Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02211366 1997-07-24
WO 96/23181 PCT/NO96/00016
Hole in the ground for transfer of geothermal energy to an
energy-carrying liquid and a method for production of the
hole
The invention relates to a hole in the ground for transferring geothermal
- energy from the ground around the hole to an energy carrier fluid which is
introduced into the hole.
In US 4 290 266 it is disclosed that a pipe loop can be placed in a blind bore
in the earth and that a fluid can be passed down into the earth via a first
section of the pipe loop and up from the earth via a second section of the
pipe loop. A disadvantage of this prior art technique is that the said pipe
loop
sections extend very close to each other whereby upwardly flowing warm
fluid is cooled by the cold, downwardly flowing fluid, with the result that
the
total efficiency is low.
Furthermore it is known that there are a number of deep bore holes or wells
which have been used or are being used for the recovery of oil or gas
together with associated installations above ground. As a consequence of the
strain on the environment which these installatior_s often represent, for
environmental and other reasons increasing demands have been made for such
installations to be removed or dismantled and the wells sealed after the oil
or
gas extraction has ceased, which is a very expensive process.
The object of the invention is to provide a hole of the above-mentioned type
whereby the above-mentioned disadvantages can be avoided.
The characteristics of the hole according to the invention are presented by
the
characteristic features indicated in the claims.
The invention will now be described in more detail with reference to the
drawing whose only figure schematically illustrates a hole according to the
invention.
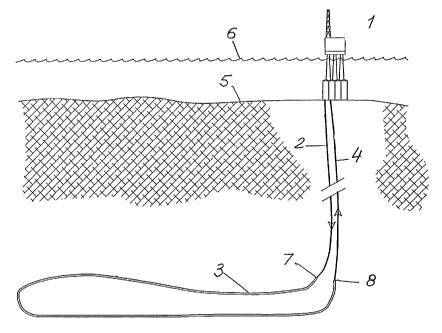
As illustrated in the figure there is located on the seabed 5 a platform 1
whose upper section projects up above the surface of the sea 6. From the
seabed 5 near the platform there extend two substantially vertical hole
sections, viz. a first hole section 2 and a third hole section 4 to locations
7
CA 02211366 2005-10-26
2
and 8 respectively in the ground formation from which oil or gas have been
extracted and
brought up via the hole sections 2,4.
Instead of removing the platform and sealing the hole sections 2,4 after the
oil or gas
recovery has ceased, it is proposed according to the invention that an
additional or second
hole section 3 should be drilled which connects the locations 7 and 8 to each
other, thus
providing a hole loop comprising the first, second and third hole sections 2,3
and 4
respectively. As those skilled art in the art would readily appreciate it, the
drilling of the
second hole section 3 can be carried out by using a method well known in the
art, such as
"Innovative Horizontal Drilling Techniques: Mufti-Lateral and Twinned
Horizontal Wells"
published by Sperry-Sun Drilling Services (1993).
By passing a suitable fluid, such as water, down into the first hole section
2, this fluid can
flow on through the second hole section 3, where it is heated by the
surrounding ground, and
subsequently up through the third hole section 4, without the heated fluid in
the third hole
section 4 being cooled by the downwardly flowing, cold water which is passed
down into
the first hole section 2.
If the substantially vertical hole sections 2 and 4 extend from the same
platform 1 as
illustrated in the figure, the additional hole section 3 can extend in a
relatively large loop
away from one location 7 before it extends towards the second section 8,
thereby ensuring
that the fluid is heated to close to the temperature of the ground around the
second hole
section 3 before flowing upwards and out of the third hole section 4, even
though the
through-flow rate is high.
There can be provided on the platform a known per se installation (not shown)
whereby the
heat energy may be converted to another suitable energy form, e.g. electrical
energy, and
supplied to a consumer. This installation may comprise, e.g. heat exchangers,
turbines,
generators etc. and it is assumed that it will be familiar to a person skilled
in the art.
As it will be understood, the invention permits a re-use of installations and
wells, the
decommissioning of which would have entailed major expenses for the owner. The
invention provides energy whose release does not pollute the environment, and
which is
obtained from an almost inexhaustible source.
In order to illustrate the costs involved for the energy amount which can be
provided, the
following information is provided.
CA 02211366 1997-07-24
3
At a depth of between 3500 m and 6000 m below the seabed the temperature
in the earth is approximately 110 - 180°C.
Two bore holes each having a length of approximately 3000 m for extracting
oil or gas at present cost approximately NOK 150 million. An additional
deviated hole which has a length of approximately 1000 m and which
connects these two bore holes costs approximately NOK 20 million.
For example, the drilling field Statfjord B in the North Sea comprises
approximately 40 wells which together with the platform will probably be
closed down around the year 2003. By applying the invention, however, these
wells could form part of 20 hole loops for the production of geothermal
energy, and the platform could be used as the mounting location for the
above-mentioned installation.
It will be understood that in the hole sections there can be inserted pipes in
which the fluid can flow.
For this oilfield the following example can be used:
Internal pipe diameter 0.215 m
Volume of water 700 m3/h
Water velocity 5.32 m/s
Inlet temperature of the water upstream of the pump 20°C
Outlet temperature of the water downstreamof the pump 40°C
Outlet temperature of the water from the well 110°C
Hole length 7000 m
Pump power 1.72 MW
Thermal power 40 MW
At a rough estimate this thermal power can provide an effective output of
approximately 5 MW. The 20 hole loops in this oilfield would thus be
capable of providing a total output of 100 MW electricity, subtracted the
pump performance 20 x 1.75 MW = 34.4 MW, which gives a total of
65.6 MW electricity
Even though it has been stated in the above description of the invention that
two hole sections have been interconnected by means of an additional hole
AMENDED SHEET
CA 02211366 1997-07-24
33
section, it will be understood that more than two hole sections can be
interconnected.
AMENDED SHECT