furyl, 2-, 3- or 4-
25 pyridyl, pyrimidyl, indolyl, quinolyl or isoquinolyl.
Examples of the aralkyl groups listed in the prec~ling definitions are benzyl,
Le A 30 844 - Foreign Countries - 9 -
- 21 10222
phenylethyl, naphthylmethyl and styryl.
The abovementioned substituents R~ to R5 are pl~r~l~bly substituted 3 times,
particularly preferably 2 times, in particular once, with the substituents which are given
m each case.
5 Ihe ranges for the individual s~lkstituPnt~ which were previously described as being
pl~r~lled are likewise pl~r~lled for the respective composite substituent definitions
(such as, for example, arylalkoxycarbonyl).
Depending on the dirrel~ substi~ nt~, compounds of the formulae I and Ia can
possess several asymmetric carbon atoms.
10 The invention relates, therefore, both to the pure stereoisomers and to mixtures thereof,
such as, for example, the ~ffili~tecl r~cf m~te.
The pure stereoisomers of the compounds of the formulae I and Ia can be prepareddirectly, or resolved subsequently, using known methods or in analogy with knownmethods.
15 Within the scope of the invention, protease inhibitors denote known peptide analogues
of differing structure which are suitable for treating retrovirus-in~lucecl diseases.
Le A 30 844 - Foreign Countries - 10 -
21 10222
The following may, in particular, be mentioned:
1. (S}N-[(alphaS~alpha-[(lR}2-[((3S,4aS,8aS}3-(tert-butylcarbamoyl)octahydro-
2(1H}i.~oqllinolinyl~l-hydroxyethyl)ph~ yl-2 quinaldamido]succinamide (EP
432 695 A2)
-- NH~
NH2 NH-C(Ct~3)3
2. 2(R)~Ber~y1-5-(2(S) (N-tert-butylcar'oamoyl)~(3-pyridylrnethyl)pipera~n-1-yl~
4(S}hydroxy-N-(2(R~hydroxyindan-l(S}yl)pr.ll~"~ ide
(L-735524, EP 569 083 Al, EP 541 168 A1)
O N OH
H3C CH3
CH3
Le A 30 844 - Foreign Countries - 11 -
21 70222
3. N-(Quinolin-2-ylcarbonyl)-asparagine- 1 (S)-benzyl-3-(3-tert-butyl- 1 -
isobutylureido}2(R}hydroxypropylamide (SC 52 151, PCT WO 92/08688 A1,
WO 92/08699 A1, WO 92/08698 A1, WO 92/08701 A1, WO 92/08700 A1)
O - CH3
o ~ NH2 OH 11 CH3 3
[ = J~NH-- ~ ~N~NH--CH3
4. N 1 -(2R-hydroxy-3 -((3 -methylbutyl)methyl sulphonyl)amino)- 1 S-
(phenylmethyl)propyl)-2S-((2-quinolinylcarbonyl)amino)butanediamide
(AM 11 686, PCT WO 94/04492)
NH~1N SO2-CH3
- NH2 OH
o CH(CH3)2
5. (2S,3S,SS)-S(N-(N-((N-methyl-N-((2-isopropyl-4-oxazolyl)methyl)amino)-
carbonyl)valinyl)amino)-2-(N-((5-thiazolyl)methoxycarbonyl)amino)- 1,6-
diphenyl-3-hydroxyhexane (A 84 538, PCT WO 94/14436)
O CH3 0 ,~ C5H
H3C~ ~ _ NH~--
H3C t3C CH3 C6H5 S
\=N
Le A 30 844 - Foreign Countries - 12 -
21 70222
- 6. (R)-N-tert-butyl-3-((2S,3S)-2-hydroxy-3-N-((R)-2-N-(isoquinolin-S-
yloxyacetyl)amino-3-methylthiopropanoyl)amino-4-phenylbutanoyl)-5,5-
dime~yl-1,3-thiazolidine~carboxamide (KNI 272 / Nippon ~ning)
CH3
H3C CH3
oJI~ ~NH~N~S
O O
7. {3-[(4-Amino-ben7enesulphonyl)-isobutyl-amino]-1-benzyl-2-hydroxypropyl}-
S carbamic acid tetrahydro-fi~ran-3-yl ester
s _~3~ NH2
O NH~N_so
OH
CH(CH3)2
8. (3S,6R}3{a-Ethylbenzyl}6{a-ethylphenethyl)~hydroxy-2H-pyran-2-one (VB
11 478, PCT WO 9411361)
OH ,~
-
~ CH3
Le A 30 844 - Foreign Countries - 13 -
- 21 70222
9. N-[5-L-[N{2-quinolinecarbonyl~L-asparaginyl]amino-(4R,3S~epoxy-6-phenyl-
hexanoyl]-isoleucine (EP 601 486 A)
_ ~ ~OCH
O ~NH2 0 H3C ~CH3
10. N-tert-butyl-1-[2-(R)-hydroxy-4-phenyl)-3(S)-[[N-(2-quinolinylcarbonyl)
asparaginyl]amino]butyl-4(R)-(phenylthio)piperidine-2(S)-carboxamide
(EP 560 268 A)
NH2
o f~ O OH ~ ~3
C(CH3)3
11. [3"'S-(3"'R*,4"'S*)]-N-[1'-oxo-1'-(3"-[1"'-oxo-2"'-a7~-3"'-phenylmethyl-4"'-
hydroxy-5"'-(2"'-N-tert-butylcarbamido)phenyl]pentyl-4"-methyl)-1,2,3,4-
tetrahydroisoquinoline (EP 609 625 A)
~N ~ N~
O NH
~ C(CH3)3
Le A 30 844 - Foreign Countries - 14 -
- 21 70222
12. 2-[2-Hydroxy-3-(3-hydroxy-2-methyl-benzoylarnino)4 phenylsulphanylbutyl]-
decahydro-isoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid tert-butylamide
