Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02202314 1997-04-10
HOECHST AKTIENGESELLSCHAFT HOE 96/F 093 Dr. KM/St
Description
5 Device for determining surface moisture level
The invention relates to a device which is suitable for determining the surface
moisture level, in particular of sorptive, liquid-absorbing or liquid-relaying two-
10 dimensional structures such as, for example, filter paper, baby diapers, sanitarynapkins, incontinence diapers, patient undersheets, nonwovens, textiles. Moreover,
in the case of materials having a homogeneous moisture distribution the
determination of the surface moisture level can be used to state the moisture level in
the interior of the material.
EP-A-0 312 919 discloses a method for measuring the surface moisture level,
whose principle is the total reflection of a continuous light beam at the base face of
a Dove prism. The scattering of the light, which occurs in addition to the totalreflection, at the base face changes its intensity when the base face is brought into
20 contact with a damp surface.
It has surprisingly be,en found that the disturbing influences of extraneous light
which occur during measurements in accordance with the prior art methods can be
minimized by using monochromatic light and/or by pulsing the light source and the
25 detector, or an amplifier, which may be connected downstream of the detector-electronically, mechanically or electro-optically at a prescribed frequency.
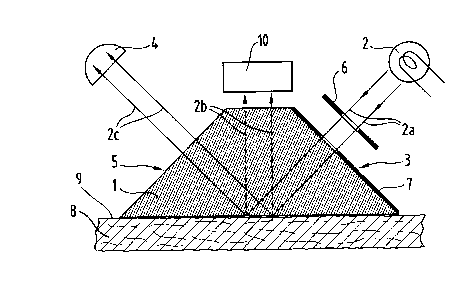
The subject-matter of the invention is a device for determining the surface moisture
level of sorptive or liquid-absorbing, two-dimensional structures and materials,30 essentially comprising a Dove inverting prism (1), a light source (2) which is
arranged such that its parallel-directed light beams (2a) impinge perpendicularly on
one of the short faces (3) of the prism (1 ) and are reflected by the hypotenuse face
of the prism (1), which is brought into contact with the surface (9) to be measured
with respect to moisture level, a light trap (4) which is arranged such that the beams
CA 02202314 1997-04-10
(2c) reflected by the hypotenuse face impinge on it, and a photoelectric transducer
(10) which is located in the right angle formed by the two short faces (3) and (5) and
arranged such that its measuring surface is situated opposite and parallel to the
hypotenuse face of the prism, and which converts the light (2b) scattered by thesurface (9) to be measured with respect to moisture level into a measuring signal,
wherein
a) the light used for the measurement has a known, fixed wavelength, and
wherein
a1 ) located upstream of the photoelectric transducer (10) is a filter which passes
only this wavelength, or wherein
a2) the photoelectric transducer (10) is sensitive only to this wavelength, or
wherein
b1) the light used for the measurement is pulsed, starting from its generation, at a
known, fixed frequency or is pulsed by a suitable device, which is located in
the light beam (2a) upstream of the entry into the prism (1), and wherein
b2) the photoelectric transducer (10) is operated with selective sensitivity to the
known fixed frequency, and wherein its output signal is amplified with
selective sensitivity to this frequency, or wherein
c) in a combination of both methods, light of a known, fixed wavelength and of a known, fixed frequency is used.
s
A preferred embodiment of this invention is represented in Figure 1. The light
source (2) is positioned above one short face (3) of a right-angled prism (1). The
25 parallel light beams (2a) originating from this light source traverse the prism and
strike the glass/air interface at the hypotenuse surface. To align the light beams in
parallel, it is possible to use stops (6) in the beam path, and the short face can be
covered with an opaque layer (7) at the points at which no light is to be incident. If
the hypotenuse face of this prism rests on a dry surface, because of the slight
30 contact between the glass and the surface of the object to be measured there is
total reflection of the incident light and the greater part (2c) leaves the prism through
the second short face (5) and is absorbed by the light trap (4). In accordance with
the slight contact between the surface (9) and the hypotenuse face, a small
CA 02202314 1997-04-10
proportion of scattered light (2b) is generated and reaches the photoelectric
transducer (10). The light trap has the form of a black cavity. In a practical
embodiment of this device, such a light trap can be provided by a housing of thedevice if said housing is roughened and blackened.
