Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02207789 1997-06-13
WO 96/18782 PCT/SE95/01504
1
FLOOR-LAYING
The present invention relates to a method of laying floors
or like surfaces of desired material, which are supported by
or themselves comprises rigid units in the form of boards or
the like which are tongued and grooved on respective sides
so as to enable mutually adjacent boards to be joined
together. The invention also relates to floor-laying material
for use when carrying out the method.
When applying the method for laying so-called hard floors
with parquet boards or rigid sheets, such as laminated board
or sheets, squares or blocks of desired material, the boards
or corresponding elements are normally placed loosely on a
sub-floor and then glued together with glue applied to the
tongues so as to obtain a floating floor. The gluing proce-
dure constitutes an additional time-consuming task and also
means that the floor will be a permanent fixture, i.e. cannot
be removed without first breaking-up the floor. A sheet of
paperboard or plastic foam is laid over the sub-floor prior
to laying the floor, as a means of damping impact sound.
There are many occasions when there is a need for temporary
floors, for instance in the case of exhibitions, trade fairs
and other organized events. Great savings could be made in
such cases if it were possible to lay the floor without
needing to join the various boards or the like permanently
together. This would enable a floor to be readily lifted
after a temporary event and reused on a later occasion. Such
a floor could also be used conveniently in, e.g., rented
apartments, so that the tenant of such an apartment could
take the floor with him when moving out. Such a floor would
have no detrimental effect on the remainder of the apartment.
A floating floor that has been loosely laid in the aforedes-
cribed manner also eliminates the time and cost involved by
the gluing procedure.
CA 02207789 1997-06-13
WO 96/18782 PCT/SE95/01504
2
A main object of the present invention is to provide a method
of loosely laying floating floors. Another object of the
invention is to provide floor-laying material for use when
applying the method.
The invention is based on the realization that floor cover-
ings or the like which in use are influenced by forces that
have at least one force component that acts perpendicularly
to the surface can be constructed of units which are loose
in relation to one another, provided that when subjected to
load there is sufficiently high friction between the loose
units and the sub-floor to prevent lateral displacement of
said units under load.
The object of the invention is achieved with a method of the
kind defined in the introductory paragraph which is charac-
terized by the steps of using boards that have a friction
layer on the underside thereof, providing the underlying
floor with a corresponding friction layer, and loosely laying
the boards on the friction layer on the sub-floor and
connecting the mutually adjacent boards solely through the
medium of mutually coacting tongues and grooves in the
absence of any binder.
The method enables a top floor to be laid very quickly and
effectively, because it is not necessary to glue the boards
together. A floor that has been laid in accordance with the
invention can be removed very easily when so desired and re-
laid in another place.
The friction layer on the sub-floor is conveniently provided
by laying-out plastic foil or some like carrier provided with
a friction layer on.
Laying of a floorboard is suitably facilitated by placing on
the friction layer on the sub-floor a thin flexible sheet,
e.g. foil, that has a smooth surface and a size which at
CA 02207789 1997-06-13
WO 96/18782 PCT/SE95/01504
3
least corresponds to the size of the board, said foil or
flexible sheet being removed only when the board concerned
has been joined to adjacent boards through the mutual
coaction of said tongues and grooves.
In a particularly preferred embodiment of the invention,
there are used boards whose undersurfaces are provided with
a friction layer that has been produced by flocking, wherein
the sub-floor is covered with plastic foil or the like having
a corresponding flocked friction layer.
It has been found that the thus treated boards will hold
together when subjected to load equally as effectively as
when glued together. Furthermore, the two flocked layers
effectively dampen impact sound.
The main characteristic features of the floor-laying material
for use when applying the inventive method are set forth in
the following Claims.
The invention will now be described in more detail with
reference to the accompanying drawing, in which
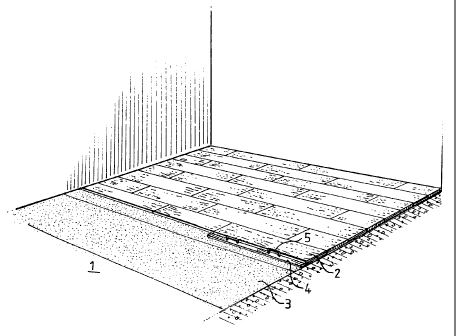
Fig. 1 is a schematic perspective view illustrating laying
of a top floor in accordance with the invention;
Fig. 2 is a horizontal view of the floor shown in Fig. 1; and
Fig. 3 is a side view showing the board last laid in the
floor.
The Figures illustrate a hard sub-floor 1, e.g. a concrete
sub-floor, on which there is to be laid a so-called top floor
comprised of parquet boards or laminate boards 2. The boards
2 have tongues and grooves on respective sides, in a typical
manner. According to the invention, each board is provided
on its underside with a friction layer 6, which in the
CA 02207789 1997-06-13
WO 96/18782 PCT/SE95/01504
4
embodiment most preferred has been produced by flocking.
The reference numeral 3 identifies layers of plastic foil or
some other pliable material which has a friction layer 7
flocked on its upper surface. The mutual coaction between
flocks or fibres in the friction layer of the foil 3 and the
friction layer on a board 2 prevents lateral displacement of
the board when subjected to load.
This effect is achieved as a result of the layers 6, 7 of
short fibres firmly glued at right angles to respective
surfaces by flocking. When the two layers are pressed
together with nothing therebetween, the fibres of the two
layers will engage one another and therewith make lateral
movement impossible.
Flocking is effected in a known manner, by first applying,
normally spraying glue onto respective surfaces. The surfaces
are then flocked by "firing" short fibres of desired material
into the adhesive electrostatically, the electric field
causing the fibres to position themselves at right angles to
the surface. The product is then dried and surplus fibres
removed if necessary. The fibres used are suitably made of
a plastic material, such as polyamide, rayon, polyester or
like material. Layers which when pressed together are highly
resistant to lateral movement of the layers relative to one
another can be achieved by appropriate selection with regard
to the coarseness and lengths of the fibres used.
The boards and the foil material are conveniently flocked at
their place of manufacture. For instance, the sheet-like
planks from which the boards are produced may be flocked
prior to sawing the planks into individual boards.
It will be understood, however, that the principle of the
invention can also be applied with friction surfaces that
have been produced on the underside of the boards and on the
CA 02207789 1997-06-13
WO 96/18782 PCT/SE95/01504
upper side of the sub-floor in some other way.
When the frictional forces acting between a board 2 and the
friction layer 7 of the underlying sub-floor are very great,
5 displacement of a board 2 in the plane of the board in order
to mate with the tongues and grooves of adjacent boards can
be facilitated by using a sliding-facilitating intermediate
element such as a semi-stiff sheet of appropriate material
or foil material 4 which is at least the same size as the
board 2. This intermediate element is first laid on the sub-
floor so as to cover a selected part of its friction layer
7. Reference number 5 identifies two handles which facilitate
handling of the sheet 4.
The sheet 4 will preferably have smooth surfaces so as to
enable the overlying board 2 to be moved easily into mating
engagement with adjacent boards. When the board has been
laid, the sheet 4 can be readily pulled out from its position
between the board and the underlying sub-floor, so that the
friction surface on the board 2 will coact with the friction
surface 6 on the sub-floor in the desired manner. The sheet
4 is then moved to the position of the next board to be laid.
The aforedescribed method can be applied in laying parquet
boards, laminated boards, laminated sheets, so-called square
laminates, parquet blocks and like floor elements. The
inventive method also provides the additional advantage of
effectively reducing sound transmissions, particularly in the
case of floors constructed from plastic-laminated boards or
sheets.