Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02203878 1997-04-28
WO 96/14307 PCT/US95/14472
Certain Substituted Benzylamine Derivatives;
A New Class of Neuropeptide Y1 Specific Ligands
Field of the Invention
This invention relates to certain substituted benzylamine derivatives which
selectively bind
to human Neuropeptide Y1 (NPY1) receptors. This invention also relates to
pharmaceutical
compositions comprising such compounds. It further relates to the use of such
compounds and
compositions in treating feeding disorders and certain cardiovascular
diseases.
Descrintion of the Related Art
Neuropeptide Y, a peptide first isolated in 1982, is widely distributed in the
central and
peripheral neurons and is responsible for a multitude of biological effects in
the brain and the
periphery. Various animal studies have shown that activation of Neutopeptide Y
1 receptors is
relaxed to vasoconstriction, Wahlestedt et aL. Regul. Peptides, ~: 307-318
(1986), McCauley and
Westfall. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. ~: 863-868 ( 1992), and Grundemar et al.,
Br. J. Pharcnacol.
jQ~: 45-50 (1992); and to stimulation of consummatory behavior, Flood and
Motley, Peptides,1Q:
963-966 (1989). Leibowitz and Alexander. Peptides, ~: 1251-1260 (1991), and
Stanley et al.,
Peptides,1,'~: 581-587 (1992).
Grundemar and Hakanson, TIPS. May 1994 [Vol. 15], 153-159, state that, in
animals,
Neuropeptide Y is a powerful stimuli of food intake, and an inducer of
vasoconstriction leading to
hypertension. They further point out that low levels of Neuropeptide Y is
associated with loss of
appetite. These reports clearly indicate that compouds that inhibit the
activity of this pmcein will
reduce hyperoension and appetite in animals.
CA 02203878 1997-04-28
WO 96114307 PCT/US95/14472
SUMMARY OF THF INVFrr~rm~r
Compounds that interact with NPY 1 receptors and inhibit the activity of
Neuropeptide Y at
those receptors are uxful in treating caring disorders such as, for example,
obesity and bulimia,
and certain cardiovascular diseases, such as, for example, hypertension.
This invention provides novel compounds of Formula I which selectively bind to
Neuropeptide Y1 (NPY1) receptors. Such compounds arc useful in treating
feeding disorders
such as obesity and bulimia as well as certain cardiovascular diseaxs such as
esxntial
hypertension.
The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising compounds
of
Formula I. The invention thus further relates to the use of such compounds and
compositons in
the treatment of eating as well as certain cardiovascular diseases.
Accordingly, a broad
embodirrxnt of the invention is directed to a compound of Formula I:
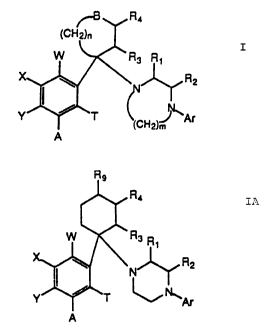
R~
f~H2)~
W , R3 Rt
R2
T
(cH2)J Ar
A
I
where
Ar is an aryl group
B is sulfur, oxygen, a substituted nitrogen atom, or a mono- or disubstituted
carbon atom;
n is 1. 2, or 3;
m is 2, 3, or 4;
CA 02203878 1997-04-28
WO 96/14307 PCT/TJS95~14472
W. X, Y, and T are the same or different and represent hydrogen, halogen,
hydroxy, straight or
branched chain lower allcyl having 1-6 carbon atoms, or straight or branched
chain lower
alkoxy having 1-6 carbon atoms;
R1 and R2 independently represent hydrogen, or straight or branched chain
lower alkyl having I-6
carbon atoms; and
R3 and R4 are the same or different and represent hydrogen, straight or
branched chain lower alkyl
having 1-6 carbon atoms, or straight or branched chain lower alkoxy having 1-6
carbon
atoms.
~ These compounds are highly selective partial agonists or antagonists at
human NPY1
receptors and are useful in the diagnosis and treatment of feeding disorders
such as obesity and
bulimia as well as certain cardiovascular diseases such as essential
hypertension and congestive
heart failure.
3
CA 02203878 1997-04-28
WO 96/14307 PCTIUS95/14472
BRIEF DFS _Rltrrtn~r nc 'tH nt! a wr~rr
Figure 1 shows reprexntative substituted benzylamines of the prexnt invention.
