Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
217893
1
TITLE OF THE INVENTION
CLOTHES DRYER USING HALOGEN-TYPE LIGHT AS
A DRYING MEANS.
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to dryer apparatuses.
More specifically, the present invention is particularly concerned with a
clothes dryer using halogen-type lights as a means for extracting humidity
from the clothes.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The field of clothes dryers is replete with various types
of structures for extracting moisture from the clothes. Most conventional
clothes dryers include a dryer drum rotatably mounted inside an
enclosure. A heating element is provided for heating an incoming flow of
air that is circulated inside the dryer drum by a ventilating system so as
to evaporate the moisture from the clothes. The moist air is continuously
allowed to flow out of the dryer drum through an air exhaust duct.
Although widely used, the conventional so-called air-
type clothes dryers are relatively inefficient. Indeed, the air-type clothes
dryers require a considerable amount of energy to operate properly.
2178993
2
Firstly, the incoming flow of air must be considerably heated by heating
elements which are usually very energy-consuming. Secondly, the moist
air exiting through an exhaust duct of the conventional clothes dryers still
contains a considerable amount of heat which indicates the relative
inefficiency of the air-type clothes dryers since this heat still contained in
the exhausted air has not been used to dry the clothes.
OBJECTS OF THE INVENTION
It is therefore an object of the present invention to
provide a dryer apparatus having an improved energy efficiency.
Another object of the present invention is to provide a
dryer apparatus capable of removing the moisture from the clothes
inserted therein in a relatively short period of time.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
More specifically, in accordance with the present
invention, there is provided a dryer apparatus for drying wet articles
comprising:
an article support structure for supporting the articles to
be dried; and
217899
3
at least one photon generating halogen-type light
assembly associated with the support structure so as to direct a flow of
photons towards the articles to be dried;
whereby the articles to be dried are placed on the support structure to be
dried by the flow of photons generated by the photon generating halogen-
type lights.
According to another aspect of the present invention,
there is provided a clothes dryer apparatus comprising:
a frame structure;
a dryer drum having a rotation axis and an inner surface
defining an internal volume; the dryer drum being mounted in the frame
structure so as to rotate about the rotation axis; and
at least one photon-generating halogen-type light
assembly mounted in the frame structure so as to direct a flow of photons
towards the internal volume of the dryer drum;
whereby wet clothes placed in the internal volume of the dryer drum are
dried by the flow of photons generated by the photon-generating halogen-
type lights.
It is to be noted that in the present disclosure, as well as
in the appended claims, the term "halogen-type light" is to be construed
as a light where the gas present in the light bulb increases the fusion
temperature of the filament used above the fusion temperature of the
filament used in a conventional incandescent light bulb. Examples of this
type of lights are: quartz-iodine lamp and quartz-halogen lamp. Also, the
term "photon" is to be construed as being an elementary particle of light.
2178993
4
Other objects, advantages and features of the present
invention will become more apparent upon reading of the following non
restrictive description of preferred embodiment thereof, given by way of
example only with reference to the accompanying drawings.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
In the appended drawings:
Figure 1 is a top sectional view of a clothes dryer in
accordance with an embodiment of the present invention;
Figure 2 is a front elevational sectional view taken along
line 2-2 of Figure 1;
Figure 3 is a rear elevational view of the clothes dryer
of Figure 1;
Figure 4 is a rear elevational sectional view taken along
line 4-4 of Figure 1;
Figure 5 is a perspective view of a halogen-type light
assembly according to an embodiment of the present invention;
'" ~ 217893
Figure 6 is a sectional view taken along line 6-6 of
Figure 4 illustrating the various components forming each halogen-type
light assembly; and
5 Figure 7 is an elevational view of a halogen-type light
bulb.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
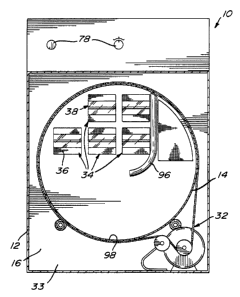
Referring to Figures 1-4, there is shown schematically
a clothes dryer 10 in accordance with an embodiment of the present
invention. The clothes dryer 10 includes a substantially parallelepiped-
shaped clothes dryer frame structure (body) 12, a cylindrical clothes dryer
drum 14, internal walls 16, 18 and 20 (Figures 1 and 4) defining, with a
rear wall 22 (Figure 3) and peripheral walls 23, an air inlet chamber 24
and an air exhaust chamber 26.
