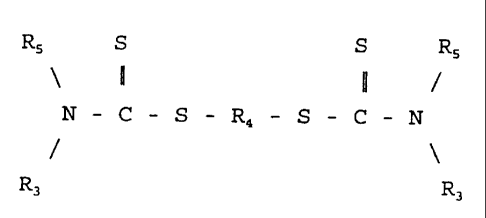Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2171924
EXTENDED LIFE RUST AND OXIDATION OILS
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
1. Field of the Invention. This invention relates to the field of
improved thermal and oxidative stability of lubricating fluids.
2. Description of the Prior Art.
Lubricating oils such as circulating oils, turbine oils, hydraulic
fluids and transformer oils as well as others require good
oxidation stability and good rust inhibition properties. Extended
life for such fluids where desired rust and oxidation (R&O)
inhibition properties are maintained for extended periods of use is
demanded by industrial users and provides important economic
benefit. R&O oils are widely used in turbine and compressor
circulating systems. Their thermal and oxidative stability are of
particular importance. In addition, R&O oils provide rust
protection, corrosion protection and metal passivation. Antiwear
protection is sometimes needed.
U. S. Patent 4,125,479 to Chesluk et al. discloses an oxidation
inhibited lubricating oil with a combination of additives
comprising methylenebis(di-n-butyldithiocarbamate)and 4-methyl-2,6-
ditertiary butyl phenol, said to provide enhanced oxidation
inhibition. U. S. Patent 4,880,551 to Doe discloses an antioxidant
composition consisting of a 1-(di(4-octylphenyl)
aminomethyl)tolutriazole and at least one antioxidant selected from
the group consisting essentially of methylenebis(di-n-
butyldithiocarbamate); 2,6-di-t-butyl-4-sec-butylphenol; 2,6-di-t-
butyl-4-methylphenol and butylated phenol mixture. International
PCT Publication Number WO 92/19703, published 12 November 1992, to
Lubrizol Corporation discloses thermally stable lubricant and
functional fluid compositions containing hydrocarbyl phosphate in
combination with at least one basic alkali or alkaline earth metal
1
217192
salt of an acidic organic compound and a metal deactivator, the
composition may additionally contain a dithiocarbamate compound for
an antiwear agent. These references do not teach or suggest the
combination of components claimed herein.
There is an increasing demand for inhibited oils with extended
lifetimes. R&O lubricant concentrate packages typically contain
phenolic, amino and other antioxidants, rust inhibitor(s), a metal
deactivator, and a demulsifying agent. They may include additional
components such as an antiwear agent depending on the final
performance properties desired. The principle function of the
antioxidants is the inhibition of oxidative degradation of R&O oils
that are obtained by blending the R&O lubricant concentrate package
in a particular basestock oil of choice. Basestock oils have
varying degrees of thermal and oxidative stability.
This invention will serve to improve the thermal and oxidative
properties of even those basestock oils that are known to have less
than satisfactory stability. The current invention relates to the
use of certain components that contribute directly to prolonging
the life of R&O oils.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
In a rust and oxidation (R&O) inhibited lubricant ccmposition
comprising a base oil and rust and oxidation inhibitors, the
invention is directed to the improvement wherein said lubricant
composition comprises (a) a dithiocarbamate compound represented by
the formula
RS S S RS
N - S - S - -
C R4 C N
- -
Ra Ra
2
2171924 __
wherein R4 is
a hydrocarbylene
group having
1 to 10 carbon
atoms,
each Rsis a hydrogen or a hydrocarbyl group having1 to 18 carbon
atoms, and each R3 a hydrocarbyl group having 1 to 18 carbon
is
atoms; and (b) an alkylphenyl-a-naphthylamine. The lubricant
composition further optionally comprises (c) a hydrocarbyl
phosphate represented by the formula
(R60)3P
where each R6 is independently C1 to C18 alkyl, Cz to C18 alkenyl, or
C6 to Cle aryl. Each component (a) and (b) , or (a) , (b) and (c) is
present in an amount sufficient to provide improved inhibition of
oxidation to the R&O lubricant composition.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
The additive combinations of this invention may be used in any
lubricating oil where oxidation inhibition is required. This may
include circulating oils used in compressor and turbine circulating
systems, transformer oils, engine oils and other oils which are
subjected to conditions where oxidation is a problem. It has been
found that a dithiocarbamate compound in combination with an
alkylphenyl-a-naphthylamine, in effective amounts, and that
combination in further combination with an effective amount of
hydrocarbyl phosphate, provide important and unexpected enhancement
of thermal and oxidation stability, with resulting improvement in
the life of the R&O oil.