CA 02203878 1997-04-28
WO 96/14307 PCT/US95/14472
The novel compounds encompassed by the instant invention can be described by
general
formula I:
Ra
~CH2)n
w
_ ~ R2
Y ~ T
(~H2)J Ar
A
I
where
Ar is an aryl group preferably selected from the group consisting of phenyl, 2-
, 3-, or 4-pyridyl, 2-
or 3-thienyl, 2-, 4- or 5-pyrimidyl, each of which is optionally mono- or
disubstitutod with
halogen, hydroxy, or straight or branched chain lower alkyl having 1-6 carbon
atoms;
B is sulfur, oxygen, N(RS) or C(R5)(R6);
n is 1, 2, or 3;
mis2,3.or4;
W, X, Y, and T are the same or different and represent hydrogen, halogen,
hydroxy, straight or
branched chain lower alkyl having 1-6 carbon atoms, or straight or branched
chain lower
alkoxy having 1-6 carbon atoms;
R 1 and R2 are the same or different and represent hydrogen, or straight or
branched chain lower
allryl having 1-6 carbon atoms;
R3 and R4 are the same or different and represent hydrogen, straight or
braachod chain lower
alkyl having 1-6 carbon atoms, or straight or branched chain lower alkoxy
having 1-6
carbon atoms;
CA 02203878 1997-04-28
WO 96114307 PGT/I1S95/14472.
RS reprexnts straight or branched chain lower alkyl having 1-6 carbon atoms,
phenyl. 2-, 3-, or
4-pyridyl, or phenyl, 2-, 3-, or 4-pyridyl straight or branched chain lower
alkyl having 1-6
carbon atoms: and
A and Rb are the same or different and repttxnt
hydrogen, hydroxyl, amino, straight or branched chain lower alkyl having 1-6
carbon
atoms, straight or branched chain lower alkoxy having 1-6 carbon atoms,
phenyl,
2-. 3-, or 4-pyridyl, phenoxy, 2- 3-, or 4- pyridyloxy, or
-(CH2)p-A'-(CH2)q-B' where
p is 0-5 , q is 1-5, and A' is a direct bond, oxygen or sulfur, and
~ B' is hydrogen, straight or branched chain lower alkyl having 1-6 carbon
atoms,
straight or branched chain lower alkoxy having 1-6 carbon atoms, phenyl,
2-. 3-, or 4-pytzdyl, phenoxy, 2-, 3-, or 4-pyridyloxy, carboxyl,
carboatkoxy, carboxamido, mono or dialkylcarboxamido, amino, or mono
or dialkylamino.
Preferred compounds according to Formula I are those where Ar is optionally
substituted
phenyl, pyrimidinyl or pyridyl, B is carbon optionally substituted with phenyl
or alkyl, and W, X,
Y, A, T, and R 1-R4 are hydrogen. Particularly, preferred compounds or Formula
I are thox
where Ar is phenyl, pyrimidinyl or pyridyl, B is carbon optionally substituted
with phenyl or
alkyl, and W, X. Y, A, T, and R1-R4 are hydrogen.
The invention also relates to compounds of formula IA:
~o
CA 02203878 1999-09-16
R4
R3 R~
R2
N
~Ar
A
where Ip
Ar is phenyl, 2-, 3-, or 4-pyridyl, 2- or 3-thienyl, 2-, 4-
or 5-pyrimidyl, each of which is optionally mono- or
disubstituted with halogen, hydroxyl, or straight or branched
chain lower alkyl having 1-6 carbon atoms;
A, W, X, Y and T are the same or different and represent
hydrogen, halogen, hydroxyl, straight or branched chain lower
alkyl having 1-6 carbon atoms, straight or branched chain lower
alkoxy having 1-6 carbon atoms, benzyloxy, methoxymethoxy or
ethoxymethoxy; or
A and Y together form methylenedioxy;
R1 and R2 are the same or different and represent hydrogen,
or straight or branched chain lower alkyl having 1-6 carbon
atoms;
R3 and R4 are the same or different and represent hydrogen,
straight or branched chain lower alkyl having 1-6 carbon atoms,
or straight or branched chain lower alkoxy having 1-6 carbon
atoms; and
R9 represents hydrogen, straight or branched chain lower
alkyl having 1-6 carbon atoms, methoxy or phenyl.