(AG 1343 Agouron Pharm~rellticals Inc., San Diego USA)
Cl 6H5
CH3 O ~S O~ NH-C(CH3)3
~ OH ~1
13 . 2H- 1 ,4-Diazepin-2-one,hexahydro-6-hydroxy- 1 ,3,4,7-tetrakis(phenylmethyl)-,
[3S'-(3.alpha, 6.beta, 7.beta)] (PCT WO 94/08977)
o ~
OH
Ouinoxalines of the general formulae (I) and (Ia) are preferred
in which
2) n is æro,
one,
two
or three,
the individual substituents R' are, independently of each other,
Le A 30 844 - Forei~n Countries - 15 -
21 10222
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, trifluoro~ lhyl, trifluoromethoxy, hydroxyl, Cl-C4-alkyl, C5-C6-cycloalkyl, C~-C4-alkoxy, (C~-C4-alkoxy}(C,-C4-alkoxy), C~-C4-
alkylthio, Cl-C4-alkyl-sulphinyl, C~-C4-alkylsulphonyl, nitro, arnino, C~-C4-
alkylamino, di(C~-C4-alkyl)amino, piperidino, morpholino, 1-pyrrolidinyl, 4- -
methyl-piperazinyl, thiomorpholino, imidazolyl, C,-C4-acyl, C,-C4-acyloxy, C,-
C4-acylamino, cyano, carbamoyl, carboxyl, (C,-C4-alkyl}oxycarbonyl,
hydroxysulphonyl or sulphamoyl,
or
are a phenyl, phenoxy, phenoxycarbonyl, phenylthio, phenylsulphinyl,
phenylsulphonyl, phenoxysulphonyl, phenylsulphonyloxy, anilinosulphonyl,
phenylsulphonylamino, benzoyl, 2-pyridyl, 3-pyridyl or ~pyridyl radical which
is substituted by up to two R6 radicals which are independent of each other,
where R6
can be fluorine, chlorine, bromine, cyano, trifluoromethyl, nitro, amino, Cl-C4-alkyl, C3-C7-cycloalkyl, C,-C4-alkoxy, C,-C4-alkylthio, C,-C4-alkyl-sulphinyl, C,-
C4-alkylsulphonyl, C~-C4-alkylarnino, di(C~-C4-alkyl}amino, (C,-C4-alkyl)-
oxycarbonyl, phenyl or phenoxy,
R2 is hydrogen and R5 is
hydrogen, hydroxyl, cyano, amino, C,-C6-alkyl
which is optionally substituted by
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, cyano, amino, nlelca~to, hydroxyl, C~-C4-
acyloxy, benzoyloxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy, C,-C4-alkoxy, C,-C4-alkylamino,
di(C,-C4-alkyl)amino, C,-C4-alkylthio, oxo, thioxo, carboxyl or carbamoyl;
C2-C8-alkenyl,
which is optionally substituted by
fluorine, chlorine, brornine, iodine, cyano, amino, mercapto, hydroxyl, C~-C4-
Le A 30 844 - Forei~n Countries - 16 -
21 70~22
acyloxy, benzoyloxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy, C,-C4-alkoxy, Cl-C4-alkylamino,
di(C,-C4-alkyl)amino, C,-C4-alkylthio, oxo, thioxo, carboxyl or carbamoyl;
C3-Cg-allenyl,
C3-C8-alkinyl,
S which is optionally substituted by
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, cyano, amino, mercapto, hydroxyl, C~-C4-
acyloxy, benzoyloxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy, C,-C4-alkoxy, C,-C4-alkylamino,
di(C,-C4-alkyl)amino, C,-C4-alkylthio, oxo, thioxo, carboxyl or carbamoyl;
C3-C8-cycloalkyl
which is optionally substituted by
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, cyano, amino, mercapto, hydroxyl, C~-C4-
acyloxy, benzoyloxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy, C,-C4-alkoxy, C,-C4-alkylamino,
di(C,-C4-alkyl)amino, C,-C4-alkylthio, oxo, thioxo, carboxyl or carbamoyl;
C3-C8-cycloalkenyl
which is optionally substituted by
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, cyano, amino, mercapto, hydroxyl, C~-C4-
acyloxy, benzoyloxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy, C,-C4-alkoxy, Cl-C4-alkylamino,
di(C,-C4-alkyl)amino, C,-C4-alkylthio, oxo, thioxo, carboxyl or carbamoyl;
(C3-Cg-cycloalkyl~(C,-C2-alkyl)
which is optionally substituted by
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, cyano, amino, mercapto, hydroxyl, Cl-C4-
acyloxy, benzoyloxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy, C,-C4-alkoxy, C,-C4-alkylamino,
di(C,-C4-alkyl)amino, C,-C4-alkylthio, oxo, thioxo, carboxyl or carbamoyl;
(C3-C8-cycloalkenyl~(C,-C2-alkyl)
which is optionally substituted by
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, cyano, amino, mercapto, hydroxyl, Cl-C4-
