Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02213839 2001-02-07
71024-275
1
TITLE OF THE INVENTION
"Cross-Connect Node for Switching Quality Detector to Incoming
Signal Specified by Request Message from Adjacent Node"
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Field of the Invention
The present invention relates generally to cross-
connect systems, and more specifically to a cross-connect
network node for monitoring signal quality for detection and
restoration of link failure.
Description of the Related Art
In high-speed communication networks, it is the usual
practice to provide a signal quality monitor circuit on a per-
link basis. In the SONET (synchronous optical network) system,
monitoring is performed on supervisory signals embedded in a
time-division multiplexed signal, using the byte-interleaved
parity contained in section, line and path overheads. However,
the provision of monitor circuits on a per-link basis would
result in an increase in the amount of OAM (operations,
administration and maintenance) information which must be
contained in the transport overhead of a frame. Additionally,
if optical communication links are used for interconnecting
nodes, routing of optical signals is implemented by an optical
cross-connect switch without conversion to electrical signals.
However, if monitor circuits are provided on a per-link basis,
it is obviously disadvantageous that optoelectrical converters
must be provided on a per-link basis.
CA 02213839 2001-02-07
71024-275
la
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
It is therefore an object of the present invention to
provide a network node which eliminates the need for monitoring
signals on a per-link basis.
Very brief this invention seeks to provide a network
node comprising: a cross-connect switch having a plurality of
input ports for receiving input signals and plurality of output
ports; a signal quality monitor connected to one of said output
ports for determining a quality level of one of said input
signals; and control means coupled to said signal quality
monitor and said switch, said control means being responsive to
add/drop control information, for controlling said switch to
selectively established connections between said input ports
and said output ports other than said one output port, said
control means being further responsive to a request message
received from another network node for controlling said switch
to establish a connection between one of said input ports which
is specified by the request message and said one output port so
that the quality level of the signal at the specified input
port is determined by said signal quality monitor, said control
means further transmitting a reply message to said another
network node, indicating said quality level of said specified
input signal.
According to the present invention, there is further
provided a cross-connect network node comprising a cross-
connect switch having a plurality of input ports and a
plurality of output ports. A single signal quality monitor is
CA 02213839 1997-09-09
NE-801
-2-
connected to one of the output ports of the cross-connect switch. The
2 switch is controlled by a processor, or control means, which causes the
3 switch to establish connections between the input ports and the output
4 ports. The processor is responsive to a request message from another
network node for causing the switch to establish a connection between one
6 of the input ports which is specified by the request message and the signal
7 quality monitor and transmitting a reply message to the another network
8 node, indicating a quality level of a signal appearing at the input port.
9 A switched telecommunications network, such as Internet, may be
1 o used for receiving the request message and transmitting the reply message.
Alternatively, multiplexed channels may be used for receiving the request
~ 2 message and transmitting the reply message.
~ 3 In one embodiment, a plurality of dc-level detectors are
additionally provided for receiving replicas of signals applied respectively
to
~ 5 the input pons of the cross-connect switch and detecting a dc-level of
each
16 of the replicas. The processor is responsive to one of the detected dc-
levels
having a predetermined value for transmitting an alarm message to another
~ 8 node and responsive to a request message therefrom for controlling the
cross-connect switch to establish a connection between one of the input
2 o ports specified by the request message and the signal quality monitor to
2 ~ allow it to determine a quality level of an idle signal which appears at
the
2 2 input port.
2 3 In a modified embodiment, a plurality of section/line overhead
2 4 extraction circuits are provided for receiving replicas of signals applied
2 5 respectively to the input ports of the cross-connect switch and extracting
2 6 section/line overheads from the replicas, respectively. A bit error rate
2 ~ monitor determines the bit error rate of a signal identified by a
section/line
2 s identifier contained in each one of the extracted overheads. The processor
2 9 is responsive to the bit error rate of a predetermined value for
transmitting
3 o an alarm message to another node and responsive to a request message
CA 02213839 1997-09-09
NE-801
-3-
t therefrom for controlling the cross-connect switch to establish a connection
2 between one of the input ports specified by the request message and the
3 path overhead extraction circuit to allow the bit error rate monitor to
determine a bit error rate of an idle signal which appears at the input port.
s BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
6 The present invention will be described in further detail with
7 reference to the accompanying drawings, in which:
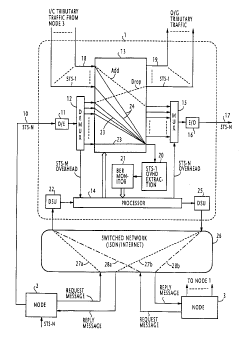
s Fig. 1 is a block diagram of a cross-connect network according to a
9 one embodiment of the present invention;
Fig. 2 is a block diagram of a modified embodiment of the present
11 invention;
~ 2 Fig. 3 is block diagram of an optical cross-connect node of the
~ 3 present invention; and
Fig. 4 is a block diagram of a modified form of the embodiment of
i s Fig. 3.
i 6 DETAILED DESCRIPTION
Referring now to Fig. l, there is shown a SONET-based
~ 8 communication network according to one embodiment of the present
invention. As a typical example, the network includes a node 1 that receives
2 o an STS-N (synchronous transport signal level-N) frame from an adjacent
2 ~ upstream node 2 via an incoming optical transmission link 10. The received
2 2 optical signal is converted to an electrical signal by an optical receiver
2 3 (optoelectrical converter) 11. The electrical STS-N frame is coupled to a
24 demultiplexer 12 where the frame is unpacked into a plurality of STS-1
2 5 frames and the STS-N transport overhead is extracted. The unpacked STS-
2 6 1 frames are fed to respective input ports of a cross-connect switch 13
and
2 7 the extracted overhead is supplied to a processor, or workstation 14. The
28 STS-1 frames supplied to the switch 13 are routed to output ports of the
2 9 switch via "transit" connections established in accordance with a control
3 o signal from the processor 14. The extracted overhead contains OAM
CA 02213839 2001-02-07
71024-275
4
information which is analyzed by processor 14 to determine
whether it is necessary to reconfigure connections already
established in the cross-connect switch 13 or relay the
received OAM (operations, administration and maintenance)
information to downstream nodes. If the latter is the case, an
OAM signal is produced by the processor :14 and contained in an
STS-N transport overhead for transmission to downstream nodes.
The routed STS-1 frames are supplied to a multiplexer
where they are packed into the synchronous payload envelope
10 (SPE) of an outgoing STS-N frame and multiplexed with the STS-N
transport overhead in which the downstream OAM information is
contained. After conversion to an optical signal by an optical
transmitter 16 (electrooptical converter), the STS-1 frame is
forwarded to a downstream node, not shown, via an outgoing
15 optical link 17.
The node 1 may also provide an add/drop multiplexing
function by inserting incoming STS-1 tributary traffic via
incoming lines 18 from an adjacent node 3 into the SPE of the
outgoing STS-N frame and dropping unpacked STS-1 frames from
the node 2 to outgoing lines 19 by establishing "add/drop"
connections in the cross-connect switch 13.
According to the present invention, an STS-1 path
overhead extraction circuit 20 is connected to one of the
output ports of the cross-connect switch 13 for extracting a
path overhead from a STS-1 frame. The extracted overhead is
supplied to a bit-error-rate monitor circuit 21. BER monitor
circuit 21 uses parity in B3-byte field of the extracted
overhead to determine the bit error rate of overhead bytes of a
predetermined bit pattern located in a field specified by a
path identifier. The output of the BER monitor circuit 21 is
representative of a quality level of any STS-1 frame which can
CA 02213839 2001-02-07
71024-275
4a
be specified by a request message.
If node 2 desires to know the signal quality of a
plurality of STS-1 frames at a receive site, it sends a request
message to node 1 via a switched network 26 such as Internet,
using an ISDN digital subscriber line. The
CA 02213839 1997-09-09
NE-801
-5-
request message is directed through the switched network 26 to node 1 as
2 indicated by a broken line 27a, where it is detected by a data service unit
22
3 and the processor 14 is informed of the identification numbers of STS-1
a frames specified by node 2.
In response to the request message from node 2, the processor 14
6 sequentially establishes a connection 23 in the switch 13 between each of
the
7 specified frames and the STS-1 path overhead extraction circuit 20. The bit
8 error rate performance of each of the specified STS-1 frames is determined
9 by the BER monitor 21 and the result of the measurement is encapsulated
in a reply message and applied to a DSU 25. The reply message is directed
1 ~ from DSU 25 to node 2 via the switched network 26 as indicated by a
~ 2 broken line 27b.
