Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02197959 2004-04-23 '
50989-45
- 1 -
PEELABLE AND HEAT SEALABLE LIDSTOCK
MATERIAL FOR PLASTIC CONTAINERS
The present invention relates to an improved
lidstock useful for making lids on plastic containers.
Peelable and heat sealable lids for plastic
containers are known in the prior art. However, there
is still a need to provide plastic container lids
having the following combination of properties:
a) approximately constant peel strength over a wide
range of heat seal temperatures; b) cohesive failure in
the heat seal layer upon peeling; and c) high burst
strength in the sealed lid.
A principal objective of the present
invention is to provide lidstock for making container
lids having the above-mentioned combination of constant
peel strength, cohesive failure in the heat seal layer
and high burst strength.
A related objective of the invention is to
provide lidstock material comprising a substrate
laminated with a film comprising a mixture of a butene-
1 and ethylene copolymer, an ethylene homopolymer or
copolymer, an inorganic filler, and optionally, a
propylene homopolymer or copolymer.
Additional objectives and advantages of my
invention will become apparent to persons skilled in
the art from the following detailed description.
In accordance with the present invention
there is provided a peelable and heat sealable lidstock
material for plastic containers. The container of the
CA 02197959 2004-04-23
50989-45
-2-
invention is suitable for holding foods such as prepared
cake frosting, pudding, yogurt, cream cheese and apple
sauce: medical devices such as disposable contact lenses:
and pharmaceuticals.
According to one aspect of the present invention,
there is provided a peelable and heat sealable lidstock
material comprising a metal or polymer substrate laminated
with a film comprising: a) about 30-70 wt.o of a butene-1
and ethylene copolymer wherein ethylene comprises about 1-15
mole percent of the copolymer; b) about 10-40 wt.o of an
ethylene homopolymer, an ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer or
an ethylene-methyl acrylate copolymer; and c) at least about
18 wt.o of a particulate inorganic filler.
According to another aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a container comprising: a) a
plastic body having an upper edge defining an opening and a
peripheral flange extending radially outward of said
opening, and b) a lid comprising a metal or polymer
substrate heat sealed to said upper edge by a film
comprising: 1) about 30-70 wt.o of a butene-1 and ethylene
copolymer wherein ethylene comprises about 1-15 mole percent
of the copolymer, 2) about 10-40 wt.% of an ethylene
homopolymer, an ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer or an
ethylene-methyl acrylate copolymer, and 3) at least
about 18 wt.o of a particulate inorganic filler.
According to another aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a lid for a plastic container
comprising a disc of the lidstock material described herein.
CA 02197959 2004-04-23
50989-45
2a
As used herein, the term "lidstock material"
refers to a metal or polymer substrate laminated with a
heat seal layer or film. Lidstock material of the
invention is made into food container lids by cutting
the material into a desired shape such as a circular
disc.
As used herein, the term "peelable" refers to
the capacity of a sealed lid to separate and to release
from sealed engagement with its underlying container
while. each substantially retains its integrity. Such
separation and release are generally achieved by a
separating force applied manually to outer edge
portions of the sealed container.
As used herein the term "heat sealable"
refers to the ability to form a bond between a plastic
food container and its lid when heat and pressure are
applied locally for a sufficient time. The bond. is
gas-tight and preferably has sufficient burst strength
to resist separation from the container.
The lidstock material of the present
invention comprises a metal or polymer substrate
laminated with a film comprising a polymer mixture. A
polymer substrate may be made from biaxially oriented
polyethylene terephthate (PET). The substrate is
preferably an aluminum foil having a thickness of about
0.25 mil to 3.0 mils (.00025 inch to .003 inch).
Aluminum foil is preferred because it provides an
excellent barrier against penetration of gases and
moisture. In addition, the foil provides protection
from ultraviolet light and gives the material an
aesthetically pleasing appearance. A particularly
preferred aluminum foil substrate has a thickness of
about 2.0 mils (.002 inch).