acyloxy, benzoyloxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy, C,-C4-alkoxy, C,-C4-alkylamino,
Le A 30 844 - Foreien Countries - 17 -
- ` 2 1 7 0222
di(C~-C4-alkyl)amino, C,-C4-alkylthio, oxo, thioxo, carboxyl or carbamoyl;
C,-C6-alkylcarbonyl
which is optionally substituted by
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, cyano, amino, mercapto, hydroxyl, C,-C4-
S acyloxy, benzoyloxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy, C~-C4-alkoxy, C~-C4-alkylamino,
di(C,-C4-alkyl)amino, C,-C4-alkylthio, oxo, thioxo, carboxyl or carbamoyl;
C2-C6-alkenylcarbonyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine or
hydroxyl, C,-C4-alkoxy, oxo or phenyl;
(C3-C6-cycloalkyl)carbonyl which is optionally substi~-te~l by fluorine, chlorine
or hydroxyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy, oxo or phenyl;
(C5-C6-cycloalkenyl)carbonyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine,
chlorine or hydroxyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy, oxo or phenyl;
(C3-C6-cycloalkyl)-(C,-C2-alkyl)carbonyl which is optionally substituted by
fluorine, chlorine or hydroxyl, C,-C4-alkoxy, oxo or phenyl;
(Cs-C6-cycloalkenyl}(C,-C2-alkyl)carbonyl which is optionally substituted by
fluorine, chlorine or hydroxyl, C,-C4-alkoxy, oxo or phenyl;
C,-C6-alkyloxycarbonyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine,
bromine, hydroxyl, C,-C4-alkoxy, C,-C4-alkylamino, di(C,-C4-alkyl)amino or
C,-C4-alkylthio;
C2-C6-alkenyloxycarbonyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine,
hydroxyl, C,-C4-alkoxy, oxo or phenyl;
C2-C6-alkinyloxycarbonyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine,
hydroxyl, C,-C4-alkoxy, oxo or phenyl;
Le A 30 844 - Foreign Countries - 18 -
~l 70222
C,-C6-alkylthiocarbonyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine,
hydroxyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy, oxo or phenyl;
C2-C6-alkenylthiocarbonyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine,hydroxyl, C,-C4-alkoxy, oxo or phenyl;
C~-C6-alkylaminocarbonyl and di(CI-C6-alkyl)aminocarbonyl which are
optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine, hydroxyl, C,-C4-alkoxy, oxo or
phenyl;
pyrrolidin-1-yl or morpholino-, piperidino-, piperazinyl- or ~methylpiperazin-l-yl-carbonyl;
C2-C6-alkenylarninocarbonyl and di(C,-C6-alkenyl)arninocarbonyl which are
optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine, hydroxyl, C,-C4-alkoxy, oxo or
phenyl;
C,-C4-alkylsulphonyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine,
hydroxyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy, oxo or phenyl;
C,-C4-alkenylsulphonyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine,
hydroxyl, C,-C4-alkoxy, oxo or phenyl;
or aryl, arylcarbonyl, aryl(thiocarbonyl), (arylthio)carbonyl,
(arylthio)thiocarbonyl, aryloxycarbonyl, arylaminocarbonyl,
(arylamino)thiocarbonyl, arylalkylaminocarbonyl, arylsulphonyl, arylalkyl,
arylalkenyl, arylalkinyl, arylalkylcarbonyl, arylalkenylcarbonyl,
aryl(alkylthio)carbonyl or arylalkoxycarbonyl which are substituted by up to
three R6 radicals which are independent of each other and where the alkyl
radical can in each case contain from 1 to S C atoms and R6 is defined as above
or 1- or 2-naphthylmethyl, 2-, 3- or ~picolyl, 2- or 3-furylmethyl, 2- or 3-
thienylmethyl, 2- or 3-pyrrolylmethyl, 2-, 3- or ~pyridylcarbonyl, 2- or 3-
Le A 30 844 - Foreign Countries - 19 -
21 70222
furylcarbonyl, 2- or 3-thienylcarbonyl, 2- or 3-thienylacetyl, 2-, 3- or ~
picolyloxycarbonyl, 2- or 3-fulylmethyloxycarbonyl or 2- or 3-
thienylmethyloxycarbonyl which are substituted by up to two R6 radicals which
are independent of each other,
S and
R3 and R4 are identical or dirr~ and are, indep~ ntly of each other,
hydrogen,
Cl-C6-alkyl
which is optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine, hydroxyl, amino, mercapto,