The parallelepiped-shaped frame structure 12 is very
similar to the frame structure of conventional air-type clothes dryers.
The clothes dryer drum 14 is mounted in the enclosure
formed by the frame structure 12 so as to be rotatable about a rotation
axis 30 by a conventional drum rotating mechanism 32 (Figure 2)
mounted in a rotating mechanism compartment 33. The rotation of the
dryer drum 14 has the conventional displacement offset on the clothes to
2178993
6
be dried (not shown) placed therein. Drum rotating arrangement 32 will
not be described in greater details herein as it is believed to be well
known in the art.
A plurality of air inlet apertures 34 extends through the
internal wall 16. The air inlet apertures 34 are provided with a filtering
screen 36 extending thereacross.
A number of photon generating halogen-type light
assemblies 38 corresponding to the number of air inlet apertures 34 are
mounted on the internal wall 16 substantially in register with the air inlet
apertures 34 so as to extend across the latter. The halogen-type light
assemblies 38 are mounted to the internal wall 16 so as to project light
inside of the dryer drum 14.
To cool the halogen-type light assemblies, the air inlet
chamber 24 is provided with a pair of inlet fans 40 and 42 which, when
energized, draw air from outside the clothes dryer 10, creating an air flow
which cools the halogen-type light assemblies 38 before penetrating the
dryer drum 14 through the air inlet apertures 34 (see arrows 44, 46 and
48 in Figures 1 and 3).
To avoid the generation of a positive pressure in the
dryer drum 14 as well as to provide an exhaust path for moisture-
containing air present in the dryer drum 14, the air exhaust chamber 26
is provided with a dryer drum exhaust aperture 50 having a filtering
screen 51, an exhaust fan 52 and a rotating mechanism compartment
2178993
7
aperture 54. When the exhaust fan 52 is energized, a negative pressure
is created in the exhaust chamber 26. This negative pressure creates a
drawing effect which tends to draw the moisture-containing air from the
dryer drum 14 through the exhaust aperture 50. Of course, air from the
rotating mechanism compartment 33 is also drawn through the aperture
54 therefore preventing excessive heating of the compartment 33. The
drawn air is exhausted through an outlet 56 (see arrow 58 in Figures 1
and 3). A rotatable baffle plate 60 is provided near the outlet 56 to
regulate the exhaust air flow as will be described hereinafter. The baffle
plate 60 includes a baffle plate actuator 61.
The general characteristic of the present invention is to
dry wet clothes by a bombardment of photons which are generated by the
halogen-type light assemblies 38. This flow of photons is directed inside
the dryer drum 14 and is preferably focused as will be discussed later.
The photons are adapted to fraction the water molecules embedded in
the clothes and to facilitate the extraction of these water molecules. Of
course, when the water molecules are extracted from the clothes, they
generate moisture in the air contained in the dryer drum 14.
The warm air entering the dryer drum 14 through the
apertures 34 will prevent the condensation of the water vapour generated
by the drying of the clothes placed in the dryer drum 14, and the exhaust
fan 52 will evacuate the moisture-containing air out of the dryer drum 14.
It has been found that it is advantageous to prevent the
halogen-type light assemblies 38 from being energized when the exhaust
' 2178993
s
fan 52 is not operating properly to prevent possible overheating of the
dryer drum 14.
Therefore, a controller 28 is provided to control the
operation of the clothes dryer 10. The controller 28 is provided with an
air flow sensor 62, electrically connected to the controller 28 through a
wire 64, acting as a fan-operation sensor to determine if the exhaust fan
52 is operating properly. The inlet fans 40 and 42 are electrically
connected to the controller 28 through a wire 66 and the exhaust fan is
electrically connected to the controller 28 through a wire 68. The
halogen-type light assemblies 38 are electrically connected to the
controller 28 through wires 70 and the baffle plate actuator 61 electrically
connected to the controller 28 through a wire 72. Finally, a heat sensor
74, mounted to the internal wall 16, is electrically connected to the
controller 28 through a wire 76. The purpose of the heat sensor 74 will
be described later. Of course, switches or other controls 78 are
electrically connected to the controller 28 to enable the controller 28 to
accept instructions from the user.
The controller 28 may therefore be configured so as to
de-energize the halogen-type light assemblies 38 should the sensor 60
detect that the exhaust fan 52 does not operate properly.
