Some of the information on this Web page has been provided by external sources. The Government of Canada is not responsible for the accuracy, reliability or currency of the information supplied by external sources. Users wishing to rely upon this information should consult directly with the source of the information. Content provided by external sources is not subject to official languages, privacy and accessibility requirements.
Any discrepancies in the text and image of the Claims and Abstract are due to differing posting times. Text of the Claims and Abstract are posted:
| (12) Patent: | (11) CA 2187208 |
|---|---|
| (54) English Title: | MULTI-PHASE ELECTRIC MACHINE WITH JOINED CONDUCTOR LANES |
| (54) French Title: | MACHINE ELECTRIQUE POLYPHASEE A CONDUCTEURS DE PHASE REUNIS |
| Status: | Deemed expired |
| (51) International Patent Classification (IPC): |
|
|---|---|
| (72) Inventors : |
|
| (73) Owners : |
|
| (71) Applicants : |
|
| (74) Agent: | RIDOUT & MAYBEE LLP |
| (74) Associate agent: | |
| (45) Issued: | 2004-06-29 |
| (86) PCT Filing Date: | 1995-04-05 |
| (87) Open to Public Inspection: | 1995-10-19 |
| Examination requested: | 2002-04-04 |
| Availability of licence: | N/A |
| (25) Language of filing: | English |
| Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT): | Yes |
|---|---|
| (86) PCT Filing Number: | PCT/DE1995/000459 |
| (87) International Publication Number: | WO1995/028026 |
| (85) National Entry: | 1996-10-04 |
| (30) Application Priority Data: | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
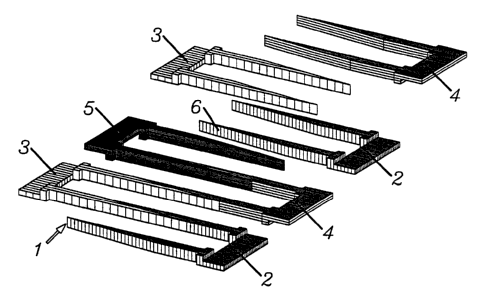
In prior art multi-phase electric machines in which
conductor parts are interlace to form conductor lanes for various
phases, the connection points are on the winding end, thus
permitting only a very limited local possibility for welding of
the conductor ends. In addition, the manufacturing cost is
increased with an odd number of phases, since the design is
asymmetrical and a number of different formers necessary is
relatively high. The invention calls for prefabricated conductor
parts (17) to be welded or soldered in the zones which will
subsequently be located in the soft magnetic body. Divided bars
with a high conductor cross-sectional area are connected before
the insertion of soft magnetic segments, connection zones which
are large relative to the conductor cross-sectional area are
realized, and problems with the insulation are avoided. In
three-phase machines, the conductor lanes are interlaced with
each other, all conductor lanes being identical in design and the
same pattern is repeated every four pole pitches. This
connection technique and conductor progression permits the
inexpensive manufacture of reliable electric motors and
generators as well as uniform space utilization in three-phase
equipment.
Dans les machines électriques polyphasées connues, à conducteurs de phase formés par des éléments conducteurs réunis, les points de jonction se situent dans la tête de bobine et ne permettent qu'un soudage par refusion extrêmement limité localement des extrémités des conducteurs. De plus, en cas de nombre impair de phases, la production devient plus complexe, en raison d'asymétries qui interviennent alors et de la diversité relativement importante des formes de construction des conducteurs. Selon l'invention, des éléments conducteurs (17) préfabriqués sont soudés ou brasés dans les zones conductrices qui sont ensuite placées dans des corps de basse coercitivité. Des tiges plastiques de section transversale conductrice importante sont connectées avant l'insertion de segments de basse coercivité, ce qui permet de réaliser des zones de jonction relativement importantes comparativement à la section transversale conductrice, et d'éviter l'émergence de problèmes d'isolation. Dans les machines triphasées, les conducteurs de phase sont entrelacés au moment où ils sont réunis. Tous les conducteurs de phase sont de structure identique et leur configuration se répète tous les quatre pas polaires. La technique de raccordement et la configuration des conducteurs permettent de produire de manière économique et fiable des moteurs électriques et des générateurs, et de parvenir à une utilisation homogène de l'espace disponible dans les machines triphasées.
Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
For a clearer understanding of the status of the application/patent presented on this page, the site Disclaimer , as well as the definitions for Patent , Administrative Status , Maintenance Fee and Payment History should be consulted.
| Title | Date |
|---|---|
| Forecasted Issue Date | 2004-06-29 |
| (86) PCT Filing Date | 1995-04-05 |
| (87) PCT Publication Date | 1995-10-19 |
| (85) National Entry | 1996-10-04 |
| Examination Requested | 2002-04-04 |
| (45) Issued | 2004-06-29 |
| Deemed Expired | 2013-04-05 |
There is no abandonment history.
| Fee Type | Anniversary Year | Due Date | Amount Paid | Paid Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application Fee | $0.00 | 1996-10-04 | ||
| Maintenance Fee - Application - New Act | 2 | 1997-04-07 | $50.00 | 1997-04-01 |
| Maintenance Fee - Application - New Act | 3 | 1998-04-06 | $50.00 | 1998-03-26 |
| Maintenance Fee - Application - New Act | 4 | 1999-04-05 | $50.00 | 1999-02-02 |
| Maintenance Fee - Application - New Act | 5 | 2000-04-05 | $75.00 | 2000-04-04 |
| Maintenance Fee - Application - New Act | 6 | 2001-04-05 | $75.00 | 2001-03-15 |
| Request for Examination | $200.00 | 2002-04-04 | ||
| Maintenance Fee - Application - New Act | 7 | 2002-04-05 | $75.00 | 2002-04-05 |
| Maintenance Fee - Application - New Act | 8 | 2003-04-07 | $75.00 | 2003-04-04 |
| Final Fee | $150.00 | 2004-03-17 | ||
| Maintenance Fee - Application - New Act | 9 | 2004-04-05 | $100.00 | 2004-04-02 |
| Maintenance Fee - Patent - New Act | 10 | 2005-04-05 | $125.00 | 2005-03-31 |
| Maintenance Fee - Patent - New Act | 11 | 2006-04-05 | $125.00 | 2006-03-13 |
| Maintenance Fee - Patent - New Act | 12 | 2007-04-05 | $125.00 | 2007-04-02 |
| Maintenance Fee - Patent - New Act | 13 | 2008-04-07 | $125.00 | 2008-03-31 |
| Maintenance Fee - Patent - New Act | 14 | 2009-04-06 | $125.00 | 2009-03-30 |
| Maintenance Fee - Patent - New Act | 15 | 2010-04-06 | $225.00 | 2010-03-30 |
| Maintenance Fee - Patent - New Act | 16 | 2011-04-05 | $225.00 | 2011-04-01 |
Note: Records showing the ownership history in alphabetical order.
| Current Owners on Record |
|---|
| HILL, WOLFGANG |
| Past Owners on Record |
|---|
| None |