C,-C4-acyloxy, benzoyloxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy, Cl-C4-alkoxy, Cl-C4-
alkylamino, di(CI-C4-alkyl)amino, C~-C4-alkylthio, C,-C4-alkylsulphonyl, C~-C4-
alkylsulphinyl, carboxyl or carbamoyl;
C2-C8-alkenyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine or chlorine, hydroxyl,amino, mercapto, C~-C4-acyloxy, benzoyloxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy, C~-C4-
alkoxy, C~-C4-alkylamino, di(C~-C4-alkyl)amino, C~-C4-alkylthio, C~-C4-
alkylsulphonyl, C,-C4-alkylsulphinyl, carboxyl or carbamoyl;
C3-C8-cycloalkyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine, hydroxyl,
amino, mercapto, C~-C4-acyloxy, benzoyloxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy, C~-C4-
alkoxy, C~-C4-alkylamino, di(C~-C4-alkyl)amino, C~-C4-alkylthio, C~-C4-
alkylsulphonyl, C,-C4-alkylsulphinyl, carboxyl or carbamoyl;
C3-C8-cycloalkenyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine or chlorine,
hydroxyl, amino, mercapto, C,-C4-acyloxy, benzoyloxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy,
Cl-C4-alkoxy, Cl-C4-alkylamino, di(CI-C4-alkyl)amino, C,-C4-alkylthio, C~-C4-
alkylsulphonyl, Cl-C4-alkylsulphinyl, carboxyl or carbamoyl;
or aryl, arylalkyl, heteroaryl or heteroalylalkyl which are substituted by up tothree R6 radicals which are independent of each other, and where the alkyl
radical can in each case contain from 1 to 3 C atoms and R6 is defined as
Le A 30 844 - Foreign Countries - 20 -
2 1 7Q222
.
above,
R3 and R4 can, in addition, also be
part of a saturated or unsaturated carbocyclic or heterocyclic ring having from
3 to 7 C atoms which can optionally be substituted by fluorine, chlorine,
S hydroxyl, amino, C,-C4-alkyl, C2-C4-alkenyl, C2-C4-alkinyl, C,-C4-acyloxy,
benzoyloxy, C,-C4-alkoxy, oxo, thioxo, carboxyl, carbamoyl or phenyl,
X denotes oxygen, sulphur or selenium
optionally in an isomeric form, in combination with protease inhibitors of the group:
1. (S}N-[(alphaS}alpha-[(lR}2-[((3S,4aS,8aS}3-(tert-butylcarbamoyl)octahydro-
2(1H~isoquinolinyl}1-hydroxyethyl)ph~t!lyl-2-quinaldamido]succinamide
2. 2(R)-Benzyl-5-(2(SHN-tert-butylcarbarnoyl)4 (3-pyridylmethyl)piperazin-1-yl} 4(S}hydroxy-N-(2(R}hydroxyindem-l(S~yl)p~t~r ~rnide
3. N-(Quinolin-2-ylcarbonyl)-asparagine- 1 (S)-benzyl-3-(3-tert-butyl- 1-
isobutylureido)-2(R)~hydroxypropylamide
4. N 1 -(2R-hydroxy-3 -((3 -methylbutyl)methylsulphonyl)amino)- 1 S-
(phenylmethyl)propyl}2S-((2-quinolinylcarbonyl)amino)butanediarnide
5. (2S,3S,SS)-5(N-(N-((N-methyl-N-((2-isopropyl-4-oxazolyl)methyl)arnino)-
carbonyl)valinyl)amino)-2-(N-((5-thiazolyl)methoxycarbonyl)amino)- 1 ,6-
diphenyl-3 -hydroxyhexane
6. (R)-N-tert-butyl-3-((2S,3S)-2-hydroxy-3-N-((R)-2-N-(isoquinolin-5-
yloxyacetyl)amino-3-methylthiopropanoyl)amino-4-phenylbutanoyl)-5,5-
dimethyl-1,3-thiazolidine~carboxamide
Le A 30 844 - Foreign Countries - 21 -
21 702Z2
7. {3-[(4-Amino-benzenesulphonyl)-isobutyl-amino]-l-benzyl-2-hydroxypropyl}-
~b~ C acid tetrahydro-furan-3-yl ester
8. (3S,6R~3-(a-Ethylbenzyl)~(a-ethylphenethyl)~hydroxy-2H-pyran-2-one (VB
11 478, PCT WO 9411361)
9. N-[5-L-[N{2-quinolinecarbonyl~L-asparaginyl]amino-(4R,3S~epoxy-6-phenyl-
hexanoyl]-isoleucine
10. N-tert-butyl-1-[2-(R)-hydroxy-4-phenyl)-3(S)-[[N-(2-quinolinylcarbonyl)-
asparaginyl]amino]butyl-4(RHphenylthio)piperidine-2(S}carboxamide
1 1. [3"'S-(3"'R*,4"'S*)]-N-[1'-oxo-1'-(3"-[1"'-oxo-2"'-aza-3"'-phenylmethyl-4"'-
hydroxy-5"'-(2"'-N-tert-butylcarbamido)phenyl]pentyl-4"-methyl)-1,2,3,4-
tetrahydroisoquinoline
12. 2-[2-Hydroxy-3-(3-hydroxy-2-methyl-benzoylamino)~phenylsulphanylbutyl]-
decahydro-isoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid tert-butylamide
13. 2H-1,4-Diazepin-2-one,hexahydro-6-hydroxy-1,3,4,7-tetrakis(phenylmethyl)-, [3S-(3.alpha, 6.beta, 7.beta)]
for use as medi~mPnt~ in the tre~tmPnt of AIDS and/or H~V infections.