The additive combinations of this invention can be incorporated in
a wide variety of lubricants and functional fluids in effective
amounts to provide suitable active ingredient concentrations. The
base oils useful herein can be hydrocarbon oils of suitable
viscosities; synthetic oils such as hydrogenated polyolefin oils;
poly-a-olefin oligomers (such as hydrogenated poly-1-decene); alkyl
esters of dicarboxylic acids; complex esters of dicarboxylic acid,
3
CA 02171924 2005-06-17
polyglycol and alcohol; alkyl esters of carbonic or phosphoric
acids; polysilicones; fluorohydrocarbon oils; and mixtures of
mineral, natural and/or synthetic oils in any proportion, etc. The
term "base oil" for this disclosure includes all the foregoing and
mixtures thereof.
The dithiocarbamate compound to be included in the combination
of the invention is represented by the formula
RS S S RS
N - - - S C -
C S R4 - N
-
Rj R3
wherein R4 is a hydrocarbylene group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms,
preferably 1 to 4 carbon atoms. Preferably, R4 is an alkylene
group, most preferably a methylene or ethylene group. Each Rsis a
hydrogen or a hydrocarbyl group having 1 to 18 carbon atoms,
preferably 2 to 10, more preferably 2 to 6_ Each R3 is a
hydrocarbyl group having 1 to 18 carbon atoms, preferably 2 to 10,
more preferably 2 to 6. A commercially available dithiocarbamate
compound appropriate for use in the invention is VANLUBE 7723,
methylenebis(di-n-butyldithiocarbamate).
Beyond a certain level, the dithiocarbamate compound may start
hurting or interfering with relevent bench tests other than R&O
tests. Higher levels of dithiocarbamate compound may result in
deterioration of thermal stability, causing undesired sludge in
thermal stability tests. Also rust problems may occur at higher
dithiocarbamate compound levels, which may result in failure of
specified rust tests. An effective amount of dithiocarbamate
compound is up to 1.0 weight percent of the finished lubricant
*Trade-mark
4
21 l 1924
composition, for example 0.01 to 1.0 weight percent, 0.02 to 0.5
preferred, 0.03-0.2 most preferred.
The alkylphenyl-a-naphthylamine for use in the invention is
represented by the formula
Rz
H
' N O
wherein Rl and RZ are independently hydrogen or Cl to Cl8 alkyl. For
purposes herein, "alkylphenyl-a-naphthylamine" includes phenyl-a-
naphthylamine (PANA), where both R1 and RZ are hydrogen. An
effective amount of alkylphenyl-a-naphthylamine for use in the
invention is up to 0.15 weight percent of the finished lubricant
composition, for example 0.025 to 0.15 weight percent, 0.03 to
0.125 weight percent preferred.
The hydrocarbyl phosphate compound for use in the invention is
represented by the formula:
(R60)3P
where each R6 is independently C1 to C18 alkyl, Cz to C18 alkenyl, or
C6 to C18 aryl. In preferred compounds, each Rsis independently C3
to C12 alkyl or C6 to C18 aryl. In most preferred compounds, R6 is C6
to C18 aryl, including triphenylphosphite, tricresylphos-phite,
trinonylphenylphosphite (C15), tridodecylphenylphosphite, and
mixtures thereof. An effective amount of the hydrocarbyl phosphate
compound for use in the invention is up to 0.075 weight percent of
the finished lubricant composition, for example 0.005 to 0.075
2171924
a
weight percent, 0.01 to 0.06 preferred.