2197959
- 3 -
The aluminum foil substrate is preferably
provided with a print primer over the substrate. The
print primer facilitates application of printed
labeling on the substrate. A particularly preferred
print primer has a weight of about 0.7 pound per 3000
square feet.
The heat seal film has a total weight of
about 15 to 30 pounds per 3000 square feet. A
particularly preferred coating has a weight of about 17
pounds per 3000 square feet of the lidstock material.
The container body preferably comprises a
propylene homopolymer. Other suitable plastic for the
container body include polyethylene; polyethylene-
polypropylene mixtures and polyethylene-polypropylene
copolymers.
The film on the lidstock material comprises a
mixture of a butene-1 and ethylene copolymer, an
ethylene homopolymer or copolymer, an inorganic filler,
and optionally, a propylene homopolymer or copolymer.
Some suitable inorganic fillers include talc,
amorphous silica and alumina trihydrate. The filler
enhances peelability of the coating by shifting seal
failure upon peeling from adhesive fai:Lure at the
container-coating layer interface to cohesive failure
in the coating layer itself. The filler comprises at
least about 18 wt.~ of the coating, preferably about
20-40 wt.~, more preferably about 20-30 wt.o and
optimally about 25 wt.~. The filler i:3 preferably a
powder having an average particle size of about 0.5-10
microns. Talc having an average particle size of about
1-2 microns is particularly preferred. The talc should
be provided with a surface coating comprising about
0.5-5 wt.~ of the filler, preferably about 1 wt.$. A
carboxylic acid surface coating is particularly
preferred.
The carboxylic acid in the surface coating
may be a mono or dicarboxylic acid or a mixture of such
2191959
- 4 -
acids. Some preferred acids include stearic acid and
isostearic acid, which is a liquid mixture of mostly
C18 saturated fatty acids having the general formula
C1~H35 COOH. Other saturated C10-C20 carboxylic acids
or mixtures thereof may also be useful.
The mixture preferably comprises about 30-70
wt.~ of a butene-1 and ethylene copolymer wherein
ethylene comprises about 1-15 mole percent of the
copolymer. More preferably, the copolymer comprises
about 30-60 wt.~ of the mixture and optimally about 40
wt.~. The ethylene content in the copolymer is
preferably about 1-5 mole percent and most preferably
about 1-2 mole percent.
The mixture preferably comprises about 10-40
wt.~ of an ethylene homopolymer or copolymer, more
preferably about 15-40 wt.~ and most preferably about
35 wt.~. The ethylene homopolymer or copolymer may be
low density polyethylene (LDPE), medium density
polyethylene (MDPE), ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer
(EVA), ethylene-methyl acrylate copolymer (EMA), or
high density polyethylene (HDPE). Low density
polyethylene (LDPE) is particularly preferred.
The mixture optionally may contain about 1-6
wt.% of a propylene homopolymer or copolymer, more
preferably about 1-3 wt.~s, and most preferably about
1-2 wt.~. A propylene homopolymer is particularly
preferred. Propylene-ethylene copolymers are also
suitable.
Brief Description of the Drawings
Figure 1 is a perspective view of a food
container made in accordance with the present
invention.
Figure 2 is an enlarged, fragmentary, cross-
sectional view taken along the lines 2-2 of Figure 1.
Figure 3 is a graph showing peel strength as
a function of heat seal temperature.
Figure 4 is a graph showing opening force as
2197959
- 5 -
a function of heat seal temperature.
Figure 5 is a graph showing burst pressure as
a function of heat seal temperature.
Figure 6 is a graph showing opening force as
a function of heat seal temperature.
There is shown in Figure 1 a perspective view
of a plastic food container 11 made in accordance with
the present invention. The container 11 has a body 15
defining a cavity 16 which holds a food product such as
a prepared cake frosting, pudding, yogurt, cream cheese
or apple sauce. The container is hermetically sealed
to prevent contamination by outside agents.