Quinoxalines of the general formulae (I) and (Ia) are particularly preferred
in which
n lS zero,
one
or two,
the individual substituents R' are, independently of each other,
Le A 30 844 - Foreign Countries - 22 -
` 2~ 70222
fluorine, chlorine, bromine, trifluoromethyl, hydroxyl, Cl-C4-alkyl, C,-C4-
alkoxy, (Cl-C4-alkoxy}(CI-C2-alkoxy), Cl-C4-alkylthio, nitro, amino, Cl-C4-
alkylamino, di(CI-C4-alkyl)amino, piperidino, morpholino, 1-pyrrolidinyl,
methylpiperazinyl, Cl-C4-acyl, Cl-C4-acyloxy, Cl-C4-acylamino, cyano,
S carbamoyl, carboxyl, (Cl-C4-alkyl}oxycarbonyl, hydroxysulphonyl or
sulphamoyl,
or
are a phenyl, phenoxy, phenylthio, phenyl~l-lphonyl, phenoxysulphonyl,
benzoyl, 2-pyridyl, 3-pyridyl or ~pyridyl radical which is substitllt~l by up totwo R6 radicals which are independent of each other,
where R6
can be fluorine, chlorine, bromine, cyano, trifluoromethyl, nitro, amino, Cl-C4-alkyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy, (C,-C4-alkyl}oxycarbonyl, phenyl or phenoxy,
R2 is hydrogen and Rs is
C,-C6-alkyl
which is optionally substituted by Cl-C4-alkoxy or Cl-C4-alkylthio;
C2-C6-alkenyl,
which is optionally substituted by oxo;
C3-C6-allenyl,
C3-C8-alkinyl, in particular 2-butinyl;
C3-C6-cycloalkyl;
C5-C6-cycloalkenyl;
Le A 30 844 - Foreign Countries - 23 -
- 21 70222
(C3-C6-cycloalkyl}(C,-C2-alkyl), in particular cyclopropylmethyl, which is
optionally substituted by C,-C4-alkyl;
(C3-C6-cycloalkenyl}(C,-C2-alkyl), in particular cyclohexenylmethyl;
C,-C6-alkylcarbonyl
which is optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine, hydroxyl, benzyloxy,
phenoxy, C,-C4-alkoxy, C,-C4-alkylamino, C,-C4-alkenylamino, di(C,-C4-
alkyl)arnino, 1-pyrrolidinyl, piperidino, morpholino, 4-methylpiperazin-1-yl or
C, -C4-alkylthio;
C2-C6-alkenylcarbonyl;
Cl-C6-alkyloxycarbonyl which is optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine,
bromine, hydroxyl, C,-C4-alkoxy, C,-C4-alkylamino, di(C,-C4-alkyl)amino or
C,-C4-alkylthio;
C2-C6-alkenyloxycarbonyl, in particular vinyloxycarbonyl, allyloxycarbonyl,
isopropenyloxycarbonyl, butenyloxycarbonyl or pentenyloxycarbonyl;
C2-C6-alkinyloxycarbonyl, in particular propinyloxycarbonyl or
butinyloxycarbonyl;
C,-C6-alkylthiocarbonyl;
C2-C6-alkenylthiocarbonyl, in particular allylthiocarbonyl;
C,-C6-alkylaminocarbonyl and di(C,-C6-alkyl)aminocarbonyl;
pyrrolidin-1-yl or morpholino-, piperidino-, piperazinyl- or ~methylpiperazin-1-yl-carbonyl;
C2-C6-alkenylaminocarbonyl and di(CI-C6-alkenyl)aminocarbonyl;
Le A 30 844 - Forei~n Countries - 24 -
2l 10222
Cl -C4-alkylsulphonyl;
Cl -C4-alkenylsulphonyl;
or aryl, in particular phenyl,
arylcarbonyl, in particular benzoyl, (arylthio)carbonyl, aryloxycarbonyl,
arylaminocarbonyl, (arylamino)thiocarbonyl, arylalkylaminocarbonyl,
arylsulphonyl,
arylalkyl, in particular benzyl, phenylethyl, arylalkenyl, a~ylalkylcarbonyl,
arylalkoxycarbonyl or aryl(alkylthio)carbonyl which are s~lbstit~lte~l by up to
two R6 radicals which are independent of each other and where the alkyl radical
can in each case contain from 1 to 3 C atoms and R6 is defined as above
or 1- or 2-naphthylmethyl, 2-, 3- or ~picolyl, 2- or 3-furylrnethyl, 2- or 3-
thienylmethyl, 2- or 3-pyrrolylmethyl, 2-, 3- or ~pyridylcarbonyl, 2- or 3-
furylcarbonyl, 2- or 3-thienylcarbonyl, 2- or 3-thienylacetyl, 2-, 3- or ~
picolyloxycarbonyl, 2- or 3-furylmethyloxycarbonyl or 2- or 3-