In one embodiment, the compounds of Formula IA are those in
which Ar is as defined above other than phenyl, 2-chlorophenyl,
2-methoxyphenyl, 2-ethoxyphenyl, 2,3-dimethylphenyl or 2-
hydroxyphenyl when A, W, X, Y and T are each hydrogen, R1 and R2
are each hydrogen, R3 and R4 are each hydrogen and Rg is
hydrogen.
The invention further encompasses compounds of Formula II:
7
CA 02203878 1997-04-28
WO 96/14307 PCT/I1S95/14472
A
~N~Ar
IN
X v
11
where A and X independently represent alkoxy and Ar represents phenyl,
pyrimidinyl, or pyridyl.
Preferred compounds of Formula II are those where X and A are methoxy, ethoxy,
isopropoxy, or butoxy, and Ar represents phenyl, pyrimidinyl, or pyridyl.
The invention further includes compounds of Formula BI:
III
Re
where X and A independently represent alkoxy and R~ and Rg are different and
represent
hydrogen or fluorine.
The invention further encompasses compounds of Formula IV:
~N~Ar
1
IV
where X represents hydroxy and Ar represents phenyl, pytimidinyl, or pyridyl.
CA 02203878 1997-04-28
WO 96/14307 PCT/US95/14472
The invention further encompasses compounds of Formula V:
~N~Ar
IJJ
V
where X represents alkoxy and Ar represents phenyl, pyrirtvdinyl, or pyridyl.
Prefemeci compounds of Formula V are those where X is methoxy, ethoxy,
isopropoxy, or
butoxy, and Ar represents phenyl. Particularly preferred compounds of Formula
V are those
where X is metltoxymethoxy or ethoxymethoxy.
The invention also includes compounds of Formula YI:
Ar
R9
yI
when X t~epresents alkoxy, R9 is alkyl, and Ar represents phenyl, pyrimidinyl,
or pyridyL
Preferred compounds of Formula VI are those where X is methoxy, ethoxy,
isopmpoxy,
or butoxy, Rg is allryl, anti Ar represents phenyl. Particularly prefertzd
compounds of Formula VI
are those where X is methoxy, ethoxy, isopropoxy, or butoxy, R9 is methyl, and
Ar represents
phenyl. Other particularly preferred compounds of Formula VI are those when X
is
nxthoxymethoxy or ethoxymethoxy, R9 is methyl, and Ar ttpresents phenyl.
CA 02203878 1997-04-28
WO 96/14307 PGT/US95/14472
The invention also encompasses compounds of Formula VII:
O ~N~Ar
O
VII
where Ar reprexnts optionally substituted phenyl, pyrimidinyl, or pyridyl.
Preferred compounds of Formula Ar represents phenyl, pyrimidinyl, or pyridyl.
Representative compounds of the prexnt invention, which are encompassed by
Formula I-
VII, include, but are not limited to the compounds in Figure I and their
phatmaoeutically acceptable
salts. Non-toxic pharmaceutically acceptable salts include salts of acids such
as hydrochloric,
phosphoric, hydrobmmic, sulfuric, sulfinic, formic, toluene sulfonic,
hydmiodic, acetic and the
like. Thox skilled in the art will recognize a wide variety of non-toxic
phartnaoeudcally acceptable
addition salts.
The invention also relaxes to compounds of formula VIII:
R9
N
Y T
Ar
A
where
/ r7
CA 02203878 1997-04-28
WO 96/14307 PCT/US95/14472
Ar is phenyl, 2-. 3-, or 4-pyridyl. 2- or 3-thienyl, 2-, 4- or 5-pyrimidyl,
each of which is
optionally mono- or disubstituted with halogen, hydroxy, or straight or
branched chain
lower alkyl having 1-6 carbon atoms;
A, X, Y, and T are the same or different and represent hydrogen, halogen,
hydmxy, straight or
branched chain lower alkyl having 1-6 carbon atoms, or straight or branched
chain lower
alkoxy having 1-6 carbon atoms; and
Rg represents hydrogen, straight or branched chain lower alkyl having 1-6
carbon atoms, or
phenyl.
' The present invention also encompasses the acylated prodrugs of the
compounds of
Formula I-VIII. Those skilled in the art will recognize various synthetic
methodologies which may
be employed to pam non-toxic pharmaceutically acceptable addition salts and
acylated prodrugs
of the compounds encompassed by Formula I.