R&O oils will typically contain a conventional quantity of one
or more antioxidants in order to protect the composition from
premature degradation in the presence of air, especially at
elevated temperatures. Typical antioxidants include various
alkylated phenols, hindered phenols and phenol derivatives such as
t-butyl hydroquinone, butylated hydroxyanisole, polybutylated
bisphenol A, butylated hydroxy toluene, alkylated hydroquinone,
2,5-ditertaryl hydroquinone; 2,6-ditert-butyl-para-cresol; 2,2'-
methylenebis(6-tert-butyl-p-cresol); 1,5-naphthalenediol; 4,4'-
thiobis(t-tert-butyl-m-cresol); p,p-biphenol; 4,4'-butylidenebis(6-
tert-butyl-m-cresol); 4-methoxy-2,6-di-tert-butylphenol; and the
like; also amino antioxidants such as aldehyde amines, ketone
amines, ketone-diarylamines, alkylated diphenylamines,
phenylenediamines, and the phenolic amines; secondary aromatic
amine antioxidants, sulfurized phenolic antioxidants, oil-soluble
copper compounds, phosphorus-containing antioxidants, and the like
as well as mixtures of antioxidants. Phenolic antioxidants are
known and may be represented by the general formula:
where R-, is hydrogen or an alkyl group with 1 to 4 carbons, Re is
an alkyl group with 1 to 4 carbons or a benzylic group, and R9 is
hydrogen, an alkyl group with 1 to 6 carbons, or an alkoxy group
with 1 to 6 carbons. In one example of a phenolic antioxidant for
use with the invention, R, is hydrogen, Re is an alkyl group with
1 to 4 carbons, and R9 is an alkyl group with 1 to 6 carbons; most
preferably both Re and R9 are t-butyl. In a second example R9 is
hydrogen, R., is an alkyl group with 1 to 4 carbons, and Re is an
6
2171924
-. ;
alkyl group with 1 to 4 carbons; most preferably both R, and Re are
t-butyl.
The R&O oil compositions useful herein will also typically
comprise a rust inhibitor and a metal deactivator. These are
commonly selected from alkenyl succinic acid esters and from
triazoles and triazole derivatives, known for these purposes_
It is also useful to this invention to employ in the lubricant
compositions and additive concentrates a suitable quantity of a
corrosion inhibitor. This may be a single compound or a mixture of
compounds having the property of inhibiting corrosion of metallic
surfaces. One type of such additives are inhibitors of copper'
corrosion. Such compounds include thiazoles, triazoles and
thiadizoles. Examples of such compounds include benzotriazole,
tolytriazole, octyltriazole, decyltriazole, dodecyltriazoie, 2-
mercaptobenzothiazole, 2, 5-dimercapto-1, 3, 4-thiadiazole, 2-
mercapto-5-hydrocarbylthio-1,3,4-thiadiazoles, 2-mercapto-5-
hydrocarbyldithio-1, 3, 4-thiadiazoles, 2, 5-bis(hydrocarbylthio)-
l, 3, 4-thiadiazoles, and 2, 5- (bis) hydrocarbyldithio) , 1, 3, 4-
thiadiazoles. The preferred compounds are the 1, 3, 4-
thiadiazoles, a number of which are available as articles of
commerce. Such compounds are generally synthesized from hydrazine
and carbon disulfide by known procedures. See for example U.S.
Pat. Nos. 2,765,289; 2,749, 311; 2,760,933; 2,850,453; 2,910,439;
3,663,561; 3,862,798; and 3,840,549. Other types of corrosion
inhibitors are known and suitable for use in the compositions of
this invention. Suitable corrosion inhibitors include ether
amines; acid phosphates; amines; polyethoxylated compounds such as
ethoxylated amines, ethoxylated and/or propoxylated phenols, and
ethoxylated alcohols; imidazolines; and the like. Materials of
these types are well known to those skilled in the art and a number
of such materials are available as articles of commerce.
The lubricating composition of the present invention may
7
2171924
further contain other additives such as extreme pressure agents
and/or antiwear agents.
The additives of the present invention can be incorporated
into a lubricating oil in any convenient way. The compounds, or
mixtures thereof, can be added directly to the oil at the desired
level or by adding concentrates of the additive to the oil.
Accordingly, the additive compounds can be blended with a suitable
oil soluble solvent such as mineral spirits and/or base oil to form
a concentrate and then the concentrate may be blended with
lubricating oil to obtain a final formulation. A complete R&O
lubricant concentrate package can be prepared containing
antioxidants, rust inhibitor, metal, deactivator, demulsifier,
additional desired components as well as the components of the
invention, i.e. the dithiocarbamate compound and the alkylphenyl-
a-naphthylamine compound; or the dithiocarbamate compound, the
alkylphenyl-a-naphthylamine compound, and the hydrocarbyl
phosphate. The components are present in the lubricant concentrate
package at a level sufficient to provide an effective level in the
finished composition to provide the enhanced oxidation inhibition
properties.