thienylmethyloxycaronyl which are substituted by up to two R6 radicals which
are independent of each other,
and
R3 and R4 are identical or different and are, independently of each other,
hydrogen,
C,-C4-alkyl
which is optionally substituted by hydroxyl, mercapto, C,-C4-alkoxy, C,-C4-
alkylthio, C,-C4-alkylsulphonyl, C,-C4-alkylsulphinyl, carboxyl or carbamoyl;
C2-C6-alkenyl,
aryl, benzyl, thienyl or thienylrnethyl which are substituted by up to two R6
radicals which are independent of each other and where R6 is defined as above,
Le A 30 844 - Foreign Countries - 25 -
21 7~222
R3 and R4 can also be
part of a saturated or unsaturated carbocyclic or heterocyclic ring having from
3 to 6 C atoms which can optionally be substituted by oxo or thioxo, and
X denotes oxygen or sulphur
5 optionally in an isomeric form in combination with protease inhibitors of the group:
1. (S}N-[(alphaS}alpha-[(lR}2-[((3S,4aS,8aS}3~tert-butylc~l,a noyl)octahydro-
2(1H}isoquinolinyl}1-hydroxyethyl)phenethyl-2-quinaldamido]succinamide
2. 2(R}Benzyl-5-(2(S~(N-tert-butylcarbamoyl)~(3-pyridylmethyl)~ -1-yl}
4(S}hydroxy-N~2(R~hydroxyindem-1(S~yl)~ ide
3. N-(Quinolin-2-ylcarbonyl)-asparagine- 1 (S)-benzyl-3-(3-tert-butyl- 1-
isobutylureido~2(R~hydroxypropylamide
4. N 1 -(2R-hydroxy-3-((3 -methylbutyl)methylsulphonyl)amino)- 1 S-
(phenylmethyl)propyl~2S-((2-quinolinylcarbonyl)amino)butanediamide
5. (2S,3S,SS)-5(N-(N-((N-methyl-N-((2-isopropyl-4-oxazolyl)methyl)amino)-
carbonyl)valinyl)amino)-2-(N-((5-thiazolyl)methoxycarbonyl)amino)- 1,6-
diphenyl-3-hydroxyhexane
6. (R)-N-tert-butyl-3-((2S,3S)-2-hydroxy-3-N-((R)-2-N-(isoquinolin-5-
yloxyacetyl)amino-3-methylthiopropanoyl)amino-4-phenylbutanoyl)-5,5-
dimethyl-1,3-thiazolidine4-carboxamide
Le A 30 844 - Foreign Countries - 26 -
21 70222
7. {3-[(4-Amino-benzenesulphonyl)-isobutyl-amino]-l-benzyl-2-hydroxypropyl}-
~l~an~ic acid tetrahydro-furan-3-yl ester
8. (3S,6R}3{a-Ethylbenzyl}6 (a-ethylph~n~,thyl)~hydroxy-2H-py~n-2-one (VB
11 478, PCT WO 9411361)
9. N-[5-L-[N{2-quinolinecarbonyl}L-asparaginyl]amino-(4R,3S}e~poxy-6-phenyl-
hexanoyl] -isoleucine
10. N-tert-butyl- 1 -[2-(R)-hydroxy-4-phenyl)-3(S)-[[N-(2-quinolinylcarbonyl)-
asparaginyl]amino]butyl-4(RHphenylthio)piperidine-2(S~carboxamide
1 1. [3"'S-(3"'R*,4"'S*)]-N-[l'-oxo-1'-(3"-[l"'-oxo-2"'-~7~-3"'-phenylmethyl-4"'-
hydroxy-5"'-(2"'-N-tert-butylcarbamido)phenyl]pentyl-4"-methyl)-1,2,3,4-
tetrahydroisoquinoline
12. 2-[2-Hydroxy-3-(3-hydroxy-2-methyl-benzoylamino}4-phenylsulphanylbutyl]-
decahydro-isoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid tert-butylamide
13. 2H-1,4-Diazepin-2-one,hexahydro-6-hydroxy-1,3,4,7-tetrakis(phenylmethyl)-, [3S-(3.alpha, 6.beta, 7.beta)]
for use as medicaments in the treatment of AIDS and/or HIV infections.
The co~ ion which is very particularly pler~lled for use in the control of AIDS
and/or ~V infections is that of S~isopropoxycarbonyl-6-methoxy-3-(methylthio-
methyl)-3,4-dihydroquinoxazolin-2(1H)-thione of the formula (A)
Le A 30 844 - Foreign Countries - 27 -
21 70222
~ NH~6;S
H3C-O~N~L "~ `CH3 (A)
O O
H3C CH3
and (S}N-[(alphaS~alpha-[(lR}2-[((3S,4aS,8aS}3~tert-butyl~l,~lloyl)-octahydro-
2(1 H)-isoquinolinyl)- 1 -hydroxyethyl)phenethyl-2-quinaldamido]-succinamide
(Saquinavir) of the formula (B)
NH ~ ~ (B)
0=~/
~ H
NH2 NH-C(CH3)3
The quinoxalines of the general formulae (I) and (Ia) are known [cf. EP 509 398 Al].