The invention encompasses both diasteriomers of the compounds having 1,4-
substitution
on the cyclohexane ring. Le, the invention encompasses both cis-, and traps-
1,4-cyclohexanes.
Preferred compounds of the invention having 1,4-substitution on the
cyclohexane ring are those
where the nitrogen atom fom~ing the pipaazitx ring and the alkyl or phenyl
group in the 4-position
of the cyclohexane ring are "cis" with respect to each other. Thus, preferred
compounds of the
invention having such substitution are those that are cis-1-piperazinyl-4-
alkyl or phenyl-
cyclohexanes.
By "aryl" and "Ar" is meant an aromatic carbocyclic group having a single ring
(e.g.,
phenyl), multiple rings (e.g., biphenyl), or multiple condensed rings in which
at least one is
aromatic. (e.g., 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthyl, naphthyl, anthryl, or
phenanthryl), which can
optionally be unsubstituted or substituted with e.g.. halogen, lower alkyl,
lower alkoxy, lower
alkylthio, trifluoromethyl, lower acyloxy, aryl, hetemaryl, and hydroxy.
~/
CA 02203878 1997-04-28
WO 96114307 P~'-T/US95/14472
By "alkyl" and "lower alkyl" is meant straight and branched chain alkyl groups
having
from 1-6 carbon atoms.
By "lower alkoxy" and "alkoxy" is meant straight and branched chain alkoxy
groups
having fmm 1-6 carbon atoms.
By "halogen" is meant fluorine, chlorine, bromine and iodine.
By 2-, 3-, and 4-pryidyloxy is meant groups of the following formulas
respectively:
N
/ ~ /
The pharmaceutical utility of compounds of this invention is indicated by the
following
assay for human NPY 1 receptor activity.
The procedure used is similar to that described by Gordon et al. (J.
Neurochem. 55:506-
513. 1990). SK-N-MC cells wen purchased from ATCC (Rockville, MD). Cells were
maintained at 37oC and SR6 C02 in Dulbecco's modifiod essential media (DMEM)
with L-
glutamine and 110 mg/L sodium pyruvate, which was supplemented with 1096 fetal
bovine serum
and 25 mM HEPES (pH 7.3). The binding assay was performed in 24-well plates
(Falcon) when
the cells were confluent. Taking care to not disturb the cells on the bottom
of the wells, the media
was aspirated, and 0.5 ml of Dulbecco's phosphate buffered saline (DPBS) with
calcium and
magnesium were added to each well. The DPBS was aspirated and an additional
aliquot of DPBS
was added and aspiraoed. To begin the assay, binding buffer consisting of
serum-free DMEM
containing 0.596 bovine serum albumin, 0.196 bacitracin and 0.1 mM
phenylmethylsulfonylfluoride was added to each well. The cells and the binding
buffer
preincubated for 30 minutes at room temperature, at which point the drug
dilution and [125nPYY
(NEN-DuPont: 50000 -75000 cpm -- 50 pM) were added to yield a final volume of
250 u1.
Nonspecific binding was defined with 1 mM NPY (porcine or human, Bachem
California). After
?i
CA 02203878 1999-09-14
a 3 hour incubation at room temperature, the plates were then put on ice and
ttie wells were
aspirated. The cells were washed 4-6 dines with 0.5 rnl of ice-cold DPBS. A
dilute solution of
TritonX-100 ( 19b) was then added to each well. After approximately 1 hour at
room temperature,
an aliquot from each well was transferred to a 12x75 mm tesuube, and the
amount of~[l~Ij was
quanticated on a gamma counter with an efficiency of 80-8596 (Genesys 5000.
Laboratory
Technologies). IC50 values were calculated with the non-linear curve fitting
pmgram RSJl (88N
Software Products Corp., Cambridge, MA). The binding characteristics for
compounds of this
invention arc shown in Table 1.
TABLE I
('nmnound Numberl
9 0.137
I3 (cis isomer) 0.067
18 (cis isomer) 0.075
20 (cis isorra) 0.076
21 (traps isomer) 0.525
29 (cis isomer) 0.039
I Compound numbers relate to compounds shown in Fgttre I.