EXAMPLES
The following tests were performed to demonstrate the
advantages of the invention:
(a) The American Society for Testing and Materials {ASTM)
provides a Standard Test Method for Oxidation Characteristics of
Inhibited Mineral Oils {ASTM D943-81{Reapproved 1991)). The D943
test method was developed for, and is used to evaluate the
oxidation stability of inhibited steam turbine oils and other oils
containing R&O inhibitors in the presence of oxygen, water, and
copper and iron metals at an elevated temperature and is considered
of value in the industry in estimating the oxidation stability of
8
CA 02171924 2005-06-17
lubricants, especially those that are prone to water contamination_
(b) ASTM D-2272-85(Reapproved 1991), Standard Test Method for
Oxidation Stability of Steam Turbine Oils by Rotating Bomb, (RBOT)
utilizes an oxygen-pressured bomb to evaluate the oxidation
stability of new and in service turbine oils having the same
composition (base stock and additives) in the presence of water and
a copper catalyst coil at 150°C.
(c) The Cincinnati Milacron Thermal Stability Test procedure
"A" (CM "A") is intended to check the thermal stability of a
designated oil sample by immersing copper and iron rods into an oil
sample, heating in an oil bath or oven (135-138° C) for one week
(168 hours), and determining the weight of resulting residue or
"sludge".
HiTec 575 Ashless Rust & Oxidation Inhibitor is a lubricant
additive concentrate package commercially available from Ethyl
Corporation. This is fully formulated for high-performance,
turbine-quality hydraulic fluids. It provides extended oxidation
life, excellent rust control, demulsibility and filterability, and
is compatible with other additives commonly used in hydraulic
fluids. HiTec 575 lubricant additive represents a typical R&O
package and has been used in the studies reported herein to
demonstrate the improved oxidation properties obtained with the
present invention. Texaco''ISO 46 basestock oil was used in
preparing the formulation of the examples below. In Example 1,
HiTec 575 lubricant additive was blended with the basestock oil at
its recommended dosage, 0.80 weight percent. HiTec 575 lubricant
additive contains PANA in an amount that provides 0.10 weight
percent to the blended lubricant composition at this recommended
dosage. For Examples 2 through 6 below, the PANA was removed from
the HiTec 575 lubricant additive. The HiTec 575 lubricant additive
without PANA was blended with the Texaco ISO 46 basestock oil at
*trade-mark 9
2111924
~_,
0.80 weight percent dosage, and the dithiocarbamate compound and
triphenylphosphite were added in the amounts indicated. Far
Examples 7 through 14, commercially available HiTec 575 lubricant
additive was blended with the basestock at 0.80 weight percent
dosage, and the dithiocarbamate compound and triphenylphosphite
were added in the amounts indicated. A commercially available
dithiocarbamate compound, VANLUBE° 7723, methylenebis(di-n-
butyldithiocarbamate), was used in the Examples in the amounts
indicated. Table I below provides the composition of Examples 1-11
and the results of D943 and RBOT testing and CM "A" Sludge testing.
The composition and the results of RBOT testing for Examples 12-14
are also provided in Table I.
2171924.-.
TABLE I
Example PANA DITHIO- TPP RBOT CM "A" D943
~AM~ SLUDGE
wt % wt % wt o minutes mg/100m1 hours
1 0.10 - - 745 14.00 2644
2 - - - 708 14.03 2634
3 - 0.025 - 765 9.92 2756
4 - 0.025 0.025 775 19.5 2523
- 0.050 - 805 12.25 2922
6 - 0.050 0.025 826 20.08 2526
7 0.10 0.025 0.025 945 23.05 2724
8 0.10 0.050 0.025 1048 22.10 3852
9 0.10 0.050 0.050 986 25.40 3684
0.10 0.100 0.025 1130 19.75 )3700*
11 0.10 0.100 0.050 1195 29.03 3850
12 0.10 0.05 - 942
13 0.10 0.10 - 1080
14 0.10 0.20 - 1335
* Test still running at time of filing
11