~ 3 If node 3 desires to know the quality of STS-1 tributary signals sent
14 to node 1, it likewise sends a request message specifying desired STS-1
~ 5 frames to node 1 via switched network 26 as indicated by a chain-dot line
28a. The processor 14 at node 1 responds to this request message by
sequentially establishing a connection 24 between each of the specified
~ 8 tributary frames and the overhead extraction circuit 20. The bit error
rate
performance of each of the specified STS-1 frames is evaluated and a reply
z o message containing the result of the test is sent from DSU 25 and routed
21 through switched network 26 to node 3 as indicated by a chain-dot line
z z 28b.
2 3 It is seen therefore that, since only one set of an STS overhead
24 extraction circuit 20 and a BER monitor circuit 21 is required for
evaluating
2 5 the quality of a plurality of STS-1 frames, a number of advantages are
2 6 achieved in terms of cost, space and memory required for monitoring.
2 7 Since request and reply messages are generated only when a need arises,
2 8 Internet can be used for transmission of these messages.
2 9 In a modified embodiment, the request and reply messages are
3 o transmitted using the transport overhead of STS-N frames. Fig. 2
CA 02213839 1997-09-09
NE-801
-G-
illustrates a network node lA in which cross-connect switches and their
2 associated circuitry are provided in a symmetrical fashion for opposite
3 directions of transmission. Node 2A is the upstream node that transmits an
STS-N frame via optical link 10 to node lA, with the frame containing a
request message in its transport overhead. A path overhead is extracted by
demultiplexer 12 and a request message is detected in the path overhead by
the processor 14. The request message specifies one or more STS-1 frames
8 whose quality the node 2A desires to know. If there is more than one
frames to be monitored, the processor 14 sequentially establishes
connections 23 in the cross-connect switch 13 between the desired STS-1
frames and the overhead extraction circuit 20 to determine their signal
~ 2 quality. An STS-1 path overhead extraction circuit and a BER monitor
~ 3 circuit may also be provided for the signals received from the link 30.
However, they are omitted for simplicity.
~ 5 An optical STS-N frame transmitted on optical link 30 in the
direction opposite to those on link 17 is received via optical link 30,
converted to an electrical signal by optical receiver 31 and unpacked into
18 STS-1 frames by demultiplexer 32. The unpacked frames are routed
through cross-connect switch 33 under control of processor 14. Some of the
20 routed STS-1 frames are merged into an STS-N frame by multiplexer 35
2 ~ and combined with an STS-N transport overhead produced by processor
2 2 14.
2 3 A reply message containing the signal quality data of the STS-1
2 4 frames specified by node 2A is inserted into an STS-N transport overhead.
2 5 This transport overhead is multiplexed with the STS-N frame by
26 multiplexer 35, converted to an optical signal by optical transmitter 3G,
and
2 ~ transmitted via an optical link 37 to node 2A.
2 8 Fig. 3 shows an optical version of the cross-connect node that
2 9 incorporates the request/reply feature of the present invention. The
optical
3 o node receives optical STS-N frames of wavelength 1.55 ~.m on a plurality
of
CA 02213839 1997-09-09
NE-801
incoming optical communication links 40. On one of the incoming
2 communication links, an STS-N frame is multiplexed with an OAM signal
3 of wavelength 1.31 um. The multiplexed signal is decomposed into its
components by an optical demultiplexer 41. The OAM signal, converted to
electrical signal by an optical receiver 42, is supplied to a processor 43,
which
6 analyzes it to determine whether it is necessary to reconfigure connections
7 already established in an optical cross-connect switch 46 or relay the
8 received OAM information to downstream nodes. If the latter is the case,
9 an OAM signal is produced by the processor 43 and applied to an optical
1 o transmitter 49 for conversion to a I.31-~m optical signal.
~ t The 1.55 ~m optical STS-N frames on optical links 40 are
~ 2 respectively supplied to optical splitters 44 where a greater proportion
of
~ 3 each incident light energy is supplied to a respective input port of cross-
connect switch 4G and the remainder is branched to one of optical level
i s sensors 45 connected to processor 43. The optical STS-N frames are
16 directly routed to output pons of cross-connect switch 4G under control of
1 ~ processor 43 and transmitted on outgoing optical communication links 47.
~ 8 One of the output ports of the cross-connect switch 46 is connected to an
optical multiplexer 48 where the optical OAM signal from the optical
2 o transmitter 49 is combined with an outgoing 1.55-~.m STS-N frame for
2 ~ transmission to a downstream node.
