Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
~. ~ 2200769
IMPROVED RAIL BOGIE AND RELATED EQUIPMENTS
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Field of the invention
The present invention is concerned with an improved rail bogie
adapted to be hooked with semi-trailers or similar road vehicles to form a trainfor riding on rails.
It is also concerned with close by related pieces of equipments,
including locomotive units for driving the so-formed train, and a cabin unit.
Brief description of the prior art
Rail bo0ies of the above mentioned type are already known in the
art. Such bogies usually comprise two axles, a rigid chassis and a pair of
oppositely oriented fifth-wheels that are mounted on top of the chassis and
adapted to be hooked to king pins provided at the front and/or rear of semi-
trailers or to form a train for riding on rails.
By way of examples, reference can be made to the following U.S.
20 patents:
4,416,571
4,547,107
4,669,391
4,685,399
4,773,335
4,766,818
4,938,151
5,107,772
Amongst the above patents, U.S. patent Nos 4,416,571 and
30 4,685,399 disclose twin axle rail bogies in which the fifth-wheels are mounted
directly onto the chassis and not adjustable in height. U.S. patent No.
4,547,107 disclose a twin axle rail bogie in which each of the fifth-wheels can
individually be lifted up by means of a power jack. U.S. patent No. 5,107,772
2200769
in the name of the present inventor discloses a twin axle rail bogie in which the
two fifth-wheels are mounted onto a "floating" platform that is mounted on
top of the chassis. Lifting means preferably of the pneumatic type, are
provided to vertically move the platform and fifth-wheels in unison with
5 respect to the chassis between low and high positions. Guiding means and
locking means are also provided to guide the platform while it moves up, and
to lock it to the chassis when it has reached its high position.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
1 0
An object of the present invention is to provide a twin axle rail
bogie which is of the same type as above, but whose structure is simpler than
and yet as efficient as those of the known rail bogies.
Another object of the invention is to provide a rail bogie of the
15 above type, which incorporates one or two electric motors for driving one or
both of its axles. Such motors can be supplied with electric energy by means
of a retractable arm sized to reach the trolley wire usually provided above the
electric railways. Alternatively, the motors can be supplied through a power
generator mounted into a semi-trailer hooked to the rail bogie. Such a
20 "combination" forms a locomotive unit that can be used to drive a train formed
of semi-trailers and rail bogies according to the invention.
A further object of the invention is to provide related pieces of
equipment for use to form a train. Such equipments include the locomotive
units mentioned hereinabove. They also include a cabin unit hookable to a rail
25 bogie according to the invention in order to accommodate the driver(s) of the train.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
The objects of the invention will be better understood upon
reading the following non-restrictive description of several preferred
embodiments thereof made with reference to the accompanying drawings, in
which:
220076q
Figs. 1 and 2 are side elevational views of a rail bogie according
to a first embodiment of the invention, having its opposite fifth-wheels in low
and high positions, respectively;
Fig. 3 is a top plan view of the rail bogie shown in Figs. 1 and 2;
Fig. 4 is a view similar to Fig. 2, showing the mechanism used
to lift up and hold the fifths-wheels in high position;
Fig. 5 is a view similar to Fig. 4, showing the fifth-wheels in low
position;
Fig. 6 is a top plan view of the fifth-wheels and mechanism used
to lift them up;
Fig. 7 is a top plan view of the supporting structure provided on
top of the frame of the rail bogie for the fifth-wheels lifting mechanism;
Fig. 8 is a side elevational view of the supporting structure shown
in Fig. 7;
Figs. 9 and 10 are side elevational views of the fifth-wheels and
mechanism used to lift them up, when the fifth-wheels are in low and high
positions, respectively;
Fig. 11 is a side elevational view of a rail bogie according to a
second embodiment of the invention, this rail bogie incorporating an electric
motor for driving one of its axles, and a retractable arm sized to reach a trolley
wire in order to supply electric energy to the motor;
Figs. 1 Z and 13 are side elevational views of a locomotive unit
comprising a pair of motorized bogies on which is mounted a semi-trailer
incorporating a power generator to supply electric energy to the bogies;
Figs. 14 and 15 are top and side elevational views of a cabin unit
for connection to a rail bogie according to the invention; and
Figs. 16 and 17 are top and side elevational views of another
locomotive unit comprising a semi-trailer that incorporates a power generator
and is permanently connected to a rriotorized bogie.