Compounds 13, 18. 20 and 29 are particularly preferred embodiments of the
prexnt
invention because of their potency in binding oo human NPY1 toctptors.
The compounds of general formula I may be administered orally. topically.
pareaterally.
by inhalation or spray or rcctally in dosage unit formulations containing
conventional non-toxic
pharmaceutically acctptable carriers, adjuvants and vehicles. The term
parenneral as used herein
includes subcutaneous injections, intravenous, intramttxtttar, incrasternal
injection or infusion
techniques. In addition, there is provided a pharmaceutical formulation
comprising a compound of
general formula I and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. One or more
compounds of general
Trade-mark
13
72222-321
CA 02203878 1997-04-28
WO 96/14307 PtrT7US95/14472
formula I may be prexnt in association with one or more non-toxic
pharmaceutically acceptable
carriers and/or diluents and/or adjuvants and if desired other active
ingredients. The
phannaoeutical compositions containing compounds of general formula I may be
in a form suitable
for oral use, for example, as tablets, troches, lozenges, aqueous or oily
suspensions, dispersible
powders or granules, emulsion, hard or soft capsules, or syrups or elixirs.
Compositions intended for oral ux may be prepared according to any method
known to the
art for the manufacture of pharmaceutical compositions and such compositions
may contain one or
more agents xlected from the group consisting of sweetening agents, flavoring
agents, coloring
agents and prexrving agents in order to provide pharmaceutically elegant and
palatable
preparations. Tablets contain the active ingredient in admixture with non-
toxic pharmaceutically
acceptable excipients which are suitable for the manufacture of tablets. These
excipients tray be
for example, inert diluents, such as calcium carbonate, sodium carbonate,
lactose, calcium
phosphate or sodium phosphate; granulating and disintegrating agents, for
acample, corn starch, or
alginic acid; binding agents, for example starch, gelatin or acacia, and
lubricating agents, for
example magnesium stearate, stearic acid or talc. The tablets may be uncoated
or they may be
coated by known techniques to delay disintegration and absorption in the
gastrointestinal tract and
hereby provide a sustained action over a longer period. For example, a time
delay manorial such as
glyceryi monosterate or glyc;ayl distearate may be employed.
Formulations for oral use may also be presented as hard gelatin capsules
wherein the active
ingredient is mixed with as inert solid diluent, for example, calcium
carbonate, calcium phosphate
or kaolin, or as soft gelatin capsules wherein the active ingredient is mixed
with water or an oil
meditun, for exatnpk peanut oil, liquid paraffin or olive oil.
Aqueous suspensions contain the active materials in admixture with excipients
suitable for
the manufacture of aqueous suspensions. Such excipients are suspending agents,
for example
sodium carboxymethylcellulox, methylcellulox, hydmpropylmethylcellulox,
soditun alginate.
polyvinylpyrrolidone, gum tragacanth and gum acacia; dispersing or wetting
agents may be a
CA 02203878 1997-04-28
WO 96/14307 PCTIUS95/14472
naturally-occurring phosphatide, for example, lecithin, or condensation
products of an alkylene
oxide with fatty acids, for example polyoxyethylene stearate, or condensation
products of ethylene
oxide with long chain aliphatic alcohols, for example
heptadecaethyleneoxycetanol, or
condensation products of ethylene oxide with partial esters derived from fatty
acids and a hexitol
such as polyoxyethylene sorbitol monooleace, or condensation products of
ethylene oxide with
partial esters derived from fatty acids and hexitol anhydrides, for example
polyethylene sorbitan
monooleate. The aqueous suspensions may also contain one or more
preservatives, for example
ethyl, or n-propyl p-hydroxybenzoate, one or more coloring agents, one or more
flavoring agents,
and one or more sweetening agents, such as sucrose or saccharin.
' Oily suspensions may be formulated by suspending the active ingredients in a
vegetable oil,
for example arachis oil, olive oil, sesame oil or coconut oil, or in a mineral
oil such as liquid
paraffin. The oily suspensions may contain a thickening agent, for example
beeswax, hard
pant or cetyl alcohol. Sweetening agents such as those set forth above, anti
flavoring agents
may be added to provide palatable oral preparations. These compositions may be
preserved by the
addition of an anti-oxidant such as ascorbic acid.