It has been found that the walls of the dryer drum 14 and
the moisture-containing exhausted air remain at a normal temperature
while the clothes to be dried placed in the dryer drum 14 are still wet.
However, the temperature increases significantly when the clothes are
,
21~8~93
9
dry. The heat sensor 74 is therefore provided to detect this significant
temperature increase so that the controller 28 may de-energized all the
electrical components of the clothes dryer 10 when the clothes placed in
the dryer drum are dry. The clothes dryer 10 is therefore automatically
stopped when the clothes are dry, which increases its overall efficiency
since no unnecessarily operation is permitted.
As will be easily understood by one of ordinary skill in
the art, the controller 28, which has been generally described as an
electrical controller, could be replaced by a mechanical controller
performing essentially the same functions.
The baffle plate 60 is provided to limit the exhaust of
moisture-containing air to thereby adjust the temperature in the dryer
drum 14 depending on various factors such as the temperature of the air
surrounding the clothes dryer 10.
It is to be noted that the baffle plate actuator 61 could
easily be replaced by a mechanical actuator (not shown).
Turning now to Figures 5 to 7, the halogen-type light
assemblies 38 will be described in greater details.
Each halogen-type light assembly 38 is provided with a
plurality of oversized heat transfer fins 80 adapted to dissipate the heat
generated by the halogen-type light assemblies 38. The heat is therefore
2178993
more efficiently transferred to the flow of air generated by fans 40 and 42
and entering the dryer drum 14.
A photon generating halogen-type light bulb 81 is used
5 to generate the light to be transmitted in the dryer drum 14.
The halogen-type light assemblies 38 are also provided
with a pair of light reflectors 82 and 84 interconnected by a bimetallic
element 86. The light reflectors 82 and 86 are shown in full lines in
10 Figure 6 as being in a position where the light generated by the halogen-
type light bulb 81 is focused at a predetermined focused location 88 in the
dryer drum 14 (see dashed lines 90).
A characteristic of the bimetallic element 86
interconnecting the light reflectors 82 and 84 is its known deformation
when a predetermined temperature is reached. Therefore, the bimetallic
element 86 is adapted to move the reflectors 82 and 84 to a position
shown in dotted lines so that the light generated by the bulb 81 becomes
unfocused (see dotted lines 92) when a temperature indicating the dry
state of the clothes placed in the dryer drum 14 is reached.
A thermal-type glass plate 93 separates the clothes from
the halogen-type light assemblies 38 to protect both the light bulb 81 and
the clothes.
Figure 7 illustrates light bulb 81 which advantageously
includes slotted tabs 94 to be electrically connected to electrical supports
217993
11
(not shown) via fasteners such as screws. Indeed, it is advantageous to
use fasteners to connect the light bulb 81 because of the continuous
vibrations of the clothes dryer 10 upon operation thereof.
Compared to conventional halogen-type light
assemblies, the halogen-type light assemblies 38 typically have
undersized reflectors 82 and 84, and oversized heat sinks elements 80.
Returning to Figures 1 and 2, a clothes spacing
structure 96 is operatively positioned inside the dryer drum 14 and is
adapted to act as a spacing means for ensuring that the clothes inside the
dryer drum 14 are spaced apart from the halogen-type light assemblies
38. Furthermore, the ramp-like profile of the clothes spacing structure 96
guides the clothes near the focused location of the halogen-type light
assemblies 38 which increases the efficiency of the clothes dryer 10 since
the intensity of photons is greater at this focused location.
To further increase the efficiency of the clothes dryer 10,
an internal surface 98 (Figure 2) of the dryer drum 14 is preferably white
so as to potentially minimize losses due to the absorption of photons by
the dryer drum' 14.
It is to be noted that the fans 40, 42 and 52 could be
operationally linked to the drum rotating mechanism 32 by suitable
mechanical links (not shown) should one want to use only one motor in
the clothes dryer 10. However, this would lead to a more complex
mechanical structure of the clothes dryer.
21'8993
12
It is also to be noted that the clothes dryer 10 could be
easily modified to dry non-clothing wet articles. In this case, the rotating
dryer drum would be replaced by a support structure adapted to support
the wet articles to be dried.
Although the present invention has been described
hereinabove by way of preferred embodiments thereof, it can be modified, ,
without departing from the spirit and nature of the subject invention as
defined in the appended claims.