The above-listed protease inhibitors are likewise known [cf. EP 432 695 A2, EP
569 083 A1, EP 541 168 A1, PCT WO 92/08688 Al, WO 92/08699 Al, WO 92/08698
A1, WO 92/08701 A1, WO 92/08700 Al, PCT WO 94/04492, PCT WO 94/14436,
PCT WO 9411361, EP 601 486 A, EP 560 268 A, EP 609 625 A, PCT WO 94/08977].
The use of the combination of these compounds offers advantages, as compared with
the monotherapy using the individual compounds, in the tr~trn~nt of retrovirus-
induced, in particular, however, HlV-induced, diseases. While the advantageous and
superior employment of the combination of these compounds for treating AIDS
infections or HlV infections is due in the main to the synergistic antiviral activity of
the compounds, it is also due to the fact that the tolerability of the substances, when
a~rnini~tered in combination, is unaltered, in the range of toxicity in which 50% of the
cells survive, as compared with the tox-50 of the individual components. In the case of
other cc,.l,binalions of compounds, for example AZT in combination with ganciclovir,
Le A 30 844 - Forei~n Countries - 28 -
21 70222
it is known that the use of these combinations results in synergistic toxicity [cf.
~N. Prichard et al.; Antimicrob. Agents Chemotherapy (1991), 35, 1060-1065].
In addition to this, the reduction in the effective dose which results from using the ~
combination of the substances for the trÇ~trn~nt limini~hes the probability of the
5 development of resistant virus isolates.
Ihe invention deals with the combination of two classes of compound of the ~V
reverse transcriptase and the HIV protease for preventing and treating infections with
HIV and for treating the diseases, such as AIDS-related complex (ARC) or AIDS,
which are induced by HIV.
10 HIV infection in cell culture
The HIV test was done according to the method of Pauwels et
al. [cf. Journal of Virological Methods 20, (1988), 309 -
321]with slight modifications.
Normal human blood Iymphocytes (PBL's) were enriched using Ficoll-Hypaque and
stim~ tefl with phytoh~t m~glutinin (90 ~lglml) and interleukin-2 (40 U/ml) in RPMI
1640 cont~ining 20% foetal calf serum. For infection with the infectious HIV, the
PBL's were pelleted and the cell pellet was then suspended, for adsorption, in 1 ml of
virus solution, with this suspension being incubated at 37C for 1 hour.
The virus adsorption solution was centrifuged and the infected cell pellet was taken up
in growth medium at a cell density of 1 x 105 cells per ml. 1 x 104 cells which had
20 been infected in this manner were pipetted into each of the wells of 9~well microtitre
plates.
As an alternative, H9 cells were used for the antiviral tests in place of the PBL's.
Ihe combined effect of the test substances was tested by means of chequerboard
titration.
25 The first, vertical row of the microtitre plate contained only growth medium and cells
which were not infected but which had otherwise been treated precisely as described
Le A 30 844 - Forei~ Countries - 29 -
21 70222
above (oell control). (~ly HIV infected cells (virus control) in growth medium were
added to the second vertical row of the microtitre plate. Ihe rPm:~ining wells contained
the novel compounds - either alone or in a~ yliate colllbi~ ions - in differing
concentrations, procee~ling from the wells of the 3rd vertical row of the microtitre
plate, from which the test substances were further diluted in doubling-dilution steps (50
~ll volume per well). In m~king the coll.bin~lions, dilutions of the 2nd substance were
prepared on a separate 96-well microtitre plate and then pipetted into the previously
prepared first plate. 100 ~ll of the previously prepared HIV-infected cells (see above)
were then added to each of these r~ wells. This resulted in test concentrations
being covered within approximately the 10-50-fold range above and below the ICsoconcentrations .
The test mixtures were inc~lb~ted at 37C until it was possible, using a microscope, to
detect the syncytial formation which is typical for HrV in the host cells in the untreated
virus control (between days 3 and 6 after infection). Under these test conditions, some
20-50 syncytia were obtained in the untreated virus control while no syncytia were
present in the untreated cell control. The su~ 1;l"l~; were then harvested from the 96-
well plate and screened for HIV-specific antigen in an HlV-specific ELISA test
(Vironostika HIV antigen, Organon Teknika).
The inhibition values were converted into per oent (/O) inhibition values in accordance
with the cut-off values from corresponding oell controls, virus controls or internal test
controls, and the IC50 values were determined as the conoentrations of the treated and
infected oells at which 50% of the virus-specific antigen was suppressed by the
trç~tm~ nt with the compounds. In order to analyse the synergistic activity of the
compounds, the values for the differenoes between calculated and measured inhibition
values were determined for each combination (Prichard, MN. et al., Antimicrob.