If, as represented in Figure 2, the hypotenuse face of the prism rests on a moist
surface, the light beam leaves the prism at the hypotenuse face and is scattered at
the irregular surface (9) of the test specimen (8). The greater part of the scattered
light (2b) passes again into the glass prism and strikes a photoelectric transducer
10 (10) which is located in the angle formed by the short faces exactly opposite the
hypotenuse face. The relevant useful signal generated in this photoelectric
transducer (10) is proportional to the moisture level of the surface of the testspecimen and is displayed using appropriate measuring units. The measuring
operations can advantageously be recorded as a function of time with the aid of a
15 chart recorder.
For acceptable measurement, the hypotenuse face of the prism must remain directly
in contact with the surface to be tested. This is already achieved by the dead weight
of the prism resting on the surface to be tested. By applying additional weights, this
20 contact with the surface to be measured can be intensified, in particular in the case
of soft, elastic objects such as diapers, for example. Conversely, it is also possible
to keep the applied weight as small as possible by inverting the prism such that the
hypotenuse face comes to lie upwards, and the object to be measured is then
placed on the hypotenuse surface.
The generation of pulsed light radiation can be performed in a mechanical way byinterrupting the light of a continuously operating light source by means of a
mechanical chopper periodically at a known frequency. Electronically, such light can
be generated by modulating the intensity of the light emitted by the light source at a
30 frequency prescribed from outside. It is likewise possible periodically to interrupt the
light beam of a continuous source by means of an electro-optic component, for
example, by means of a Pockels cell.
CA 02202314 1997-04-10
Owing to the use according to the invention of monochromatic light, pulsed lightsources, spectral filters and frequency-selective photoelectric transducers (10)and/or amplifiers, the device is insensitive to the incidence of extraneous light.
5 Lasers, for example helium neon lasers, or laser diodes are preferably used as light
sources. The wavelength can be in the visible or infrared spectral region.
The device according to the invention is particularly suitable for examining hygiene
articles such as, for example, baby diapers, incontinence diapers, sanitary napkins,
10 hospital bed undersheets, nonwovens and textile fabrics.
Surprisingly, it has been found that this measuring system can also be extended to
technical applications. Thus, for example, it is also possible to examine technical
two-dimensional absorbent materials in the case of which the surface moisture level
15 is caused not only by aqueous solutions but also by organic liquids such as, for
example, isopropanol, ethanol or oils, such as, for example, paraffin oil, silicone oil
and mineral oil.
Example 1
The surface moisture level of diapers was measured with and without incidence ofextraneous light. The light source used was a type LD 242 laser diode, which emits
light of wavelength 880 nm at a power of
8 mW/sr. The radiation of the light source was modulated with a frequency taken
25 from a trigger generator. A type BPW 43 diode was used as photoelectric
transducer. Its output signal was amplified by means of a frequency-selective
amplifier into which the frequency of the trigger generator was fed as reference.
Table 1 shows the measurement results which were obtained without the incidence
of extraneous light, as well as the results which where obtained with lateral
30 irradiation of the measuring device and of the diaper using a fluorescent lamp with a
power of 11 W.
CA 02202314 1997-04-10
Table 1
Surface moisture level (%)
Without extraneous light With extraneous light
68 69
24 24
Comparative Example
10 The same measuring arrangement as in Example 1 was selected, but the light
source and the detecting amplifier were not operated in the pulsed fashion. The
measurement values obtained from the same measuring objects are shown in Table
2.
Table 2
Surface moisture level (%)
Without extraneous light With extraneous light
38 50
25 ~ 35
13
The following Examples 2 and 3 describe other methods of generating light.
Example 2
A 12V/5W halogen lamp was used as light source. The emitted light was choppered
mechanically at 9600 Hz by a slotted disc. The measurement signals were receivedby a BPY 47P silicon photoelectric cell and subsequently processed for
30 measurement purposes ina PC.
CA 02202314 1997-04-10
Example 3
A helium-neon laser of wavelength 632.8 nm was used as light source. The emittedlight was choppered mechanically at 9600 Hz by a slotted disc. The measured
5 signals were received by a BPW 21 photodiode, which has a measuring range of
350 - 820 nm and a sensitivity peak 550 nm, and subsequently processed
metrologically in a PC.