- 2200769
- 4
DESCRIPTION OF PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS OF THE INVENTION
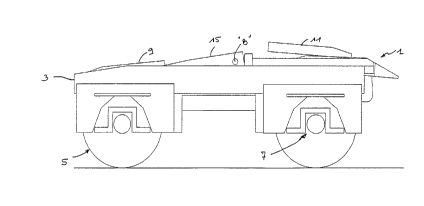
. The basic structure of the rail bogie 1 according to the invention
is shown in Figs. 1 to 10. Such a bogie is of the twin-axle type and comprises
5 a chassis 3 mounted on a pair of wheel assemblies 5, 7 via a suspension
system known per se (an example of such a suspension system is disclosed
in international laid-open patent application WO 96/12636 in the name of the
present inventor) . A braking system known perse may also be provided. A pair
of oppositely oriented fifth-wheels 9, 11 are mounted on top of the chassis 3.
10 Each fifth-wheel is positioned in such a manner as to be insertable under thebottom front and/or rear portion of a semi-trailer or any similar road vehicle,
and then be connected to the same by means of a king pin downwardly
projecting from said bottom front and/or bot~om rear portions. Once again, this
kind of assembly that permits to form a train for riding on rails, is known per
15 se and needs not be further described.
The fifth-wheels 9, 11 are mounted onto the chassis 3 in such
a manner as to be movable up and down in unison by means of a single power
jack 13 of a conventional structure, which extend longitudinally and centrally
onto the chassis 3. This power jack 13 is preferably pneumatic but it could be
20 hydraulic or electric.
More specifically, as is better shown in Figs. 4, 5, 9 and 10, the
left hand side fifth-wheel 9 is pivotably mounted at one end of a lifting frame
15 comprising two parallel arms pivotably connected to a supporting structure
17 by a pair of brackets 19 (see Figs. 7 and 8). The supporting structure 17
25 is rigidly fixed in the upper portion of the chassis 3 and both the fifth-wheel 9
and the lifting frame 15 are pivotable about horizontal axes A and B that are
transverse to the longitudinal axis of the bogie.
The lifting frame 15 is connected to the free end of the piston 21
of the power jack 13 by means of links 23. These links 23 have "upper" ends
30 connected to the bottoms of the arms of the lifting frame 15 close to the endof the same so as to be pivotable about an horizontal transverse axis C. The
links 23 also have "lower" ends pivotably connected about an horizontal
transverse axis D to a transverse member 25 slidably mounted onto a pair of
2200769
supporting rails 29 forming part of the supporting structure 17. The transverse
member 25 is itself pivotably connected about an horizontal transverse axis E
to the free end of the piston 21 of the power jack.
As is better shown when comparing in Figs. 9 and 10, actuation
of the power jack 13 causes the piston 21 to expand in the left hand side
direction and the links 23 to pivot in such a manner as to lift up the frame 15,thereby causing lifting of the fifth-wheel 9. As is also shown in the drawings,
a pair of wedye-shaped support members 27 are mounted under the arms of
the lifting frame 15 in order to prevent this frame from moving down up too
close to the rails 29 and thus from damaging the links 23 and their pivots.
At the opposite end of the bogie 1, the right hand side fifth-wheel
11 is pivotably mounted about an horizontal transverse axis F on top of a
tilting body 31. The tilting body 31 comprises two upper arms 33 on which the
fifth-wheel is mounted, and two lower arms 35. These arms 33, 35 extend in
planes parallel to the lon0itudinal axis of the bogie 1 and they are pivotably
connected at one end both to each other in pair, and to the supporting
structure 17 about a common transverse axis G by means of brackets 37 (see
Figs,. 3 and i). The other ends of the upper and lower arms 33, 35 of the
body 31 are connected to each other by means of shock-absorbing springs 41.
As can be seen, the other end of each lower arm 35 comprises an upwardly
extending projection 42 integral thereto.
The tilting body 31 is connected to the rear end of the cylinder
43 of the power jack 13 by means of other links 45. These linlcs 45 have
"upper" ends connected to the upwardly extending projections 41 of the
lower arms 35 of the tilting body 31, so as to be pivotable about an horizontal
transverse axis H. The links 45 also have "lower" ends pivotably connected
about an horizontal transverse axis I to another transverse member 47 slidably
mounted onto another p air of support rails 49 forming part of the supporting
structure 17 (see Fig. 8) .
