Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
21 709~r~
TITLE OF THE INVENTION
V A R I A B L E S P E E D G E A R
BACKGROUND AND SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
This invention relates to a variable speed gear which is attached
to a bicycle in order to facilitate pedaling.
In conventional variable speed gears of this kind, for example,
some groups of big gears and small gears are engaged for changing speed
in several stages, some groups of roll friction wheels are combined for
changing speed in several stages, or a V-belt and a spring are used for
changing speed.
However, the foregoing conventional variable speed gears are
extremely complicated in construction and require many parts.
Consequently, it is difficult to assemble the parts, and the parts are
fragile even when the respective parts are precise, and moreover, it is
bothersome to take charge of the parts before assembly.
It is therefore an obiect of an aspect of the present invention to
provide a variable speed gear which accurately changes speed of rotation
with a small number of parts and rarely develops trouble.
An aspect of the invention is as follows:
A variable speed gear comprising:
2170920
a rotator having a circumferential wall in which a gear portion is
formed on an inner circumferential face of the circumferential wall;
a rotating shaft which is inserted into the rotator and freely
rotates;
a gear placed unitedly on an outer circumferential face of said
rotating shaft;
planetary gears which are arranged on an outer circumferential side
of said gear, surrounded by the circumferential wall of said rotator,
engaged with said gear and the gear portion of said circumferential
wall, and are able to revolve on said rotating shaft; and
an output gear which rotates owing to revolution of said planetary
gears.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
The present invention will be described with reference to the
accompanying drawings, in which:
Figure 1 is an elevation partly in section showing a variable speed
gear of the present invention;
Figure 2 is a side elevation partly in section of the variable
speed gear;
Figure 3 is an exploded side elevation partly in section of the
variable speed gear;
217092~
Figure 4 is a block diagram of the variable speed gear; and
Figure 5 is an explanatory view of the variable speed gear applied
to a bicycle.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
Preferred embodiments of the present invention will now be
described with reference to the accompanying drawings.
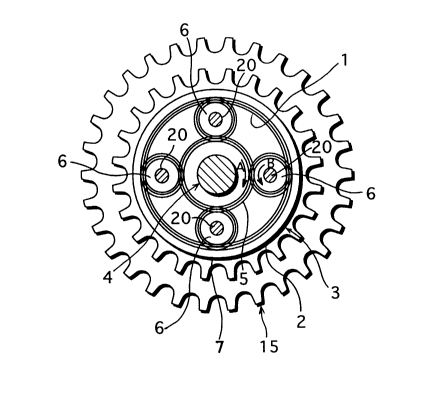
Figures 1 to 3 show a variable speed gear according to the present
invention, and this variable speed gear is provided with a rotator 3
having a circumferential wall 2 in which a gear portion 1 is formed on
an inner circumferential face of the circumferential wall 2, a rotating
shaft 4 which is inserted into the rotator 3 and freely rotates, a gear
5 placed unitedly on an outer circumferential face of the rotating shaft
4, and planetary gears 6 engaged with the gear 5. In this illustration,
four planetary gears 6 are arranged along the circumferential direction
at intervals of 90 between each other.
The rotator 3 is provided with a short cylindrical main body 7, and
the gear portion 1 is formed on an inner circumferential face of the
main body 7. In other words, this main body 7 becomes the above-
mentioned circumferential wall 2. Gear teeth are arranged on an outer
circumferential face of the main body 7 to form a sprocket portion 9
(i.e. an input gear), and a side plate 8 is fitted inside of the main
217092~
body 7 and covers an opening end of the main body 7.
The rotating shaft 4 is, for examPle, a crank axle (a pedal axle)
of a crank 12 connected to a pedal 11 of a bicycle 10 (see Figure 5).
A pair of circumferential depressed grooves 13, 14 are formed on the
outer circumference of the rotating shaft 4, and a big diameter portion
is arranged between the circumferential depressed grooves 13, 14, and
the gear 5 described above is formed on an outer circumferential face
of the big diameter portion. This gear 5 is placed inside of the main
body 7 of the rotator 3, and an outer diameter of the gear 5 is arranged
to be sufficiently smaller than an inner diameter of the gear portion 1.
An end portion 4a of the rotating shaft 4 is fitted inside of a
through hole 24 of an output gear 15 (a big gear). The output gear 15
is, as shown in Figure 5, engaged with a chain 16 which is engaged with
a small gear (not shown in the attached drawings), and when the output
gear 15 rotates and the small gear rotates, a rear wheel 17 of a
bicycle 10 rotates and this bicycle 10 moves.
The side plate 8 corresponds to the circumferential depressed
groove 14, the output gear 15 corresPonds to the circumferential
depressed groove 13, and the planetary gears 6 are arranged between the
side plate 8 of the rotator 3 and the output gear 15. The side plate 8
and the output gear 15 are respectively provided with through holes 18,
19, and the end portions 20a of a shaft 20 of each planetary gear 6 are
fitted inside of the facing through holes 18, 19 and the gear 5 is
~17~20
arranged between the side plate 8 and the output gear 15. The
planetary gears 6 surrounded by the circumferential wall 2 are
respectively engaged with the gear 5 and the gear portion 1. By way of
parenthesis, 25 in the attached drawings indicates a through hole of
the side plate 8 where the rotating shaft 4 is inserted.