Agents Chemoth. (1993), 37, 540-545).
Differenoe values > æro denote that there was a synergistic effect. As an example, the
following results were obtained:
Tah 1 Table indicating the differenoes in the calculated and measured effects ofsaquinavir (B) together with the example of the formula (A)
Le A 30 844 - Foreign Countries - 30 -
- 2 1 70222
E~ample of fonn~a(A) 50 25 12 6 3 1.5 0.7
nM
nM
0 0 0 13 32 30 16
0 0 0 29 49 20 3
12 0 0 0 37 40 0 0
6 0 0 0 32 57 23 0
3 0 0 0 27 0 0 0
10 Synergistic activit,v is obtained for the combinations within the concentration window
of 0.7 - 6 nM for the example of the formula (A) and 6 - 50 nM for the protease
inhibitor (B).
In order to measure the synergistic toxicit,v of the compounds, substance concentrations
were tested which were around the tox-50 value of the individual compounds; the tests
15 involved microscopic e~min~tion for cell-toxic features and vital staining using trypan
blue. None of the combi~ ions which was examined exhibited any synergistic toxicity.
It was found, surprisingly, that a synergistic effect on HIV is obtained by using the
combination of the compounds. This was demonstrated, in an exemplary manner, by
studies on the combination of the quinoxaline derivative and s~ in~vir (Tab. 1).
20 The novel combinations can be used in human and veterinary medicine for the
treatment and prophylaxis of diseases which are caused by retroviruses.
The following may be mentioned, by way of example, as indications in human
medicine:
1.) The tre~tm~nt and prophylaxis of retroviral infections in hllm~n.~.
Le A 30 844 - Foreien Countries - 31 -
21 70222
2.) For the tre~tm~nt or prophylaxis of diseases (AIDS), and the phases which are
associated therewith, such as ARC (AIDS-related complex) and LAS
(lymphadenopathy syndrome) which are caused by HIV I (hurnan
immunodeficiency virus; previously termed HTLV III/LAV), and also of the
immlln~ deficiency and encephalopathy which are caused by the virus.
3.) For the tre~lm~lt or the prophylaxis of an HTLV-I or HTLV-II infection.
4.) For the tre~tm~nt or the prophylaxis of the AlDS-carrier state.
The following may be listed, by way of exarnple, as indications in veterinary medicine:
Infections with
10 a) maedivisna (in sheep and goats)
b) progressive pneumonia virus (PPV) (in sheep and goats)
c) caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus (in sheep and goats)
d) zwoegersiekte virus (in sheep)
e) infectious ~n~mi:~ virus (of the horse)
15 f) infections which are caused by feline leuk~mi~ virus
g) infections which are caused by feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV)
h) infections which are caused by simian immlmodeficiency virus (SIV).
The human medicine indications listed in items 2, 3 and 4 above are ~lef~llcd.
The present invention includes ph~rm~celltical pl~ions which, in addition to non-
Le A 30 844 - Foreign Countries - 32 -
21 70222
toxic, inert, pharm~(~Rutically suitable carrier substances, contain one or morecompounds of the formulae (I) / (Ia) in c~ lion with one of the given protease
inhibitors, or which consist of one or more active compounds of the formulae (1) / (Ia)
and the protease inhibitors, and also procRsses for producing these pl~lions, in5 particular the combination of the test compounds.
The active compounds of the formulae (I) and (Ia), and the protease inhibitors, are to
be present in the above-listed pharm~ceutical ~ lions at a con(æntration which is
preferably from about 0.1 to 99.5 % by weight, plef~l~bly of from about 0.5 to 95%
by weight, of the total mixture.
10 The above-listed I~h~rm~(~ltical ~ ions can also contain further ph~rm~elltical
active compounds in addition to the compounds of the form~ . (I) / Cla) in
combination with one of the abovementioned protease inhibitors.
The above-listed ph~rm~relltical pl~al~lions are prepared in a customary manner using
known methods, for example by mixing the active compound(s) with the carrier
1 5 substance(s).
In general, it has been found to be advantageous, both in human and veterinary
medicine, to ;~(lmini~ter the novel active compound(s) in total quantities of from about
0.5 to about 500, preferably of from 1 to 100, mg/kg of body weight every 24 hours,
where ~plu~liate in the form of several single doses, in order to achieve the desired
20 results. A single dose preferably contains the active compound(s) in quantities of from
about 1 to about 80, in particular of from 1 to 30, mg/kg of body weight. However, it
may be nf ~s~ry to deviate from the given dosages depenclin& specifically, on the
nature and the body weight of the subject to be treated, on the nature and the severity
of the disease, on the nature of the preparation and the ~ini.~tration of the
25 medicament, and on the period of time and/or interval within which the arlnlini~tration
takes place.
Le A 30 844 - Forei~n Countries - 33 -
21 70222
The invention also extends to a commercial package
containing a protease inhibitor and a quinoxaline of formula
(I) or (Ia)/ together with instructions for their use in the
treatment or prophylaxis of retroviral infections in human
or veterinary medicine.
- 33a -
23189-7912