As is better shown when comparing Figs.9 and 10, actuation of
the power jack 13 causes the cylinder 43 of the power jack 13 to move to the
right hand side direction and the links 45 to pivot in such a manner as to tilt
2200769
up the tilting body about the axis G, thereby causing lifting of the fifth-
wheel 1 1 .
Thus, as it can now be better understood, both fifth-wheels 9
and 11 are lifted up by actuation of the power jack 13 that is exclusively
connected to the sliding transverse members 25 and 47.
The fact that only one power jack 13 is used to lift up both fifth-
wheels does not mean that these fifth-wheels necessarily move up
simultaneously. Indeed, if only one of the fifth-wheels is loaded, actuation of
the power jack will result in a liftin0 of the other fifth-wheel first, followed,
when the first lifting is completed, with a lifting of the loaded fifth-wheel.
Fig. 11 of the drawings shows a rail bogie 101 according to a
second embodiment of the invention. This rail bogie 101 is identical to the railbogie 1 that has just been described, in terms of wheel axles, suspension,
opposite fifth-wheels and mechanism to lift them up. As a matter of fact, the
bogie 101 distinguishes from the bogie 1 only in that:
- it incorporates an electric motor 103 transversally mounted
within its chassis for driving one of its axles via a transmission gear box 105;and
- it also incorporates a telescopically retractable arm 107
which is sized to reach in expanded position, a trolley wire 109 like those
usually provided above the electric railways so as to supply electric power to
the motor 103.
In practice, the bogie 101 may comprise one motor 103 as
shown in Fig. 1 1, or two motors 103, 103' (one for each axle) as is shown in
the right hand side of Fig. 12. The retractable arm 107 is optional only. Indeed,
when there is no trolley wire, such arm 107 is of no use and thus not required.
In such a case, use can be made of a semi-trailer 111 that is hitchable onto a
pair of bogies 101 and comprises a power generator to supply the requested
electric energy to the motors 1 03, 1 03' (see Figs . 1 2 and 1 3) .
The resulting assembly forms a locomotive unit that can be used
to drive a train formed of a number of semi-trailers hitched to each other
through a corresponding number of bogies 1.
2200769
~ '
~, 7
The locomotive unit shown in Fig. 12 incorporates two bogies
101, one of which comprises two motors 103, 103'. Its power generator is
devised to provide a power of 1900 HP. The unit shown in ~ig. 13
incorporates two bo~ies 101 each comprising only one motor 103. Its power
5 generator is thus devised to produce a power of 1200 HP only.
In both cases, the trailer 111 of each unit comprises a radiator
113, a diesel reservoir 115, an electric control panel 117, an electric generator
119, a diesel motor 121 to operate the generator 119, an air reservoir 123 and
a compressor 125 to operate the piston 13 of the bogies 1, 101 and the
10 braking means of such bogies, a hydraulic pump 127 and, when required, a
dead wei~qht 129. All these components are standard and the way they
cooperate is well known to those skilled in the art. ~s a matter of fact, they
are present in all the existing diesel-powered electric locomotives.
To complete the train, a cabin unit 131 can also be provided, as
is shown in Figs.14 and 15. Such a cabin unit has a rear portion 133 hitchable
to a bogie 1 (not shown) and comprises two sets of wheels on its front
portion, including one rigidly mounted set of wheels 135 for use on rails and
another upwardly retractable set of wheels 137 for use on road to facilitate
displacement and installation of the cabin 131. As any conventional cabin unit,
20 the cabin unit 131 may comprise the following components in a plurality of
separate chambers closed with doors: a power generator 139, a set of
batteries 141, a battery charger 143, an electric panel 145, an air exchanger
147, a microwave oven 149, a refrigerator 151 and a toilet bowl 153.
Instead of using a locomotive unit consisting of a semi-trailer 111
25 hitchable onto bogies 101, use can be made of a locomotive unit consisting ofsemi-trailer 161 incorporating a powered bogie as part of its structure, as is
shown in Figs. 16 and 17. More particularly, the semi-trailer 161 comprises
two set of wheels 171, 173 for use on rails and a retractable set of wheels
175 for use on road. The wheels 171 and 173 are driven by a power
30 generating equipment contained in the trailer, which, like the one previous
disclosed comprises a radiator 177, an electric panel 179, an electric generator
2200769
.
181, a diesel motor 183, a hydraulic pump 185, an air reservoir 189 and a
compressor 191. A fifth-wheel 193 is provided at the rear of the unit 161 for
connection to another semi-trailer.