If the rotating shaft 4 rotates while the rotator 3 is halted, the
planetary gears 6 engaged with the gear portion 1 and the gear 5 rotate
along with the gear 5. As shown in Figure 1, when the rotating shaft 4
rotates toward right (clockwise) as shown with an arrow A, the planetary
gears 6 rotate toward left (counterclockwise) as shown with an arrow B
and revolve on the rotating shaft 4 along the inner circumferential face
of the circumferential wall 2 because the planetary gears 6 are engaged
with the gear portion 1. When the planetary gears 6 revolve on the
rotating shaft 4, the side plate 8 and the output gear 15, which hold
the shafts 20 of the planetary gears 6, rotate. The rotating shaft 4
and the output gear 15 decelerate in the ratio of the distances to the
center line between the crests and the bottoms of the gear teeth.
When the rotator 3 rotates synchronously with the rotating shaft 4,
the planetary gears 6 do not rotate, and the rotating shaft 4 and the
output gear 15 rotate in the ratio of one to one, and the rotator 3 and
the big gear 15 unitedly rotate. That is to say, when the rotator 3
rotates toward right, deceleration ratio of the rotating shaft 4 and the
output gear 15 changes due to a rotating speed of the rotator 3.
2170~
The above-mentioned rotator 3 is driven to rotate by driving force
of an electric motor 21 as shown in Figure 4. This electric motor 21 is
driven by current supply from, for example, a charging battery (such as
a lead storage battery, a nickel-cadmium battery). An output shaft of
the electric motor 21 and the rotator 3 are connected through an
interlock connecting member. It is possible to arrange so that a
sprocket is attached to the output shaft of the electric motor 21 and
an endless chain is suspended at this sprocket and the sprocket portion
9 of the rotator 3, or that a pulley is attached to the output shaft of
the electric motor 21 and an endless belt is suspended at the pulley of
the electric motor 21 and a pulley portion which is substituted for the
sprocket portion 9 and formed on the rotator 3. The battery is not
restricted to a charging battery.
When the electric motor 21 drives and the output shaft of the
electric motor 21 rotates, the rotator 3 rotates through the interlock
connecting member. As shown in Figure 5, the electric motor 21 and the
battery are contained in a case 27 attached to a frame 26 of the bicycle
10.
A controlling means 22 arranged in the case 27 (see Figure 4)
controls a number of revolution of the output shaft of the electric
motor 21. A sensor 23 detects a number of revolution of a pedal 11 of
the bicycle, the number of revolution is inputted into the controlling
means 22, and on the basis of this number of revolution, the
-
~1 7Q~2~
controlling means 22 decides a number of revolution of the electric
motor 21. A tachometer is used as the sensor 23.
According to the variable speed gear composed as described above,
when the pedal 11 of the bicycle is worked and the rotating shaft 4
rotates, the sensor 23 detects the number of revolution of the pedal 11
The controlling means 22 drives the electric motor 21 on the basis of
this number of revolution, and the rotator 3 rotates. The electric
motor 21 rotates the rotator 3 owing to change in a rotation speed (a
number of revolution) of the pedal 11, transmission gear ratio of the
pedal 11 and the output gear 15 is changed, and the output of the
electric motor 21 can be combined with the rotation of the rotating
shaft (the pedal shaft) 4. This makes it easier to pedal this bicycle
on an uphill road.
It is possible to change transmission gear ratio when the bicycle
is loaded heavily, for example, when starting to pedal the bicycle or
pedaling on an uphill road, and the electric motor 21 can be used under
an effective situation (a number of revolution). Therefore, it is
possible to effectively use battery capacity and lower maximum output of
the electric motor 21.
According to the present invention, transmission gear ratio of
rotating speed is accurately changed, and moreover, only small number of
parts are required and the parts can be assembled easily, and
occurrence of trouble is prevented to the utmost. It is possible to
21 7~92f~
effectively use battery capacity and lower maximum output of the
electric motor 21, and the variable speed gear becomes extremely
effective. Besides, the apparatus as a whole is light and simple as
compared with a conventional variable speed gear of this kind,
therefore it can be easily applied to an ordinary bicycle without a
large-scale remodeling, and the cost is low. A number of revolution of
the rotator 3 changes owing to a number of revolution of the pedal 11,
therefore power to work the pedal 11 does not change on a plane and on
an uphill road, and it is possible to work the pedal 11 of the bicycle
10 under a stable situation.
While preferred embodiments of the present invention have been
described in this specification, it is to be understood that the
invention is illustrative and not restrictive, because various changes
are possible within the spirit and indispensable features.
That is to say, the number of the planetary gears 6 can be freely
increased or decreased, and it is possible to change the gear 5 and the
planetary gears 6 in numbers of teeth and diameters of pitch circles,
and in conformity with this, it is possible to change the gear of the
gear portion 1 of the circumferential wall 2.