Dispersible powders and granules suitable for preparation of an aqueous
suspension by the
addition of water provide the active ingredient in admixture with a dispersing
or wetting agent,
suspending agent and one or more preservatives. Suitable dispersing or wetting
agents and
suspending agents are exemplified by those already mentioned above. Additional
excipients, for
example sweetening, flavoring and coloring agents, may also be present.
Pharmaceutical compositions of the invention may also be in the form of oil-in-
water
emulsions. The oily phase may be a vegetable oil, for example olive oil or
atachis oil, or a mineral
oil, for example liquid paraffin or mixtures of these. Suitable emulsifying
agents may be naturally-
occurring gums, for example gum acacia or gum tragacanth, naturally-occurring
phosphatides, for
example soy bean, lecithin, and esters or partial esters derived from fatty
acids and hexitol.
anhydrides, for example sorbitan monoleate, and condensation products of the
said partial esters
CA 02203878 1997-04-28
WO 96/14307 PCT/US95/14472
with ethylene oxide, for example polyoxyethylene sorbitan monoleate. The
emulsions may also
contain sweetening and flavoring agents.
Syrups and elixirs may be formulated with sweetening agents, for example
glycerol,
propylene glycol, sorbitol or sucrose. Such formulations may also contain a
demulcent, a
preservative and flavoring and coloring agents. The pharmaceutical
compositions may be in the
form of a sterile injectable aqueous or oleaginous suspension. This suspension
may be formulated
according to the known art using those suitable dispersing or wetting agents
and suspending agents
which have been mentioned above. The sterile injectable preparation may also
be sterile injectable
solution or suspension in a non-toxic parentally acceptable diluent or
solvent, for example as a
solution in 1.3-butanediol. Among the acceptable vehicles and solvents that
may be employed art
water, Ringer's solution and isotonic sodium chloride solution. In addition,
sterile, fixed oils are
conventionally employed as a solvent or suspending medium. For this purpose
any bland fixed oil
may be employed including synthetic mono-or diglycerides. In addition, fatty
acids such as oltic
acid find use in the prepaisoion of injectables.
The compounds of general formula I may also be administered in the form of
suppositories
for rectal administration of the drug. These compositions can be prepared by
mixing the drug with
a suitable non-irritating excipient which is solid at ordinary temperatures
but liquid at the rectal
temperature and will therefore melt in the rectum to release the drug. Such
materials are cocoa
butter and polyethylene glycols.
Compounds of general formula I may be administered parenteraUy in a sterile
medium.
The drug, depending on the vehicle and concentration used, can either be
suspended or dissolved
in the vehicle. Advaatageousiy, adjuvants such as local anaesthetics,
preservatives and buffering
agents can be dissolved in the vehicle.
Dosage levels of the ordtr of from about 0.1 mg to about 140 mg per kilogram
of body
weight per day are useful in the oreatrnent of the above-indicated conditions
(about 0.5 mg tn about
7 g per patient per day). 'The amount of active ingredient that may be
combined with the carrier
CA 02203878 1999-09-16
materials to produce a single dosage form will vary depending
upon the host treated and the particular mode of administration.
Dosage unit forms will generally contain between from about 1 mg
to about 500 mg of an active ingredient.
It will be understood, however, that the specific dose
level for any particular patient will depend upon a variety of
factors including the activity of the specific compound
employed, the age, body weight, general health, sex, diet, time
of administration, route of administration, and rate of
excretion, drug con~ination and the severity of the particular
disease undergoing therapy.
As well known in the art, the pharmaceutical compositions
may be put in commercial packages for practical use. Such
commercial packages often include written matters which describe
instructions that the pharmaceutical compositions should or can
be used for the purposes described in this specification.
An illustration of the prepared compounds of the present
invention is given in Scheme I. Those having skill in the art
will recognize that the starting materials may be varied and
additional steps employed to produce compounds encompassed by
the present invention.