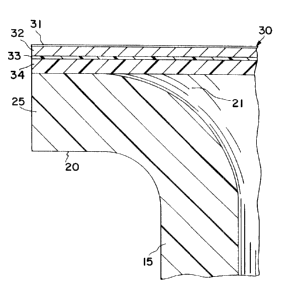
Referring now to Figure 2, it can be seen
that the container body 15 has an upper edge 20
defining an opening 21. A peripheral flange 25 extends
radially outward from the opening 21. A lid 30
comprises a generally circular disc that is peelably
heat sealed to the flange 25.
The lid 30 is made from a lidstock material
comprising a print primer 31 over an aluminum foil
substrate 32 having a urethane adhesive layer 33 and a
film 34 over the adhesive layer 33. The foil 32 has a
thickness of about 2.0 mils (.002 inch). The print
primer 31 has a weight of about 0.7 pounds per 3000
square feet. The urethane adhesive 33 has a weight of
about 2.4 pounds per 3000 square feet. The film 34 has
a thickness of about 1 mil, corresponding to a weight
of about 17 pounds per 3000 square feet.
The particularly preferred container 11 shown
in Figures 1 and 2 has a polypropylene body 15 and a
lid 30 laminated with a film 34 having the particularly
preferred composition A shown in the Table. Some other
preferred compositions (B and C) are also shown in the
Table.
2197959
- 6 -
FILM COMPOSITION
Ingredient Amount
(wt.~)
.A B C
Butene-1 and Ethylene Copolymer 40 40 60
Low Density Polyethylene 35 0 0
High Density Polyethylene 0 35 15
Talc 2~5 25 25
TOTAL 1 ~0 10 0 10 0
0
A series of tests were performed on the
lidstock material of the present invention. For
comparison, a prior art lidstock material having a heat
seal layer comprising 90 wt.% ethylene-vinyl acetate
copolymer and 10 wt.~ talc was also tested. Results of
the tests are shown in Figures 3-6.
Strips of lidstock material having a one inch
width were heat sealed to polypropylene homopolymer
strips at 40 psi applied pressure. Peel strength was
measured on a 90 degree L wheel as a function of heat
seal temperature. Results are shown in Figure 3. The
three lidstock material samples of the present
invention (A, B, and C) showed constanit peel strength
over a wide range of heat seal temperatures whereas the
prior art sample had a considerable variation in peel
strength over the same temperature range.
Samples of lids were heat sealed to 4 ounce
polypropylene cups at 40 psi applied pressure with a
0.6 second dwell time. Peel strength <~t 45° applied
force was measured as a function of heat seal
temperature. The results are plotted :Ln Figure 4.
Both samples (A and B) made in accordance with the
present invention demonstrated a smaller variation in
peel strength as a function of heat seal temperature
2197959
than the prior art sample. In addition, sample A had a
lower peel strength over the 325-550°F. heat seal range
than the prior art sample.
Samples of lids heat sealed to 4 ounce
polypropylene cups at 40 psi applied pressure for 0.6
seconds were also tested for burst pressure. Results
are shown in Figure 5. Sample B made in accordance
with the present invention performed better than the
prior art sample. Sample A was similar to the prior
art sample in burst strength, even though sample A had
lower peel strength than the prior art sample.
Samples of 4 ounce polypropylene cups were
also sealed at 40 psi for 0.5 seconds with a contoured
sealing head. Opening force for these samples as a
function of heat seal temperature is plotted in Figure
6. The prior art samples showed a much greater
variation in opening force than sample A of the present
invention.
The foregoing detailed description of my
invention has been made with reference to some
preferred embodiments. Persons skilled in the art will
understand that various modifications can be made in
the claimed lidstock material and food container
without departing from the spirit and acope of the
following claims.
~!?t~~it i~c 1. ~ T'
I~~ta~r~ a, ~~~~:~ T~:~
Pata~~ ~,.~... . .