2 2 For the opposite direction of transmission, STS-N frames of
2 3 wavelength 1.55 ~.m from other nodes are received via optical
24 communication links 60. They are terminated at input ports of an optical
2 5 cross-connect switch 61 and routed under control of the processor 43 to
2 6 output ports leading to outgoing optical communication links 62. An
2 ~ optical transmitter 63 is connected to the processor 43 for converting an
2 8 OAM signal into a 1.31-um optical signal and multiplexed by an optical
2 9 multiplexer 64 with a 1.55-~.m outgoing STS-N frame from the switch 61.
3 o Each of the optical Ievel sensors 45 produces a signal indicating the
CA 02213839 1997-09-09
NE-801
-g_
dc-level of the corresponding incoming STS-N frame as an instant alarm of
2 a link failure if the detected dc-level falls below a predetermined value.
3 If a failure occurs in one of the incoming optical links, the output of
the corresponding optical level sensor drops and the processor 43 knows that
a link failure has occurred and produces an alarm message for the faulty
6 link. This alarm message is converted to a 1.31-um optical signal by optical
transmitter 63 and multiplexed with an STS-N frame from switch 61 and
8 transmitted on a link 62 to the upstream node.
After protection switching of the affected frame to a spare link, a
troubleshooting procedure is provided for precisely determining the quality
of the link under repair. This is achieved by sending an idle STS-N frame
~ 2 through the faulty link and a request message from the upstream node for
~ 3 monitoring the bit error rate of this idle frame at node 1. For this
purpose,
an STS-N path overhead extraction circuit 51 is connected to one of the
~ s output ports of the switch 46 via an optical receiver 50 to extract a path
overhead from the idle STS-N frame.
Processor 43 receives the request message from the upstream node
t 8 via optical demultiplexer 41 and optical receiver 42 and controls the
switch
46 to establish a connection between one of the input ports specified by the
2 o request message and the path overhead extraction circuit 51. The extracted
2 ~ path overhead is fed to a BER monitor 52. BER monitor 52 uses parity in
22 the B3-byte field of the extracted overhead to determine the bit error rate
2 3 of overhead bytes located in a position specified by a path identifier
2 4 contained in the path overhead. The idle frame is monitored in this way as
2 5 an instantaneous recovering condition of an affected link.
2 6 A reply message will then be produced by processor 43 and
2 ~ transmitted to the upstream node via optical transmitter 63 and
multiplexer
2 8 64, indicating the monitored result of the faulty link.
2 9 The embodiment of Fig. 3 can be modified as shown in Fig. 4. In
3 o this modification, optical receivers 70 are connected to the sputters 44.
A
CA 02213839 1997-09-09
NE-801
plurality of STS-N section or line overhead extraction circuits 71 are
2 provided for an extracting STS-N section or line overhead from each
3 incoming STS-N frame. The outputs of overhead extraction circuits 71 are
4 sequentially scanned and selected by a selector 72 under control of
processor 43 and supplied to a bit error rate monitor circuit 73. The BER
monitor circuit 73 uses parity in B 1-byte field of the extracted section
7 overhead or parity in B2-byte field of the extracted line overhead to
8 determine the bit error rate of overhead bytes specified by a section or
line
9 identifier. The output of BER monitor circuit 73 provides an instant
o indication of a failure on a section or line of a SONET system.
Processor 43 determines that one of the incoming optical links 40
12 has failed when the output of BER monitor circuit 73 has a predetermined
~ 3 value and transmits an alarm message to the upstream node. Upon
4 receiving a request message from the upstream node, processor 43 controls
~ 5 the switch 46 to establish a connection between the input port specified
by
6 the request message and an STS-N path overhead extraction circuit 74
17 connected to the output of optical receiver 50. An idle STS-N frame is then
s transmitted over the faulty link from the upstream node, following
9 protection switching of the affected frame to a spare link.
2 0 The STS-N path overhead extraction circuit 74 extracts an STS-N
2 ~ path overhead from the idle STS-N frame. The extracted path overhead is
2 2 supplied to a BER monitor 75, which uses parity in B3-byte field of the
2 3 extracted path overhead to determine the bit error rate of overhead bytes
2 4 specified by a path identifier. The output of the BER monitor circuit 75
is
2 5 representative of a quality level of an idle STS-N frame transmitted over
a
2 5 faulty path, and hence the recovering state of the faulty link. The output
of
2 7 the BER monitor 75 is contained in a reply message and transmitted to the
2 g upstream node. This embodiment is suitable for instant protection
2 9 switching in the event of a faulty light modulator associated with an
optical
3 0 communication link.