17
CA 02203878 1997-04-28
WO 96/14307 pCT/US95/14472
Scheme I
R,
R
R' KCN '
i I R,
+ ~ (CHz~ Nx
(CHzk~ A
p (CHZnnJ NC N
A
(cH~, J
u~s_
g Re
i
(CHz~ Rt
(cHa.~' Rz . w N
A
N C ~ A (CIi~ J
(CHz~n J x ~ / T
E
where
A is ArN or ArCH where Ar is phenyl, 2. 3, or 4 pyridyl, 2 or 3 thienyl, 2, 4
or 5 pyrimidyl either
unsubstituted or mono or disubstituted with halogen, hydroxy, or straight or
branched
chain lower alkyl having 1-6 carbon atoms;
B is sulfur, oxygen NRS or CRSR6
n is l, 2, or 3;
mis2,3,or4;
W. X, Y, Z, T are the same or different and represent hydrogen, halogen,
hydroxy, straight or
branched chain lower alkyl having 1-6 carbon atoms, or straight or branched
chain lower
alkoxy having 1-6 carbon atoms;
CA 02203878 1997-04-28
WO 96/14307 PCTIUS95114472
R 1 and R2 are the same or different and represent hydrogen, or straight or
branched chain lower
alkyl having 1-6 carbon atoms;
R3 and R4 are the same or different and represent hydrogen, straight or
branched chain lower
alkyl having 1-6 carbon atoms, or straight or branched chain lower alkoxy
having 1-6
carbon atoms;
RS represents straight or branched chain lower alkyl having 1-6 carbon atoms,
phenyl, 2, 3, or 4
pyridyl, or phenyl, 2, 3, or 4 pyridyl straight or branched chain lower alkyl
having 1-6
carbon atoms;
E and R6 are the same or different and represent hydrogen, hydroxyl, amino,
straight or branched
' chain lower alkyl having 1-6 carbon awms, straight or branched chain lower
alkoxy having
1-6 carbon atoms, phenyl, 2. 3, or 4 pyridyl, phenyloxy, 2, 3, or 4
pyridyloxy, or
-(CH2)p-A'-(CH2)q-B' where p represents.0-5 and q represents 1-5 and A' is a
direct
bond oxygen or sulfur and B' is hydrogen, straight or breached chain lower
alkyl having
1-6 carbon atoms, straight or branched chain lower alkoxy having 1-6 carbon
atoms,
phenyl, 2, 3, or 4 pyridyl, phenyloxy, 2. 3, or 4 pyridyloxy, carboxyl,
carboalkoxy,
unsubstituted, mono or dialkylcarboxamido, amino, or mono or dialkylamino.
The invention is illustrated further by the following examples which are not
to be construed
as limiting the invention in scope or spirit to the specific procedures and
compounds described in
them
CA 02203878 1997-04-28
WO 96/14307 PCT/US95/14472
I-Phenylpiperazine (11.3 mL, 12 g, 75 mmol) was suspended in 100 mL water. The
pH
was adjusted to 3 using 1096 HCI. Cyclohexanone (7.8 mL. 7.4 g, 75 mmol) was
added followed
by KCN (5 g, 75 mmol). The mixture was stirred 15 hours at room temperature
during which
time the product solidified. The product was collected by filtration, washed
with water, then
rccrystalliud from ethanol to give 14.5 g of 1-Cyano- 1-(4-phenylpiperarin-I-
yl)-cyclohexane as a
white solid (73 9fo yield), mp = 133-135 °C.
~~'~l
1-Cyano-1-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)-cyclohexane (300 mg, 1.1 mmol) was
dissolved in
10 mL ether under N2 at room temperawre. Phenyl magnesium bromide (4 mL of a 3
M ether
solution) was added and the reaction mixture stirred 15 hours. The mixture was
diluted with 10
mL ether, transferred to a separatory funnel, washed 1 X 10 mL saurratod NH4C1
solution, then
exa~acted 3 X 10 mL 5 96 HCl solution. The acidic extracts were basifiod using
concentrated
2a
CA 02203878 1997-04-28
WO 96/14307 PCT/US95/14472
NH40H solution then extracted 3 X 15 mL ether. The organic extracts were
filtered through a
silica gel pad thea concentrated to afford 280 mg of the free base of the
desired compound as a
white solid (80 R6 yield). This material was dissolved in 5 mL ethyl acetate.
Ethyl acetate
saturated with HCl (5 mL) was added. 1-Phenyl-1-(4-phenyl-piperazin-1-yl)-
cyclohexane
dihydrochloride (Compound 1 ) which precipitated out of solution (88 mg) was
collected by
filtration , washod with ethyl acetate and dried in vacuo.
The following compounds were prepared essentially according to the procedure
described
in Examples I-II:
a) 1-(3-Methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)-cyclohexane dihydrochloride
(Compound 2).
b) 1-(3-Methoxyphenyl~l-{4-(2-pyrimidinyl~piptrazin-1-yl]~yclohexaae
dihydrochloride (Compound 3).
c) 1-(3-Methoxyphenyl}-1-[4-(2-pyridinyl)-pipetazin-I-yl]-cyclohexane
dihydrochloride (Compound 4).
d) 1-(3-Methoxypheayl)-1-[4-(2-tluomphenyl~piperaan-1-yl]~yclohexane
dihydrochloride (Compound ~.
e) I-(3-Methoxypheayl~l-[4-(4-fluoropheayl}-piperazin-1-yl]-cyclohexaae
dihydrochloride (Compound ~.
Zr
CA 02203878 1997-04-28
WO 96/14307 PCTIUS951144~2
1-(3-Hydroxyphenyl)-l-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)-cyclohexane dihydrochloride
(Compound 7).
g) 1-(3. 5-Dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(4-phenyipiperazin-1-yl)~yclohexane
dihydrochloride
S (Compound 8).
h) 1-(3-Ethoxyphenyl)-1-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)-cyclohexane dihydrochloride
(Compound 9).
~ i) 1-(3-Methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)-4~-phenyl~yclohexane
dihydrochloride (cis isomer: Compound 10, traps isomer: Compound 11).
j) 1-(3-n-Butoxyphenyl)-1-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)-cyclohexane dihydrochloride
(Compound 12).
k) 1-(3-Methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-phenylpipaarin-1-yl)-4-methyl-cyclohexane
dihydrochloride (cis isomer. Compound 13, traps isomer: Compound 14).
1) 1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)-cyclohexane dihydrochloride
(Compound 15).
m) 1-(2-Methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-phcnylpipetazin-1-yl)-cyclohexane dihydrochloride
(Compound 16).
n) 1-(3.4-Methenodioxyphenyl~l-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)-cyclobexane
dihydrochloride (Compound 1'n.
CA 02203878 1997-04-28
WO 96/14307 PCT/US95/14472
o) 1-(3-Ethoxyphenyl)-1-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-y1~4-methyl-cyclohexane
dihydrochioride (cis isomer. Compound 18, traps isomer: Compound 19).
p) 1-(3-Ethoxyphenyl~l-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-ethyl-cyclohexane
dihydrochloride (cis isomer: Compound 20, traps isomer: Compound 21).
1-(3-Isopropoxyphenyl~ l-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-methyl~yclohexane
dihydrochioride (cis isomer: Compound 22, traps isomer: Compound 23).
r) 1-(3-Methoxyphenylrl-(4-phenylpipQaan-1-yl)-3-methyl- cyclohexane
dihydrochloride (cis isomer: Compound 24, traps isomer: Compound 25).
s) 1-(3-Benzyioxyphenyl)-1-(4-phenyipiperazin-1-yl)-cyclohexane
dihydrochloride
(Compound 26).
t) 4-(3-Ethoxyphenyl)-4-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)-tetrahydropyran
dihydrochloride
(Compound 27).
u) 4-(3-Ethoxyphenyi}-4.-(4-phenylpiperarin-1-yl~tstrahydrothiopytan
dihydrochioride (Compound 28).
v) I-(3-Methoxyrtxthoxyphenylrl-(4-phenylpiperaiin-1-y1~4-methyl-cyclohexane
dihydrochloride (cis isomer: Compound 29, traps isomer: Compound 30).
23
CA 02203878 1997-04-28
WO 96/14307 PCT/US95/14472
w) 1-(3-Ethoxymethoxyphenyl)-1-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-methyl-cyclohexane
dihydrochloride (cis isomer: Compound 31, craps isomer: Compound 32).
x) 1-(3-Ethoxyphenylrl-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-methoxy-cyclohexane
dihydrochloride (cis isomer: Compound 33, traps isomer. Compound 34).
The invention and the manner and process of making and using it, are now
described in
such full, clear, concise and exact terms as to enable any person skilled in
the art to which it
pertains, to make and use the same. It is to be understood that the foregoing
describes preferred
embodiments of the present invention and that modifications may be made
therein without
departing from the spirit or scope of the present invention as set forth in
the claims. To particularly
point out and distinctly claim the subject matter regarded as invention, the
following claims
conclude this specification.
2~